无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 473-480.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240445 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240445
所属专题: 【能源环境】氢能材料(202506); 【能源环境】化工催化(202506)
杨茗凯1( ), 黄泽皑1,2, 周芸霄1, 刘彤1, 张魁魁1, 谭浩1, 刘梦颖1, 詹俊杰1, 陈国星3, 周莹1,2(
), 黄泽皑1,2, 周芸霄1, 刘彤1, 张魁魁1, 谭浩1, 刘梦颖1, 詹俊杰1, 陈国星3, 周莹1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-25
修回日期:2025-01-10
出版日期:2025-05-20
网络出版日期:2025-01-24
通讯作者:
周 莹, 教授. E-mail: yzhou@swpu.edu.cn作者简介:杨茗凯(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: yangmk97@163.com
基金资助:
YANG Mingkai1( ), HUANG Zeai1,2, ZHOU Yunxiao1, LIU Tong1, ZHANG Kuikui1, TAN Hao1, LIU Mengying1, ZHAN Junjie1, CHEN Guoxing3, ZHOU Ying1,2(
), HUANG Zeai1,2, ZHOU Yunxiao1, LIU Tong1, ZHANG Kuikui1, TAN Hao1, LIU Mengying1, ZHAN Junjie1, CHEN Guoxing3, ZHOU Ying1,2( )
)
Received:2024-10-25
Revised:2025-01-10
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-01-24
Contact:
ZHOU Ying, professor. E-mail: yzhou@swpu.edu.cnAbout author:YANG Mingkai (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: yangmk97@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
甲烷热解是一种利用化石能源制备高附加值碳材料和氢气的技术。然而, 传统的化学气相沉积(CVD)法和熔融金属催化法在制备石墨烯时存在固体催化剂失活、石墨烯与催化剂分离困难以及反应温度高(≥1100 ℃)等问题, 限制了其工业化应用。本研究提出了通过金属Cu与金属氧化物-KCl熔融介质催化甲烷热解制备石墨烯的创新方案。通过添加金属氧化物(Al2O3、TiO2、ZrO2、MgO、SiO2)作为分散剂, 增强了Cu球活性位点的分散性, 特别是Cu球体积分数为50%的Cu/ZrO2和Cu球体积分数为75%的Cu/MgO催化剂, 可有效制备少层石墨烯。前者表现出最佳活性, 其甲烷转化率为22%, 氢气产率为21.5 mmol/h, 而且能产生大面积、平整的少层石墨烯。本研究为甲烷热解联产石墨烯与氢气的工业化发展提供了新的技术路线, 未来有望实现石墨烯的规模化制备。
中图分类号:
杨茗凯, 黄泽皑, 周芸霄, 刘彤, 张魁魁, 谭浩, 刘梦颖, 詹俊杰, 陈国星, 周莹. 基于Cu与金属氧化物-KCl熔融介质的甲烷热解制备少层石墨烯与氢气联产研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 473-480.
YANG Mingkai, HUANG Zeai, ZHOU Yunxiao, LIU Tong, ZHANG Kuikui, TAN Hao, LIU Mengying, ZHAN Junjie, CHEN Guoxing, ZHOU Ying. Co-production of Few-layer Graphene and Hydrogen from Methane Pyrolysis Based on Cu and Metal Oxide-KCl Molten Medium[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 473-480.
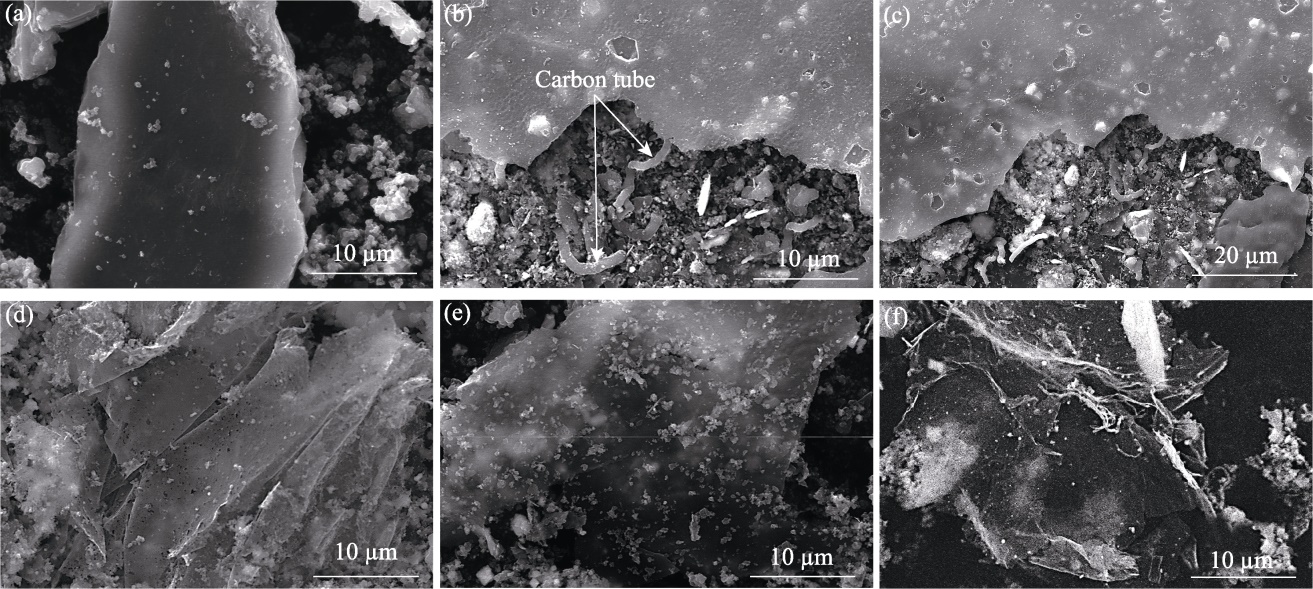
图4 xCu/ZrO2催化剂制备碳材料的SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of carbon materials produced using xCu/ZrO2 catalysts (a) x=0; (b, c) x=25%; (d) x=50%; (e) x=75%; (f) x=100%
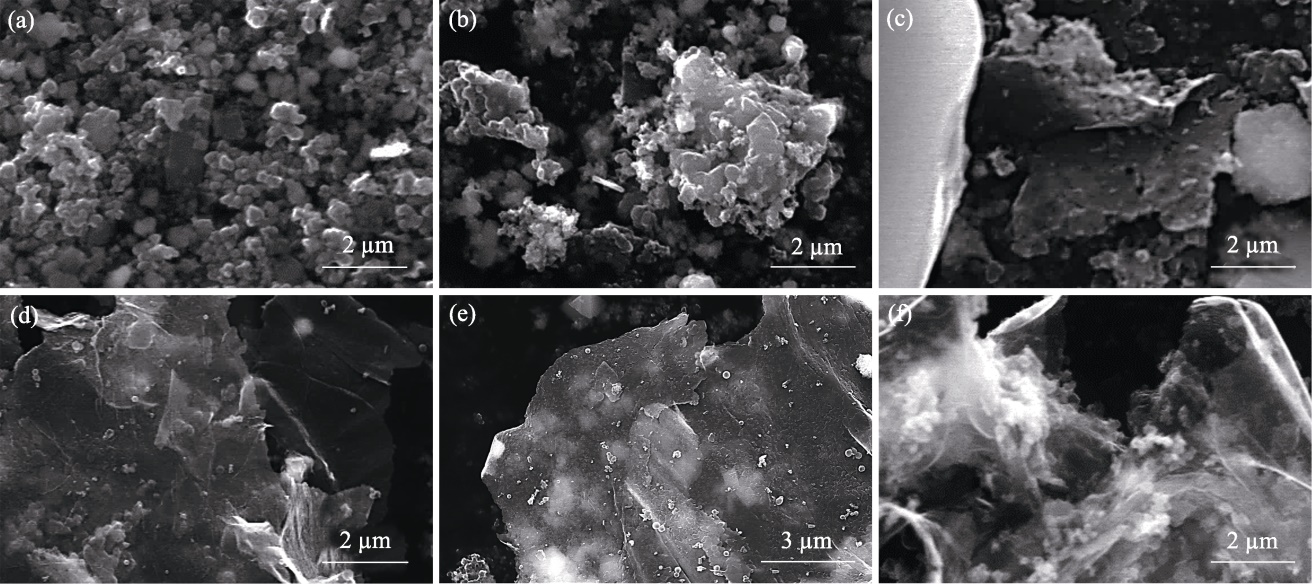

图5 xCu/MgO催化剂制备碳材料的SEM照片
Fig. 5 SEM images of carbon materials produced using xCu/MgO catalysts (a) x=0; (b) x=25%; (c) x=50%; (d, e) x=75%; (f) x=100%
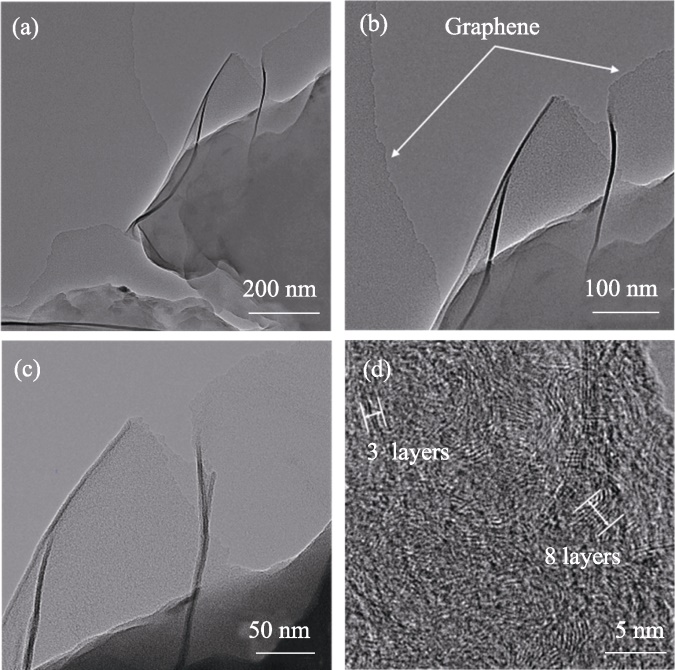
图6 (a~c) 50%Cu/ZrO2催化剂制备的碳材料的TEM照片; (d) 75%Cu/MgO催化剂制备的碳材料的HRTEM照片
Fig. 6 (a-c) TEM images of carbon materials produced using 50%Cu/ZrO2 catalysts; (d) HRTEM image of carbon materials produced using 75%Cu/MgO catalysts
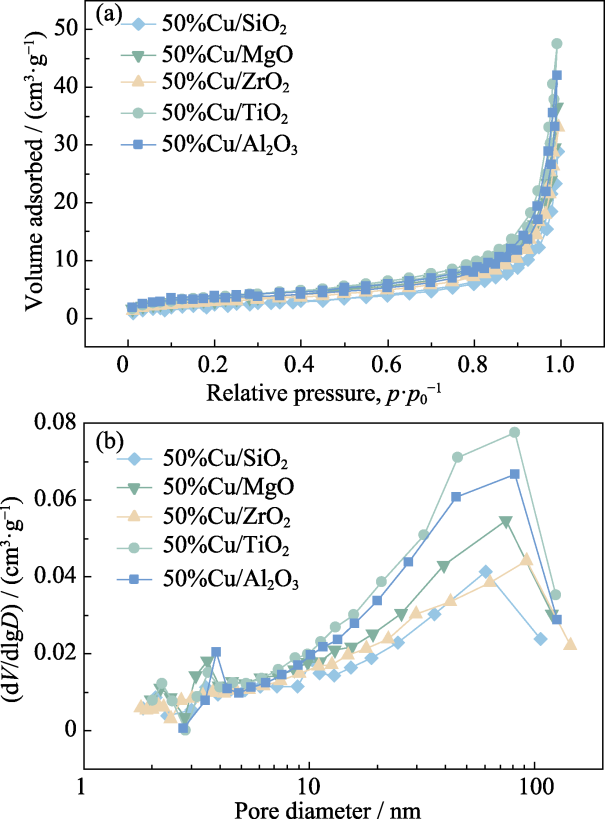
图9 50%Cu/MO催化剂制备的碳材料的氮气吸脱附曲线(a)和孔径分布图(b)
Fig. 9 Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms (a) and pore size distributions (b) of carbon materials produced using 50%Cu/MO catalysts
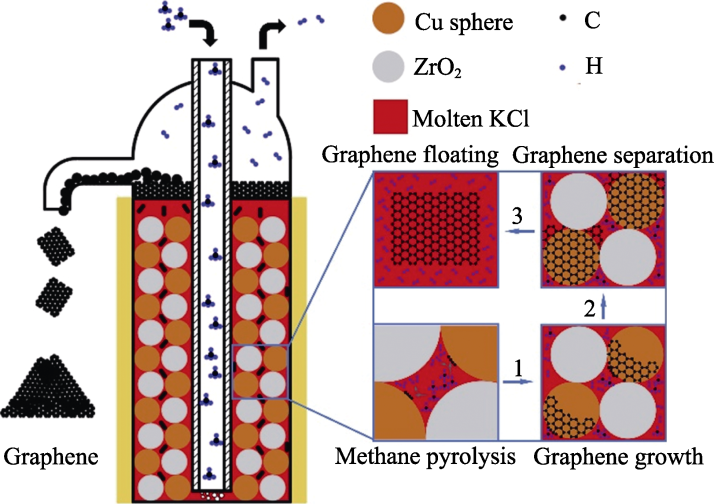
图10 反应机理示意图
Fig. 10 Schematic diagram of the reaction mechanism 1. Methane pyrolysis to few-layer graphene growth; 2. Few-layer graphene growth to separation; 3. Few-layer graphene separation to floating
| Sample | Carbon/% (in mass) | Impurity/% (in mass) |
|---|---|---|
| 50%Cu/SiO2 | 43.4 | 56.6 |
| 50%Cu/MgO | 67.5 | 32.5 |
| 50%Cu/ZrO2 | 52.2 | 47.8 |
| 50%Cu/TiO2 | 62.2 | 37.8 |
| 50%Cu/Al2O3 | 80.2 | 19.8 |
表S1 50%Cu/MO催化剂制备的碳材料及杂质的含量
Table 1 S1 Contents of carbon materials and impurity produced using 50%Cu/MO catalysts
| Sample | Carbon/% (in mass) | Impurity/% (in mass) |
|---|---|---|
| 50%Cu/SiO2 | 43.4 | 56.6 |
| 50%Cu/MgO | 67.5 | 32.5 |
| 50%Cu/ZrO2 | 52.2 | 47.8 |
| 50%Cu/TiO2 | 62.2 | 37.8 |
| 50%Cu/Al2O3 | 80.2 | 19.8 |
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50%Cu/SiO2 | 9.03 | 0.04 | 19.75 |
| 50%Cu/MgO | 11.76 | 0.06 | 19.26 |
| 50%Cu/ZrO2 | 10.33 | 0.05 | 19.76 |
| 50%Cu/TiO2 | 13.45 | 0.07 | 21.86 |
| 50%Cu/Al2O3 | 12.52 | 0.07 | 20.78 |
表S2 50%Cu/MO催化剂制备碳材料的BET数据
Table 2 S2 BET data for carbon materials produced using 50%Cu/MO catalysts
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50%Cu/SiO2 | 9.03 | 0.04 | 19.75 |
| 50%Cu/MgO | 11.76 | 0.06 | 19.26 |
| 50%Cu/ZrO2 | 10.33 | 0.05 | 19.76 |
| 50%Cu/TiO2 | 13.45 | 0.07 | 21.86 |
| 50%Cu/Al2O3 | 12.52 | 0.07 | 20.78 |
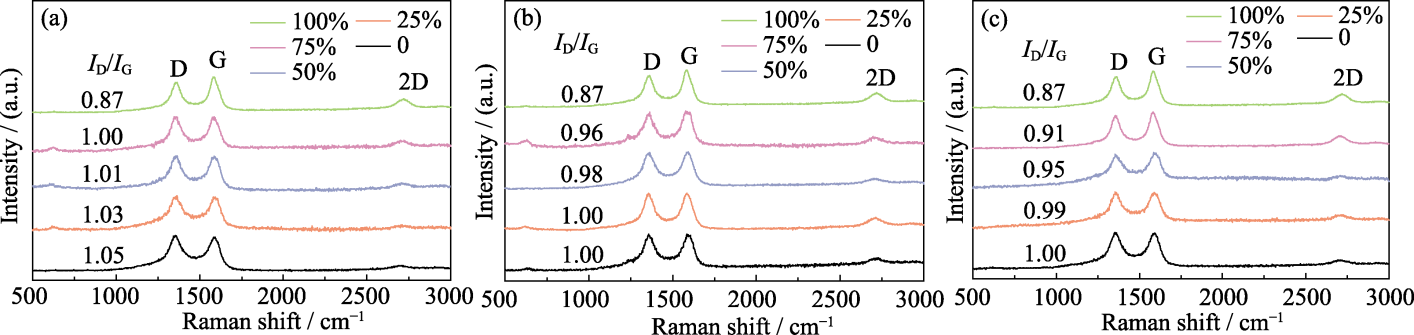
图S1 xCu/Al2O3(a)、xCu/TiO2(b)和xCu/SiO2(c)催化剂制备碳材料的Raman光谱图
Fig. 11 S1 Raman spectra of carbon materials produced using xCu/Al2O3 (a), xCu/TiO2 (b) and xCu/SiO2 (c) catalysts
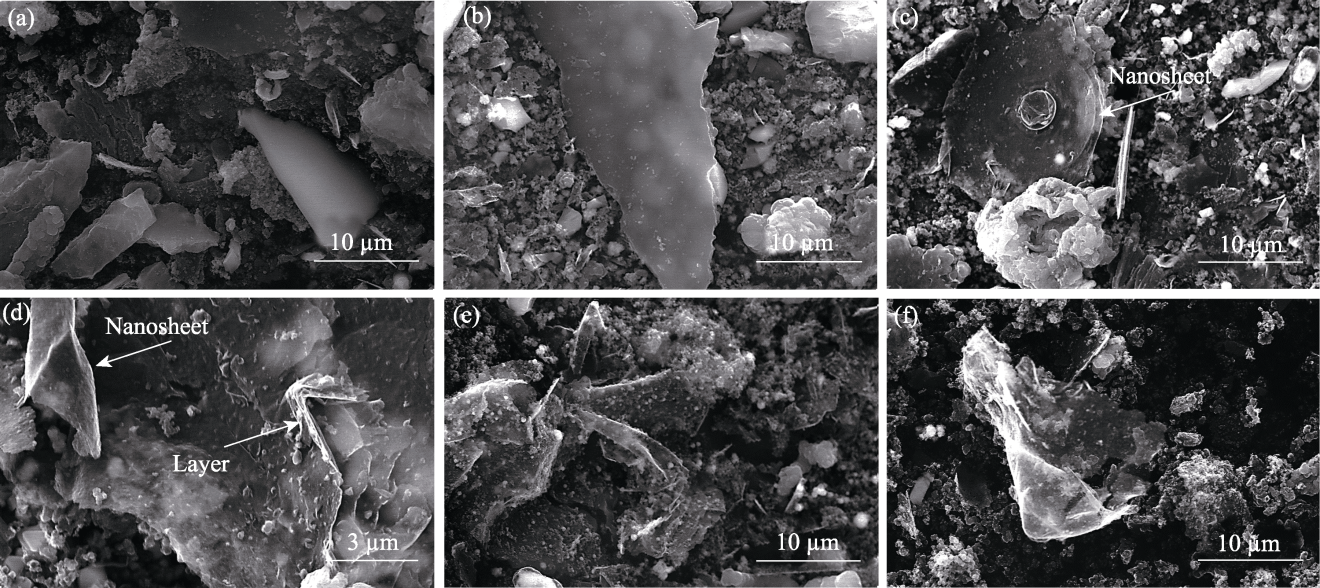
图S2 xCu/Al2O3催化剂制备碳材料的SEM照片
Fig. 12 S2 SEM images of carbon materials produced using xCu/Al2O3 catalysts (a) x=0; (b) x=25%; (c, d) x=50%; (e) x=75%; (f) x=100%
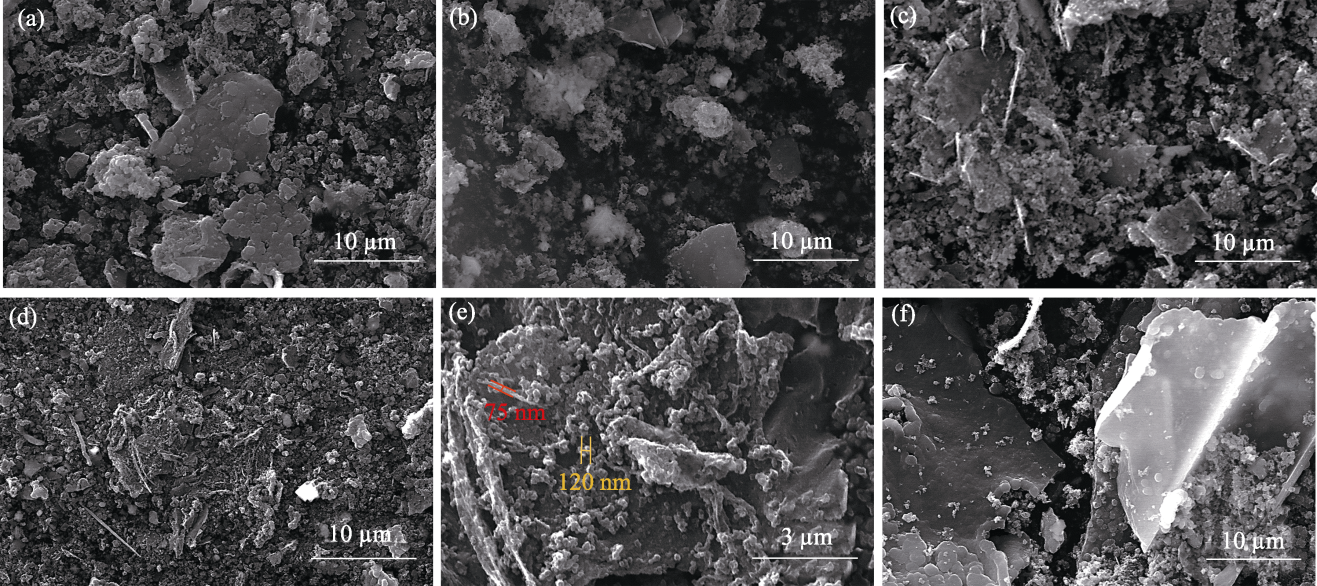
图S3 xCu/TiO2催化剂制备碳材料的SEM照片
Fig. 13 S3 SEM images of carbon materials produced using xCu/TiO2 catalysts (a) x=0; (b) x=25%; (c) x=50%; (d, e) x=75%; (f) x=100%
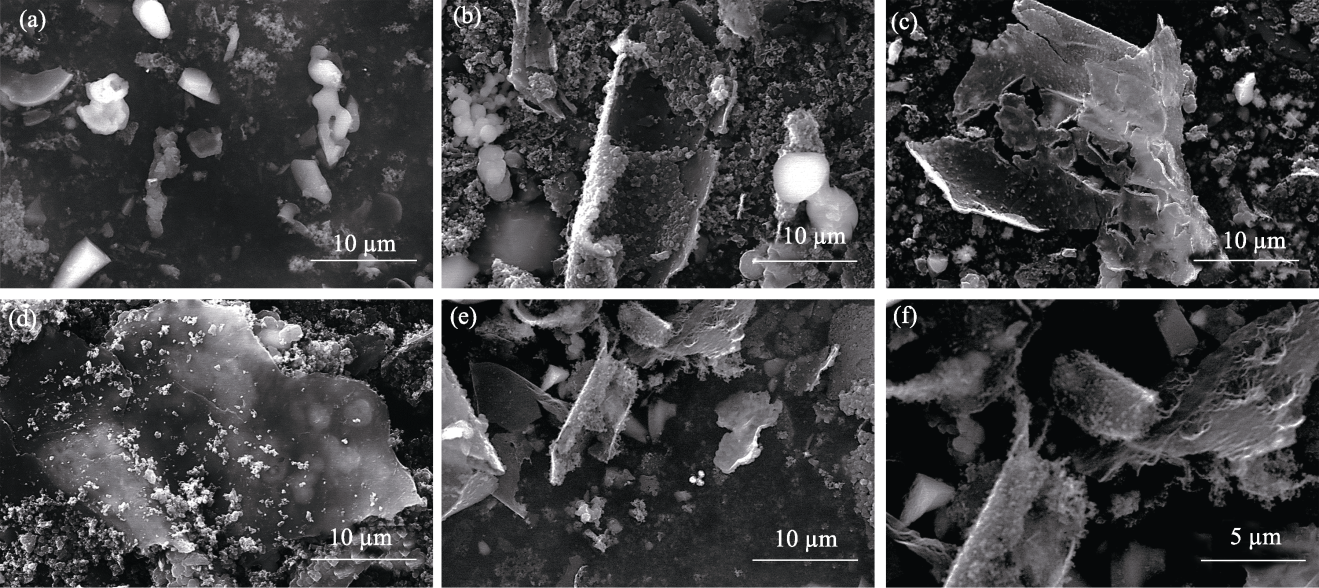
图S4 xCu/SiO2催化剂制备碳材料的SEM照片
Fig. 14 S4 SEM images of carbon materials produced using xCu/SiO2 catalysts (a) x=0; (b) x=25%; (c) x=50%; (d) x=75%; (e, f) x=100%
| [1] | 马新华, 张国生, 唐红君, 等. 天然气在构建清洁低碳能源体系中的地位与作用. 石油科技论坛, 2022, 41(1): 18. |
| [2] | 何展军, 黄敏, 林铁军, 等. 光热催化甲烷干重整研究进展. 物理化学学报, 2023, 39(9): 28. |
| [3] | PINAEVA L, NOSKOV A. Modern level of catalysts and technologies for the conversion of natural gas into syngas. Catalysis in Industry, 2022, 14(1): 66. |
| [4] | LI H, PEI W, YANG X, et al. Pt overlayer for direct oxidation of CH4 to CH3OH. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(11): 108292. |
| [5] | SUN C, ZHAO K, YI Z. Research progress in catalytic total oxidation of methane. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245. |
| [6] | SHEN X, WU D, FU X Z, et al. Highly selective conversion of methane to ethanol over CuFe2O4-carbon nanotube catalysts at low temperature. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2022, 33(1): 390. |
| [7] | CAO Y, YU W, HAN C, et al. Methane photooxidation with nearly 100% selectivity towards oxygenates: proton rebound ensures the regeneration of methanol. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 135(18):e202302196. |
| [8] | 黄泽皑, 周芸霄, 张魁魁, 等. 甲烷裂解制氢和碳材料工艺研究进展. 低碳化学与化工, 2024, 49(9): 1. |
| [9] | ABÁNADES A, RATHNAM R K, GEISSLER T, et al. Development of methane decarbonisation based on liquid metal technology for CO2-free production of hydrogen. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(19): 8159. |
| [10] | LIU M, HUANG Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Optimized process for melt pyrolysis of methane to produce hydrogen and carbon black over Ni foam/NaCl-KCl catalyst. Processes, 2023, 11(2): 360. |
| [11] | ZHANG K, HUANG Z, YANG M, et al. Recent progress in melt pyrolysis: fabrication and applications of high-value carbon materials from abundant sources. SusMat, 2023, 3(5): 558. |
| [12] | ZHOU Y, HUANG Z, ZHANG K, et al. Economic analysis of hydrogen production and refueling station via molten-medium- catalyzed pyrolysis of natural gas process. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 62: 1205. |
| [13] | WALIMBE P, CHAUDHARI M. State-of-the-art advancements in studies and applications of graphene: a comprehensive review. Materials Today Sustainability, 2019, 6: 100026. |
| [14] | QAMAR S, RAMZAN N, ALEEM W. Graphene dispersion, functionalization techniques and applications: a review. Synthetic Metals, 2024, 307: 117697. |
| [15] | WANG L, LIRA P, HU G, et al. Graphene-based electrodes and catalysts for electroreduction of CO2 to low-carbon alcohols. Materials Reports: Energy, 2023, 3(2): 100192. |
| [16] | WONG S I, LIN H, MA T, et al. Binary ionic liquid electrolyte design for ultrahigh-energy density graphene-based supercapacitors. Materials Reports: Energy, 2022, 2(2): 100093. |
| [17] | WU J, YU L, LIU S, et al. NiN4/Cr Embedded graphene for electrochemical nitrogen fixation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1141. |
| [18] | 程熠, 王坤, 亓月, 等. 石墨烯纤维材料的化学气相沉积生长方法. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38(2): 40. |
| [19] | LI X, CAI W, AN J, et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science, 2009, 324(5932): 1312. |
| [20] | CHAE S J, GÜNEŞ F, KIM K K, et al. Synthesis of large-area graphene layers on poly-nickel substrate by chemical vapor deposition: wrinkle formation. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(22): 2328. |
| [21] | LUO D, WANG M, LI Y, et al. Adlayer-free large-area single crystal graphene grown on a Cu(111) foil. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(35): 1903615. |
| [22] | AMONTREE J, YAN X, DIMARCO C S, et al. Reproducible graphene synthesis by oxygen-free chemical vapour deposition. Nature, 2024, 630(8017): 636. |
| [23] | UPHAM D C, AGARWAL V, KHECHFE A, et al. Catalytic molten metals for the direct conversion of methane to hydrogen and separable carbon. Science, 2017, 358(6365): 917. |
| [24] | TANG Y, PENG P, WANG S, et al. Continuous production of graphite nanosheets by bubbling chemical vapor deposition using molten copper. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(19): 8404. |
| [25] | 敖东羿. 多层高品质石墨烯的大量制备及其应用研究. 成都: 电子科技大学博士学位论文, 2020. |
| [26] | QIAO C, CHE J, WANG J, et al. Cost effective production of high quality multilayer graphene in molten Sn bubble column by using CH4 as carbon source. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 930: 167495. |
| [27] | PARKINSON B, PATZSCHKE C F, NIKOLIS D, et al. Methane pyrolysis in monovalent alkali halide salts: kinetics and pyrolytic carbon properties. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(9): 6225. |
| [28] | WANG H Y, LUA A C. Hydrogen production by thermocatalytic methane decomposition. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2013, 34(11/12): 896. |
| [29] | JONES R R, HOOPER D C, ZHANG L, et al. Raman techniques: fundamentals and frontiers. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2019, 14: 231. |
| [30] | LUONG D X, BETS K V, ALGOZEEB W A, et al. Gram-scale bottom-up flash graphene synthesis. Nature, 2020, 577(7792): 647. |
| [31] | LOSIC D, FARIVAR F, YAP P L, et al. Accounting carbonaceous counterfeits in graphene materials using the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) approach. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(34): 11859. |
| [32] | FARIVAR F, YAP P L, HASSAN K, et al. Unlocking thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) in the fight against “fake graphene” materials. Carbon, 2021, 179: 505. |
| [1] | 侯琦, 王茂槐, 刘森, 董宏斌, 郭文跃, 鲁效庆. 类石墨烯碳氮分离膜氢气提纯特性的机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1234-1238. |
| [2] | 淡猛, 张骞, 钟云倩, 周莹. 不同晶相MnS制备及光解H2S制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(12): 1308-1314. |
| [3] | 曹适意, 王 军, 王 浩, 王小宙. 自由碳的脱除对SiC纤维微观结构和性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 529-534. |
| [4] | 陈 辰, 张海斌, 彭述明, 赵林杰, 朱建国. Ti3AlC2体材料的高温临氢行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(8): 864-868. |
| [5] | 闫云飞, 张 力, 李丽仙, 唐 强. 膜催化反应器及其制氢技术的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(12): 1233-1243. |
| [6] | 袁文辉, 周辰辰, 李 莉. 改进溶胶-凝胶法合成CeO2-ZrO2固溶体及催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(8): 820-824. |
| [7] | 于威,杜洁,张丽,崔双魁,路万兵,傅广生. 氢流量对纳米SiC薄膜微结构和光学特性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 540-544. |
| [8] | 韦奇,李健林,宋春林,刘卫,陈初升. 憎水二氧化硅膜的制备、表征及水热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(2): 417-423. |
| [9] | 韦奇,李健林,宋春林,刘卫,陈初升. 微孔二氧化硅膜的制备、氢气分离以及水热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(1): 133-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||