无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 281-289.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240438 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240438
所属专题: 【结构材料】高导热陶瓷(202506)
穆浩洁1( ), 张源江1, 喻彬2, 付秀梅2, 周世斌2, 李晓东1(
), 张源江1, 喻彬2, 付秀梅2, 周世斌2, 李晓东1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-17
修回日期:2024-11-22
出版日期:2025-03-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-12
通讯作者:
李晓东, 教授. E-mail:xdli@mail.neu.edu.cn作者简介:穆浩洁(1999-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail:2110169@stu.neu.edu.cn
基金资助:
MU Haojie1( ), ZHANG Yuanjiang1, YU Bin2, FU Xiumei2, ZHOU Shibin2, LI Xiaodong1(
), ZHANG Yuanjiang1, YU Bin2, FU Xiumei2, ZHOU Shibin2, LI Xiaodong1( )
)
Received:2024-10-17
Revised:2024-11-22
Published:2025-03-20
Online:2025-03-12
Contact:
LI Xiaodong, professor. E-mail: xdli@mail.neu.edu.cnAbout author:MU Haojie (1999-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: 2110169@stu.neu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷与单相Y2O3陶瓷相比具有更高的机械强度、硬度、热导率以及优异的红外波段透光性, 是一种良好的红外窗口材料。然而, 恶劣的热、机械工作环境对红外窗口材料的光学和力学性能提出了更高的要求。本研究以高纯Y2O3-MgO纳米复合粉体为原料, 通过在球磨过程中添加硝酸锆水溶液制备了不同ZrO2掺杂量(Zr4+离子分别占Y3+离子的1%、3%、5%)的Y2O3-MgO纳米复合粉体。利用该粉体成型后的坯体在1350 ℃、35 MPa条件下热压烧结30 min制备得到ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷, 研究了ZrO2掺杂量对陶瓷物相、微观结构、红外透光率、硬度和抗弯强度的影响。结果表明: ZrO2掺杂改变了Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的微观结构并引起了晶格畸变, 从而显著影响陶瓷的光学性能和力学性能。ZrO2固溶并均匀分布在Y2O3晶格中, 对MgO相没有影响。微观结构观察结果显示, ZrO2掺杂量增大, 抑制了陶瓷致密化, 因此在5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO陶瓷中存在明显的孔洞。同时, ZrO2掺杂可以强化Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷, 这是由于晶格畸变抑制了位错运动。当ZrO2掺杂量为3%时, 致密的微观结构使其在3~5 μm波段的透过率达到~82%, 硬度和抗弯强度分别达到11.43 GPa和276.67 MPa。
中图分类号:
穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289.
MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289.
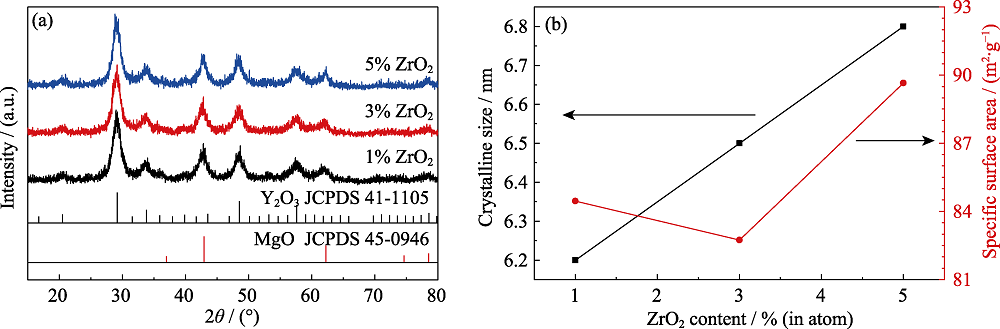
图2 不同ZrO2掺杂量(原子分数)的Y2O3-MgO纳米复合粉体的(a)XRD图谱和(b)晶粒尺寸及比表面积
Fig. 2 (a) XRD patterns, (b) crystalline sizes and specific surface areas of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite powders doped with different ZrO2 concentrations (atom fraction)

图3 不同ZrO2掺杂量(原子分数)的Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的(a)XRD图谱, (b)Y2O3(222)晶面和(c)MgO(200)晶面的衍射峰
Fig. 3 (a) XRD patterns and diffraction peaks of (b) Y2O3 (222) and (c) MgO (200) crystal planes of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics doped with different ZrO2concentrations (atom fraction)
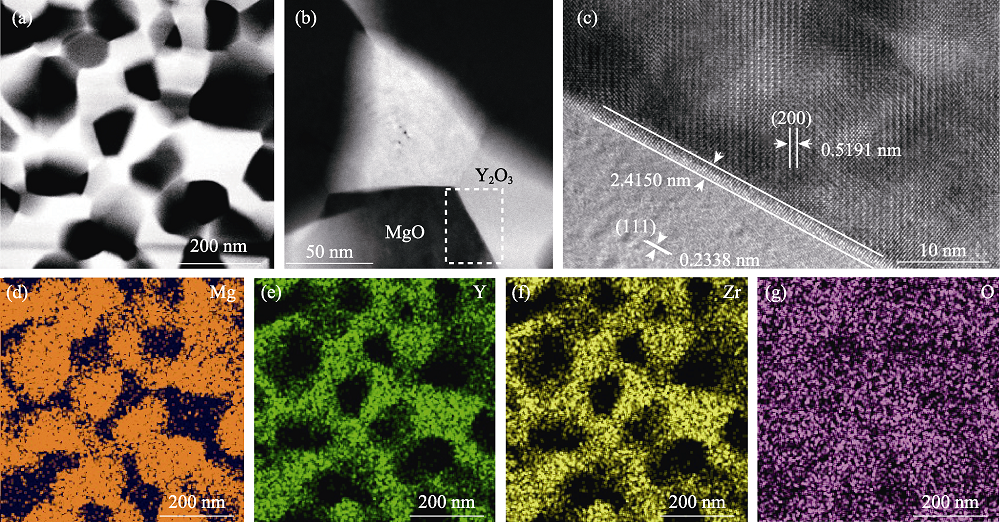
图4 (a, b) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的明场像, (c)晶界的高分辨图像和(d~g) Mg、Y、Zr、O元素分布情况
Fig. 4 (a, b) Bright field images of 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramic, (c) high resolution image of grain boundary, and (d-g) element mappings of Mg, Y, Zr, and O
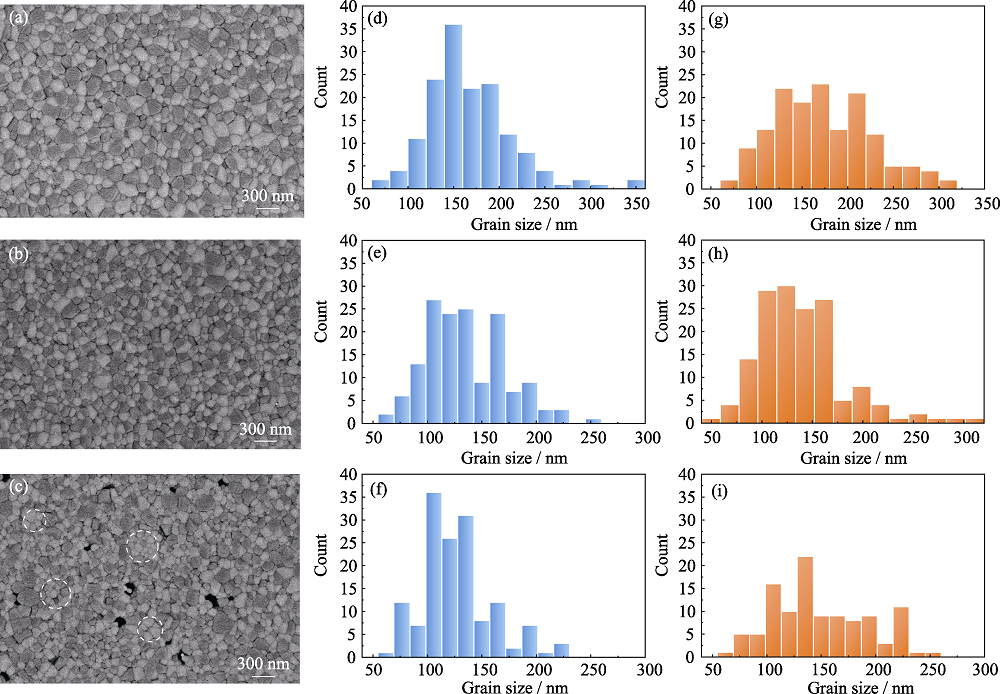
图5 ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的表面形貌以及Y2O3相和MgO相的晶粒尺寸分布
Fig. 5 Surface morphologies and grain size distributions of Y2O3 and MgO phases of ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics (a-c) Surface morphologies of (a) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (b) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (c) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics; (d-f) Grain size distributions of Y2O3 phase in (d) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (e) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (f) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics; (g-i) Grain size distributions of MgO phase in (g) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (h) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (i) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics

图8 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷中(a~d)Y2O3和(e, f)MgO相的(a, e)明场像和(b~d, f)HAADF原子像
Fig. 8 (a, e) Bright field images and (b-d, f) HAADF atomic images of (a-d) Y2O3 phase and (e, f) MgO phase in 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramic
| [1] | LIU Z Y, IKESUE A, LI J. Research progress and prospects of rare-earth doped sesquioxide laser ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 3895. |
| [2] | WANG J, ZHAO Y G, YIN D L, et al. Holmium doped yttria transparent ceramics for 2-μm solid state lasers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4): 1986. |
| [3] | MA Z Z, CHEN L, CHEN J, et al. Fabrication of Y2O3 transparent ceramics by pressure-assisted alcoholic slip casting. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(23): 37729. |
| [4] | ZHANG L, YANG J, YU H Y, et al. High performance of La- doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(4): 493. |
| [5] | 李江, 姜楠, 徐圣泉, 等. 红外透明MgO-Y2O3纳米复相陶瓷研究进展. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(9): 1302. |
| [6] | HARRIS D C, CAMBREA L R, JOHNSON L F, et al. Properties of an infrared-transparent MgO:Y2O3 nanocomposite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(12): 3828. |
| [7] | LIU L H, MORITA K, SUZUKI T S, et al. Synthesis of highly- infrared transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites by colloidal technique and SPS. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 13669. |
| [8] | ABBASLOO M, SHOKROLLAHI H, ALHAJI A. Slip-casting process of MgO-Y2O3 nanocomposite: investigation of powder synthesis method. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 254: 123387. |
| [9] | MA H J, JUNG W K, BAEK C, et al. Influence of microstructure control on optical and mechanical properties of infrared transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(15): 4902. |
| [10] | XU S Q, LI J, LI C Y, et al. Infrared-transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites fabricated by the glucose Sol-Gel combustion and hot-pressing technique. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(9): 2796. |
| [11] | FURUSE H, HORIUCHI N, KIM B N. Transparent non-cubic laser ceramics with fine microstructure. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 10300. |
| [12] | ITATANI K, TSUJIMOTO T, KISHIMOTO A. Thermal and optical properties of transparent magnesium oxide ceramics fabricated by post hot-isostatic pressing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(4/5): 639. |
| [13] | LIU L K, ZHU Q H, ZHU Q Q, et al. Fabrication of fine-grained undoped Y2O3 transparent ceramic using nitrate pyrogenation synthesized nanopowders. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5): 5339. |
| [14] | YIN D L, WANG J, NI M, et al. Fabrication of highly transparent Y2O3 ceramics with CaO as sintering aid. Materials, 2021, 14(2): 444. |
| [15] | WANG J, YIN D L, MA J, et al. Pump laser induced photodarkening in ZrO2-doped Yb:Y2O3 laser ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2/3): 635. |
| [16] | ZHU L L, PARK Y J, GAN L, et al. Effects of ZrO2-La2O3 co-addition on the microstructural and optical properties of transparent Y2O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(11): 8525. |
| [17] | YI Q, ZHOU S M, TENG H, et al. Structural and optical properties of Tm:Y2O3 transparent ceramic with La2O3, ZrO2 as composite sintering aid. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(2): 381. |
| [18] | LI X K, MAO X J, FENG M H, et al. Optical absorption and mechanism of vacuum-sintered ZrO2-doped Y2O3 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(16): 4181. |
| [19] | HOU X R, ZHOU S M, LI W J, et al. Study on the effect and mechanism of zirconia on the sinterability of yttria transparent ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(15): 3125. |
| [20] | CAO Y F, LI H Y, ZHENG X Y, et al. Simultaneous precipitation of Zr4+ and Y3+ ions induced refinement of precursors and powders in fabrication of Zr4+ doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Optical Materials, 2023, 139: 113802. |
| [21] | WANG J W, ZHANG L C, CHEN D Y, et al. Y2O3-MgO-ZrO2 infrared transparent ceramic nanocomposites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(3): 1033. |
| [22] | LU K. Sintering of nanoceramics. International Materials Reviews, 2008, 53(1): 21. |
| [23] | STANCIU G, VOICU F, BRANDUS C A, et al. Enhancement of the laser emission efficiency of Yb:Y2O3 ceramics via multi-step sintering method fabrication. Optical Materials, 2020, 109: 110411. |
| [24] | ZHANG L, PAN W. Structural and thermo-mechanical properties of Nd:Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(10): 3326. |
| [25] | ZHOU H X, YANG Q H, XU J, et al. Preparation and spectroscopic properties of 2%Nd:(Y0.9La0.1)2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 471(1/2): 474. |
| [26] | CHEN P L, CHEN I W. Grain boundary mobility in Y2O3: defect mechanism and dopant effects. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1996, 79(7): 1801. |
| [27] | REN Y, LI X D, MU H J, et al. The origin of microstructural inhomogeneity in vacuum-sintered ZrO2‐doped Lu2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(2): 1105. |
| [28] | XU S Q, LI J, KOU H M, et al. Spark plasma sintering of Y2O3-MgO composite nanopowder synthesized by the esterification Sol-Gel route. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(2): 3312. |
| [29] | XU S Q, LI J, LI C Y, et al. Hot pressing of infrared-transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites using Sol-Gel combustion synthesized powders. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(3): 1019. |
| [30] | PERMIN D A, BOLDIN M S, BELYAEV A V, et al. IR-transparent MgO-Y2O3 ceramics by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis and spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10): 15786. |
| [31] | ZHANG L P, LIU Q, YU D Z, et al. Effect of sintering process on the properties of transparent Al2O3. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 39(8): 926. |
| [32] | LU T C, CHANG X H, QI J Q, et al. Low-temperature high- pressure preparation of transparent nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 ceramics. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(21): 213120. |
| [33] | SHAHBAZI H, TATAEI M. Influence of porosity on transparency behavior of MgAl2O4 spinel, experiment vs Mie theory. Optical Materials, 2019, 90: 289. |
| [34] | APETZ R, VAN BRUGGEN M P B. Transparent alumina: a light-scattering model. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2003, 86(3): 480. |
| [35] | ZHAO X M, FANG Q L, XIA C J, et al. Evaluation of pore scattering in transparent ceramics: a simplified model for nanometric spherical pores. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(1): 527. |
| [36] | YONG S M, CHOI D H, LEE K, et al. Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2019, 20(1): 59. |
| [37] | ZHANG R, ZHANG K, YUAN M Y, et al. Nitrogen vacancy regulated lattice distortion on improvement of (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films: mechanical properties and wear resistance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 715. |
| [38] | CHEN Z, HUANG Y, KOUTNÁ N, et al. Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 8387. |
| [39] | WANG P, WU Y, LIU J B, et al. Impacts of atomic scale lattice distortion on dislocation activity in high-entropy alloys. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2017, 17: 38. |
| [40] | ZHU L L, LIU H L, LIN H T, et al. Effects of ZrO2 concentration on the properties of pressureless-sintered highly transparent Er2O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(23): 39076. |
| [41] | LI C R, LI S, AN D, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered SiC ceramics aided by B4C. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8): 10142. |
| [1] | 钟卫民, 赵科, 王珂玮, 刘佃光, 刘金铃, 安立楠. 振荡压力振幅对碳化钨微观结构和摩擦磨损性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 964-970. |
| [2] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [3] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [4] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [5] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [6] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [7] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [8] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [9] | 姜灵毅, 庞生洋, 杨超, 张悦, 胡成龙, 汤素芳. C/SiC-BN复合材料的制备及氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [10] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [11] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [12] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [13] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [14] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [15] | 张睿, 张侃, 袁梦雅, 谷鑫磊, 郑伟涛. 氮空位调控晶格畸变度强化(NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜的力学性质和耐磨损性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 715-725. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||