无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 647-655.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240512 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240512
黄子鹏1,2,3( ), 贾文晓1,2,3, 李玲霞1,2,3(
), 贾文晓1,2,3, 李玲霞1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-10
修回日期:2025-02-27
出版日期:2025-06-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-06
通讯作者:
李玲霞, 教授. E-mail: tjulingxiali_666@163.com作者简介:黄子鹏(1994-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: hzptju613@163.com
基金资助:
HUANG Zipeng1,2,3( ), JIA Wenxiao1,2,3, LI Lingxia1,2,3(
), JIA Wenxiao1,2,3, LI Lingxia1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-12-10
Revised:2025-02-27
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-03-06
Contact:
LI Lingxia, professor. E-mail: tjulingxiali_666@163.comAbout author:HUANG Zipeng (1994-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: hzptju613@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
MgNb2O6陶瓷具有烧结温度适中和介电损耗低等优点, 在无线通信领域有着广泛的应用。随着6G通信技术研发工作的开展, 通信频率将从微波频段迈向太赫兹频段。MgNb2O6陶瓷应用于太赫兹通信器件中可有效降低插入损耗, 增大相对带宽, 提高增益。然而, 目前仍缺乏关于MgNb2O6结构与太赫兹介电性能关联机制的深入研究。针对上述问题, 本研究采用固相反应法制备了MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷。采用Rietveld精修、复杂化学键理论和太赫兹时域光谱等分析手段研究了MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能之间的关联机制。基于上述分析手段, 在单相MgNb2O6体系中引入整体不稳定性指数表征晶格内应变, 建立了晶格内应变以及晶格能与太赫兹介电损耗的关联机制。研究结果表明, 掺入的(Ti0.5W0.5)5+离子可修饰晶体结构, 随着掺杂量增加, 减小了内应变, 增加了晶体结构的稳定性, 增大了晶格能, 进而降低了介电损耗。此外, 原子堆积密度随(Ti0.5W0.5)5+离子掺杂量增加而增大, 这意味着离子间排列更加紧密, 从而有效抑制了晶体的非简谐性振动, 进一步降低了介电损耗。最终, 1340 ℃烧结的MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0.03)陶瓷具有优异的太赫兹介电性能: 介电常数(εr)为19.32, 介电损耗为0.003(@0.30 THz), 吸收系数为1.64 cm-1(@0.30 THz)。本研究制备的MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0.03)陶瓷在太赫兹器件中具有良好的应用前景。
中图分类号:
黄子鹏, 贾文晓, 李玲霞. (Ti0.5W0.5)5+掺杂MgNb2O6陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 647-655.
HUANG Zipeng, JIA Wenxiao, LI Lingxia. Crystal Structure and Terahertz Dielectric Properties of (Ti0.5W0.5)5+ Doped MgNb2O6 Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 647-655.
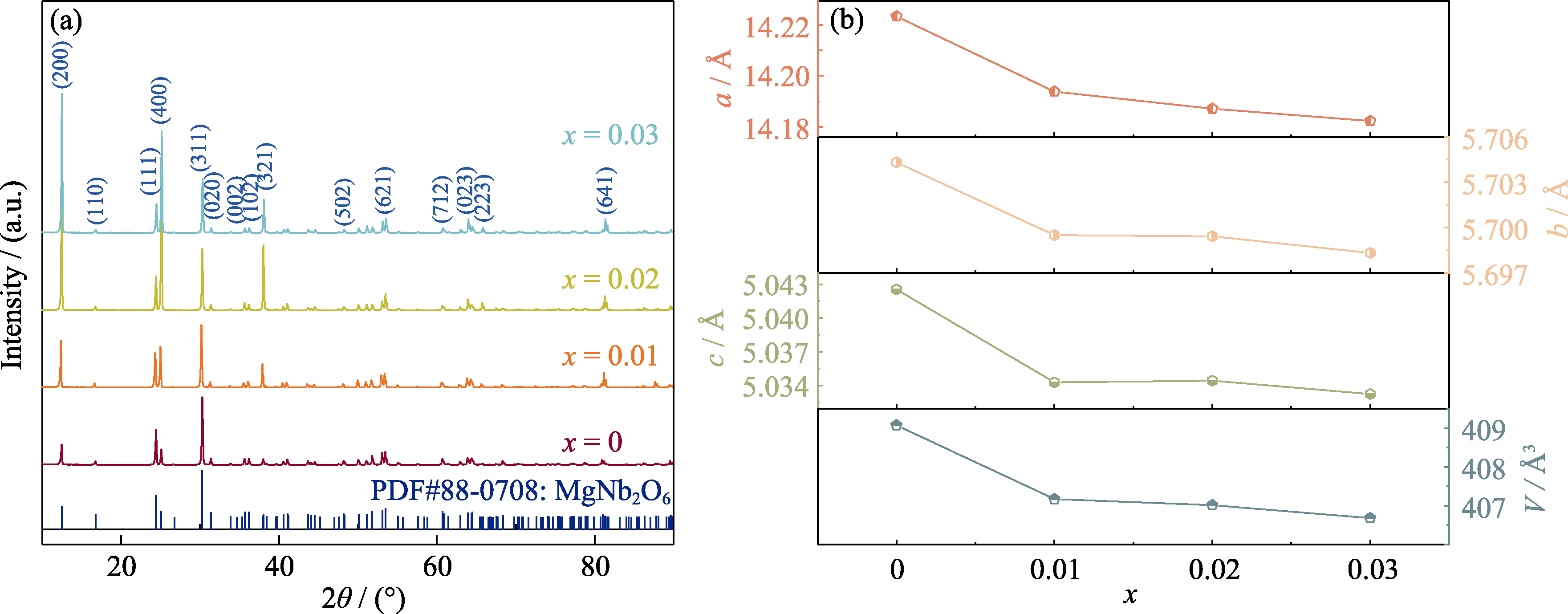
图1 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的XRD分析
Fig. 1 XRD analyses of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics (a) XRD patterns; (b) Cell parameters obtained by XRD refinement
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rwp/% | 10.36 | 13.56 | 7.95 | 6.32 |
| Rp/% | 6.52 | 8.56 | 5.56 | 4.33 |
表1 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷XRD精修结果的可靠因子
Table 1 Reliability factor of XRD refinement results of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rwp/% | 10.36 | 13.56 | 7.95 | 6.32 |
| Rp/% | 6.52 | 8.56 | 5.56 | 4.33 |
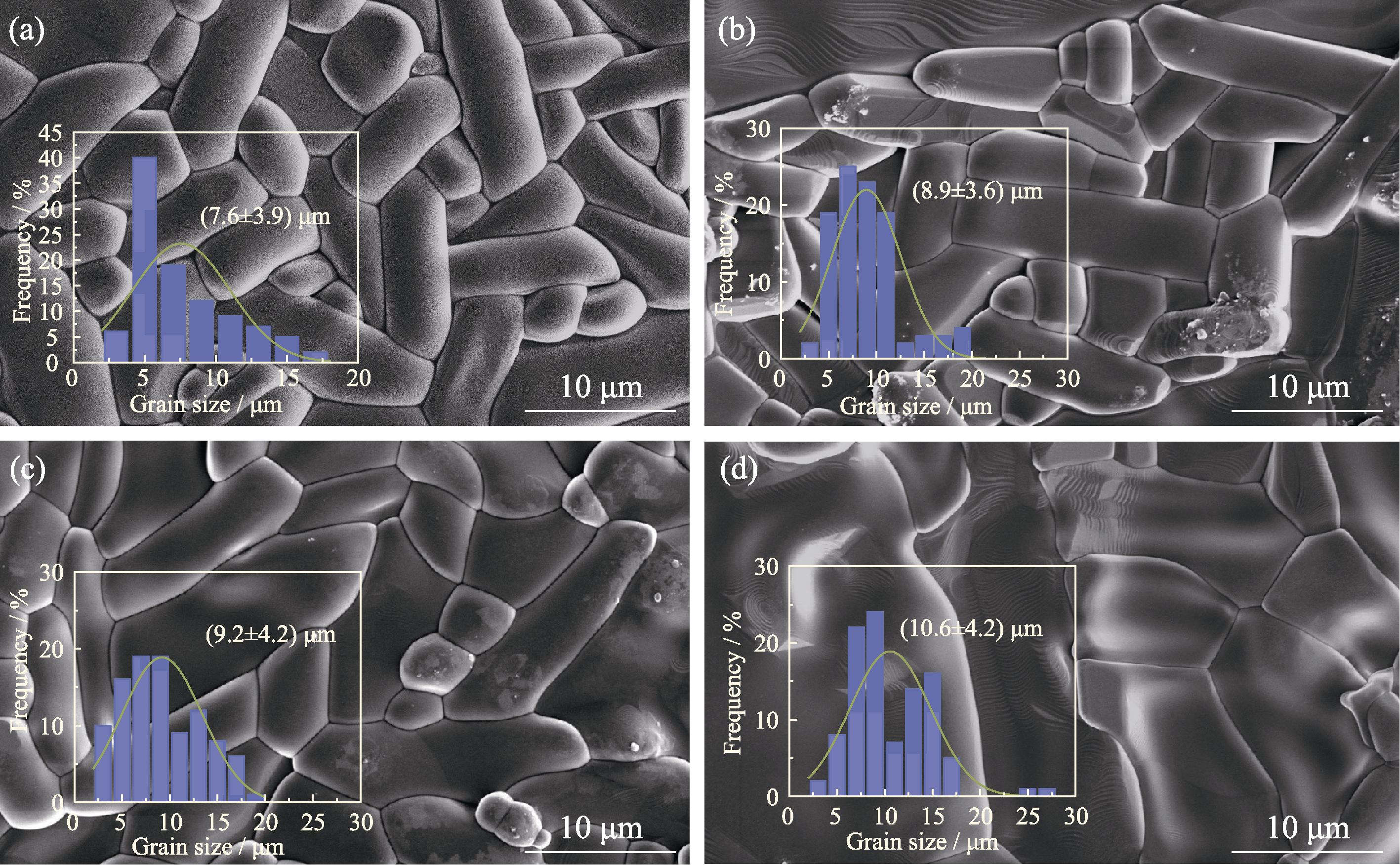
图3 1340 ℃烧结的MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的表面微观形貌
Fig. 3 Surface morphologies of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics sintered at 1340 ℃ (a) x=0; (b) x=0.01; (c) x=0.02; (d) x=0.03; Insets: particle size distribution
| Bond | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg–O1 | 2.0012 | 1.9033 | 2.0632 | 2.0821 | ||
| Mg–O2(1) | 1.9892 | 2.0423 | 2.0032 | 2.0262 | ||
| Mg–O2(2) | 2.0122 | 2.4343 | 2.0792 | 2.0631 | ||
| Nb–O1(1) | 2.0223 | 2.1123 | 2.0642 | 2.0322 | ||
| Nb–O1(2) | 2.1072 | 2.1612 | 2.0092 | 2.0082 | ||
| Nb–O2 | 1.9621 | 1.8313 | 1.8341 | 1.8441 | ||
| Nb–O3(1) | 2.1461 | 1.9962 | 2.1121 | 2.1431 | ||
| Nb–O3(2) | 2.0542 | 2.1362 | 2.1362 | 2.1191 | ||
| Nb–O3(3) | 2.0662 | 2.1723 | 2.0152 | 2.0002 | ||
表2 XRD精修得到的MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷中的键长(Å)
Table 2 Bond lengths (Å) in MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics obtained from XRD refinement
| Bond | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg–O1 | 2.0012 | 1.9033 | 2.0632 | 2.0821 | ||
| Mg–O2(1) | 1.9892 | 2.0423 | 2.0032 | 2.0262 | ||
| Mg–O2(2) | 2.0122 | 2.4343 | 2.0792 | 2.0631 | ||
| Nb–O1(1) | 2.0223 | 2.1123 | 2.0642 | 2.0322 | ||
| Nb–O1(2) | 2.1072 | 2.1612 | 2.0092 | 2.0082 | ||
| Nb–O2 | 1.9621 | 1.8313 | 1.8341 | 1.8441 | ||
| Nb–O3(1) | 2.1461 | 1.9962 | 2.1121 | 2.1431 | ||
| Nb–O3(2) | 2.0542 | 2.1362 | 2.1362 | 2.1191 | ||
| Nb–O3(3) | 2.0662 | 2.1723 | 2.0152 | 2.0002 | ||
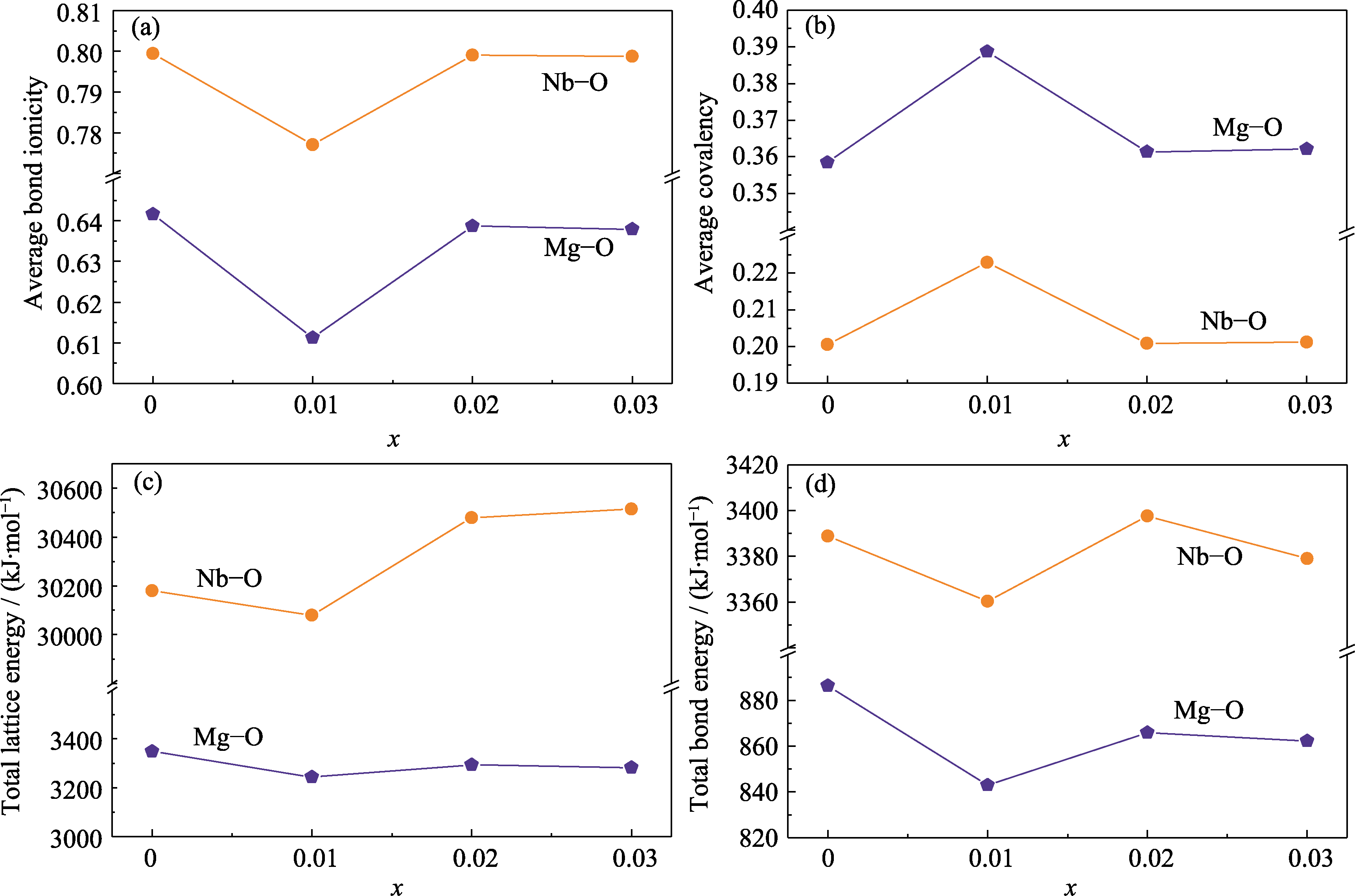
图4 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷中Mg-O、Nb-O键的化学键特性
Fig. 4 Chemical bond characteristics of Mg-O and Nb-O bonds in MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics (a) Average bond ionicity; (b) Average covalency; (c) Total lattice energy; (d) Total bond energy
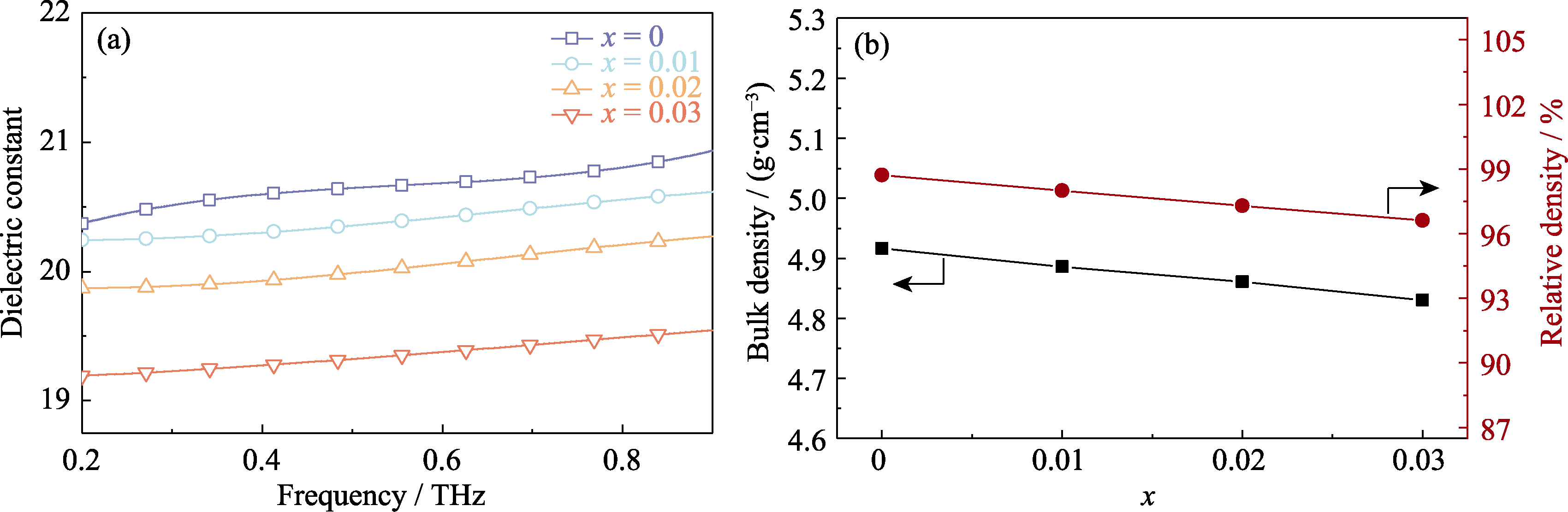
图5 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的(a)太赫兹介电常数和(b)密度
Fig. 5 (a) Terahertz dielectric constants and (b) densities of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics
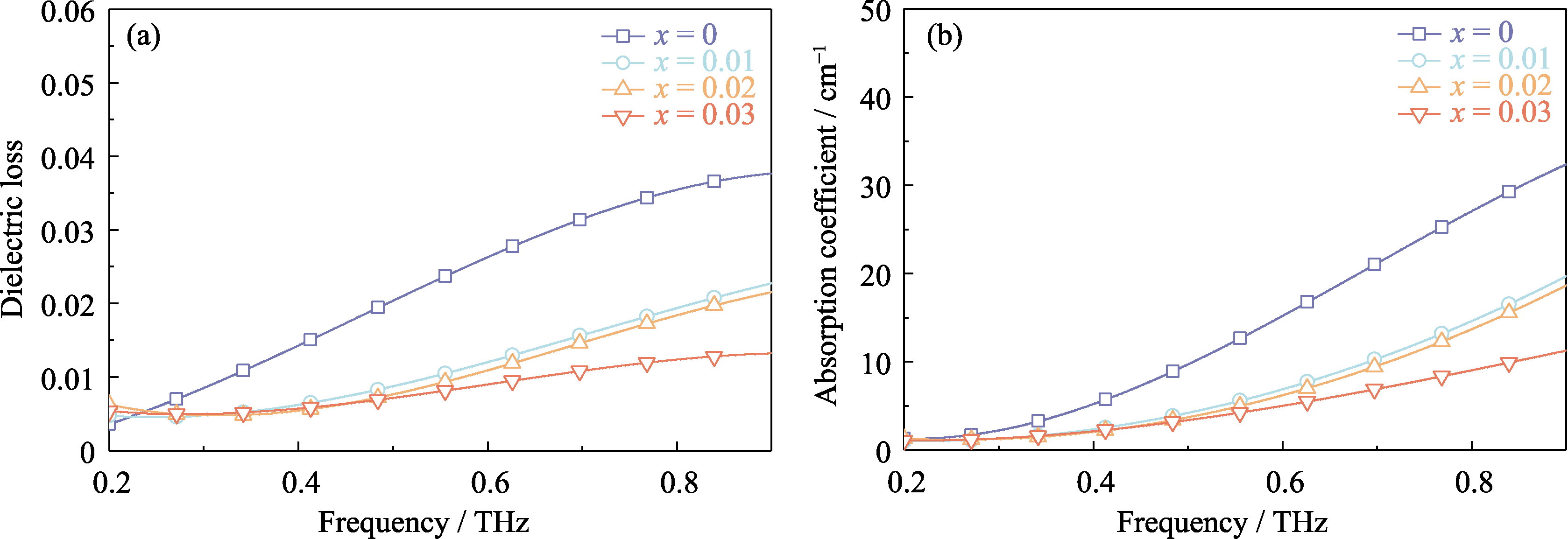
图6 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的(a)太赫兹介电损耗与(b)吸收系数
Fig. 6 (a) Terahertz dielectric loss and (b) absorption coefficient of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sij(B-O) | 4.0657 | 4.1612 | 4.5383 | 4.5777 |
| GII | 0.7896 | 0.6069 | 0.3914 | 0.3458 |
表3 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的B位化学键键价(Sij(B-O))和整体不稳定性指数(GII)
Table 3 B position chemical bond valences (Sij(B-O)) and global instability indexes (GII) of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sij(B-O) | 4.0657 | 4.1612 | 4.5383 | 4.5777 |
| GII | 0.7896 | 0.6069 | 0.3914 | 0.3458 |
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic packing density/% | 71.25 | 71.33 | 71.46 | 71.50 |
表4 MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6(x=0~0.03)陶瓷的原子堆积密度
Table 4 Atomic packing densities of MgNb2-x(Ti0.5W0.5)xO6 (x=0-0.03) ceramics
| Parameter | x=0 | x=0.01 | x=0.02 | x=0.03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic packing density/% | 71.25 | 71.33 | 71.46 | 71.50 |
| [1] |
YANG X, VASWANI C, SUNDAHL C, et al. Terahertz-light quantum tuning of a metastable emergent phase hidden by superconductivity. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(7): 586.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | HORIUCHI N. Terahertz surprises. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12: 128. |
| [3] | ZHOU D, PANG L X, WANG D W, et al. Crystal structure, impedance and broadband dielectric spectra of ordered scheelite- structured Bi(Sc1/3Mo2/3)O4 ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4): 1556. |
| [4] | YAO B C, LIU Y, HUANG S W, et al. Broadband gate-tunable terahertz plasmons in graphene heterostructures. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12: 22. |
| [5] | LUO C Y, LI D, LUO Q, et al. Design of a tunable multiband terahertz waves absorber. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 652: 18. |
| [6] | NIKITIN A Y. Telecom meets terahertz. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12: 3. |
| [7] | BAO J, ZHANG Y P, KIMURA H, et al. Crystal structure, chemical bond characteristics, infrared reflection spectrum, and microwave dielectric properties of Nd2(Zr1-xTix)3(MoO4)9 ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(1): 82. |
| [8] | TIAN H R, ZHANG Y Y, WANG R H, et al. Effect of Ge4+- substituted on the structure characteristics and microwave/terahertz dielectric properties of ultra-low εr, high Q·f cordierite ceramics. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2025, 216: 165. |
| [9] | TIAN H R, ZHANG X H, ZHANG Z D, et al. Low-permittivity LiLn(PO3)4 (Ln=La, Sm, Eu) dielectric ceramics for microwave/ millimeter-wave communication. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(5): 602. |
| [10] |
XUE K L, ZHANG W N, SONG J L, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction method for layered structures based on a frequency modulated continuous wave terahertz radar. Optics Express, 2024, 32(16): 27303.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | FU Y, REN Y Q, SUN D W. Novel analysis of food processes by terahertz spectral imaging: a review of recent research findings. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2024, 147: 104463. |
| [12] | JIANG W, ZHOU Q H, HE J G, et al. Terahertz communications and sensing for 6G and beyond: a comprehensive review. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024, 26(4): 2326. |
| [13] | SATPATHY S, KHALAF O I, SHUKLA D K, et al. Consumer electronics based smart technologies for enhanced terahertz healthcare having an integration of split learning with medical imaging. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 10412. |
| [14] | WITHAYACHUMNANKUL W, YAMADA R, FUJITA M, et al. All-dielectric rod antenna array for terahertz communications. APL Photonics, 2018, 3(5): 051707. |
| [15] | SUN D D, QI L M, LIU Z Y. Terahertz broadband filter and electromagnetically induced transparency structure with complementary metasurface. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102887. |
| [16] | AKO R T, UPADHYAY A, WITHAYACHUMNANKUL W, et al. Dielectrics for terahertz metasurfaces: material selection and fabrication techniques. Advanced Optical Materials, 2020, 8(3): 1900750. |
| [17] |
WANG K M, GU J Q, SHI W Q, et al. All-dielectric nanograting for increasing terahertz radiation power of photoconductive antennas. Optics Express, 2020, 28(13): 19144.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | HUANG J B, YANG B, YU C Y, et al. Microwave and terahertz dielectric properties of MgTiO3-CaTiO3 ceramics. Materials Letters, 2015, 138: 225. |
| [19] | YU C Y, ZENG Y, YANG B, et al. Titanium dioxide engineered for near-dispersionless high terahertz permittivity and ultra-low-loss. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 6639. |
| [20] | WENG Z Z, SONG C X, XIONG Z X, et al. Microstructure and broadband dielectric properties of Zn2SiO4 ceramics with nano- sized TiO2 addition. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(10): 13251. |
| [21] | ZHANG B, GE M L. Investigation of optical pumping on the dielectric properties of 0.3SrTiO3-0.7NdAlO3 ceramics in THz range. Optical Materials, 2020, 109: 110226. |
| [22] | HUANG Z P, QIAO J L, LI L X. Crystal structure, Raman spectra, and microwave dielectric performances of TiW-substituted magnesium niobite ceramics. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(3): 5013. |
| [23] | ZHANG Q, SU H, TANG X L, et al. Effects of Cu2+ substitution on bond characteristics, Raman spectra, and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Mg0.6Zn0.4SiO4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3432. |
| [24] | HUANG Z P, LI L X, QIAO J L. Trace additive enhances microwave dielectric performance significantly to facilitate 5G communications. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(12): 7426. |
| [25] | SHANKER V, GANGULI A K. Comparative study of dielectric properties of MgNb2O6 prepared by molten salt and ceramic method. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2003, 26(7): 741. |
| [26] | SARKAR K, MUKHERJEE S. Synthesis, characterization and property evaluation of single phase MgNb2O6 by chemical route. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2016, 52(2): 32. |
| [27] | WANG S, LI L X, WANG X B. Low-temperature firing and microwave dielectric properties of MgNb2-xVx/2O6-1.25x ceramics. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(1): 199. |
| [28] | TZOU W C, CHEN Y C, YANG C F, et al. Microwave dielectric characteristics of Mg(Ta1-xNbx)2O6 ceramics. Materials Research Bulletin, 2006, 41(7): 1357. |
| [29] | HE L, YU H T, ZENG M S, et al. 0.73ZrTi2O6-0.27MgNb2O6 microwave dielectric ceramics modified by Al2O3 addition. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(11): 5110. |
| [30] | ZHANG Q, TANG X L, HUANG F Y, et al. Enhanced microwave dielectric properties of wolframite structured Zn1-xCuxWO4 ceramics with low sintering temperature. Journal of Materiomics, 2021, 7(6): 1309. |
| [31] | ADAMS S, MORETZKI O, CANADELL E. Global instability index optimizations for the localization of mobile protons. Solid State Ionics, 2004, 168(3/4): 281. |
| [32] | FAN X C, CHEN X M, LIU X Q. Structural dependence of microwave dielectric properties of SrRAlO4 (R = Sm, Nd, La) ceramics: crystal structure refinement and infrared reflectivity study. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(12): 4092. |
| [33] | ZHANG Q, XU L L, TANG X L, et al. Structural characteristics and microwave dielectric properties of Zn1-xBixVxW1-xO4-based ceramics for LTCC applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(13): 5691. |
| [1] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [2] | 赵凯旋, 刘文鹏, 丁守军, 窦仁勤, 罗建乔, 高进云, 孙贵花, 任浩, 张庆礼. 熔融法制备Nd:YLF原料及其晶体生长和性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 529-535. |
| [3] | 郭佳芯, 陈美娟, 吴浩, 郑潇然, 闵楠, 田辉, 齐东丽, 李全军, 都时禹, 沈龙海. 高压下新型MAX相Zr3InC2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1414-1424. |
| [4] | 黄建锋, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. W/Cr共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 887-894. |
| [5] | 宋云霞, 韩颖磊, 颜涛, 罗敏. Rb3Hg2(SO4)3Cl新型紫外非线性光学晶体材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 778-784. |
| [6] | 赵伟, 徐阳, 万颖杰, 蔡天逊, 穆金潇, 黄富强. 金属氰胺化合物的结构、合成及电化学储能应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 140-151. |
| [7] | 彭帆, 曾毅. 利用菊池衍射花样鉴定晶体结构的方法研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1193-1198. |
| [8] | 李淑芳,赵爽,周潇,李满荣. Zn3-xMnxTeO6的晶体结构与吸收光谱和磁性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 895-901. |
| [9] | 李淑芳, 赵爽, 李满荣. 助熔剂法合成钨氧氯化合物Li23CuW10O40Cl5[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 834-838. |
| [10] | 黄冲,赵伟,王东,卜克军,王思顺,黄富强. Pd插层NbSe2化合物的制备、晶体结构和电学性质研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 505-510. |
| [11] | 曾祥雄, 杨进超, 左联, 杨奔奔, 秦峻, 彭志航. Li/Ce/La共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 379-386. |
| [12] | 黄龙, 丁士华, 张晓云, 严欣堪, 李超, 朱惠. Li2O-B2O3-SiO2玻璃相对BaAl2Si2O8结构及微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1091-1096. |
| [13] | 周鑫, 马垒, 刘涛, 郭永斌, 王岛, 董培林. Si3N4/FePd/Si3N4薄膜的晶体结构和磁性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 909-913. |
| [14] | 孟凡斌, 马晓帆, 张 炜, 吴光恒, 张玉洁. Mn和Fe掺杂对尖晶石氧化物Co2MnO4结构和磁性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 609-614. |
| [15] | 王晴晴, 史 坚, 李焕英, 陈晓峰, 潘尚可, 卞建江, 任国浩. Cs2LiYCl6:Ce闪烁晶体的光学及闪烁性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(2): 175-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||