无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 719-728.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240537 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240537
周阳阳1,2( ), 张艳艳1,2, 于子怡1, 傅正钱1, 许钫钫1, 梁瑞虹1, 周志勇1(
), 张艳艳1,2, 于子怡1, 傅正钱1, 许钫钫1, 梁瑞虹1, 周志勇1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-26
修回日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-06-20
网络出版日期:2025-02-19
通讯作者:
周志勇, 研究员. E-mail: zyzhou@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:周阳阳(1999-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: zhouyangyang21@mails.ucas.ac.cn
ZHOU Yangyang1,2( ), ZHANG Yanyan1,2, YU Ziyi1, FU Zhengqian1, XU Fangfang1, LIANG Ruihong1, ZHOU Zhiyong1(
), ZHANG Yanyan1,2, YU Ziyi1, FU Zhengqian1, XU Fangfang1, LIANG Ruihong1, ZHOU Zhiyong1( )
)
Received:2024-12-26
Revised:2025-02-17
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-02-19
Contact:
ZHOU Zhiyong, professor. E-mail: zyzhou@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:ZHOU Yangyang (1999-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhouyangyang21@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
高温压电振动传感器是高温、复杂振动等严苛环境下用于结构健康监测的首选传感器。具有高居里温度(TC)的铋层状结构CaBi4Ti4O15(CBT)高温压电陶瓷是500 ℃及以上压电振动传感器的核心元件, 但其压电系数d33低, 极大限制了其高温应用。本研究采用独特的Bi3+自掺杂策略, 提高了CBT压电陶瓷内部晶界数量, 增加了空间电荷的聚集位点, 促进了空间电荷极化的形成。进一步地, 基于空间电荷极化主要在低频下产生的特性, 利用不同频率介电温谱阐明了空间电荷极化提升CBT压电陶瓷压电性能的重要机制。最终获得了综合性能优异的CBT基高温压电陶瓷: TC高达778 ℃; d33提高了30%以上, 达到20.1 pC/N; 电阻率提高了1个数量级(在500 ℃下达到6.33×106 Ω·cm)。本工作为500 ℃及以上压电振动传感器的实际应用提供了性能优异的关键功能材料。
中图分类号:
周阳阳, 张艳艳, 于子怡, 傅正钱, 许钫钫, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. 通过Bi3+自掺杂增强CaBi4Ti4O15基陶瓷压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 719-728.
ZHOU Yangyang, ZHANG Yanyan, YU Ziyi, FU Zhengqian, XU Fangfang, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Properties in CaBi4Ti4O15-based Ceramics through Bi3+ Self-doping Strategy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 719-728.
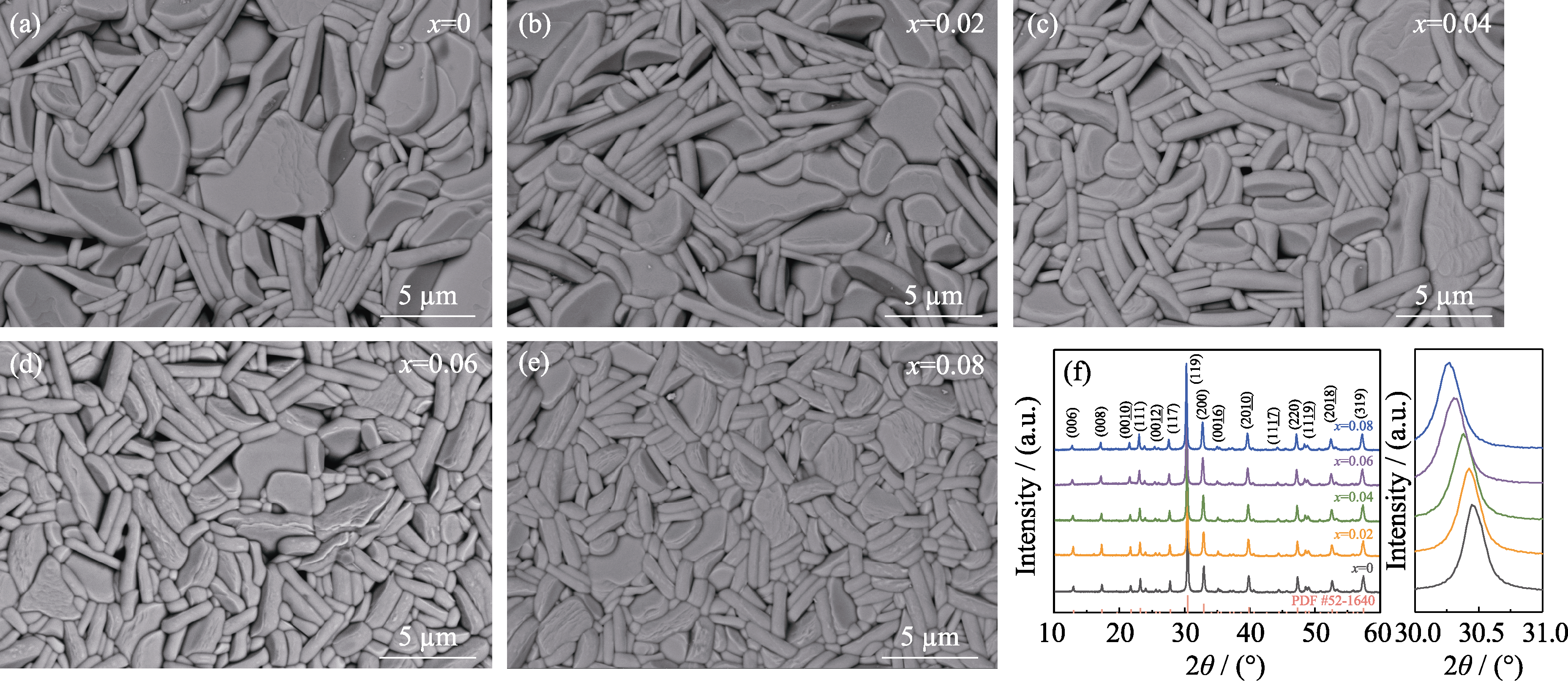
Fig. 1 (a-e) Surface SEM images of CBT-xBi ceramics after thermal etching; (f) XRD patterns of CBT-xBi ceramics and corresponding localized enlarged patterns (a) x=0; (b) x=0.02; (c) x=0.04; (d) x=0.06; (e) x=0.08
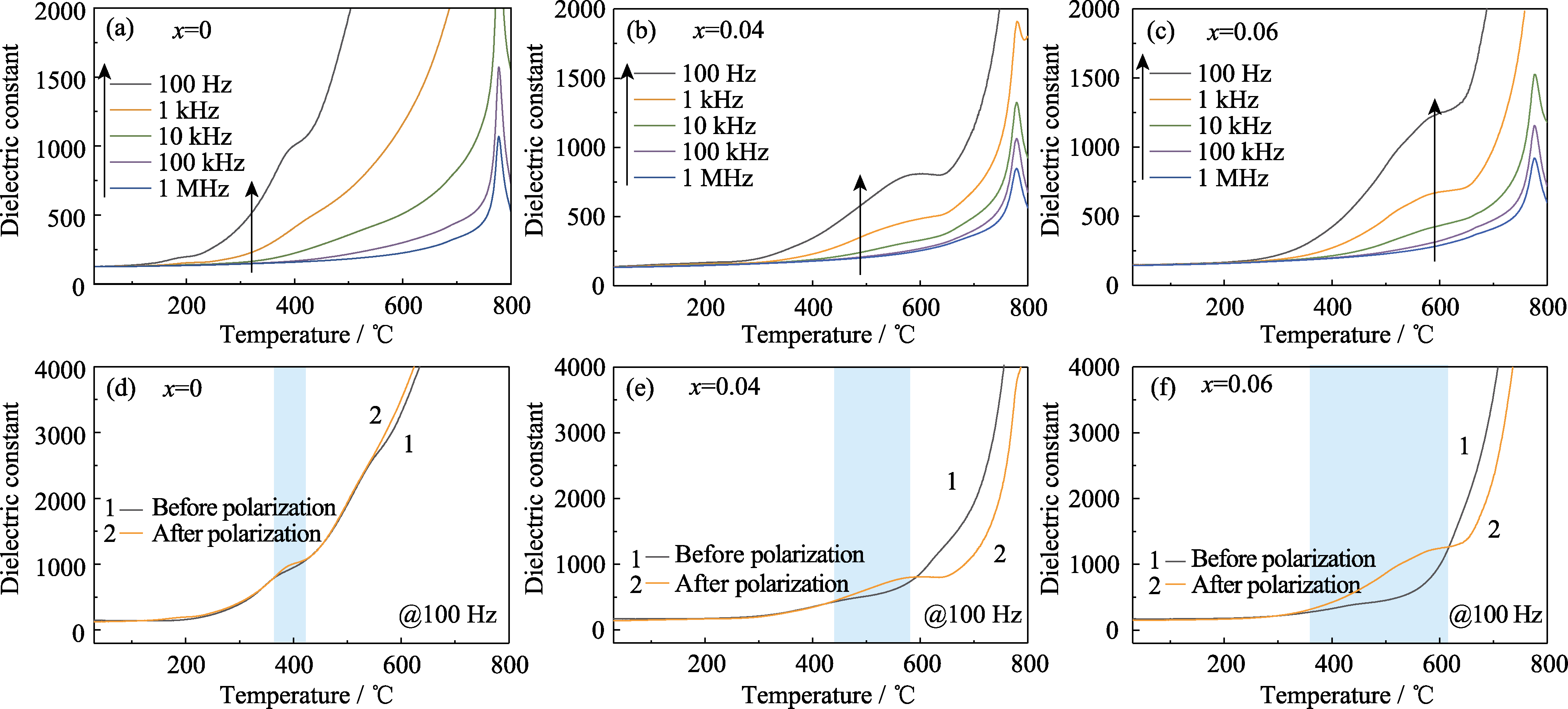
Fig. 2 Dielectric properties of CBT-xBi ceramics (a-c) Dielectric constant as a function of temperature at different frequencies after polarization: (a) x=0, (b) x=0.04 and (c) x=0.06; (d-f) Dielectric constant as a function of temperature at 100 Hz before and after polarization: (d) x=0, (e) x=0.04 and (f) x=0.06
| x | S1 (Oxygen vacancy area) | S2 (Lattice oxygen area) | S (Total area, S1+S2) | S1/S2 | S1/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5581.86 | 23546.90 | 29128.76 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| 0.04 | 5635.40 | 28758.79 | 34394.19 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| 0.06 | 5078.49 | 27836.63 | 32915.12 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| 0.06 (Oxygen sintering) | 3969.83 | 24463.16 | 28432.99 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
Table 1 Results of CBT-xBi ceramics O1s XPS peak fitting analysis
| x | S1 (Oxygen vacancy area) | S2 (Lattice oxygen area) | S (Total area, S1+S2) | S1/S2 | S1/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5581.86 | 23546.90 | 29128.76 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| 0.04 | 5635.40 | 28758.79 | 34394.19 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| 0.06 | 5078.49 | 27836.63 | 32915.12 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| 0.06 (Oxygen sintering) | 3969.83 | 24463.16 | 28432.99 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
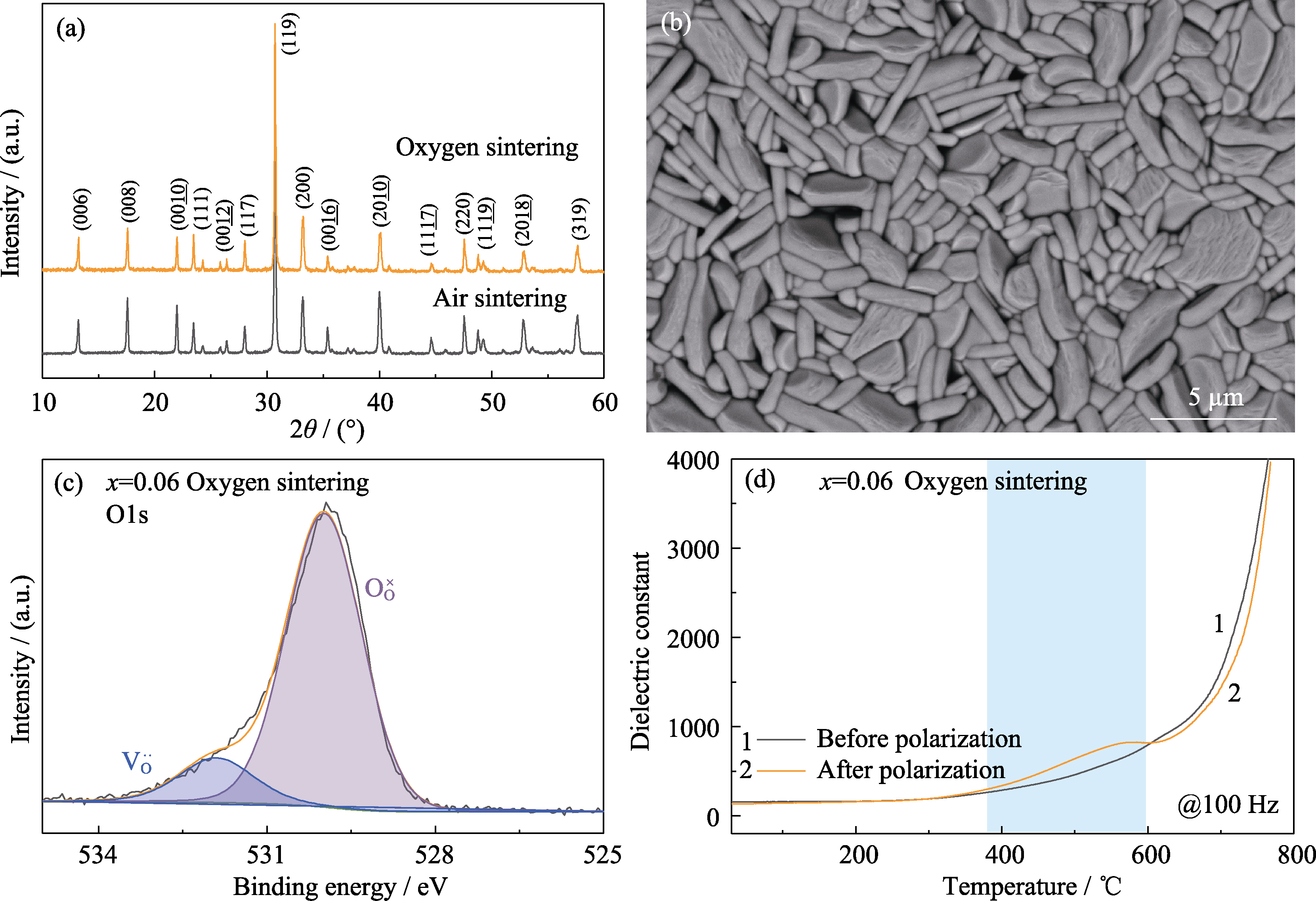
Fig. 4 Characterization of CBT-0.06Bi ceramic sintered in a flowing oxygen atmosphere (a) XRD patterns; (b) SEM image of the thermal etching surface; (c) O1s XPS spectrum; (d) Dielectric temperature spectra at 100 Hz before and after polarization
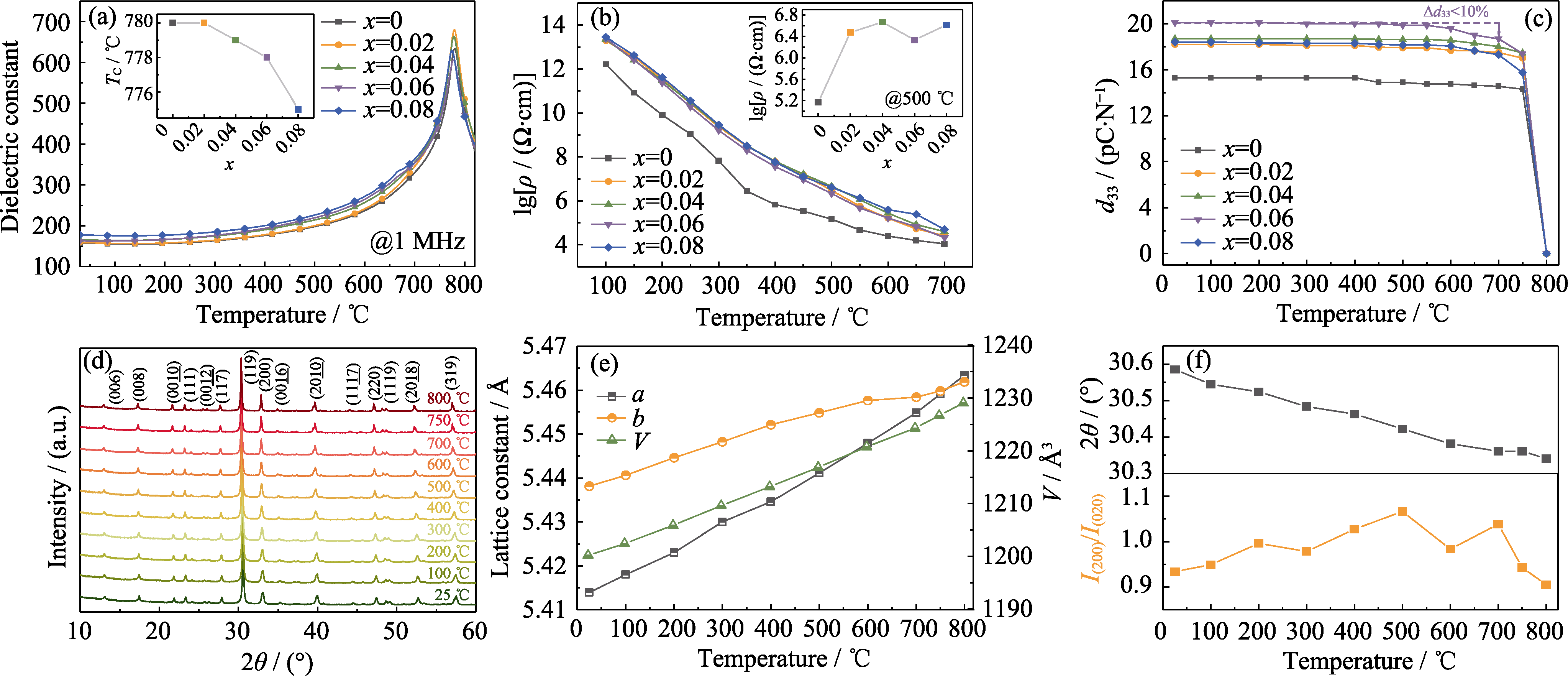
Fig. 5 (a) Dielectric temperature spectra of CBT-xBi ceramics; (b) Temperature dependence of DC resistivity of CBT-xBi ceramics; (c) Effect of heat treatment on the piezoelectric constants of CBT-xBi ceramics (set temperature annealing 2 h); (d) In-situ XRD patterns of CBT-0.06Bi ceramic; (e) Relationship between lattice constants and unit cell volume with temperature; (f) (119) peak position and I(200)/I(020) changed with temperature
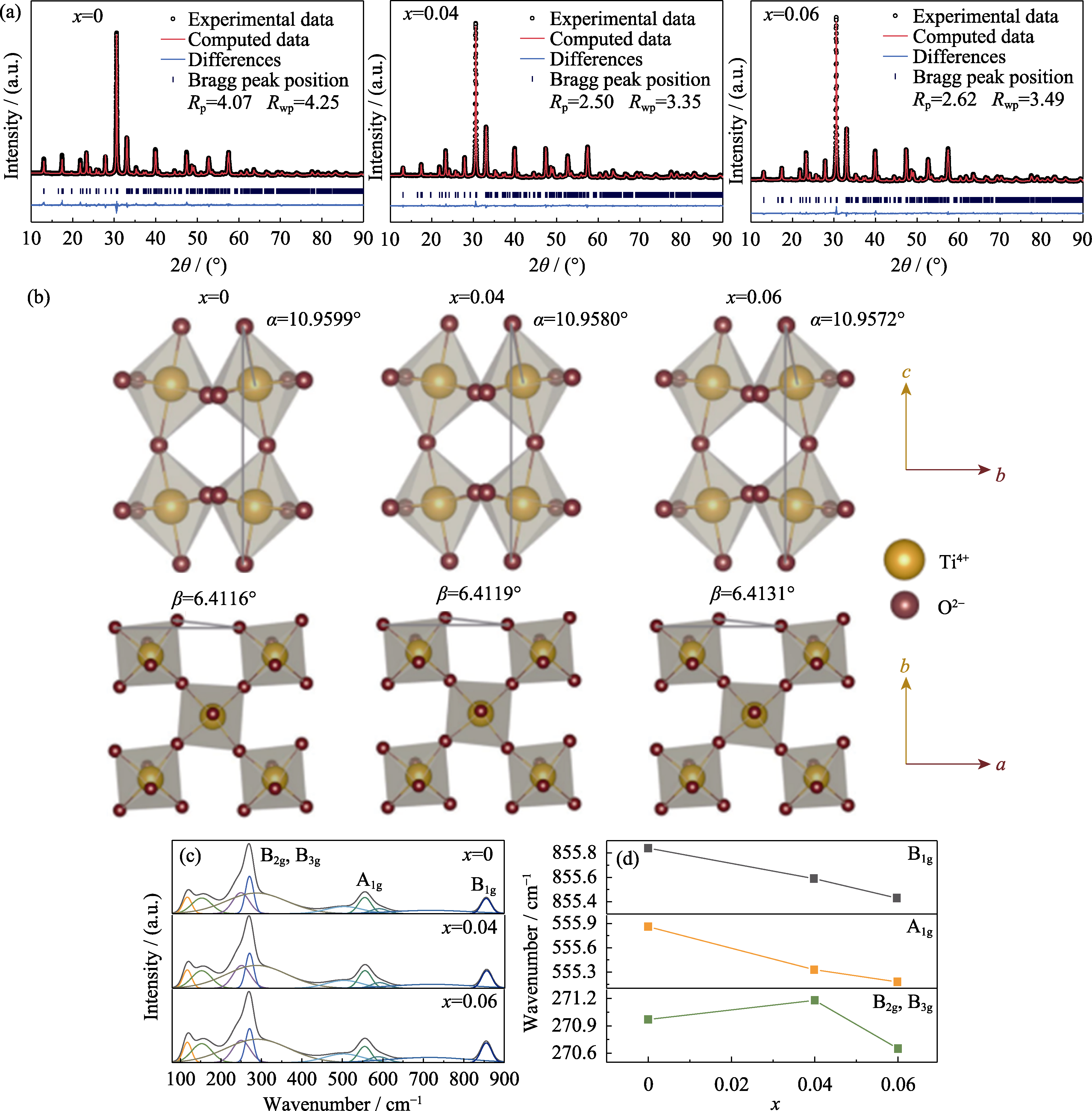
Fig. 6 (a) XRD refinement results of CBT-xBi ceramics; (b) Visual crystal structures of CBT-xBi ceramics; (c) Raman scattering spectra in the range of 80-900 cm-1; (d) Wavenumber displacements of B2g, B3g, A1g, and B1g modes
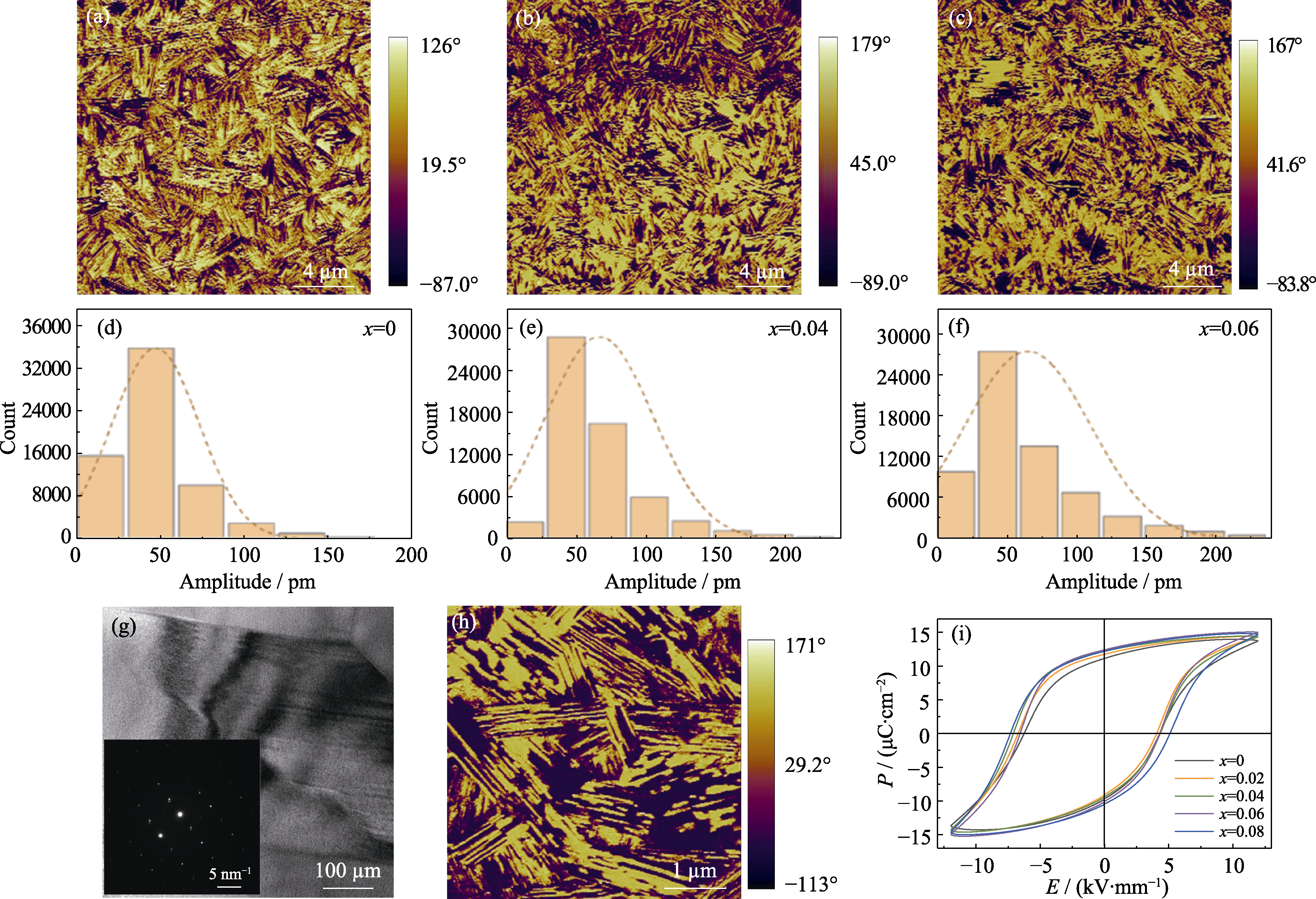
Fig. 7 PFM characterization of CBT-xBi ceramics (a-c) PFM phase images for (a) x=0, (b) x=0.04, and (c) x=0.06; (d-f) PFM amplitude distribution histograms for (d) x=0, (e) x=0.04, and (f) x=0.06; (g) TEM image of CBT-0.06Bi; (h) 5 μm×5 μm PFM phase image of CBT-0.06Bi; (i) Hysteresis loops of CBT-xBi ceramics after polarizing at 180 ℃ and 1 Hz. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | WU J G, HU Z Q, GAO X Y, et al. Unconventional piezoelectric coefficients in perovskite piezoelectric ceramics. J. Materiomics, 2021, 7(2): 254. |
| [2] | WEI H G, WANG H, XIA Y J, et al. An overview of lead-free piezoelectric materials and devices. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, 6(46): 12446. |
| [3] | DE U, SAHU K R, DE A. Ferroelectric materials for high temperature piezoelectric applications. Solid State Phenom., 2015, 232: 235. |
| [4] |
JIANG X N, KIM K, ZHANG S J, et al. High-temperature piezoelectric sensing. Sensors, 2013, 14(1): 144.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | ZHANG S J, YU F P. Piezoelectric materials for high temperature sensors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 94(10): 3153. |
| [6] | XI J W, CHEN H, TAN Z, et al. Origin of high piezoelectricity in CBT-based Aurivillius ferroelectrics: glide of (Bi2O2)2+ blocks and suppressed internal bias field. Acta Mater., 2022, 237(15): 118146. |
| [7] | XIE X C, ZHOU Z Y, WANG T Z, et al. High temperature impedance properties and conduction mechanism of W6+-doped CaBi4Ti4O15 Aurivillius piezoceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2018, 124(20): 204101. |
| [8] | LIU Y, ZHANG Y H, ZHU L L, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric activity with good thermal stability and improved electrical resistivity in Ta-Mn co-doped CaBi4Ti4O15 high-temperature piezoceramics. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(14): 22532. |
| [9] | XI J W, CHEN H, PENG X, et al. Achieving significantly enhanced piezoelectricity in Aurivillius ceramics by improving initial polarization and dielectric breakdown strength. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(11): 4757. |
| [10] | ZHAO L, LI G H, ZHAI X, et al. Enhanced electrical performance in CaBi4Ti4O15 ceramics through synergistic chemical doping and texture engineering. J. Materiomics, 2024, 10(2): 471. |
| [11] | CHEN H, XI J W, TAN Z, et al. Decoding intrinsic and extrinsic contributions for high piezoelectricity of CBT-based piezoelectric ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023, 11(35): 12048. |
| [12] | DAMJANOVIC D. Contributions to the piezoelectric effect in ferroelectric single crystals and ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88(10): 2663. |
| [13] | LI Y G, ZHOU Z Y, LIANG R H, et al. A simple Bi3+ self-doping strategy constructing pseudo-tetragonal phase boundary to enhance electrical properties in CaBi2Nb2O9 high-temperature piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 42(6): 2772. |
| [14] | ZHANG Y H, HUANG P M, ZHU L L, et al. Doping level effects in Nb self-doped Bi3TiNbO9 high-temperature piezoceramics with improved electrical properties. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Tec., 2020, 17(5): 2407. |
| [15] | CAO W J, LIN R J, HOU X, et al. Interfacial polarization restriction for ultrahigh energy-storage density in lead-free ceramics. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(29): 2301027. |
| [16] | DUAN C G, MEI W N, YIN W G, et al. Simulations of ferroelectric polymer film polarization: the role of dipole interactions. Phys. Rev. B, 2004, 69: 235106. |
| [17] | PRODROMAKIS T, PAPAVASSILIOU C. Engineering the Maxwell- Wagner polarization effect. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255(15): 6989. |
| [18] | TURIK A V, CHERNOBABOV A I, RADCHENKO G S, et al. Giant piezoelectric and dielectric enhancement in disordered heterogeneous systems. Phys. Solid State, 2004, 46(12): 2213. |
| [19] | TIAN G, DENG W L, YANG T, et al. Insight into interfacial polarization for enhancing piezoelectricity in ferroelectric nanocomposites. Small, 2023, 19(16): 2207947. |
| [20] | XIE J, ZHONG J Q, WU C, et al. Enhanced electrical properties related to structural distortion of CaBi2Nb2O9-based piezoelectric ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 102(3): 1287. |
| [21] | ZOU W, WANG J L, CHEN Z Z, et al. Anisotropic electrical and magnetic properties in grain-oriented Bi4Ti3O12-La0.5Sr0.5MnO3. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, 6(42): 11272. |
| [22] | ZHUK N A, LUTOEV V P, MAKEEV B A, et al. Magnetic susceptibility, EPR, NEXAFS and XPS spectra of Fe-doped CaBi2Nb2O9. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(3): 4173. |
| [23] | HUSSAIN A, JABEEN N, HASSAN N U, et al. Influence of Mn ions' insertion in pseudo-tetragonal phased CaBi4Ti4O15-based ceramics for highly efficient energy storage devices and high- temperature piezoelectric applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(21): 12723. |
| [24] | YAO Y Y, SONG C H, BAO P, et al. Doping effect on the dielectric property in bismuth titanate. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 95(6): 3126. |
| [25] | SUÁREZ D Y, REANEY I M, LEE W E. Relation between tolerance factor and Tc in Aurivillius compounds. J. Mater. Res., 2001, 16(11): 3139. |
| [26] | CAI K, HUANG C C, GUO D. Significantly enhanced piezoelectricity in low-temperature sintered Aurivillius-type ceramics with ultrahigh Curie temperature of 800 ℃. J. Phys. D, 2017, 50(15): 111287. |
| [27] | SUBBARAO E C, MCQUARRIE M C, BUESSEM W R. Domain effects in polycrystalline barium titanate. J. Appl. Phys., 1957, 28(10): 1194. |
| [28] | GLAZOUNOV A E, HOFFMANN M J. Investigation of domain switching in fractured ferroelectric ceramics by using imaging of X-ray diffraction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2001, 21(10/11): 1417. |
| [29] | XIE X C, ZHOU Z Y, GAO B T, et al. Ion-pair engineering- induced high piezoelectricity in Bi4Ti3O12-based high-temperature piezoceramics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(12): 14321. |
| [30] | ZHANG Y Y, KE X C, ZHAO K Y, et al. Ca2+ doping effects on the structural and electrical properties of Na0.5Bi4.5Ti4O15 piezoceramics. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(21): 31265. |
| [31] | NIE R, YUAN J, LI W, et al. Microstructure and electric property of (1-x)CaBi4Ti4O15-xBi4Ti3O12 ceramics with high-Curie temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2019, 30: 6482. |
| [32] | LI L L, YUAN H B, HUANG P M, et al. Enhanced piezoelectricity and excellent thermal stabilities in Nb-Mg co-doped CaBi4Ti4O15 Aurivillius high Curie temperature ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(2): 2178. |
| [33] | XIE X C, ZHOU Z Y, LIANG R H, et al. Superior piezoelectricity in bismuth titanate-based lead-free high-temperature piezoceramics via domain engineering. Adv. Electron. Mater., 2022, 8(7): 2101266. |
| [34] | ZHANG Y Y, LIANG R H, ZHOU Z Y. Enhanced electrical properties of Cr2O3 addition NBT-based high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 106(4): 2357. |
| [1] | 李汶金, 娄程广, 张帅, 苏兴华. 金属Cu和5YSZ陶瓷的“闪连”研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 957-963. |
| [2] | 孙雨萱, 王政, 时雪, 史颖, 杜文通, 满振勇, 郑嘹赢, 李国荣. 缺陷偶极子热稳定性对Fe掺杂PZT陶瓷机电性能影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [3] | 范小暄, 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心, 王绩伟. 基于富氧空位LiYScGeO4: Bi3+长余辉光催化剂的自激活余辉驱动有机污染物芬顿降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [4] | 黄建锋, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. W/Cr共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 887-894. |
| [5] | 邹凯, 张文斌, 关胜, 孙海轶, 彭凯伦, 邹家杰, 李学红, 王成, 冷雨欣, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. 压电式高温液滴喷射元件研制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 987-988. |
| [6] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [7] | 贾鑫, 李晋宇, 丁世豪, 申倩倩, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Pd纳米颗粒协同氧空位增强TiO2光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1301-1308. |
| [8] | 张文进, 申倩倩, 薛晋波, 李琦, 刘旭光, 贾虎生. 具有高度有序氧空位的α-Fe2O3纳米带的制备及光电催化水氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1290-1296. |
| [9] | 李鹏鹏, 王兵, 王应德. 基于火焰退火多孔CeO2纳米片的环境监测用超快CO气体传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1223-1230. |
| [10] | 刘亚鑫, 王敏, 沈梦, 王强, 张玲霞. 铋掺杂提高氧化铈中氧空位浓度增强CO2光催化还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 88-94. |
| [11] | 伍凡, 赵梓俨, 黎邦鑫, 董帆, 周莹. Bi2O2CO3/PPy界面氧空位构建及其可见光下NO氧化机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 541-548. |
| [12] | 胡浩, 江向平, 陈超, 聂鑫, 黄枭坤, 苏春阳. Ce 3+掺杂Na0.5Bi8.5Ti7O27铋层状陶瓷的结构与电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 997-1003. |
| [13] | 李金, 刘廷禹, 姚舒安, 付明雪, 鲁晓晓. 第一原理研究LuPO4中氧空位的性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 879-884. |
| [14] | 曾祥雄, 杨进超, 左联, 杨奔奔, 秦峻, 彭志航. Li/Ce/La共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 379-386. |
| [15] | 周志勇, 陈涛, 董显林. 超高居里温度钙钛矿层状结构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 251-258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||