无机材料学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 972-978.DOI: 10.15541/jim20130686 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20130686
周 友, 刘 秀, 王 芳, 郝建薇, 杜建新
收稿日期:2013-12-30
修回日期:2014-02-16
出版日期:2014-09-17
网络出版日期:2014-08-21
作者简介:周 友(1986–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: ydzhouyou@126.com
基金资助:ZHOU You, LIU Xiu, WANG Fang, HAO Jian-Wei, DU Jian-Xin
Received:2013-12-30
Revised:2014-02-16
Published:2014-09-17
Online:2014-08-21
About author:ZHOU You. E-mail: ydzhouyou@126.com
摘要:
金属氧化物(MO)可显著影响膨胀阻燃体系的热解成炭过程, 进而改善膨胀阻燃涂层的耐火性能。将Fe2O3、ZnO、TiO2分别添加到双环笼状磷酸酯膨胀阻燃环氧涂层中, 研究了MO对涂层耐火及成炭性能的影响规律。燃烧背温测试结果表明, MO可产生显著的协效耐火作用, 三种MO对耐火性能的增效能力为Fe2O3>ZnO>TiO2。热失重(TGA), 激光拉曼光谱(LRS)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析表明, MO促进了残炭的耐高温氧化性能及类石墨化程度的提高, 增加了涂层的高温残炭量, 三种MO提升涂层成炭性能的能力为Fe2O3>ZnO>TiO2。
中图分类号:
周 友, 刘 秀, 王 芳, 郝建薇, 杜建新. 金属氧化物对膨胀阻燃涂层耐火及成炭性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 972-978.
ZHOU You, LIU Xiu, WANG Fang, HAO Jian-Wei, DU Jian-Xin. Effect of Metal Oxides on Fire Resistance and Char Formation of Intumescent Flame Retardant Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(9): 972-978.
| No. | Sample | Fire resistance time/s | V300℃a /(℃•s-1) | V400℃/(℃•s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t300℃ | t400℃ | ||||
| 1 | EP/T-IFR | 200 | 1040 | 1.50 | 0.38 |
| 2 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% Fe2O3 | 230 | 2200 | 1.30 | 0.18 |
| 3 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 280 | 2360 | 1.07 | 0.17 |
| 4 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% Fe2O3 | 220 | 2010 | 1.36 | 0.20 |
| 5 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% ZnO | 320 | 1780 | 0.94 | 0.22 |
| 6 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 340 | 2140 | 0.88 | 0.19 |
| 7 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% ZnO | 530 | 1710 | 0.57 | 0.23 |
| 8 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% TiO2 | 220 | 1440 | 1.36 | 0.28 |
| 9 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 260 | 1520 | 1.15 | 0.26 |
| 10 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% TiO2 | 240 | 1380 | 1.25 | 0.29 |
表1 MO在不同添加量下对涂层耐火性能的影响
Table 1 Effect of MO contents on the fire resistance properties of coatings
| No. | Sample | Fire resistance time/s | V300℃a /(℃•s-1) | V400℃/(℃•s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t300℃ | t400℃ | ||||
| 1 | EP/T-IFR | 200 | 1040 | 1.50 | 0.38 |
| 2 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% Fe2O3 | 230 | 2200 | 1.30 | 0.18 |
| 3 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 280 | 2360 | 1.07 | 0.17 |
| 4 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% Fe2O3 | 220 | 2010 | 1.36 | 0.20 |
| 5 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% ZnO | 320 | 1780 | 0.94 | 0.22 |
| 6 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 340 | 2140 | 0.88 | 0.19 |
| 7 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% ZnO | 530 | 1710 | 0.57 | 0.23 |
| 8 | EP/T-IFR/2.3wt% TiO2 | 220 | 1440 | 1.36 | 0.28 |
| 9 | EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 260 | 1520 | 1.15 | 0.26 |
| 10 | EP/T-IFR/4.5wt% TiO2 | 240 | 1380 | 1.25 | 0.29 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR300℃ /% | △CRb300℃ /% | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | ||||
| EP/T-IFR | -/238 | - | -/86 | - | -/27 | - |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 242/271 | 29 | 87/91 | 4 | 29/39 | 10 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt%ZnO | 242/270 | 28 | 87/93 | 6 | 29/36 | 7 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 242/268 | 26 | 87/89 | 2 | 29/32 | 3 |
表2 EP/T-IFR与EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO涂层在空气气氛中的TG数据
Table 2 TG data of EP/T-IFR and EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO coatings in air
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR300℃ /% | △CRb300℃ /% | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | ||||
| EP/T-IFR | -/238 | - | -/86 | - | -/27 | - |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 242/271 | 29 | 87/91 | 4 | 29/39 | 10 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt%ZnO | 242/270 | 28 | 87/93 | 6 | 29/36 | 7 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 242/268 | 26 | 87/89 | 2 | 29/32 | 3 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | |||
| EP | -/123 | - | -/5.7 | - |
| EP/5wt%Fe2O3 | 125/183 | 58 | 10.4/15.9 | 5.5 |
| EP/5wt%ZnO | 125/186 | 61 | 10.4/18.7 | 8.3 |
| EP/5wt%TiO2 | 125/172 | 47 | 10.4/12.6 | 2.2 |
表3 EP和EP/5wt% MO复合物在氮气气氛中的TG数据
Table 3 TG data of EP and EP /5wt% MO composites in N2
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti /℃ | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | Calcd./Exp. | |||
| EP | -/123 | - | -/5.7 | - |
| EP/5wt%Fe2O3 | 125/183 | 58 | 10.4/15.9 | 5.5 |
| EP/5wt%ZnO | 125/186 | 61 | 10.4/18.7 | 8.3 |
| EP/5wt%TiO2 | 125/172 | 47 | 10.4/12.6 | 2.2 |
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | /℃ | Calcd./Exp. | /% | |
| T-IFR | -/320 | - | -/49 | - |
| T-IFR/Fe2O3 | 326/315 | -11 | 53/66 | 13 |
| T-IFR/ZnO | 326/312 | -14 | 53/62 | 9 |
| T-IFR/TiO2 | 326/318 | -8 | 53/57 | 4 |
表4 T-IFR和T-IFR/MO复合物在氮气气氛中的TG数据
Table 4 TG data of T-IFR and T-IFR / MO composites in N2
| Sample | Ti /℃ | △Ti | CR700℃ /% | △CR700℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd./Exp. | /℃ | Calcd./Exp. | /% | |
| T-IFR | -/320 | - | -/49 | - |
| T-IFR/Fe2O3 | 326/315 | -11 | 53/66 | 13 |
| T-IFR/ZnO | 326/312 | -14 | 53/62 | 9 |
| T-IFR/TiO2 | 326/318 | -8 | 53/57 | 4 |
| Sample | BE/eV | Ca/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | Cox/Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP/T-IFR | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /53.18 | 285.8 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/32.83 | 287.6 | -COO- /7.07 | 289.7 | -COOH /6.92 | 0.88 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /71.13 | 286.1 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/20.37 | 287.7 | -COO- /3.82 | 289.2 | -COOH /4.68 | 0.41 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /67.10 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/17.37 | 287.6 | -COO- /5.53 | 289.7 | -COOH /10.00 | 0.49 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /63.81 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/31.05 | 287.7 | -COO- /1.43 | 289.3 | -COOH /3.72 | 0.62 |
表5 EP/T-IFR和EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO涂层650℃残炭的C1s图谱拟合数据
Table 5 Fitting results for the C1s spectra of char residues obtained from EP/T-IFR and EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% MO coatings at 650℃
| Sample | BE/eV | Ca/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | BE/eV | Cox/% | Cox/Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP/T-IFR | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /53.18 | 285.8 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/32.83 | 287.6 | -COO- /7.07 | 289.7 | -COOH /6.92 | 0.88 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% Fe2O3 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /71.13 | 286.1 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/20.37 | 287.7 | -COO- /3.82 | 289.2 | -COOH /4.68 | 0.41 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% ZnO | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /67.10 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/17.37 | 287.6 | -COO- /5.53 | 289.7 | -COOH /10.00 | 0.49 |
| EP/T-IFR/3.5wt% TiO2 | 284.8 | C-C,C-H /63.81 | 285.9 | C-O,C-O-P, C-N/31.05 | 287.7 | -COO- /1.43 | 289.3 | -COOH /3.72 | 0.62 |
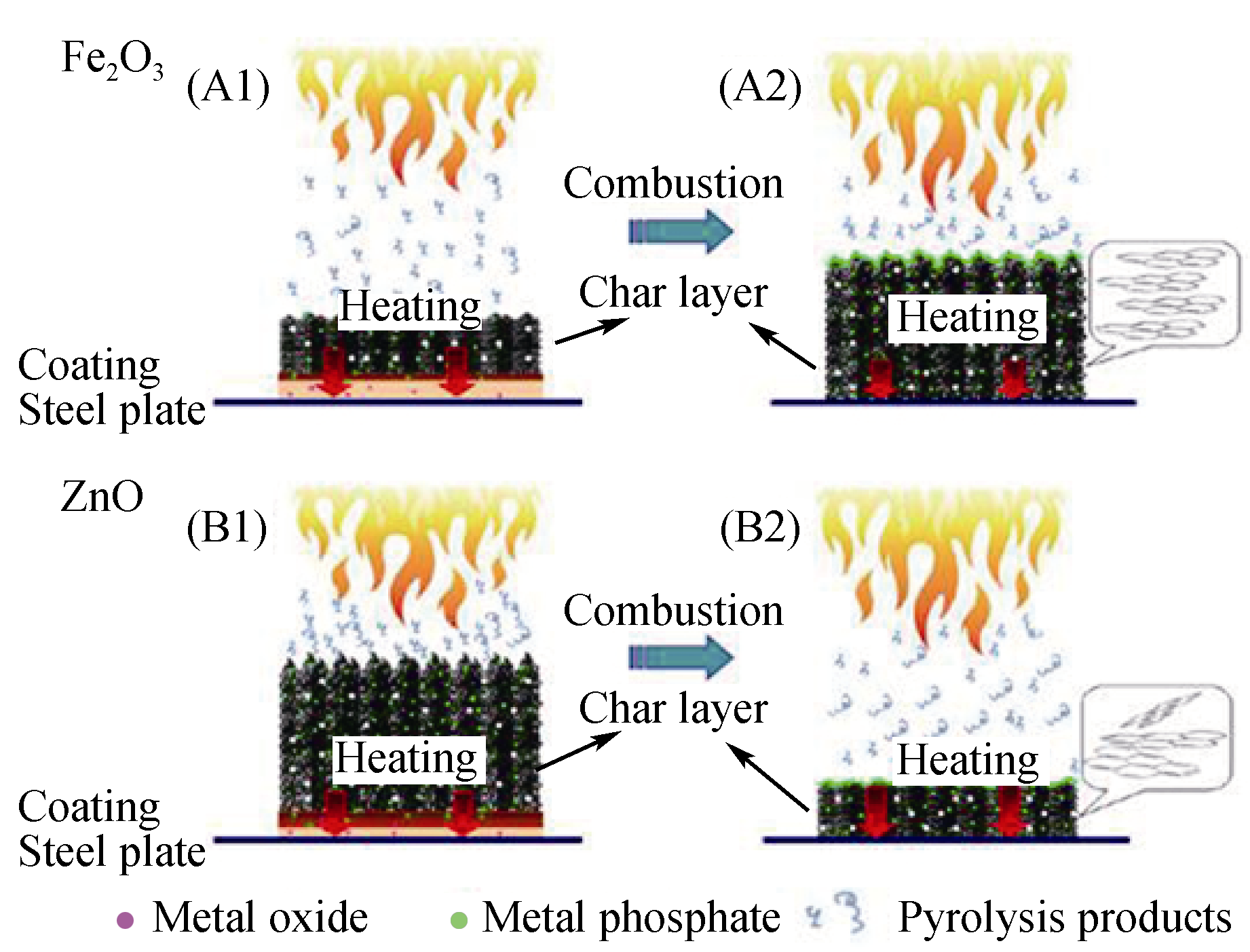
图6 MO对膨胀涂层的协效机理示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic drawing for the synergistic mechanism between MO and intumescent coating The initial combustion stage: A1 and B1; the end of combustion stage: A2 and B2
| [1] | CAMINO G, COSTA L, MARTINASSO G. Intumescent fire-retardant systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1989, 23(4): 359-376. |
| [2] | 杨荣杰,王建祺. 聚合物纳米复合物加工、热行为与阻燃性能. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 200-201. |
| [3] | DAI X H, WANG Y C, BAILEY C G. Effects of partial fire protection on temperature developments in steel joints protected by intumescent coating. Fire Saf. J., 2009, 44(3): 376-386. |
| [4] | ROBERT J A, BRIAN L, CHRIS M, et al. Thermo-physical performance of a fire protective coating for naval ship structures. Composites Part A, 2009, 40(1): 11-18. |
| [5] | STAGGS J E J, CREWE R J, BUTLER R. A theoretical and experimental investigation of intumescent behaviour in protective coatings for structural steel. Chem. Eng. Sci., 2012, 71: 239-251. |
| [6] | WANG G J, YANG J Y. Influences of glass flakes on fire protection and water resistance of waterborne intumescent fire resistive coating for steel structure. Prog. Org. Coat., 2011, 70(2/3): 150-156. |
| [7] | YEW M C, SULONG N H R. Fire-resistive performance of intumescent flame-retardant coatings for steel. Mater. Des., 2012, 34: 719-724. |
| [8] | WU K, ZHANG Y K, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of microencapsulation on thermal properties and flammability performance of epoxy composite. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2012, 94: 196-201. |
| [9] | SUN L S, QU Y T, LI S X. Co-microencapsulate of ammonium polyphosphate and pentaerythritol in intumescent flame-retardant coatings. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2013, 111(2): 1099-1106. |
| [10] | 屈红强. 聚硅氧烷对聚磷酸铵的表面包覆改性及其在环氧树脂中的阻燃应用研究. 北京: 北京理工大学博士论文, 2013. |
| [11] | LI B, XU M J. Effect of a novel charring-foaming agent on flame retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, 91(6): 1380-1386. |
| [12] | LI Y T, LI B, DAI J F, et al. Synergistic effects of lanthanum oxide on a novel intumescent flame retardant polypropylene system. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2008, 93(1): 9-16. |
| [13] | HAO JIAN-WEI, CHEN SU, DU JIAN-XIN, et al. An investigation on caged bicyclic phosphate applied to intumescent flame retar dant coating. J. Beijing. Inst. Technol., 2007, 27(11): 1027-1031. |
| [14] | HAO JIAN-WEI, WEN HAI-XU, DU JIAN-XIN, et al. Studies on fire resistance mechanism of intumescent flame retarded epoxy coating containing zinc borate as a synergistic agent. J. Beijing. Inst. Technol., 2012, 32(10): 1091-1100. |
| [15] | WANG Z Y, HAN E H, KE W. Influence of nano-LDHs on char formation and fire-resistant properties of flame-retardant coating. Prog. Org. Coat., 2005, 53(1): 29-37. |
| [16] | XIA LIAO-YUAN, WU YI-QIANG, HU YUN-CHU. Study on smoke catalytic conversion by Sn-substituted mesoporous silica composite in wood fire retardance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 532-536. |
| [17] | HU YUN-CHU, WU ZHI-PING, SUN HAN-ZHOU, et al. Synthesis of nano zinc borate fire retardant by solid state reaction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 815-820. |
| [18] | WANG Z Y, HAN E H, KE W. Effect of nanoparticles on the improvement in fire-resistant and anti-ageing properties of flame- retardant coating. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200(20/21): 5706-5716. |
| [19] | ZOU MIN, WANG QI-LIN. Improvement of performance of steel structural fireproofing dope with ZnO whisker and nanometer TiO2. Nano Technol. Precis. Eng, 2009, 7(1): 25-30. |
| [20] | CAMINO G, MARTINASSO G, COSTA L. Thermal degradation of pentaerythritol diphosphate, model compound for fire retardant intumescent systems: Part I—Overall thermal degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1990, 27(3): 285-296. |
| [21] | CAMINO G, MARTINASSO G, COSTA L, et al. Thermal degradation of pentaerythritol diphosphate, model compound for fire retardant intumescent systems: Part II—Intumescence step. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1990, 28(1): 17-38. |
| [22] | MENACHEM L, ENDO M. Catalysis of intumescent flame retardancy of polypropylene by metallic compounds. Polym. Adv. Technol., 2003, 14(1): 3-11. |
| [23] | LIU GUO-SHENG, ZHOU YOU, HAO JIAN-WEI. Thermal degradation mechanism of Bi2O3 synergistic intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Chin. Synth. Res. Plast., 2013, 30(5): 15-19. |
| [24] | LI GUO-XIN, HE YAN-SHU, NAN FENG, et al. Influence of MoO3, MoSi2 and Fe2O3 on residual chars of intumescent fire-retardant coating. J. Build. Mater., 2012, 15(3): 349-355. |
| [25] | ZHOU YOU, HAO JIAN-WEI, LIU GUO-SHENG, et al. Influencing mechanism of transition metal oxide on thermal decomposition of ammonium polyphosphate. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(6): 1115-1122. |
| [26] | JIMENEZ M, DUQUESNE S, BOURBIGOT S. Intumescent fire protective coating: toward a better understanding of their mechanism of action. Thermochim. Acta, 2006, 449(1/2): 16-26. |
| [27] | 胡 源,宋 磊. 阻燃聚合物纳米复合材料. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 156-157. |
| [28] | BAI Z M, WANG X, TANG G, et al. Structure-property relationships of synthetic organophosphorus flame retardant oligomers by thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta, 2013, 565(10): 17-26. |
| [29] | BOURBIGOT S, BRAS M L, GENGEMBRE L, et al. XPS study of an intumescent coating application to the ammonium polyphosphate/pentaerythritol fire-retardant system. Appl. Surf. Sci., 1994, 81(3): 299-307. |
| [30] | JIANG W Z, HAO J W, HAN Z D. Study on the thermal degradation of mixtures of ammonium polyphosphate and a novel caged bicyclic phosphate and their flame retardant effect in polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2012, 97(4): 632-637. |
| [31] | 韩维屏. 催化化学导论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 392-393. |
| [32] | 麦松威,周公度,李伟基. 高等无机结构化学, 2版. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2001: 47-49. |
| [33] | ZHU J, UHL F M, MORGAN A B, et al. Studies on the mechanism by which the formation of nanocomposites enhances thermal stability. Chem. Mater., 2001, 13(12): 4649-4654. |
| [1] | 杨茗凯, 黄泽皑, 周芸霄, 刘彤, 张魁魁, 谭浩, 刘梦颖, 詹俊杰, 陈国星, 周莹. 基于Cu与金属氧化物-KCl熔融介质的甲烷热解制备少层石墨烯与氢气联产研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [2] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [3] | 杨鑫, 韩春秋, 曹玥晗, 贺桢, 周莹. 金属氧化物电催化硝酸盐还原合成氨研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 979-991. |
| [4] | 谢天, 宋二红. 弹性应变对C、H、O在过渡金属氧化物表面吸附的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [5] | 郭凌翔, 唐颖, 黄世伟, 肖博澜, 夏东浩, 孙佳. C/C复合材料高熵氧化物涂层抗烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 61-70. |
| [6] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [7] | 孙佳伟, 宛心怡, 杨婷, 马董云, 王金敏. Ti2Nb10O29薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1434-1440. |
| [8] | 杨言言, 李永国, 祝小雯, 杜晓, 马旭莉, 郝晓刚. 电活性镍钴双金属氧化物高选择性去除/回收水中磷酸盐离子[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 292-298. |
| [9] | 郑时有, 董飞, 庞越鹏, 韩盼, 杨俊和. 纳米金属氧化物基锂离子电池负极材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1295-1306. |
| [10] | 吕元杰, 宋旭波, 何泽召, 谭鑫, 周幸叶, 王元刚, 顾国栋, 冯志红. 基于Al2O3介质的Ga2O3 MOSFET器件制备研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(9): 976-980. |
| [11] | 梁继然, 张叶, 杨然, 赵一瑞, 郭津榜. VO2(B)/ZnO异质复合纳米棒结构的室温NH3敏感性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1323-1329. |
| [12] | 田晓冬, 李 肖, 杨 桃, 宋 燕, 刘占军, 郭全贵. 双金属氧化物和复合材料的合成及其在超级电容器中的应用进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 459-468. |
| [13] | 王伟琦, 郑惠锋, 陆冠宏, 刘阳桥, 孙 静, 高 濂. 纳米金属氧化物在钙钛矿电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(9): 897-907. |
| [14] | 杨斌华, 刘雪强, 张 威, 李响潭, 张丽艳, 胡丽丽. 几种重金属氧化物和GeO2的加入对掺Yb3+氟磷玻璃 的光谱和激光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 961-966. |
| [15] | 徐理华, 曾虹燕, 廖梦尘, 徐 圣, 张治青, 李 巧. 吸附温度对MgAl金属氧化物微观结构和吸附Cr(VI)性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(5): 529-533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||