无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 639-646.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240476 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240476
何国强( ), 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪(
), 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-11
修回日期:2025-01-04
出版日期:2025-06-20
网络出版日期:2025-01-24
通讯作者:
周 迪, 教授. E-mail: zhoudi1220@xjtu.edu.cn作者简介:何国强(1998-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: Guoqiang_0327@163.com
基金资助:
HE Guoqiang( ), ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di(
), ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di( )
)
Received:2024-11-11
Revised:2025-01-04
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-01-24
Contact:
ZHOU Di, professor. E-mail: zhoudi1220@xjtu.edu.cnAbout author:HE Guoqiang (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: Guoqiang_0327@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
微波介质陶瓷是电子通信领域中不可或缺的材料, 尤其是在高频通信领域。因其独特的介电特性, 如高相对介电常数εr、低介质损耗和接近零的谐振频率温度系数τf, 而被广泛应用于微波谐振器、滤波器、振荡器等微波元器件中。本研究制备了一种具有中介电常数的Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3(BNN)陶瓷, 通过X射线衍射(XRD)和Rietveld精修确认其为单斜晶系, 空间群为C12/m1。随着烧结温度的升高, 陶瓷的密度先增大后减小, 其体积密度(ρobs)和相对密度(ρrel)在1550 ℃烧结时达到最大值, 分别为6.32 g/cm3和98%。在1525 ℃烧结时, 陶瓷展现出最佳的微波介电性能: εr=38.44, 品质因数Q×f=25400 GHz, τf=-6×10-6 ℃-1。值得注意的是, 与文献研究报道的11700 GHz相比, 本研究制备的BNN陶瓷的Q×f提升了117%, 这表明BNN陶瓷的微波介电性能可能因测试方法、原料性质及制备工艺等因素而被低估。此外, 利用这种陶瓷材料设计并仿真了一款全介质频率选择表面(Frequency Selective Surface, FSS), 其相对带宽约为23.3%, 显示出优异的选频性能。BNN陶瓷的上述特性不仅显示了其在微波介质陶瓷材料中的潜力, 而且其在FSS仿真中的出色表现也进一步被证实是一种被低估的微波介质陶瓷材料。
中图分类号:
何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646.
HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646.
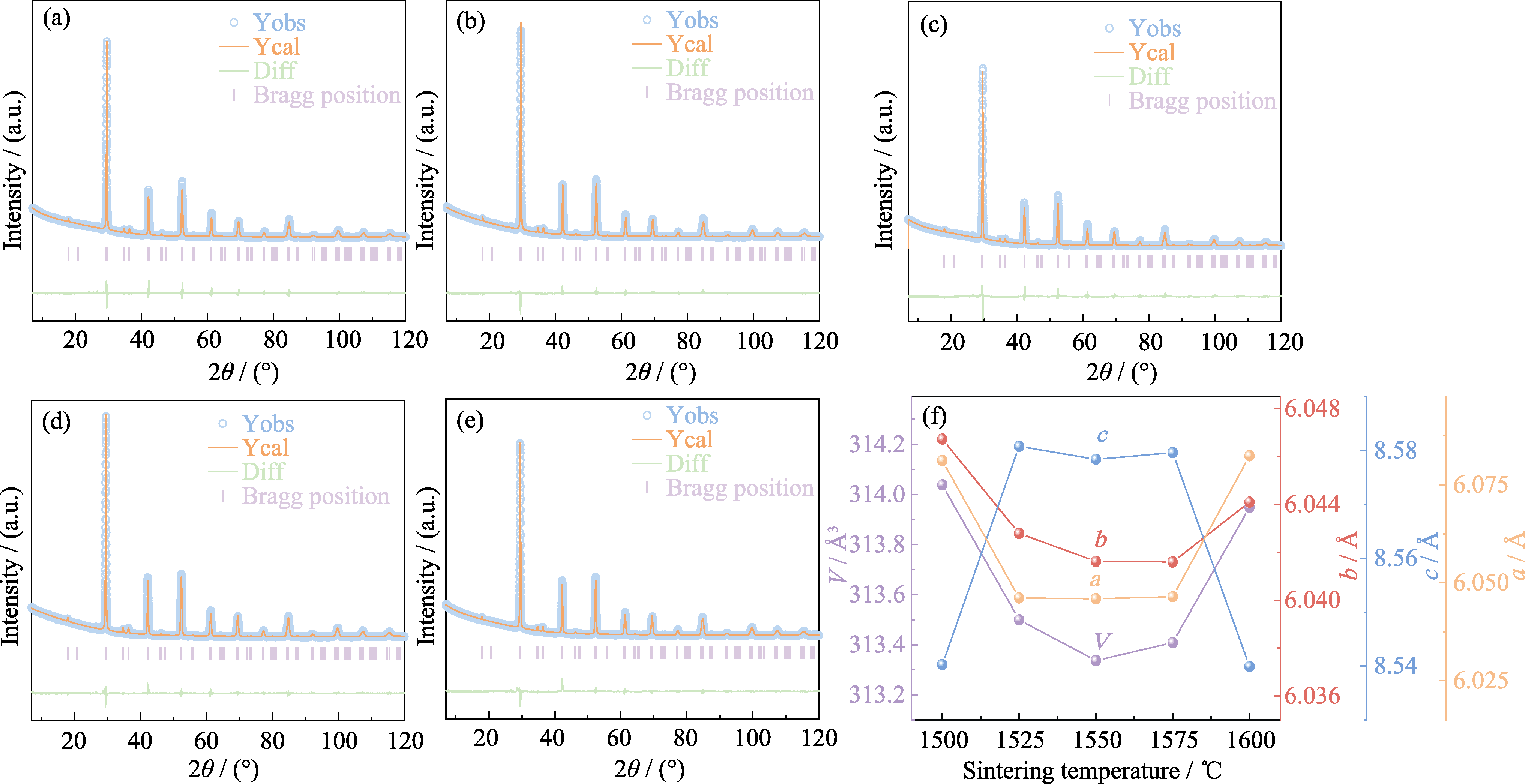
图2 不同温度烧结的BNN陶瓷的XRD精修图谱(a~e)和晶格参数随烧结温度的变化趋势(f)
Fig. 2 XRD refinement patterns (a-e) and variations of lattice parameters with sintering temperature (f) of BNN ceramics sintered at different temperatures (a) 1500 ℃; (b) 1525 ℃; (c) 1550 ℃; (d) 1575 ℃; (e) 1600 ℃. Colorful figures are available on website
| Sintering temperature/℃ | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/Å3 | Rwp/% | GOF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | 6.08122 | 6.04673 | 8.54026 | 90 | 90 | 90.1595 | 314.038 | 5.33 | 2.56 |
| 1525 | 6.04613 | 6.04279 | 8.58079 | 90 | 90 | 90.3715 | 313.499 | 4.97 | 2.48 |
| 1550 | 6.04591 | 6.04162 | 8.57837 | 90 | 90 | 90.3576 | 313.337 | 4.65 | 2.30 |
| 1575 | 6.04643 | 6.04159 | 8.57961 | 90 | 90 | 90.3573 | 313.408 | 5.00 | 2.48 |
| 1600 | 6.08241 | 6.04409 | 8.53991 | 90 | 90 | 90.1503 | 313.949 | 5.90 | 2.83 |
表1 BNN陶瓷的晶体学参数及R因子
Table 1 Crystallographic parameters and R-factors of BNN ceramics
| Sintering temperature/℃ | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/Å3 | Rwp/% | GOF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | 6.08122 | 6.04673 | 8.54026 | 90 | 90 | 90.1595 | 314.038 | 5.33 | 2.56 |
| 1525 | 6.04613 | 6.04279 | 8.58079 | 90 | 90 | 90.3715 | 313.499 | 4.97 | 2.48 |
| 1550 | 6.04591 | 6.04162 | 8.57837 | 90 | 90 | 90.3576 | 313.337 | 4.65 | 2.30 |
| 1575 | 6.04643 | 6.04159 | 8.57961 | 90 | 90 | 90.3573 | 313.408 | 5.00 | 2.48 |
| 1600 | 6.08241 | 6.04409 | 8.53991 | 90 | 90 | 90.1503 | 313.949 | 5.90 | 2.83 |
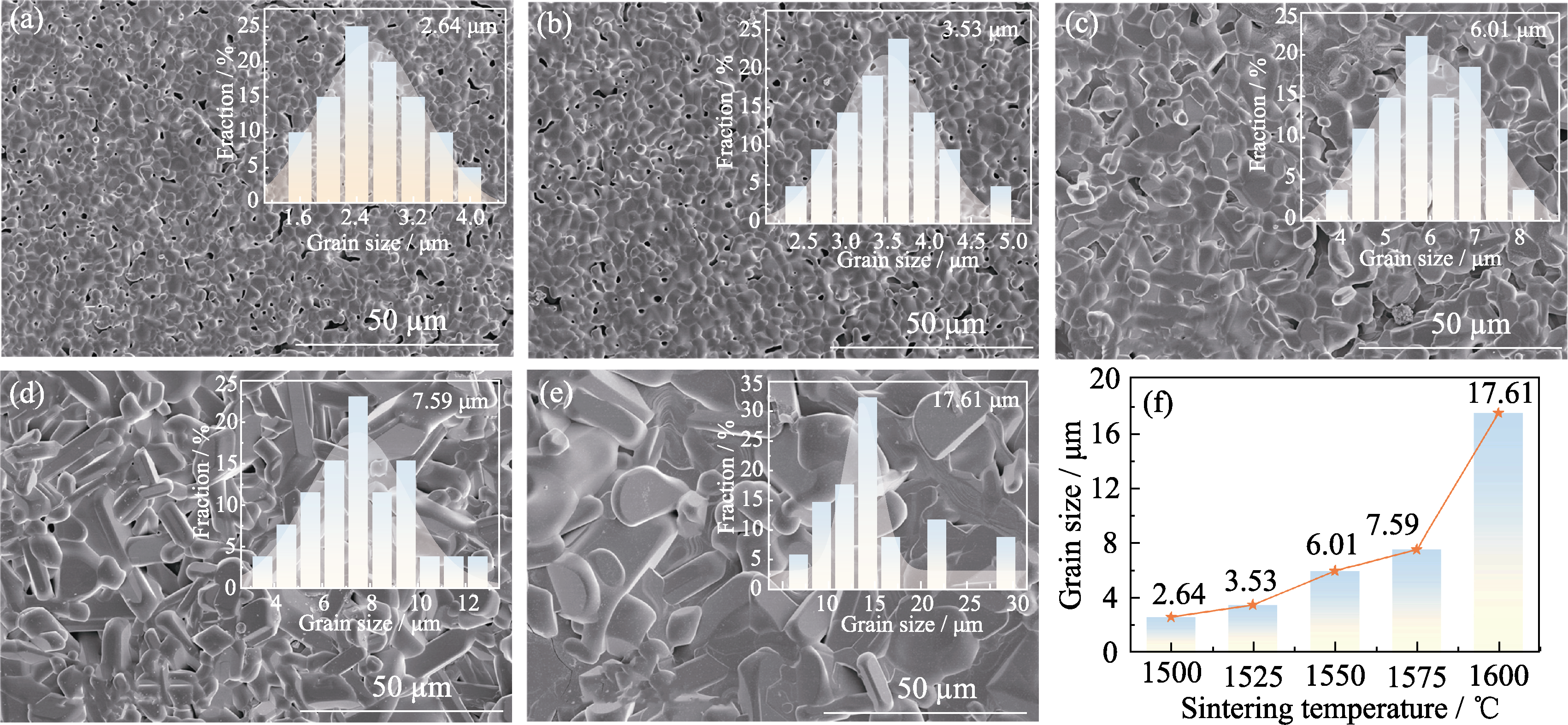
图4 (a~e)不同温度烧结的BNN陶瓷的SEM照片, 插图为晶粒尺寸分布图; (f)平均晶粒尺寸随烧结温度的变化趋势
Fig. 4 (a-e) SEM images of sintered BNN ceramics at different temperatures with insets showing grain size distributions; (f) Variation of average grain size with sintering temperature (a) 1500 ℃; (b)1525 ℃; (c)1550 ℃; (d)1575 ℃; (e)1600 ℃
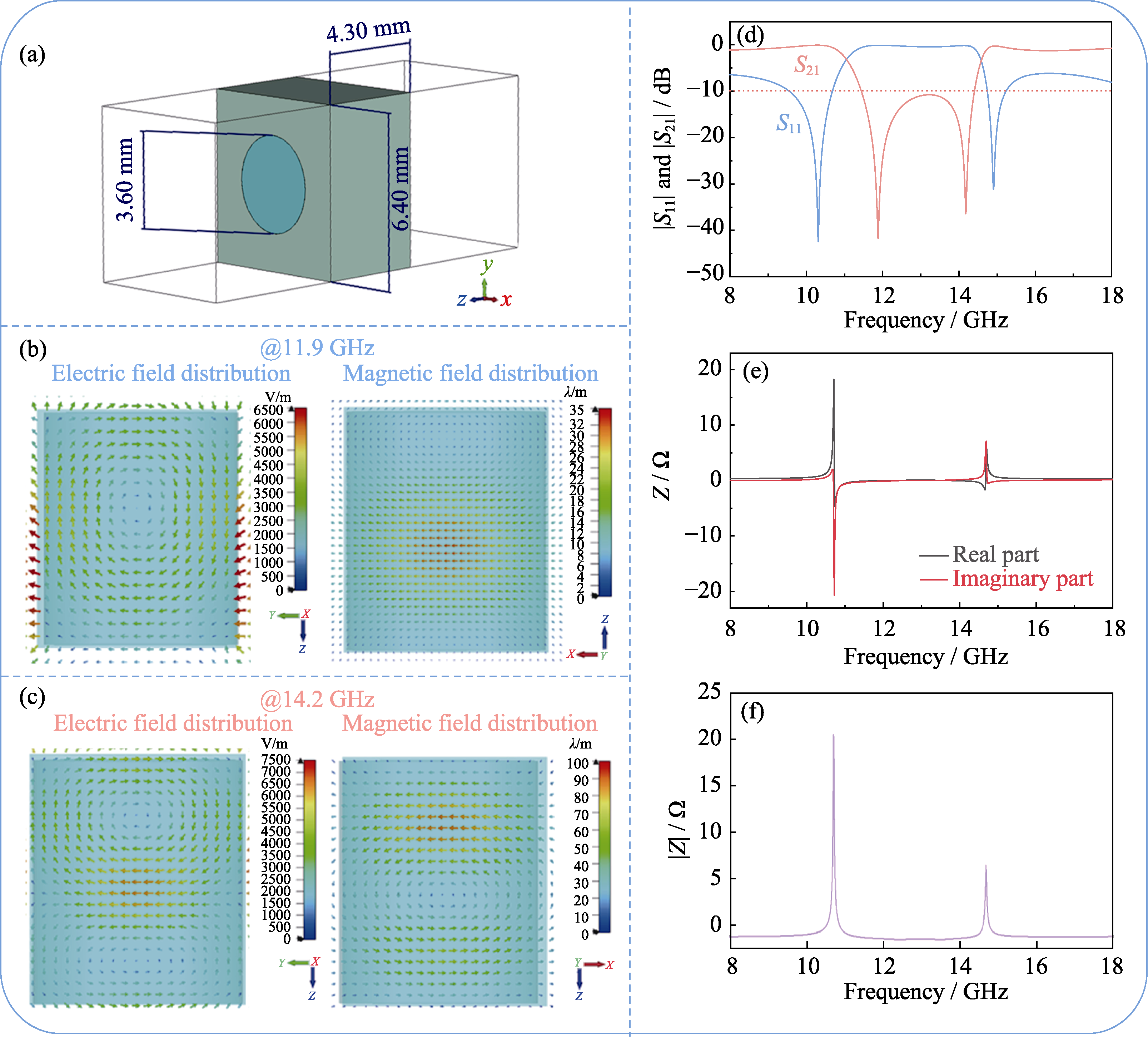
图8 全介质频率选择表面
Fig. 8 All-dielectric frequency selection surface (a) Simulation model; (b, c) Distributions of electric field and magnetic field of the sample under two reflection pole; (d) Reflection and transmission characteristics of FSS; (e) FSS normalized the real and imaginary parts of the impedance; (f) Simulation results. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | SEBASTIAN M T, UBIC R, JANTUNEN H. Low-loss dielectric ceramic materials and their properties. International Materials Reviews, 2015, 60(7): 392. |
| [2] | PENG S, ZHANG Y, YI T. Research progress of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 microwave dielectric ceramics: a review. Materials, 2023, 16(1): 423. |
| [3] | SEBASTIAN M T, WANG H, JANTUNEN H. Low temperature co-fired ceramics with ultra-low sintering temperature: a review. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2016, 20(3): 151. |
| [4] | SEBASTIAN M T, JANTUNEN H. Low loss dielectric materials for LTCC applications: a review. International Materials Reviews, 2008, 53(2): 57. |
| [5] | YANG H, ZHANG S, YANG H, et al. Usage of P-V-L bond theory in studying the structural/property regulation of microwave dielectric ceramics: a review. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2020, 7: 4711. |
| [6] | SHEHBAZ M, DU C, ZHOU D, et al. Recent progress in dielectric resonator antenna: materials, designs, fabrications, and their performance. Applied Physics Reviews, 2023, 10: 021303. |
| [7] | HILL M D, CRUICKSHANK D B, MACFARLANE I A. Perspective on ceramic materials for 5G wireless communication systems. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118: 120501. |
| [8] | REANEY I M, IDDLES D. Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7): 2063. |
| [9] | WANG X, ZHOU T, WANG W, et al. Effect of B-site complex substitutions on orthorhombic distortion and microwave dielectric properties of Ca(Zr0.95Ti0.05)O3 perovskites. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12: 3124. |
| [10] | 石锋. A(B'1/3B''2/3)O3型复合钙钛矿微波介质陶瓷材料的发展. 硅酸盐通报, 2006, 25(4): 5. |
| [11] | KAWASHIMA S, NISHIDA M, UEDA I, et al. Ba(Zn1/3Ta2/3)O3 ceramics with low dielectric loss at microwave frequencies. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1983, 66: 421. |
| [12] | NOMURA S, TOYAMA K, KANETA K. Ba(Mg1/3Ta2/3)O3 ceramics with temperature-stable high dielectric constant and low microwave loss. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1982, 21(10A): L624. |
| [13] | WU H, DAVIES P K. Influence of non-stoichiometry on the structure and properties of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 microwave dielectrics: Ⅱ. Compositional variations in pure BZN. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7): 2250. |
| [14] | NOMURA S, TOYAMA K, KANETA K. Ba(Mg1/3Ta2/3)O3 ceramics with temperature-stable high dielectric constant and low microwave loss. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1982, 21(10A): L624. |
| [15] | VARMA M R, SEBASTIAN M T. Effect of dopants on microwave dielectric properties of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(8/9): 2827. |
| [16] | KHALAM L A, ANJANA P S, SEBASTIAN M T. The effect of dopants on the dielectric properties of Ba(B'1/2Ta1/2)O3 (B=La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Y, Yb, and In) microwave ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2008, 5(5): 571. |
| [17] | GUO H H, FU M S, ZHOU D, et al. Design of a high-efficiency and-gain antenna using novel low-loss, temperature-stable Li2Ti1-x(Cu1/3Nb2/3)xO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 13(1): 912. |
| [18] | WANG K, ZHAO Y, CHEN X, et al. Effects of sintering temperature on microstructure and varistor performances of ZnO-SrCO3-Co2O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(23): 51162. |
| [19] | SWIKKER K R J, KANAGASABAPATHY H, MANICKAM I N, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on grain growth and mechanical properties of copper/graphene nanosheet composite. Diamond and Related Materials, 2020, 110: 108111. |
| [20] | PAREDES-GOYES B, JAUFFRES D, MISSIAEN J M, et al. Grain growth in sintering: a discrete element model on large packings. Acta Materialia, 2021, 218: 117182. |
| [21] | HE G, JIANG Y, SONG K, et al. UltrahighQ Sr1+xY2O4+x (x=0-0.04) microwave dielectric ceramics for temperature-stable millimeter-wave dielectric resonator antennas. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(2): 155. |
| [22] | DU C, FU M S, ZHOU D, et al. Dielectric resonator antenna with Y3Al5O12 transparent dielectric ceramics for 5G millimeter-wave applications. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(9): 4659. |
| [23] | DU C, ZHOU D, HAO S Z, et al. High-quality-factor AlON transparent ceramics for 5 GHz Wi-Fi aesthetically decorative antennas. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(39): 46866. |
| [24] | HE G, ZHAO Z, LIU Y, et al. Sintering characteristics, phase structure and microwave dielectric properties of novel BaCeO3 ceramics. Materials Research Bulletin, 2024, 172: 112790. |
| [25] | QI C, WANG F, LAI Y, et al. Temperature stability of Li2TiO3- Zn2SiO4 microwave dielectric ceramics. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 2022(29): e202200380. |
| [26] | LIU Y, HE G, NIE Y, et al. Influence of sintering characteristics and structural properties on the microwave dielectric properties of non-stoichiometric Ca3Mn2+xGe3O12+δ (x=0-0.2) ceramics. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(18): 6615. |
| [27] | PAN H L, CHENG L, WU H T. Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Li2(Mg1-xCox)3TiO6 (0≤x≤0.4) ceramics. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15018. |
| [28] | LIN I N, CHIA C T, LIU H L, et al. Intrinsic dielectric and spectroscopic behavior of perovskite Ba(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3-Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102: 044112. |
| [29] | LIU B, HUANG Y H, SONG K X, et al. Structural evolution and microwave dielectric properties in Sr2(Ti1-xSnx)O4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(11): 3833. |
| [30] | WANG G, ZHANG D, GAN G, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure and low loss of Li3Mg2NbO6 ceramics by reaction sintering process. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(16): 19766. |
| [31] | SHANNON R D. Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 73(1): 348. |
| [32] | BOSMAN A J, HAVINGA E E. Temperature dependence of dielectric constants of cubic ionic compounds. Physical Review, 1962, 129(4): 1593. |
| [33] | PENN S J, ALFORD N M, TEMPLETON A, et al. Effect of porosity and grain size on the microwave dielectric properties of sintered alumina. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 80(7): 1885. |
| [34] | LIAO Q, LI L, REN X, et al. New low-loss microwave dielectric material ZnTiNbTaO8. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(10): 3237. |
| [1] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [2] | 唐莹, 李洁, 相怀成, 方维双, 林慧兴, 杨俊峰, 方亮. Rattling效应: 一种影响微波介质陶瓷谐振频率温度系数的新机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [3] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [4] | 李海涛, 李 谦, 闫焉服, 许荣辉. ZnO掺杂对Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3陶瓷烧结性能和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [5] | 刘 林, 方有维, 邓新峰, 庄文东, 唐 斌, 张树人. (Ba1-xSrx)La4Ti4O15(x=0.8~0.95)陶瓷的微结构及微波介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3): 281-284. |
| [6] | 姚晓刚, 林慧兴, 姜少虎, 陈 玮, 罗 澜. Al2O3掺杂对Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54陶瓷显微结构和介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(12): 1266-1270. |
| [7] | 范跃农, 聂 彦, 廖章奇, 王 鲜, 龚荣洲. 嵌入分形频率选择表面的低频超薄吸波层的设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(12): 1336-1340. |
| [8] | 刘 昊, 沈春英, 卢正东, 丘 泰. (1-x)(Mg0.9Co0.1)TiO3-x(Ca0.61La0.26)TiO3陶瓷的微波介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(6): 664-668. |
| [9] | 李月明1,宋婷婷1,尤源2,胡元云2,刘维良1,唐春宝1. Ca0.3(Li1/2Sm1/2)0.7TiO3微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1293-1297. |
| [10] | 姚国光,刘鹏. V5+取代对 Mg4(SbNb1-xVx)O9陶瓷介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(5): 877-880. |
| [11] | 周东祥,余晓华,王鹤,赵俊. BaO-CeO2-TiO2微波介质陶瓷的烧结特性及物相组成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(6): 1197-1200. |
| [12] | 宿新泰,刘瑞泉,胡云霞,谢娅红,王吉德. 柠檬酸盐溶胶-凝胶法制备Ba3(Ca1.18Nb1.82)O9-δ纳米粉末[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(1): 229-233. |
| [13] | 杨秋红,金应秀,徐军. Nd3+A位置换对(Pb0.5Ca0.5)(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3陶瓷微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(5): 1051-1056. |
| [14] | 王宁,赵梅瑜,殷之文. 微波介质陶瓷的中低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(5): 915-924. |
| [15] | 严清峰,张一玲,李强. 铅基驰豫型复合钙钛矿结构PLZST的合成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2001, 16(4): 0-654. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||