无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 971-980.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250031 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250031
所属专题: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料(202512)
收稿日期:2025-01-21
修回日期:2025-03-11
出版日期:2025-09-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
任科, 助理教授. E-mail: renke@bit.edu.cn作者简介:陈斌(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1839412972@qq.com
基金资助:
CHEN Bin( ), REN Ke(
), REN Ke( ), WANG Yiguang
), WANG Yiguang
Received:2025-01-21
Revised:2025-03-11
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-03-19
Contact:
REN Ke, assistant professor. E-mail:renke@bit.edu.cn
About author:CHEN Bin (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1839412972@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
连续碳化硅纤维增强碳化硅(SiCf/SiC)复合材料因其优异的力学性能和耐高温特性, 已广泛应用于航空发动机热端部件。为了确保SiCf/SiC复合材料部件在服役过程中的安全性, 研究其在长时间高温下的力学性能演变具有重要意义。本研究采用Cansas-II SiC纤维制备了具有BN界面的mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料, 在1100、1200、1350 ℃下分别进行5、10、50、100、200 h的热处理, 以探究长时间高温热处理对mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料力学性能的影响。研究结果表明: 在1100 ℃下, 热处理对mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的力学性能未产生显著影响, 各阶段对力学性能的贡献占比几乎保持不变。在1200 ℃下, 短时间热处理对于mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的作用不明显, 其拉伸强度未显著变化; 然而, 长时间热处理会导致SiC纤维损伤, 从而降低复合材料的拉伸强度。在1350 ℃下, 热处理显著改善了BN界面性能, 导致SiC纤维损伤严重, mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的力学性能显著降低, 且随着热处理时间延长, 纤维损伤程度加深, 复合材料力学性能持续恶化。
中图分类号:
陈斌, 任科, 王一光. Mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料长时间高温下的力学性能演变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 971-980.
CHEN Bin, REN Ke, WANG Yiguang. Evolution of Mechanical Properties of Mini-SiCf/SiC Composites at High Temperatures over a Long Period of Time[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 971-980.
| Fiber | Diameter/ μm | C/Si | Oxygen/ % (in atom) | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Linear density/(g·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cansas-Ⅱ | 13±1 | 1.61 | <0.8 | 2.7±0.1 | 0.2 |
表1 Cansas-II SiC纤维的一般性能
Table 1 General properties of Cansas-II SiC fibers
| Fiber | Diameter/ μm | C/Si | Oxygen/ % (in atom) | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Linear density/(g·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cansas-Ⅱ | 13±1 | 1.61 | <0.8 | 2.7±0.1 | 0.2 |
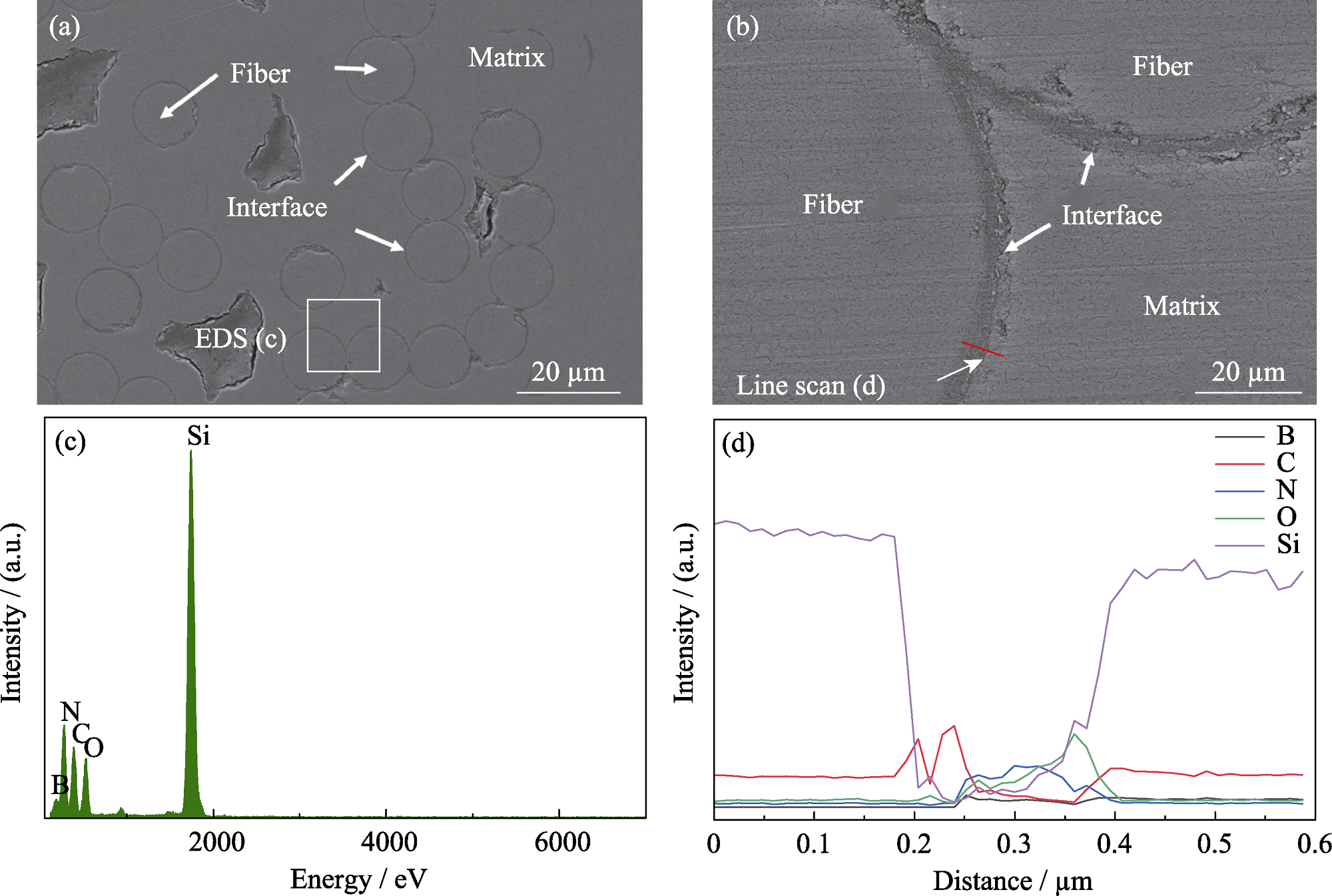
图2 mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的截面形貌及其EDS分析
Fig. 2 Cross-sectional morphologies and EDS analyses of mini-SiCf/SiC composites (a) Low magnification; (b) High magnification; (c) EDS results of white square marked in (a); (d) Line scan results of red line shown in (b) Colorful figures are available on website
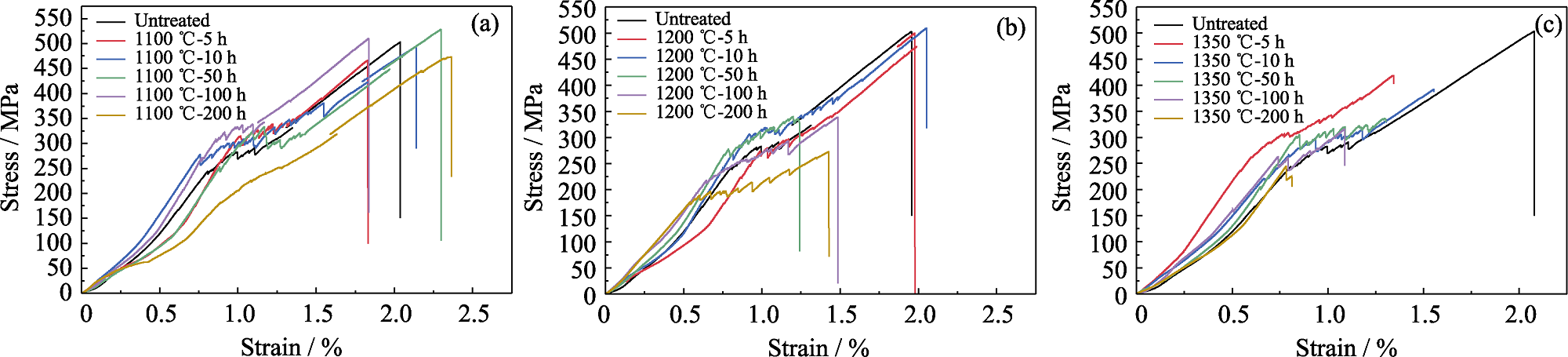
图3 在1100 (a)、1200 (b)、1350 ℃ (c)下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 3 Stress-strain curves of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1100 (a), 1200 (b), and 1350 ℃ (c) for different periods Colorful figures are available on website
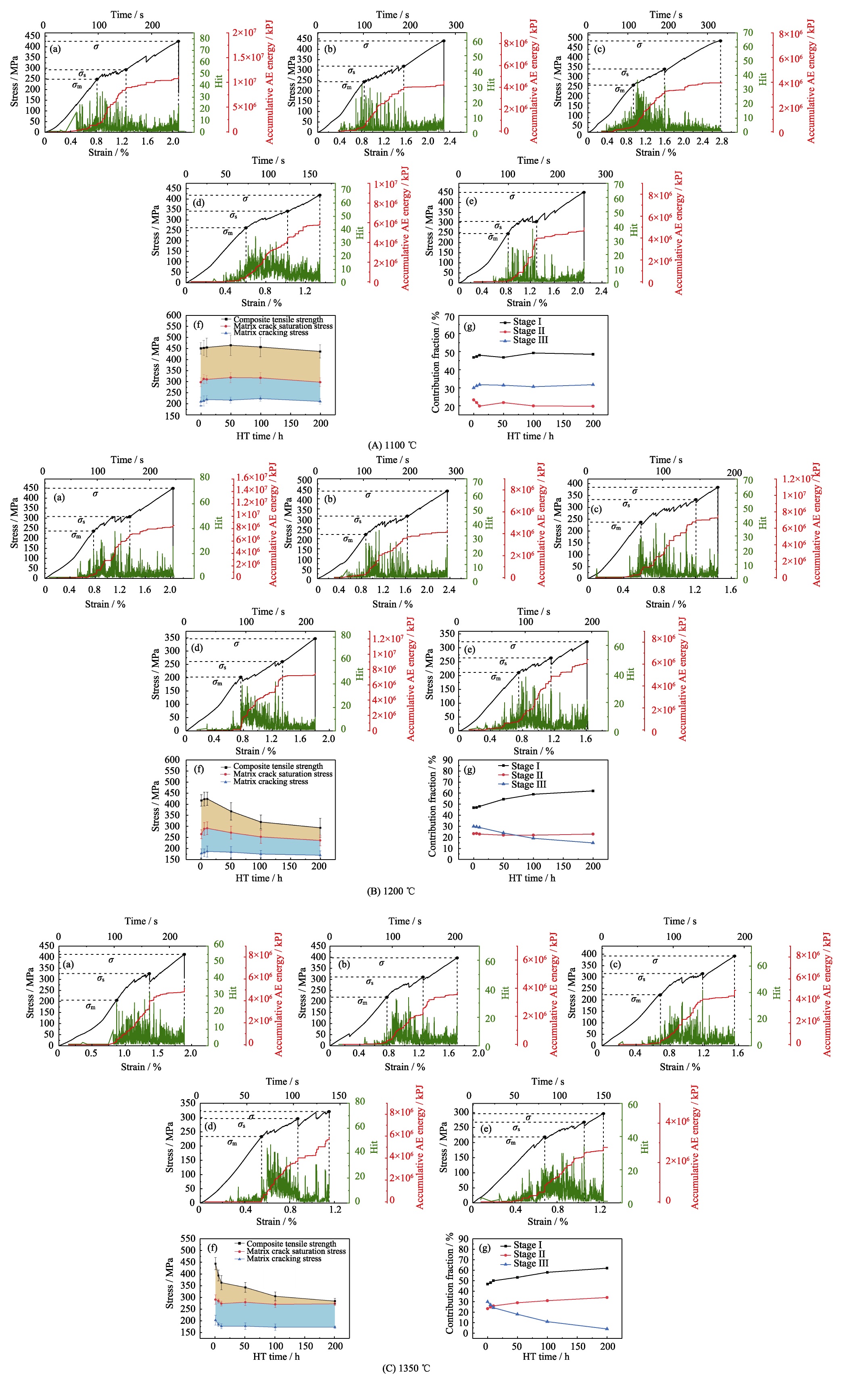
图4 在1100 (A)、1200 (B)、1350 ℃ (C)下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的拉伸应力-应变曲线和声发射测试结果、各阶段最大应力变化趋势及各阶段贡献占比
Fig. 4 Tensile stress-strain curves and acoustic emission test results of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1100 (A), 1200 (B), and 1350 ℃ (C) for different periods, change trend of the stress of each stage and the contribution fraction of each stage (a-e) Tensile stress-strain curves and acoustic emission test results for 5 (a), 10 (b), 50 (c), 100 (d), and 200 h (e); (f) Change trend of the stress of each stage; (g) Contribution fraction of each stage. Colorful figures are available on website
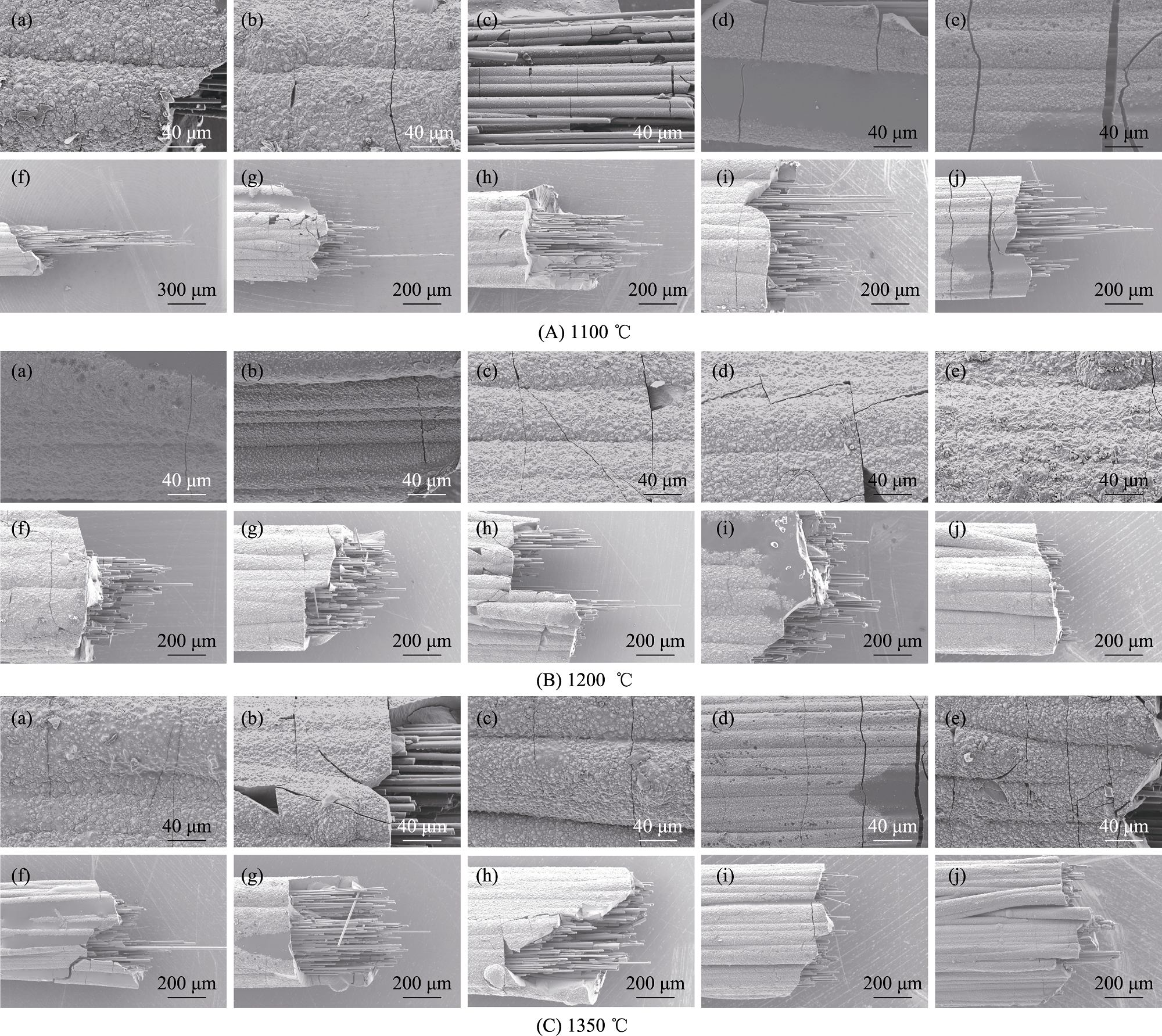
图5 1100 (A)、1200 (B)、1350 ℃ (C)下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料的基体断裂和纤维拔出形貌
Fig. 5 Morphologies of matrix fracture and fiber pull-out of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1100 (A), 1200 (B), 1350 ℃ (C) for different periods (a, f) 5 h; (b, g) 10 h; (c, h) 50 h; (d, i) 100 h; (e, j) 200 h
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 254±12 |
| 10 | 247±15 |
| 50 | 253±13 |
| 100 | 246±12 |
| 200 | 248±17 |
表2 1100 ℃下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料经拉伸试验后的SMCS
Table 2 SMCS after tensile test of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1100 ℃ for different periods
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 254±12 |
| 10 | 247±15 |
| 50 | 253±13 |
| 100 | 246±12 |
| 200 | 248±17 |
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 243±16 |
| 10 | 239±15 |
| 50 | 231±18 |
| 100 | 197±16 |
| 200 | 184±13 |
表3 1200 ℃下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料经拉伸试验后的SMCS
Table 3 SMCS after tensile test of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1200 ℃ for different periods
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 243±16 |
| 10 | 239±15 |
| 50 | 231±18 |
| 100 | 197±16 |
| 200 | 184±13 |
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 187±20 |
| 10 | 176±15 |
| 50 | 159±17 |
| 100 | 146±13 |
| 200 | 138±12 |
表4 1350 ℃下热处理不同时间后mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料经拉伸试验后的SMCS
Table 4 SMCS after tensile test of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at 1350 ℃ for different periods
| HT time/h | SMCS/μm |
|---|---|
| 5 | 187±20 |
| 10 | 176±15 |
| 50 | 159±17 |
| 100 | 146±13 |
| 200 | 138±12 |
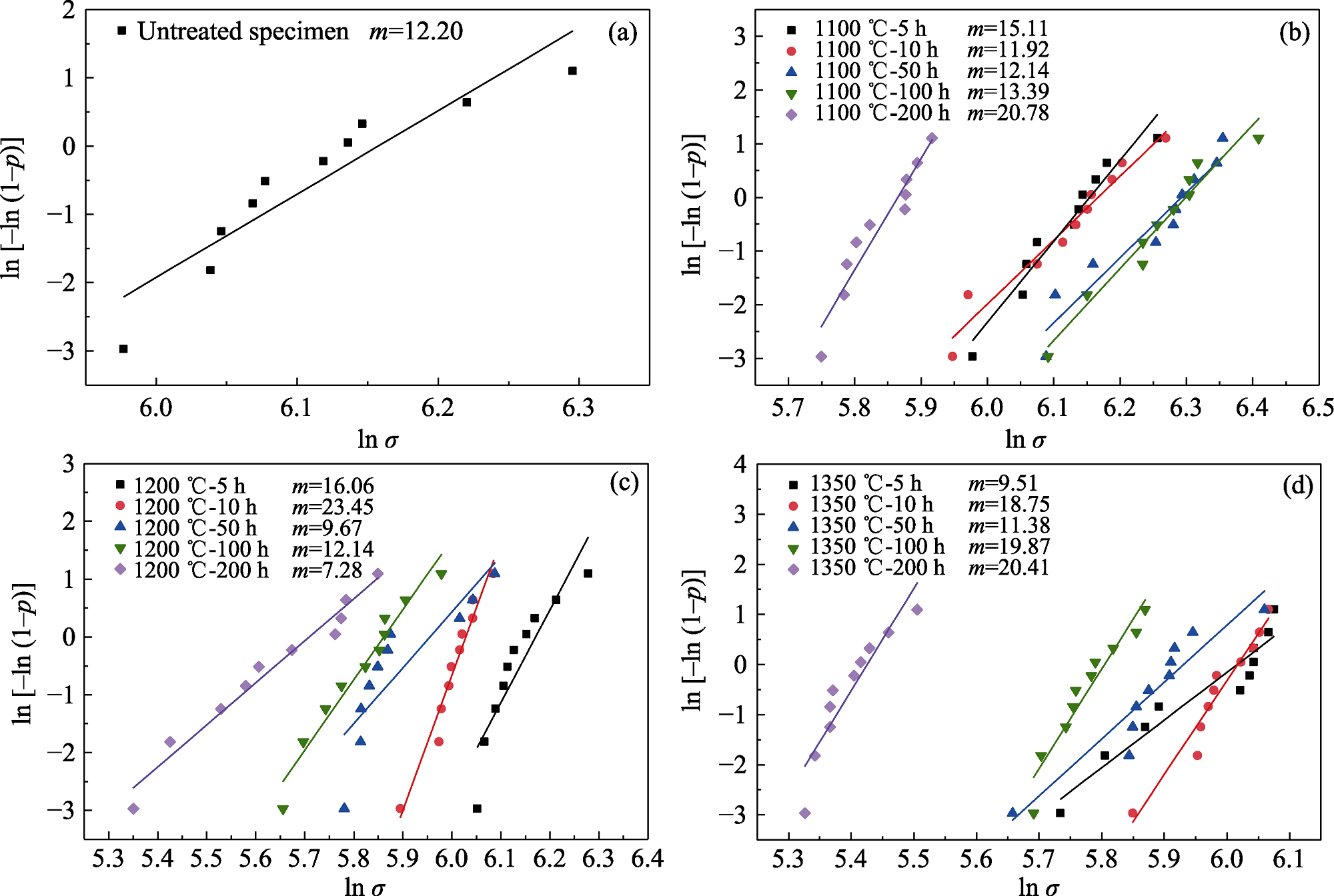
图6 不同温度热处理的mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料拉伸强度的Weibull分布图
Fig. 6 Weibull distributions of tensile strengths of mini-SiCf/SiC composites after heat treatment at different temperature (a) Untreated specimen; (b) 1100 ℃; (c) 1200 ℃; (d) 1350 ℃
| HT time/h | m | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 ℃ | 1200 ℃ | 1350 ℃ | |
| 5 | 15.11 | 16.06 | 9.51 |
| 10 | 11.92 | 23.45 | 18.75 |
| 50 | 12.14 | 9.67 | 11.38 |
| 100 | 13.39 | 12.14 | 19.87 |
| 200 | 20.78 | 7.28 | 20.41 |
表5 不同mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料拉伸试验后的Weibull分布模量m
Table 5 Weibull modulus (m) of distributions of different mini-SiCf/SiC composites after tensile test
| HT time/h | m | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 ℃ | 1200 ℃ | 1350 ℃ | |
| 5 | 15.11 | 16.06 | 9.51 |
| 10 | 11.92 | 23.45 | 18.75 |
| 50 | 12.14 | 9.67 | 11.38 |
| 100 | 13.39 | 12.14 | 19.87 |
| 200 | 20.78 | 7.28 | 20.41 |
| [1] | LV X X, QI Z, YANG J H, et al. The effect of boron nitride interphase on the thermal stability of SiC fibers. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 844: 156193. |
| [2] | 张立同. 纤维增韧碳化硅陶瓷复合材料:模拟, 表征与设计. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009. |
| [3] | SHEN X Y, MA Q, XUE Y D, et al. Effects of multilayered interfaces on mechanical damage of SiCf/SiC composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 917. |
| [4] | GUAN H Y, ZHANG L, JING K K, et al. Interfacial mechanical properties of the domestic 3rd generation 2.5D SiCf/SiC composite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 259. |
| [5] | YOU B J, LI B, LI X Q, et al. Thermal shock damage and in-plane shear performance degradation of 2D SiCf/SiC at medium temperature. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1367. |
| [6] | NASLAIN R. Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: an overview. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64(2): 155. |
| [7] | WICAKSONO S, CHAI G B. A review of advances in fatigue and life prediction of fiber-reinforced composites. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications, 2013, 227(3): 179. |
| [8] |
YUAN Q, SONG Y C. Research and development of continuous SiC fibers and SiCf/SiC composities. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1157.
DOI |
| [9] | WANG P, LIU F, WANG H, et al. A review of third generation SiC fibers and SiCf/SiC composites. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(12): 2743. |
| [10] | UDAYAKUMAR A, GANESH A S, RAJA S, et al. Effect of intermediate heat treatment on mechanical properties of SiCf/SiC composites with BN interphase prepared by ICVI. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2011, 31(6): 1145. |
| [11] | MA X, YIN X, CAO X, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of SiCf/BN/SiC fabricated by CVI. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(2): 3652. |
| [12] | ZHAO S, ZHOU X, YU J, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of PIP-SiC/SiC composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 559: 808. |
| [13] | ZHAO S, ZHOU X, YU J. Effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of PIP-SiC/SiC composites fabricated with a consolidation process. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(3): 3879. |
| [14] | NASLAIN R, LAMON J, PAILLER R, et al. Micro/mini composites: a useful approach to the design and development of non-oxide CMCs. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1999, 30(4): 537. |
| [15] | QIAO S R, HAN D, LUO G Q. Mini-composites C/SiC tensile strength at elevated temperature in vacuum. Key Engineering Materials, 2005, 297: 435. |
| [16] | PADMAVATHI N, KUMARI S, PRASAD V V B, et al. Processing of carbon-fiber reinforced (SiC+ZrC) mini-composites by soft-solution approach and their characterization. Ceramics International, 2009, 35(8): 3447. |
| [17] | FLORES O, BORDIA R K, NESTLER D, et al. Ceramic fibers based on SiC and SiCN systems: current research, development, and commercial status. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2014, 16(6): 621. |
| [18] | GONCZY S T, SPRANDEL R C, FABER K T. Tensile tests of miniature fiber reinforced ceramic composites for screening process-property relations//SINGH J P. Proceedings of the 21st Annual Conference on Composites, Advanced Ceramics, Materials, and Structures—A:Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1997: 729. |
| [19] |
赵文青, 齐哲, 吕晓旭, 等. 界面层对CVI-mini SiCf/SiC复合材料力学性能的影响. 材料工程, 2021, 49(7): 71.
DOI |
| [20] | HAN X, GAO X, SONG Y. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of SiCf/SiC mini-composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 746: 94. |
| [21] | SUZUKI H, TAKEMOTO M, ONO K. A study of fracture dynamics in a model composite by acoustic emission signal processing. Journal of Acoustic Emission, 1993, 11(3): 117. |
| [22] | HUANG X P, WANG B, YANG C P, et al. Evaluating damage evolution of three-dimension needled C/SiC composite based on acoustic emission signal analysis. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 609. |
| [23] | MEI H, CHENG L. Thermal cycling response behavior of ceramic matrix composites under load and displacement constraints. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 486(1/2): 235. |
| [24] | YANG X F, KNOWLES K M. On the first-matrix-cracking stress in unidirectional fiber-reinforced brittle materials. Journal of Materials Research, 1993, 8(2): 371. |
| [25] | LARA-CURZIO E, RUSS C M. On the matrix cracking stress and the redistribution of internal stresses in brittle-matrix composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1998, 250(2): 270. |
| [26] | WANG Y Q, ZHANG L T. Tensile behaviour and damage evolution of a C/SiC minicomposite fabricated by chemical vapour infiltration. Advanced Composites Letters, 2010, 19(2): 85. |
| [27] | SU K, CHEN Z, LI L, et al. Effects of single-phase and co-deposited inter-phases on mechanical hysteresis behavior in T700TM mini-Cf/SiC composites. International Journal of Fatigue, 2023, 168: 107473. |
| [28] | 福建立亚新材有限公司. Cansas 3300系列连续碳化硅纤维: Q/LY 20010––2001. 福建立亚新材有限公司企业标准, 2021. |
| [29] | CHEN X, SUN Z, NIU X, et al. Evolution of the structure and mechanical performance of Cansas-II SiC fibres after thermal treatment. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(19): 27217. |
| [1] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [2] | 李捷, 罗志新, 崔阳, 张广珩, 孙鲁超, 王京阳. 大气等离子喷涂Y3Al5O12/Al2O3陶瓷涂层的CMAS腐蚀抗力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 671-680. |
| [3] | 沈轩逸, 马沁, 薛玉冬, 廖春景, 朱敏, 张翔宇, 杨金山, 董绍明. 复合界面层对SiCf/SiC复合材料力学损伤行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 917-922. |
| [4] | 吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [5] | 张硕, 付前刚, 张佩, 费杰, 李伟. C/C多孔体的高温热处理对C/C-SiC复合材料摩擦磨损行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [6] | 安文然, 黄晶琪, 卢祥荣, 蒋佳宁, 邓龙辉, 曹学强. 热处理温度对LaMgAl11O19涂层热/力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [7] | 朱勇, 顾军, 于涛, 何海佟, 姚睿. 铂钴合金纳米电催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| [8] | 张亚晨, 孟佳, 蔡坤, 盛晓晨, 乐军, 宋力昕. 基于声发射技术的Si-Cr-Ti高温抗氧化涂层弯曲失效机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [9] | 李陇彬, 薛玉冬, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增韧碳化硅纤维/碳化硅基体损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| [10] | 魏玉全,杨勇,刘盟,郦其乐,黄政仁. 高温热处理对SiBCN/HfC复相陶瓷物相组成及微观结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 931-938. |
| [11] | 王志虎,张菊梅,白力静,张国君. AZ31镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层表面Mg(OH)2膜层的制备及耐蚀性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [12] | 张勇祯, 童小燕, 姚磊江, 李斌, 白国栋. 基于改进遗传算法的C/SiC拉伸损伤声发射模式识别[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 593-600. |
| [13] | 付亚康,翁杰,刘耀文,张科宏. 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [14] | 吕晓旭, 姜卓钰, 周怡然, 齐哲, 赵文青, 焦健. BN/SiC复合界面层对SiC纤维和PIP-Mini复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1099-1104. |
| [15] | 汪丹丹, 田无边, 丁健翔, 马爱斌, 张培根, 何炜, 孙正明. 等通道转角挤压制备Ag/Ti3AlC2复合材料及其热处理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 46-52. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||