无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 1292-1300.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240085 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240085
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-02-28
修回日期:2024-06-12
出版日期:2024-11-20
网络出版日期:2024-06-24
通讯作者:
宋二红, 副研究员. E-mail: ehsong@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:谢 天(1993-), 男, 博士. E-mail: xietian1993@sjtu.edu.cn
Received:2024-02-28
Revised:2024-06-12
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2024-06-24
Contact:
SONG Erhong, associate professor. E-mail: ehsong@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:XIE Tian (1993-), male, PhD. E-mail: xietian1993@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目前铂(Pt)基贵金属催化剂(PGMs)是应用最广泛的商业催化剂, 但存在成本高、储量低、易引发小分子中毒的问题, 过渡金属氧化物(TMOs)因在氧化环境中具有较好的稳定性和出色的催化性能而被视为PGMs的潜在替代品。本研究通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算, 全面分析了弹性应变对TMOs表面上碳(C)、氢(H)和氧(O)吸附能的影响。系统探究了这些影响在四方结构(PtO2、PdO2)和六方结构(ZnO、CdO)中的作用, 以及它们与各自过渡金属的关系。结果显示, 在金属氧化物表面上, 最有利的吸附位点主要位于氧原子顶部或金属原子顶部, 而过渡金属则更倾向于面心立方(FCC)和六方密排(HCP)的空位。此外, 在弹性应变的影响下, 虽然TMOs和过渡金属对H和O的吸附能存在很大差异, 但弹性应变对TMOs上C、H和O吸附能的影响与过渡金属类似: 在压缩应变下吸附能增加、吸附减弱, 而在拉伸应变下吸附能减小、吸附增强。这种现象可以用基于吸附发生在金属原子顶部时的d带模型或吸附发生在O原子顶部时的p带模型来合理解释。因此, 调控弹性应变也可用于改变TMOs的催化特性。
中图分类号:
谢天, 宋二红. 弹性应变对C、H、O在过渡金属氧化物表面吸附的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300.
XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300.
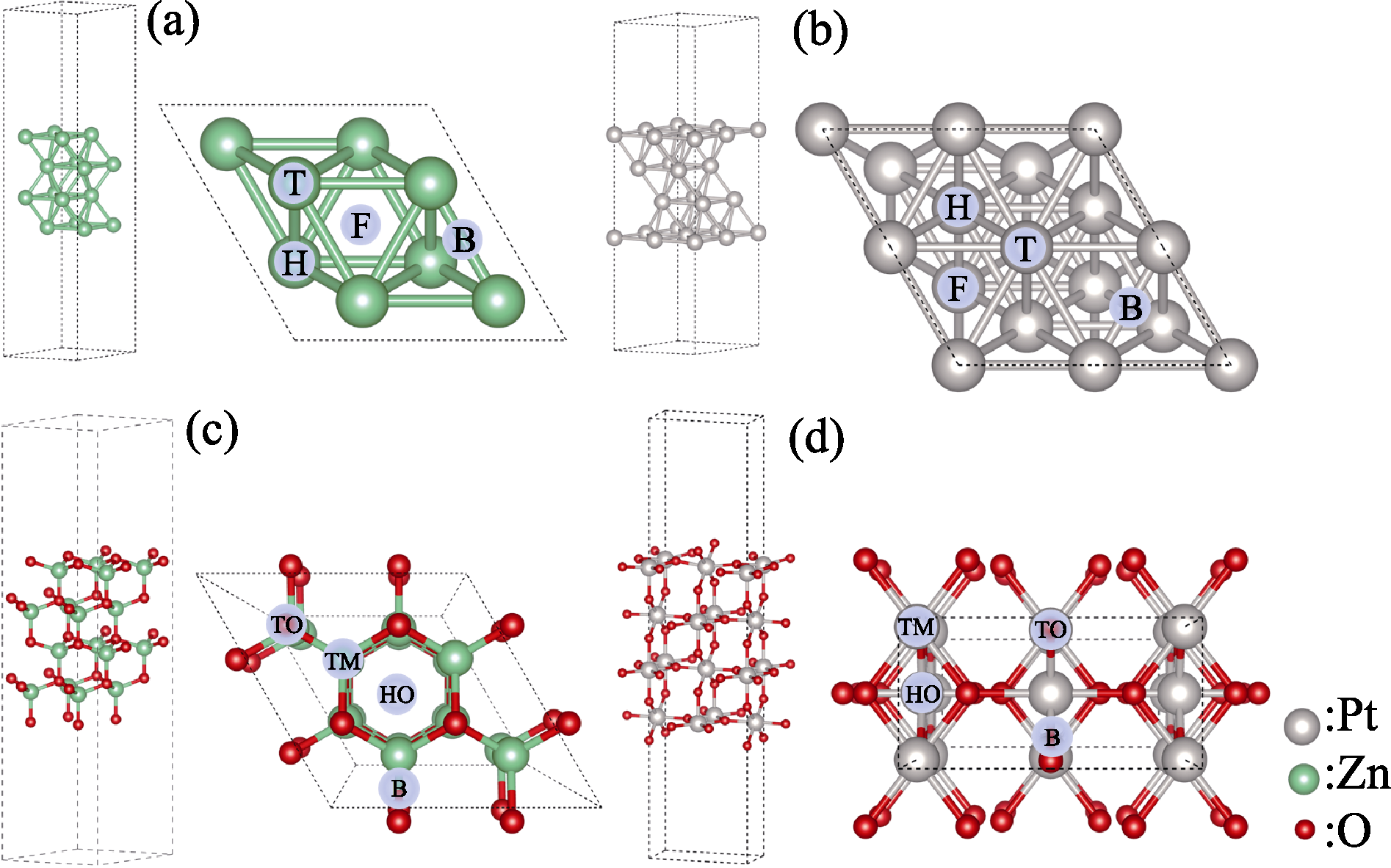
Fig. 1 Lateral and top views of (2×2×4) slab models (a) (0001) surface of hexagonal close-packed Zn; (b) (111) surface of face-centered cubic Pt; (c) (0001) surface of hexagonal ZnO; (d) (110) surface of tetragonal PtO2; Surfaces are separated by 15 Å of vacuum; T, B, H, and F stand for top, bridge, HCP hollow, and FCC hollow adsorption sites in (a, b); TO, TM, HO, and B stand for top of O, top of metal, hollow, and metal-oxygen bridge adsorption sites in (c, d) Colorful figures are available on website
| Zn | Cd | Pd | Pt | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.63 | 0.81 | -0.57 | -0.49 | -1.94 | -0.69 | -2.13 | -1.05 | |
| Adsorption site (H) | HCP | FCC | FCC | FCC | O top | O top | O top | O top |
| -2.41 | -2.24 | -2.11 | -2.16 | -0.25 | 1.17 | -0.43 | -0.72 | |
| Adsorption site (O) | HCP | FCC | FCC | FCC | O top | O top | M top | M top |
| -5.04 | -4.70 | -7.97 | -8.39 | -8.32 | -4.62 | -9.86 | -5.43 | |
| Adsorption site (C) | FCC | FCC | HCP | FCC | O top | O top | M top | M top |
Table 1 Adsorption energies and preferred adsorption sites for H, O, and C on TM and TMO
| Zn | Cd | Pd | Pt | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.63 | 0.81 | -0.57 | -0.49 | -1.94 | -0.69 | -2.13 | -1.05 | |
| Adsorption site (H) | HCP | FCC | FCC | FCC | O top | O top | O top | O top |
| -2.41 | -2.24 | -2.11 | -2.16 | -0.25 | 1.17 | -0.43 | -0.72 | |
| Adsorption site (O) | HCP | FCC | FCC | FCC | O top | O top | M top | M top |
| -5.04 | -4.70 | -7.97 | -8.39 | -8.32 | -4.62 | -9.86 | -5.43 | |
| Adsorption site (C) | FCC | FCC | HCP | FCC | O top | O top | M top | M top |
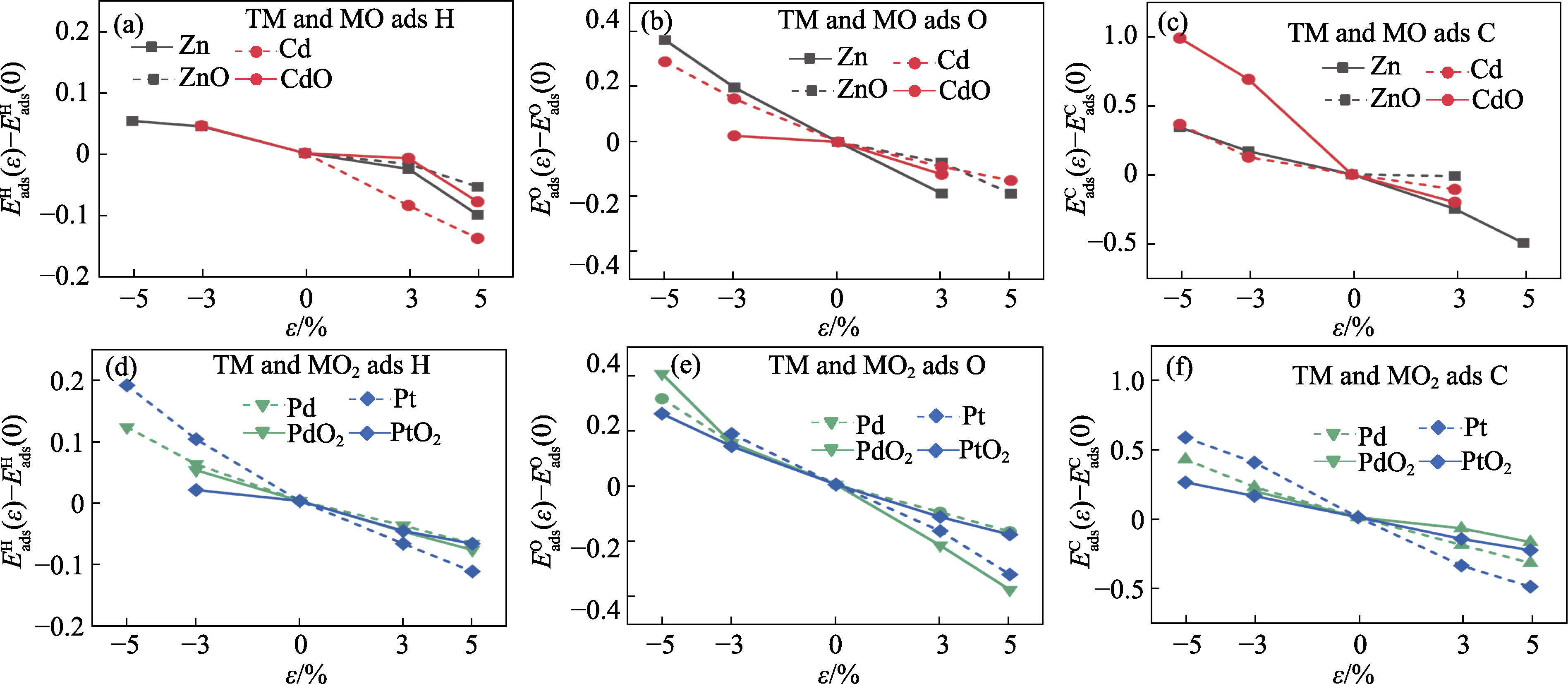
Fig. 2 Variation of the adsorption energy under biaxial strain with respect to the unstrained state $E_{\text{ads}}^{\text{X}}(\varepsilon )-E_{\text{ads}}^{\text{X}}(0)$ for different absorbates as a function of the biaxial strain $\varepsilon $ Hexagonal Zn and Cd as well as ZnO and CdO, adsorbed with (a) H, (b) O, and (c) C; Cubic Pd and Pt as well as tetragonal PdO2 and PtO2, adsorbed with (d) H, (e) O and (f) C
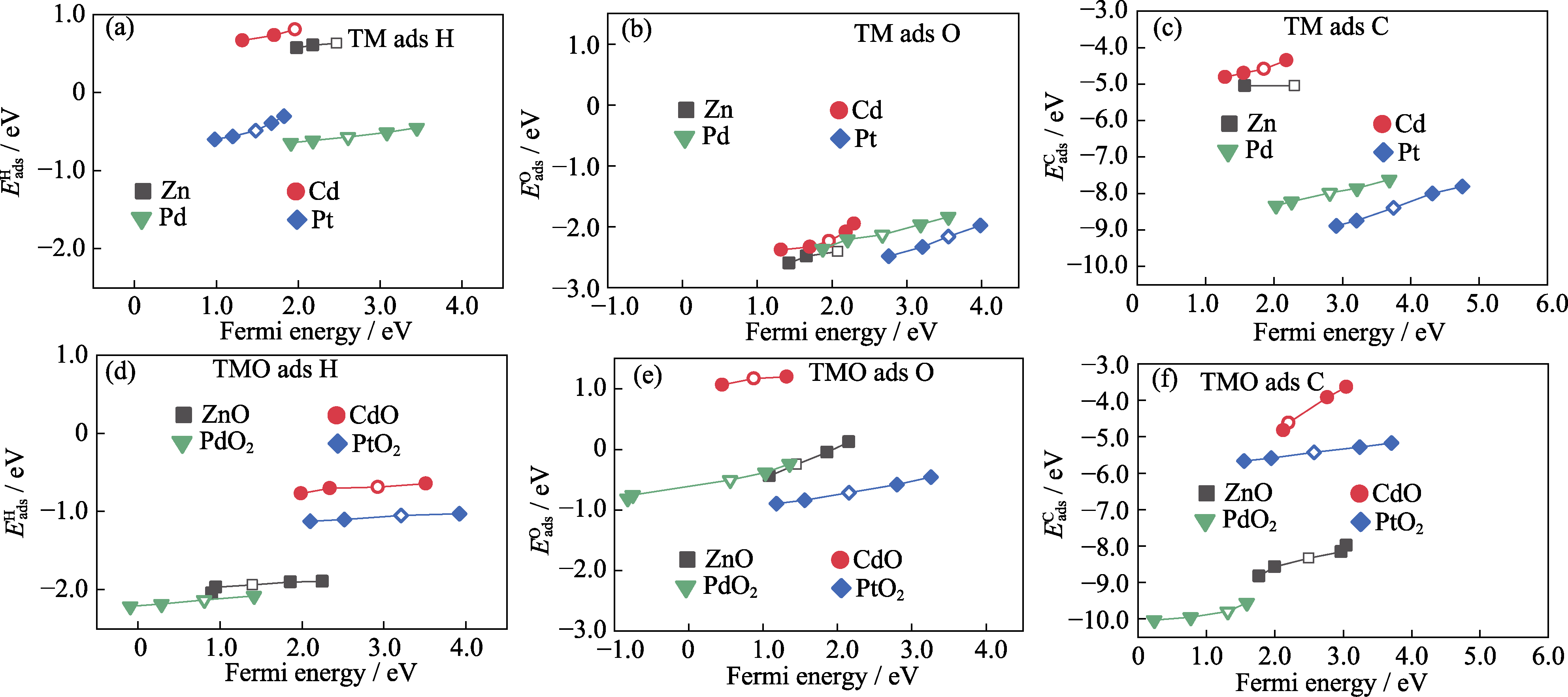
Fig. 3 Adsorption energies of strained slabs as a function of the Fermi energy in the strained slab with the corresponding adsorbate (a) H, (b) O and (c) C adsorption on TM; (d) H, (e) O and (f) C adsorption on TMO Empty symbol: adsorption energy without strain; Solid symbol on the left of empty symbol: adsorption energy under biaxial tensile strains; Solid symbol on the right of empty symbol: adsorption energy under biaxial compressive strains
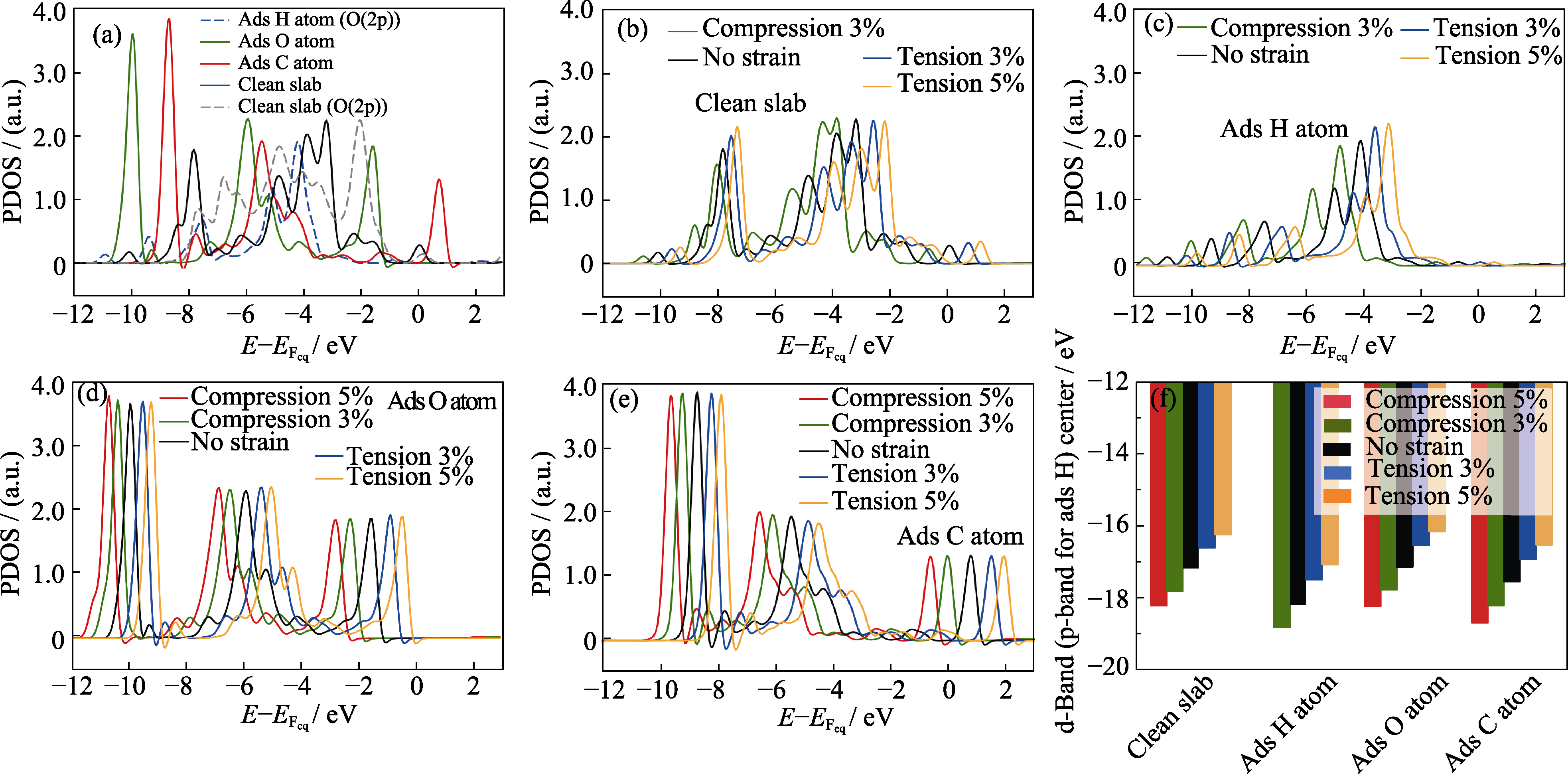
Fig. 4 PDOS onto d orbital of the Pt atom nearest to the C or O adsorbate and PDOS onto p orbital of the O atom nearest to the H adsorbate on the (111) PtO2 surface (a) Unstrained, clean slab and unstrained slab with different adsorbates; (b) Clean slab subjected to different biaxial strains; Slabs with (c) H, (d) O, and (e) C adsorbed and subjected to different biaxial strains; (f) Positions of the d-band center of Pt atom close to the C or O adsorbate and of the p-band center of O atom nearest to the H adsorbate on the (111) PtO2 surfaces subjected to different strains; Energy values are referenced to the Fermi level of the slab; Colorful figures are available on website
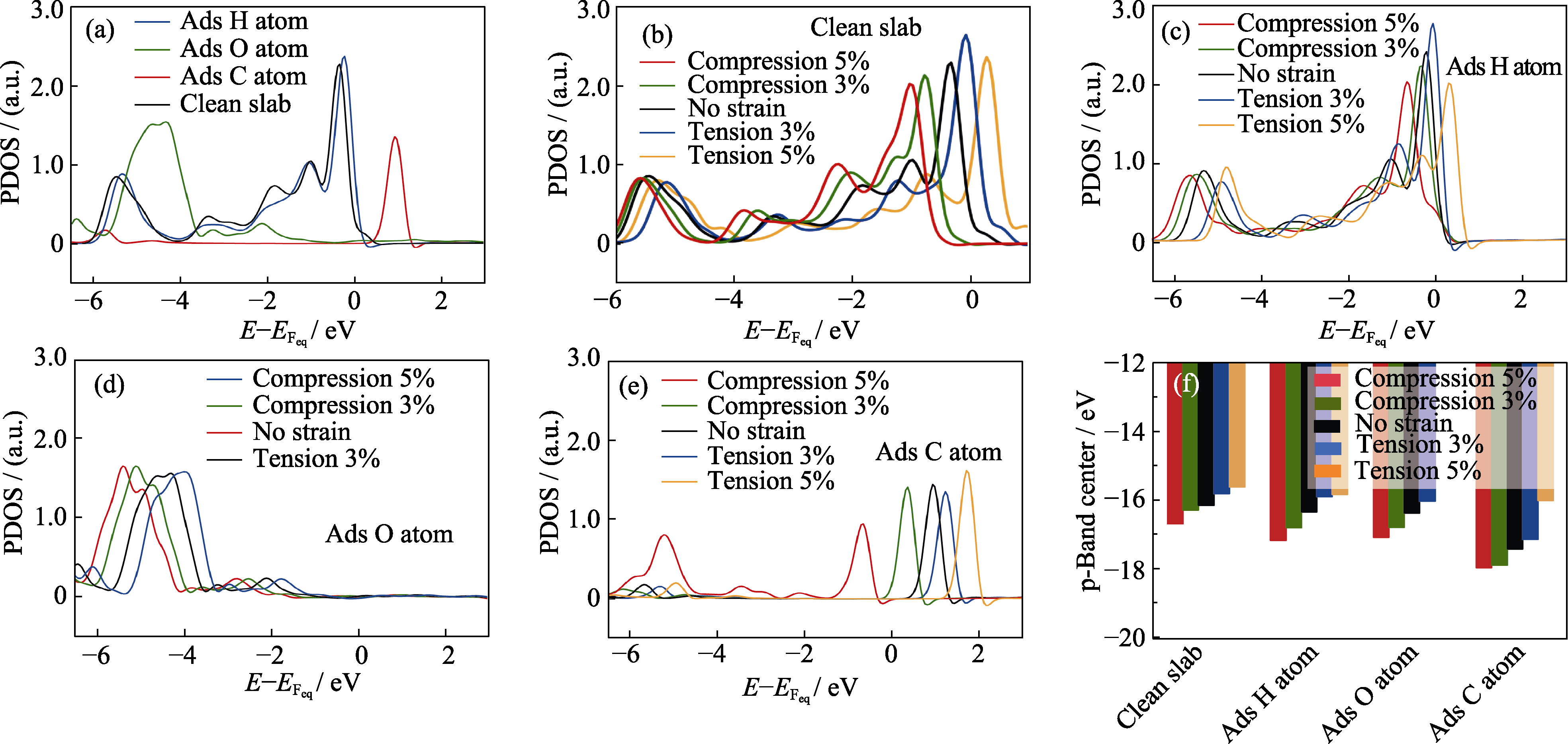
Fig. 5 PDOS onto p orbital of the O atom nearest to the H adsorbate on the (110) ZnO surface (a) Unstrained, clean slab and unstrained slab with different adsorbates; (b) Clean slab subjected to different biaxial strains; Slabs with (c) H, (d) O, and (e) C adsorbed and subjected to different biaxial strains; (f) Positions of the p-band of O atom nearest to the adsorbate on the (110) ZnO surfaces subjected to different strains; Energy values are referenced to the Fermi level of the slab; Colorful figures are available on website
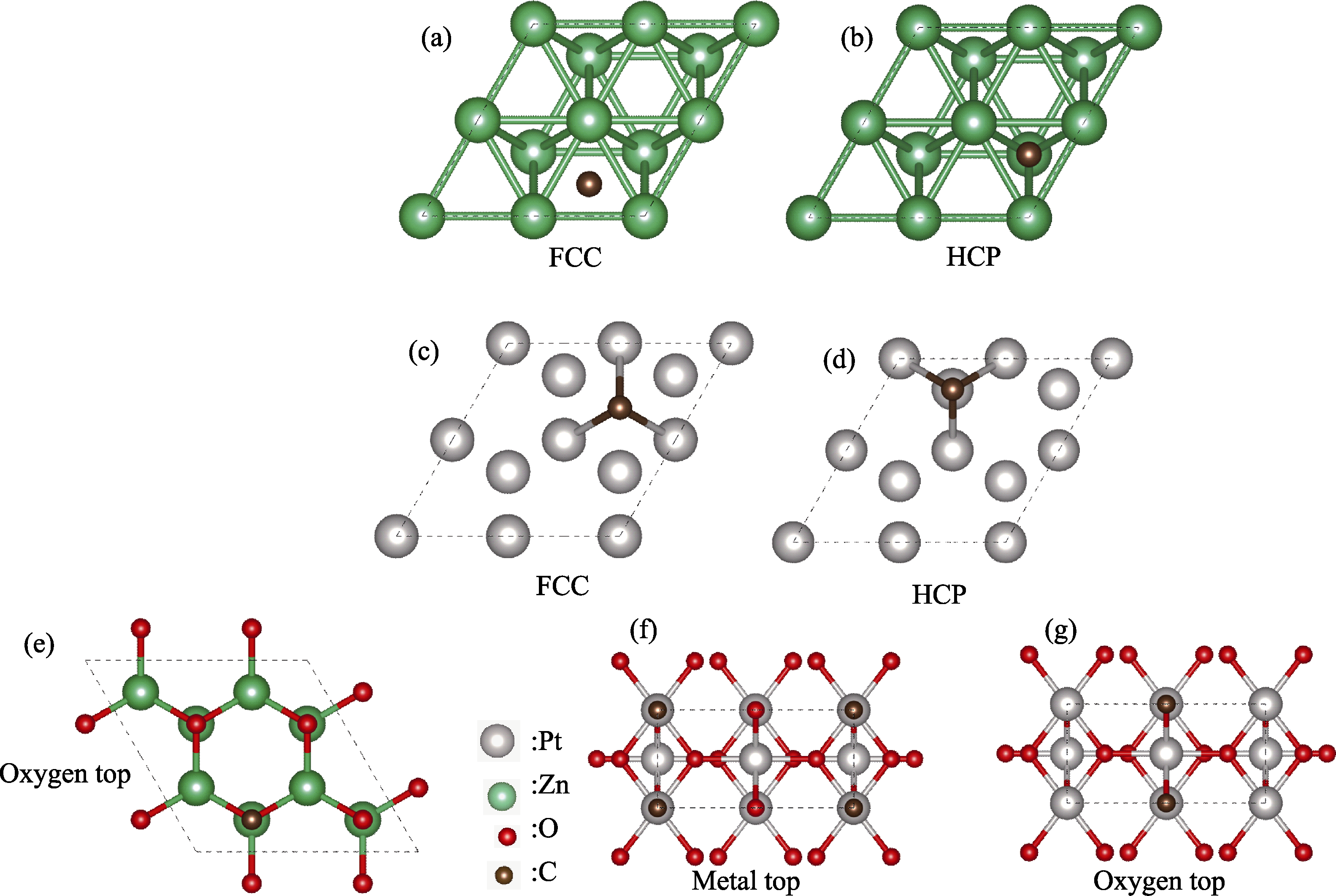
Fig. S1 Schematic diagram of the most stable adsorption site (a, b) C adsorbed on Zn surface (a) FCC site and (b) HCP site; (c, d) C adsorbed on Pt surface (c) FCC site and (d) HCP site; (e) The most stable adsorption site for C atom on the ZnO surface; (f, g) C adsorbed on PtO2 surface (f) metal top site and (g) oxygen top site Colorful figures are available on website
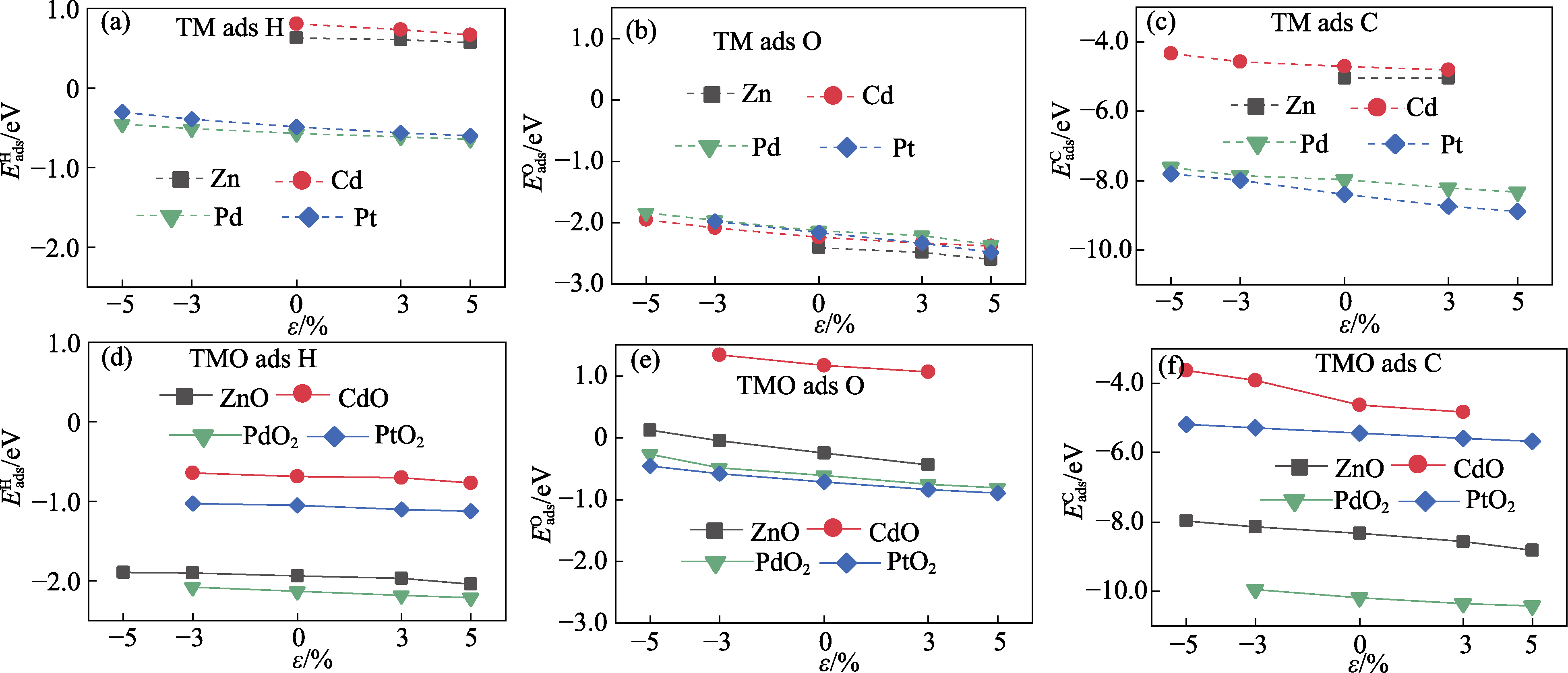
Fig. S2 Effect of biaxial elastic strains $\varepsilon $ on adsorption energies of H, O and C on TM and TMO (a) H on TM; (b) O on TM; (c) C on TM; (d) H on TMO; (e) O on TMO; (f) C on TMO
| Adsorbate | Zn | Cd | Pd | Pt | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | |
| Top metal | 0.88 | -0.23 | -4.33 | 1.13 | -0.19 | -2.88 | -0.18 | -0.77 | -6.92 | -0.11 | -0.48 | -6.36 |
| Bridge | 0.71 | -1.55 | -4.57 | 0.84 | -1.69 | -3.04 | -0.41 | -1.65 | -7.13 | -0.35 | -1.76 | -7.22 |
| FCC | 0.68 | -2.26 | -5.04 | 0.81 | -2.24 | -3.92 | -0.57 | -2.11 | -7.97 | -0.49 | -2.16 | -8.39 |
| HCP | 0.63 | -2.41 | -4.79 | 0.83 | -2.21 | -3.85 | -0.48 | -1.98 | -7.63 | -0.44 | -2.14 | -8.13 |
Table S1 Adsorption energy (eV) for H, O, and C on TM
| Adsorbate | Zn | Cd | Pd | Pt | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | |
| Top metal | 0.88 | -0.23 | -4.33 | 1.13 | -0.19 | -2.88 | -0.18 | -0.77 | -6.92 | -0.11 | -0.48 | -6.36 |
| Bridge | 0.71 | -1.55 | -4.57 | 0.84 | -1.69 | -3.04 | -0.41 | -1.65 | -7.13 | -0.35 | -1.76 | -7.22 |
| FCC | 0.68 | -2.26 | -5.04 | 0.81 | -2.24 | -3.92 | -0.57 | -2.11 | -7.97 | -0.49 | -2.16 | -8.39 |
| HCP | 0.63 | -2.41 | -4.79 | 0.83 | -2.21 | -3.85 | -0.48 | -1.98 | -7.63 | -0.44 | -2.14 | -8.13 |
| Adsorbate | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | |
| M top | 1.37 | 1.91 | -6.16 | 1.68 | 3.14 | -1.12 | -0.77 | -0.43 | -9.86 | 1.12 | -0.72 | -5.43 |
| O top | -1.94 | -0.25 | -8.32 | -0.69 | 1.17 | -4.61 | -2.13 | 0.99 | -6.45 | -1.05 | 1.03 | -2.17 |
| M-O Bridge | -0.13 | -0.15 | -7.16 | 1.63 | 2.17 | -3.85 | -1.02 | 0.36 | -6.52 | 0.98 | -0.32 | -2.22 |
| Hollow | -0.37 | -0.22 | -8.22 | -0.64 | 1.51 | -4.26 | -1.35 | 0.03 | -6.88 | 0.86 | -0.66 | -2.85 |
Table S2 Adsorption energy (eV) and preferred adsorption sites for H, O, and C on TMO
| Adsorbate | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | H | O | C | |
| M top | 1.37 | 1.91 | -6.16 | 1.68 | 3.14 | -1.12 | -0.77 | -0.43 | -9.86 | 1.12 | -0.72 | -5.43 |
| O top | -1.94 | -0.25 | -8.32 | -0.69 | 1.17 | -4.61 | -2.13 | 0.99 | -6.45 | -1.05 | 1.03 | -2.17 |
| M-O Bridge | -0.13 | -0.15 | -7.16 | 1.63 | 2.17 | -3.85 | -1.02 | 0.36 | -6.52 | 0.98 | -0.32 | -2.22 |
| Hollow | -0.37 | -0.22 | -8.22 | -0.64 | 1.51 | -4.26 | -1.35 | 0.03 | -6.88 | 0.86 | -0.66 | -2.85 |
| ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbed O | 0.02 | -0.41 | -0.36 | -0.47 | Adsorbed O | 0.43 | -0.07 | 0.49 | 0.56 |
| Charge O | -0.47 | -0.98 | -0.57 | -0.71 | Charge O | -1.08 | -1.07 | -0.76 | -0.76 |
| Charge M | 1.32 | 1.23 | 1.68 | 1.98 | Charge M | 1.26 | 1.15 | 1.62 | 1.81 |
| Surface O average | -1.03 | -1.04 | -0.72 | -0.83 | Surface O average | -1.15 | -1.10 | -0.85 | -0.92 |
| Surface M average | 1.26 | 1.22 | 1.66 | 1.93 | Surface M average | 1.24 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.61 |
| -0.25 | 1.17 | -0.43 | -0.72 | -1.94 | -0.69 | -2.13 | -1.05 |
Table S3 Bader charges for selected atoms in ZnO, CdO, PdO2, and PtO2
| ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ZnO | CdO | PdO2 | PtO2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbed O | 0.02 | -0.41 | -0.36 | -0.47 | Adsorbed O | 0.43 | -0.07 | 0.49 | 0.56 |
| Charge O | -0.47 | -0.98 | -0.57 | -0.71 | Charge O | -1.08 | -1.07 | -0.76 | -0.76 |
| Charge M | 1.32 | 1.23 | 1.68 | 1.98 | Charge M | 1.26 | 1.15 | 1.62 | 1.81 |
| Surface O average | -1.03 | -1.04 | -0.72 | -0.83 | Surface O average | -1.15 | -1.10 | -0.85 | -0.92 |
| Surface M average | 1.26 | 1.22 | 1.66 | 1.93 | Surface M average | 1.24 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.61 |
| -0.25 | 1.17 | -0.43 | -0.72 | -1.94 | -0.69 | -2.13 | -1.05 |
| [1] | KWEON D H, JEON I Y, BAEK J B. Electrochemical catalysts for green hydrogen energy. Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research, 2021, 2(7): 2100019. |
| [2] | GUO J, JIAO S, YA X, et al. Ultrathin Pd‐based perforated nanosheets for fuel cells electrocatalysis. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(21): e202200729. |
| [3] | WIJAYA D T, LEE C W. Metal-organic framework catalysts: a versatile platform for bioinspired electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446(3): 138311. |
| [4] | XU H, MA Y, CHEN J, et al. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate-a step towards a sustainable nitrogen cycle. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51: 2710. |
| [5] | FRYDENDAL R, PAOLI E A, KNUDSEN B P, et al. Benchmarking the stability of oxygen evolution reaction catalysts: the importance of monitoring mass losses. ChemElectroChem, 2014, 1(12): 2075. |
| [6] | LEE Y, SUNTIVICH J, MAY K J, et al. Synthesis and activities of rutile IrO2 and RuO2 nanoparticles for oxygen evolution in acid and alkaline solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2012, 3(3): 399. |
| [7] |
WU T, HAN M, ZHU X, et al. The electrochemical corrosion of an air thermally-treated carbon fiber cloth electrocatalyst with outstanding oxygen evolution activity under alkaline conditions. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(15): 2344.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | SUEN N T, HUNG S F, QUAN Q, et al. Electrocatalysis for the oxygen evolution reaction: recent development and future perspectives. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(2): 337. |
| [9] |
NIE Y, LI L, WEI Z. Recent advancements in Pt and Pt-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(8): 2168.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
KULKARNI A, SIAHROSTAMI S, PATEL A, et al. Understanding catalytic activity trends in the oxygen reduction reaction. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(5): 2302.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
DOYLE R L, GODWIN I J, BRANDON M P, et al. Redox and electrochemical water splitting catalytic properties of hydrated metal oxide modified electrodes. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(33): 13737.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
LANG R, DU X, HUANG Y, et al. Single-atom catalysts based on the metal-oxide interaction. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(21): 11986.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | SUN Y, CHEN G, XI S, et al. Catalytically influential features in transition metal oxides. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(22): 13947. |
| [14] | KUHLENBECK H, SHAIKHUTDINOV S, FREUND H J. Well- ordered transition metal oxide layers in model catalysis -- a series of case studies. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(6): 3986. |
| [15] | XIONG W, YIN H, WU T, et al. Challenges and opportunities of transition metal oxides as electrocatalysts. Chemistry, 2023, 29(5): e202202872. |
| [16] | XU L, WANG Z, WANG J, et al. N-doped nanoporous Co3O4 nanosheets with oxygen vacancies as oxygen evolving electrocatalysts. Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(16): 165402. |
| [17] | MOCK S A, SHARP S E, STONER T R, et al. CeO2 nanorods- supported transition metal catalysts for co oxidation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 466: 261. |
| [18] | MEFFORD J T, RONG X, ABAKUMOV A M, et al. Water electrolysis on La1-XSrXCoO3-δ perovskite electrocatalysts. Nature Communication, 2016, 7: 11053. |
| [19] | KUANG X, KANG B, WANG Z, et al. Sulfur-doped CoO nanoflakes with loosely packed structure realizing enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Chemistry, 2018, 24(65): 17288. |
| [20] | LUO M, GUO S. Strain-controlled electrocatalysis on multimetallic nanomaterials. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(11): 17059. |
| [21] | KHORSHIDI A, VIOLET J, HASHEMI J, et al. How strain can break the scaling relations of catalysis. Nature Catalysis, 2018, 1(4): 263. |
| [22] |
JIAO Y, ZHENG Y, JARONIEC M, et al. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen- and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(8): 2060.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | ESCUDERO-ESCRIBANO, MALACRIDA M P, HANSEN M H, et al. Tuning the activity of Pt alloy electrocatalysts by means of the lanthanide contraction. Science, 2016, 352(6281): 73. |
| [24] | AMAKAWA K, SUN L, GUO C, et al. How strain affects the reactivity of surface metal oxide catalysts. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(51): 13553. |
| [25] | LING T, YAN D Y, WANG H, et al. Activating cobalt(II) oxide nanorods for efficient electrocatalysis by strain engineering. Nature Communication, 2017, 8: 1509. |
| [26] | NØRSKOV J K, BLIGAARD T, LOGADOTTIR A, et al. Trends in the exchange current for hydrogen evolution. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(3): J23. |
| [27] | MARTÍNEZ-ALONSO C, GUEVARA-VELA J M, JAVIER L L. Understanding the effect of mechanical strains on the catalytic activity of transition metals. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2022, 24(8): 4832. |
| [28] | MARTÍNEZ-ALONSO C, GUEVARA-VELA J M, JAVIER L L. The effect of elastic strains on the adsorption energy of H, O, and OH in transition metals. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(37): 21295. |
| [29] | BAHN S R, JACOBS K W. An object-oriented scripting interface to a legacy electronic structure code. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2002, 4(3): 56. |
| [30] | JAIN A, ONG S P, HAUTIER G, et al. Commentary: the materials project: a materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Materials, 2013, 1(1): 011002. |
| [31] | GIANNOZZI P, BARONI S, BONINI N, et al. Quantum espresso: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2009, 21(39): 395502. |
| [32] | PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 50(24): 308. |
| [33] | TANG W, SANVILLE E, HENKELMAN G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2009, 21(8): 084204. |
| [34] | SANVILLE E, KENNY S D, SMITH R, et al. Improved grid- based algorithm for Bader charge allocation. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2007, 28(5): 899. |
| [35] | HENKELMAN G, ARNALDSSON A, JÓNSSON H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density. Computational Materials Science, 2006, 36(3): 354. |
| [36] | HAN J, SUN H, SHI T, et al. Rationalization of nonlinear adsorption energy-strain relations and Bronsted-Evans-Polanyi and transition state scaling relationships under strain. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12(47): 11578. |
| [37] | HAMMER B N, NØRSKOV J K. Electronic factors determining the reactivity of metal surfaces. Surface Science, 1995, 343: 211. |
| [38] | HAMMER B N, NØRSKOV J K. Why gold is the noblest of all the metals. Nature, 1995, 376(20): 238. |
| [39] | MAVRIKAKIS M, HAMMER B N, NØRSKOV J K. Effect of strain on the reactivity of metal surfaces. Physical Review B, 1998, 81(13): 2819. |
| [40] | PANG Q, ZHANG Y, ZHANG J M, et al. Structural and electronic properties of atomic oxygen adsorption on Pt(111): a density-functional theory study. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(7): 3047. |
| [41] | KATTEL S, WANG G. Beneficial compressive strain for oxygen reduction reaction on Pt (111) surface. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 141(12): 124713. |
| [42] | JACOBS R, HWANG J, SHAO-HORN Y, et al. Assessing correlations of perovskite catalytic performance with electronic structure descriptors. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(3): 785. |
| [43] | DEMAISON J, CSÁSZÁR A G. Equilibrium Co bond lengths. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2012, 1023: 7. |
| [1] | 郭子玉, 朱云洲, 王力, 陈健, 李红, 黄政仁. Zn2+催化剂对酚醛树脂/乙二醇制备多孔碳微观孔结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 466-472. |
| [2] | 李建军, 陈芳明, 张梨梨, 王磊, 张丽亭, 陈慧雯, 薛长国, 徐良骥. CoFe2O4/MgAl-LDH催化剂活化过氧一硫酸盐促进抗生素降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 440-448. |
| [3] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [4] | 信震宇, 郭瑞华, 乌仁托亚, 王艳, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt-Fe/GO纳米催化剂的制备及其电催化乙醇氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [5] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [6] | 李娜, 曹锐霄, 魏进, 周晗, 肖红梅. 铁基正仲氢转化催化剂的影响因素[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 47-52. |
| [7] | 连敏丽, 苏佳欣, 黄鸿杨, 嵇玉寅, 邓海帆, 张彤, 陈崇启, 李达林. Ni-Mg-Al类水滑石衍生镍基催化剂的制备及其氨分解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 53-60. |
| [8] | 刘磊, 郭瑞华, 王丽, 王艳, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt3Co高指数晶面氧还原过程的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 39-46. |
| [9] | 靳宇翔, 宋二红, 朱永福. 3d过渡金属单原子掺杂石墨烯缺陷电催化还原CO2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 845-852. |
| [10] | 叶梓滨, 邹高昌, 吴琪雯, 颜晓敏, 周明扬, 刘江. 阳极支撑型锥管串接式直接碳固体氧化物燃料电池组的制备及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 819-827. |
| [11] | 李红兰, 张俊苗, 宋二红, 杨兴林. Mo/S共掺杂的石墨烯用于合成氨: 密度泛函理论研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 561-568. |
| [12] | 吴光宇, 舒松, 张洪伟, 李建军. 接枝内酯基活性炭增强苯乙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [13] | 张文宇, 郭瑞华, 岳全鑫, 黄雅荣, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 高熵磷化物双功能催化剂的制备及高效电解水性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1265-1274. |
| [14] | 何倩, 唐婉兰, 韩秉锟, 魏佳元, 吕文轩, 唐昭敏. pH响应铜掺杂介孔硅纳米催化剂增强肿瘤化疗-化学动力学联合治疗的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 90-98. |
| [15] | 郭凌翔, 唐颖, 黄世伟, 肖博澜, 夏东浩, 孙佳. C/C复合材料高熵氧化物涂层抗烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 61-70. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
