无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 177-183.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240292 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240292
李伟( ), 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松(
), 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-17
修回日期:2024-09-09
出版日期:2025-02-20
网络出版日期:2024-09-23
通讯作者:
王 松, 研究员. E-mail: wangs_0731@163.com作者简介:李 伟(1979-), 男, 副研究员. E-mail: liwei79@nudt.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Wei( ), XU Zhiming, GOU Yanzi, YIN Senhu, YU Yiping, WANG Song(
), XU Zhiming, GOU Yanzi, YIN Senhu, YU Yiping, WANG Song( )
)
Received:2024-06-17
Revised:2024-09-09
Published:2025-02-20
Online:2024-09-23
Contact:
WANG Song, professor. E-mail: wangs_0731@163.comAbout author:LI Wei (1979-), male, associate professor. E-mail: liwei79@nudt.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
SiC纤维烧结陶瓷(Fiber-bonded ceramics, FBCs)是由SiC纤维直接烧结而成的一种新型SiC材料, 材料中不存在基体相, 其孔隙率小于3%且纤维体积分数超过90%, 具有耐高温、高强度、抗氧化与耐辐照等优异性能, 是未来航空发动机和先进核能领域的重要候选材料。本工作在国内率先开展SiC FBCs的制备以及性能研究, 以国产KD-SA型第三代含铝SiC纤维为原料, 通过预处理在纤维表面原位构筑石墨(in-situ graphite, iG)层, 采用热压烧结工艺直接烧结纤维, 制备SiC(Al) FBCs。实验表征了纤维及材料的宏/微观结构, 测试了材料的力学与氧化性能。结果表明: 通过预处理SiC(Al)纤维, iG/SiC(Al)纤维表面可生成厚度为300~400 nm的碳层, 且iG层与纤维结合较好。采用热压烧结工艺制备的iG/SiC(Al) FBCs密度为3.15 g/cm3, 气孔率仅为0.52%, 基体完全致密, 纤维发生变形呈六棱柱状, 且纤维之间有明显的界面; 材料弯曲强度、断裂韧性与断裂功分别为320 MPa、9.5 MPa·m1/2与1169 J·m-2; 经1500、1600 ℃空气氧化100 h, 材料弯曲强度保留率分别高达86%与72%, 且维持伪塑性断裂模式。
中图分类号:
李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183.
LI Wei, XU Zhiming, GOU Yanzi, YIN Senhu, YU Yiping, WANG Song. Preparation and Performance of Sintered SiC Fiber-bonded Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 177-183.
| Sample | Composition/% (in atom) | C/Si | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | C | O | Al | ||
| SiC(Al) fiber | 47.70 | 51.50 | 0.30 | <1.00 | 1.08 |
表1 SiC(Al)纤维的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of SiC(Al) fiber
| Sample | Composition/% (in atom) | C/Si | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | C | O | Al | ||
| SiC(Al) fiber | 47.70 | 51.50 | 0.30 | <1.00 | 1.08 |
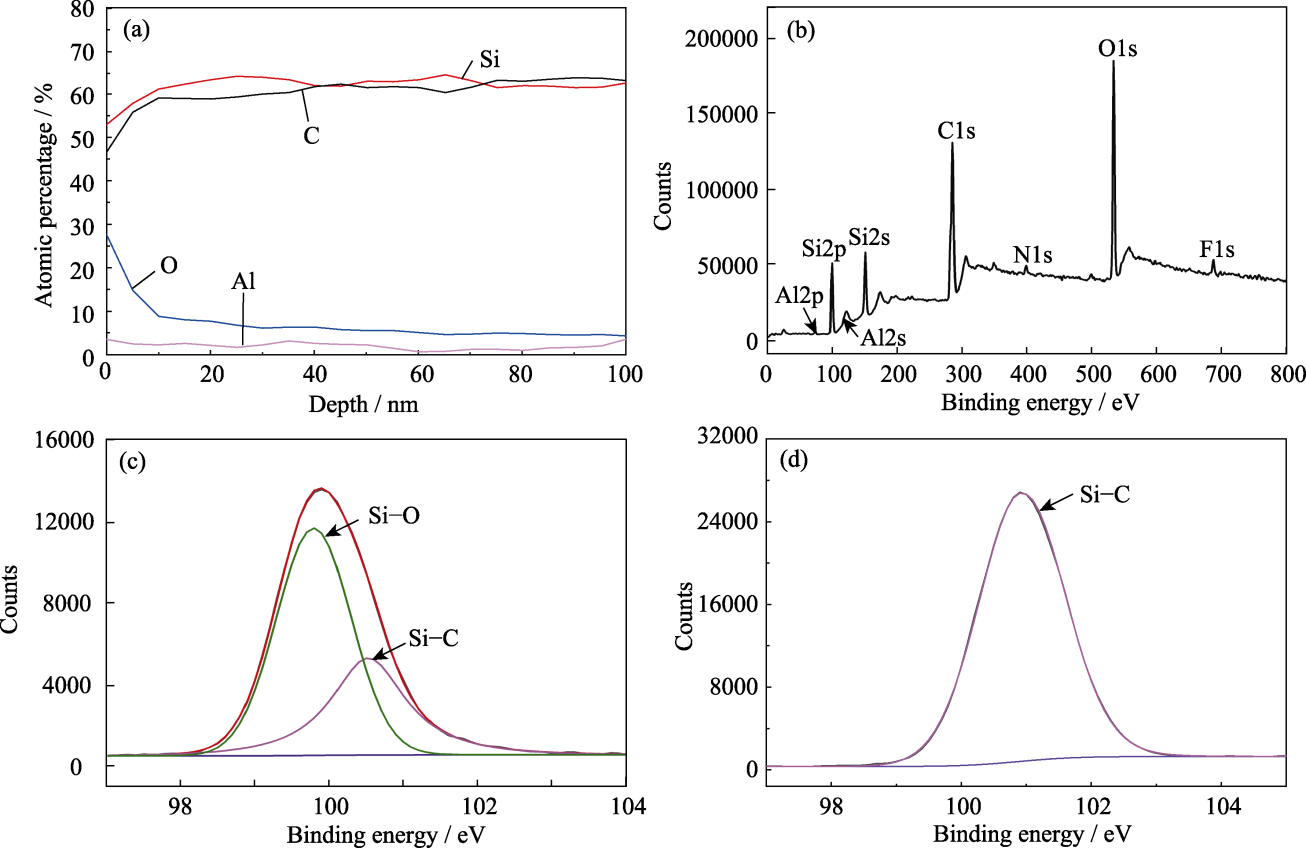
图1 SiC(Al)纤维的化学组成
Fig. 1 Chemical composition of SiC(Al) fiber (a) AES depth profile; (b) Total XPS spectra of surface; (c, d) Si2p XPS spectra of SiC(Al) fiber (c) before and (d) after etching

图3 (a, b) SiC(Al)纤维与(c, d) iG/SiC(Al)纤维的(a, c)表面与(b, d)截面SEM照片
Fig. 3 (a, c) Surface and (b, d) cross-sectional SEM images of (a, b) SiC(Al) fiber and (c, d) iG/SiC(Al) fiber
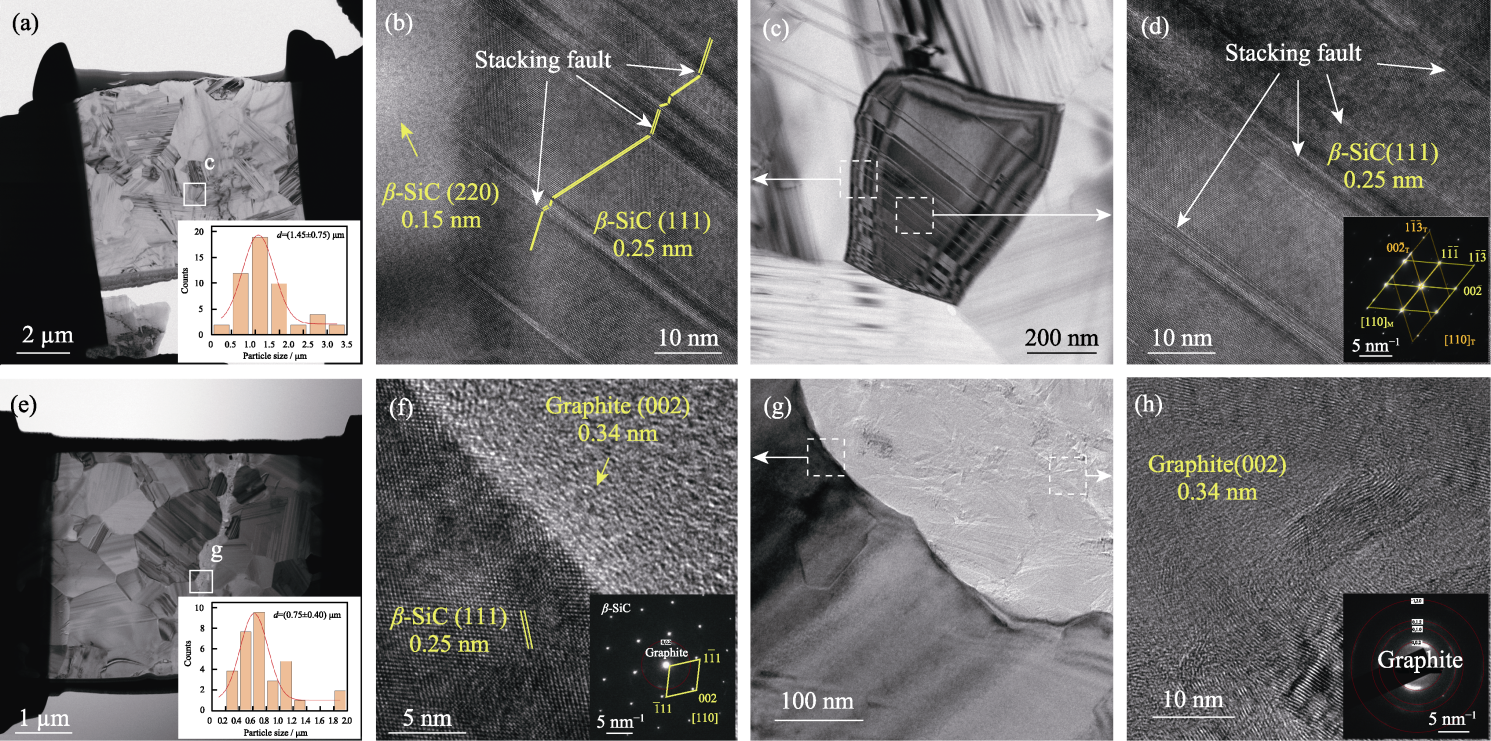
图6 (a~d) SiC(Al) FBC与(e~h) iG/SiC(Al) FBC的(a, c, e, g)TEM和(b, d, f, h)HRTEM照片((a, e)中的插图为相应的粒径分布图, (d, f, h)中的插图为SAED图案)
Fig. 6 (a, c, e, g) TEM and (b, d, f, h) HRTEM images of (a-d) SiC(Al) FBC and (e-h) iG/SiC(Al) FBC with insets in (a, e) showing corresponding distributions of crystal diameters and insets in (d, f, h) showing selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns
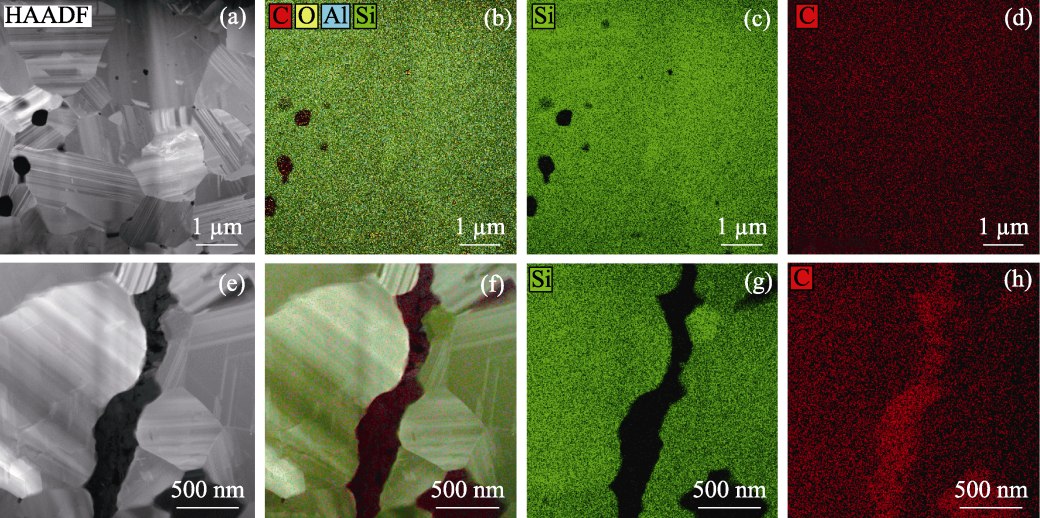
图7 (a~d) SiC(Al) FBC与(e~h) iG/SiC(Al) FBC的(a, e)HAADF图像和(b~d, f~h)元素分布图
Fig. 7 (a, e) HAADF images and (b-d, f-h) elemental mappings of (a-d) SiC(Al) FBC and (e-h) iG/SiC(Al) FBC
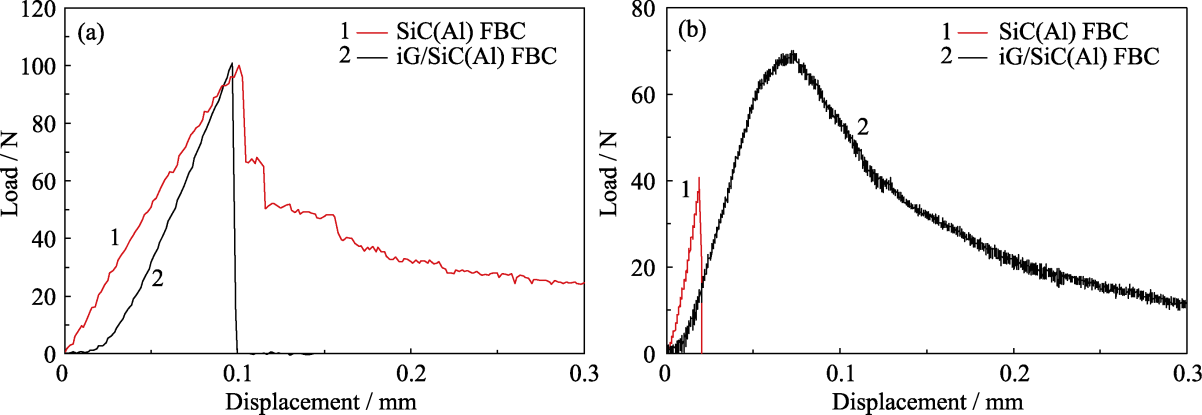
图8 SiC(Al) FBC与iG/SiC(Al) FBC在(a)弯曲强度与(b)断裂韧性测试过程中的载荷-位移曲线
Fig. 8 Load-displacement curves during the (a) flexural strength and (b) fracture toughness tests of SiC(Al) FBC and iG/SiC(Al) FBC

图11 iG/SiC(Al) FBC经不同温度氧化考核100 h的(a)弯曲强度测试过程中的载荷-位移曲线与(b)剩余弯曲强度
Fig. 11 (a) Load-displacement curves during the flexural strength test and (b) residual bending strength of iG/SiC(Al) FBC after 100 h oxidation at different temperatures
| [1] | YIN F, RAO A G. Performance analysis of an aero engine with inter-stage turbine burner. The Aeronautical Journal, 2017, 121(1245): 1605. |
| [2] | SRINIVAS G, RAGHUNANDANA K, SATISH SHENOY B. Recent developments in turbomachinery component materials and manufacturing challenges for aero engine applications. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 314: 012012. |
| [3] | LIN Z M. The current development and future trends of fighter engines. Aeroengine, 2006, 32(1): 1. |
| [4] | BERGS T, GRÜNEBAUM T, FRICKE K, et al. Life cycle assessment for milling of Ti-and Ni-based alloy aero engine components. Procedia CIRP, 2021, 98: 625. |
| [5] | WANG X G, LIU J L, JIN T, et al. Tensile behaviors and deformation mechanisms of a nickel-base single crystal superalloy at different temperatures. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 598: 154. |
| [6] |
ZHANG G, ZHANG Y, ZHENG L, et al. Research progress in powder metallurgy superalloys and manufacturing technologies for aero-engine application. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 55(9): 1133.
DOI |
| [7] | FAN X, YIN X. Progress in research and development on matrix modification of continuous fiber-reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2018, 1: 685. |
| [8] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 804.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | KARADIMAS G, SALONITIS K. Ceramic matrix composites for aero engine applications--a review. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(5): 3017. |
| [10] | KATOH Y, SNEAD L L, HENAGER J C H, et al. Current status and recent research achievements in SiC/SiC composites. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 455(1/2/3): 387. |
| [11] | DICARLO J A, YUN H M, MORSCHER G N, et al. SiC/SiC composites for 1200 ℃ and above//BANSAL N P. Handbook of ceramic composites. Boston: Springer US, 2005: 77-98. |
| [12] | LUTHRA K L, CORMAN G S. Melt infiltrated (MI) SiC/SiC composites for gas turbine applications//KRENKEL W, NASLAIN R, SCHNEIDER H. High temperature ceramic matrix composites. Ohio: Wiley-American Ceramic Society, 2001: 744-753. |
| [13] | 武安华, 曹文斌, 马芳, 等. SiC的固相热压烧结. 北京科技大学学报, 2000, 22(4): 328. |
| [14] | ISHIKAWA T, KAJII S, MATSUNAGA K, et al. A tough, thermally conductive silicon carbide composite with high strength up to 1600 ℃ in air. Science, 1998, 282(5392): 1295. |
| [15] | HO C Y, TSAI S C, LIN H T, et al. Microstructural investigation of Si-ion-irradiated single crystal 3C-SiC and SA-Tyrannohex SiC fiber-bonded composite at high temperatures. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 443(1/2/3): 1. |
| [16] | XU Z M, YU Y P, WANG S, et al. Research progress of SiC fiber-bonded ceramics. Journal of Material Engineering, 2023, 51(8): 23. |
| [17] | VERA M C, MARTÍNEZ-FERNÁNDEZ J, SINGH M, et al. Strength and thermal shock resistance of Si-Al-C-O and Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2022, 19(2): 1126. |
| [18] | GOU Y, WANG H, JIAN K. Formation of carbon-rich layer on the surface of SiC fiber by sintering under vacuum for superior mechanical and thermal properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(3): 907. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y, CHEN J, YAN D, et al. Conversion of silicon carbide fibers to continuous graphene fibers by vacuum annealing. Carbon, 2021, 182: 435. |
| [20] | 王堋人. SA型SiC纤维烧结致密化机理及高温性能研究. 长沙: 国防科技大学博士学位论文, 2020. |
| [21] | YAMAMOTO H, BABA Y, SASAKI T A. Electronic structures of N2+ and O2+ ion-implanted Si (100). Surface and Interface Analysis, 1995, 23(6): 381. |
| [22] | KAJII S, MATSUNAGA K, SATO M, et al. Mechanical behavior of SiC-Polycrystalline fiber-bonded-cermics. 28th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and Composites B:Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Hoboken, 2004, 25: 43-48. |
| [23] | CORMAN G S, LUTHRA K L. Silicon melt infiltrated ceramic composites (HiPerComp™)//BANSAL N P. Handbook of ceramic composites. Boston: Springer US, 2005: 99-115. |
| [24] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Long-term oxidation performance of SiCf/SiC composites at 1200 ℃ in air atmosphere manufactured by PIP and hybrid CVI/PIP techniques. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(7): 10259. |
| [1] | 陈斌, 任科, 王一光. Mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料长时间高温下的力学性能演变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 971-980. |
| [2] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [3] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [4] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 王堋人. 烧结条件对制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [5] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [6] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [7] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [8] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [9] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [10] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [11] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [12] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [13] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [14] | 郑斌, 康凯, 张青, 叶昉, 解静, 贾研, 孙国栋, 成来飞. 前驱体转化陶瓷法制备Ti3SiC2陶瓷及其热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 733-740. |
| [15] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||