无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1109-1114.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170036 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170036
汪为磊1,2,3, 刘卫丽1,3, 白林森3, 宋志棠1,3, 霍军朝1,3
收稿日期:2017-01-17
出版日期:2017-10-20
网络出版日期:2017-09-21
作者简介:汪为磊. E-mail: awelly@mail.sim.ac.cn
WANG Wei-Lei1,2,3, LIU Wei-Li1,3, BAI Lin-Sen3, SONG Zhi-Tang1,3, HUO Jun-Chao1,3
Received:2017-01-17
Published:2017-10-20
Online:2017-09-21
About author:WANG Wei-Lei(1990–), male, candidate of Master degree. E-mail: awelly@mail.sim.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
为了提高氧化铝颗粒的CMP性能, 本工作探索了一种合适的改性方法。同时, 为了改善其化学机械性能, 通过与其表面羟基的硅烷化化学反应和与Al和仲胺的络合两种作用, 用N-(2-氨基乙基)-3-氨基丙基三甲氧基硅烷表面改性氧化铝颗粒。本工作给出了化学反应机理, 即N-(2-氨基乙基)-3-氨基丙基三甲氧基硅烷接枝到氧化铝表面。通过傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)表征了改性氧化铝颗粒的组成和结构。结果表明: N-(2-氨基乙基)-3-氨基丙基三甲氧基硅烷已被成功地接枝到氧化铝颗粒的表面, 导致改性比未改性的氧化铝颗粒具有更好的化学和机械性能。测试了未改性和改性的氧化铝颗粒在蓝宝石基底上的CMP性能。结果显示: 改性氧化铝颗粒比未改性氧化铝颗粒有更高的材料去除速率和更好的表面质量。即, 改性氧化铝颗粒在pH=10时比未改性氧化铝颗粒在pH=13.00时表现出更高的材料去除率, 这将为减少设备腐蚀提供新思路。
中图分类号:
汪为磊, 刘卫丽, 白林森, 宋志棠, 霍军朝. 氧化铝颗粒的表面改性及其在C平面(0001)蓝宝石衬底上的化学机械抛光(CMP)性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1109-1114.
WANG Wei-Lei, LIU Wei-Li, BAI Lin-Sen, SONG Zhi-Tang, HUO Jun-Chao. Surface Modified Alumina Particles and Their Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) Behavior on C-plane (0001) Sapphire Substrate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1109-1114.
| Elements in sample | Al2p | O1s |
|---|---|---|
| Binding energy/eV | 74.03 73.08 | 531.06 530.87 |
Table 1 Binding energy of abrasives containing before and after modified alumina particles
| Elements in sample | Al2p | O1s |
|---|---|---|
| Binding energy/eV | 74.03 73.08 | 531.06 530.87 |
| Atomic% | Al | O | C | N | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmodified alumina | 30.67 | 52.44 | 16.89 | 0 | 0 |
| Modified alumina | 27.35 | 46.41 | 21.19 | 2.77 | 2.28 |
Table 2 Cmposition of elements on the surface of alumina particles before and after modification
| Atomic% | Al | O | C | N | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmodified alumina | 30.67 | 52.44 | 16.89 | 0 | 0 |
| Modified alumina | 27.35 | 46.41 | 21.19 | 2.77 | 2.28 |
| Chemical state | Band energy/eV |
|---|---|
| (-Si(OCH3)2O-)xAly | 73.8 |
| AlN | 73.1 |
Table 3 Binding energy of Al2p
| Chemical state | Band energy/eV |
|---|---|
| (-Si(OCH3)2O-)xAly | 73.8 |
| AlN | 73.1 |
| Chemical state | Band energy/eV |
|---|---|
| (-Si(OCH3)2O-)xAly | 531.10 |
| Al2O3 | 530.30 |
Table 4 Binding energy of O1s
| Chemical state | Band energy/eV |
|---|---|
| (-Si(OCH3)2O-)xAly | 531.10 |
| Al2O3 | 530.30 |
| pH | Type of particles | MRR (0.0001 g/30 min) | Before polishing Rq Roughness/nm | After polishing Rq Roughness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.00 | Pure alumina | 46 | 0.968 | 0.610 |
| 10.00 | Modified alumina | 127 | 0.610 | 0.329 |
| 10.00 | Modified alumina | 139 | 0.981 | 0.315 |
| 13.00 | Pure alumina | 93 | 0.916 | 0.552 |
| 13.00 | Modified alumina | 122 | 0.552 | 0.311 |
Table 5 Surface roughness (Rq) and material removal rate(MRR)by applying before and after modified alumina particles in different pH
| pH | Type of particles | MRR (0.0001 g/30 min) | Before polishing Rq Roughness/nm | After polishing Rq Roughness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.00 | Pure alumina | 46 | 0.968 | 0.610 |
| 10.00 | Modified alumina | 127 | 0.610 | 0.329 |
| 10.00 | Modified alumina | 139 | 0.981 | 0.315 |
| 13.00 | Pure alumina | 93 | 0.916 | 0.552 |
| 13.00 | Modified alumina | 122 | 0.552 | 0.311 |
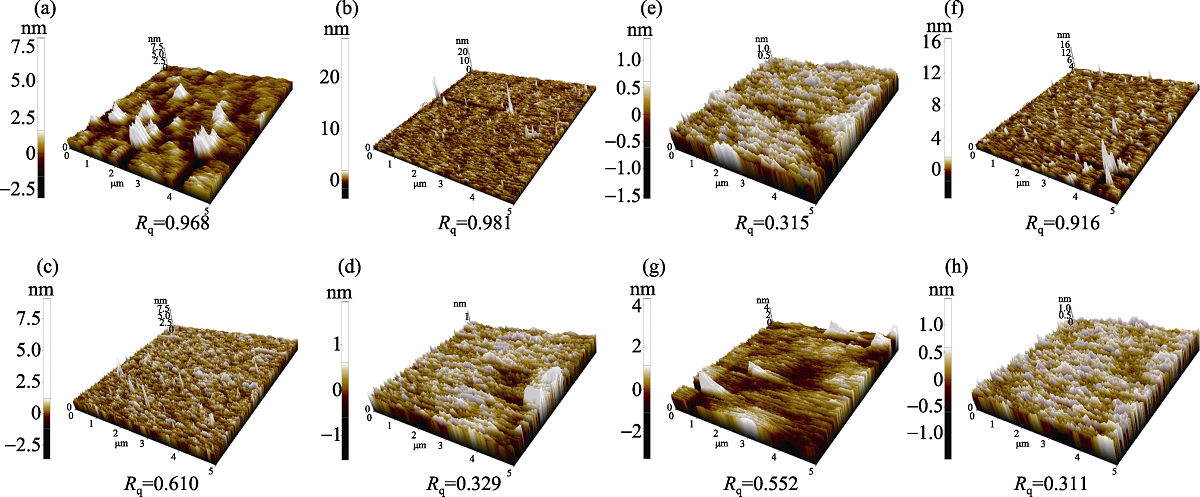
Fig. 6 (a, b, f) AFM morphologies of sapphire substrate before polishing; (c) polished by pure alumina particles at pH 10.00; (d) polished by modified alumina particle (using sapphire substrate polished by pure alumina particles (c)) at pH 10.00; (e) polished by modified alumina particle at pH 10.00; (g) polished by modified alumina particle at pH 13.00; (h) polished by pure alumina particles (using sapphire substrate polished by pure alumina particles (g)) at pH 13.00
| [1] | SAITO T, HIRAYAMA T, YAMAMOTO T, et al.Lattice strain and dislocations in polished surfaces on sapphire.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88: 2277-2285. |
| [2] | NIU X H, LIU Y L, TAN B M, et al.Method of surface treatment on sapphire substrate.Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16: 732-734. |
| [3] | TAKEUCHI T, TAKEUCHI H, SOTA S, et al.Optical properties of strained AlGaN and GaInN on GaN.Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 1997, 36: L177-L179. |
| [4] | LIMA R S, MARPLE B R.Thermal spray coatings engineered from nanostructured ceramic agglomerated powders for structural, thermal barrier and biomedical applications: a review.J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2007, 16: 40-63. |
| [5] | KIM K T, KOO H Y, LEE G G, et al.Synthesis of alumina nanoparticle-embedded-bismuth telluride matrix thermoelectric composite powders.Mater. Lett. , 2012, 82: 141-144. |
| [6] | ZOIS D, LEKATOU A, VARDAVOULIAS M, et al.Nanostructured alumina coatings manufactured by air plasma spraying: correlation of properties with the raw powder microstructure.J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 495: 611-616. |
| [7] | TANG E J, CHENG G X, MA X L, et al.Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticle by PMAA and its dispersion in aqueous system.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252: 5227-5232. |
| [8] | LEI H, LU H S, LUO J B, et al.Preparation of α-alumina- g-polyacrylamide composite abrasive and chemical mechanical polishing behavior.Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516: 3005-3008. |
| [9] | LEI H, ZHANG P Z.Preparation of alumina/silica core-shell abrasives and their CMP behavior.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253: 8754-8761. |
| [10] | ZHANG Z F, LEI H.Preparation of α-alumina/polymethacrylic acid composite abrasive and its CMP performance on glass substrate.Microelectron. Eng., 2008, 85: 714-720. |
| [11] | SHEN X C, FANG X Z, ZHOU Y H, et al.Synthesis and characterization of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-modified superpar- amagnetic magnetite nanoparticles.Chem. Lett., 2004, 33: 1468-1469. |
| [12] | ZHANG Z F, YU L, LIU W L, et al.Surface modification of ceria nanoparticles and their chemical mechanical polishing behavior on glass substrate.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, 256: 3856-3861. |
| [13] | HOMMA Y.Dynamical mechanism of chemical mechanical polishing analyzed to correct Preston's empirical model.J. Electroanal. Chem., 2006, 153: G587-G590. |
| [14] | MATSUDA T, TAKAHASHI H, TSURUGAYA M, et al.Characteristics of abrasive-free micelle slurry for copper CMP.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150: G532-G536. |
| [15] | ABIADE J T, CHOI W, SINGH R K.Effect of pH on ceria-silica interactions during chemical mechanical.J. Mater. Res., 2005, 20: 1139-1145. |
| [16] | LIANG H, CRAVEN D R.Tribology in Chemical-Mechanical Planarization. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, Fla., 2005. |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 汤新丽, 丁自友, 陈俊锐, 赵刚, 韩颖超. 基于稀土铕离子荧光标记的磷酸钙纳米材料体内分布与代谢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [5] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [6] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [10] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [11] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [12] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [13] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [14] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [15] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||