无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 234-244.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250180 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250180
聂晓双1,2( ), 李丹丹1, 王芳1,2, 欧阳丽萍3, 李恒1(
), 李丹丹1, 王芳1,2, 欧阳丽萍3, 李恒1( ), 邱家军1(
), 邱家军1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-27
修回日期:2025-05-19
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-05
通讯作者:
李 恒, 副研究员. E-mail: liheng@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:聂晓双(2000-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: niexiaoshuang0908@163.com
基金资助:
NIE Xiaoshuang1,2( ), LI Dandan1, WANG Fang1,2, OUYANG Liping3, LI Heng1(
), LI Dandan1, WANG Fang1,2, OUYANG Liping3, LI Heng1( ), QIU Jiajun1(
), QIU Jiajun1( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Revised:2025-05-19
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
LI Heng, associate professor. E-mail: liheng@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:NIE Xiaoshuang (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: niexiaoshuang0908@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
有效控制细菌感染并促进血管生成是加速感染性创面愈合面临的重要挑战。开发一种兼具抗菌和促进血管生成的多功能水凝胶创面敷料具有重要研究价值。本研究以Ti3C2Al为前驱体, 采用选择性化学刻蚀法制备Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片, 并将其与可注射性聚乙烯醇(PVA)/阳离子瓜尔胶(CGG)水凝胶形成动态交联网络, 构建了具有超声响应特性的PVA/CGG/MXene(PCM)复合水凝胶。实验结果表明, CGG分子链中的季铵阳离子基团通过静电相互作用显著增强了PCM水凝胶的抗菌性能, 对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抗菌率分别达到97.34%和95.40%。MXene纳米片赋予水凝胶稳定的导电及压电特性, 在低频超声刺激下, PCM水凝胶可通过压电效应产生电信号, 进而促进细胞增殖、迁移和血管再生。大鼠全层皮肤感染创面模型证实, PCM水凝胶通过抗菌、促进血管生成和胶原沉积, 显著加快了创面愈合过程, 10 d内创面几乎完全愈合。本工作成功开发了一种集超声响应电刺激、抗菌与促进血管再生功能于一体的多功能水凝胶敷料, 为感染创面修复治疗提供了新策略。
中图分类号:
聂晓双, 李丹丹, 王芳, 欧阳丽萍, 李恒, 邱家军. Ti3C2Tx压电复合水凝胶用于感染创面修复研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 234-244.
NIE Xiaoshuang, LI Dandan, WANG Fang, OUYANG Liping, LI Heng, QIU Jiajun. Ti3C2Tx Piezoelectric Composite Hydrogels for Bacterial-infected Skin Wound Healing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 234-244.
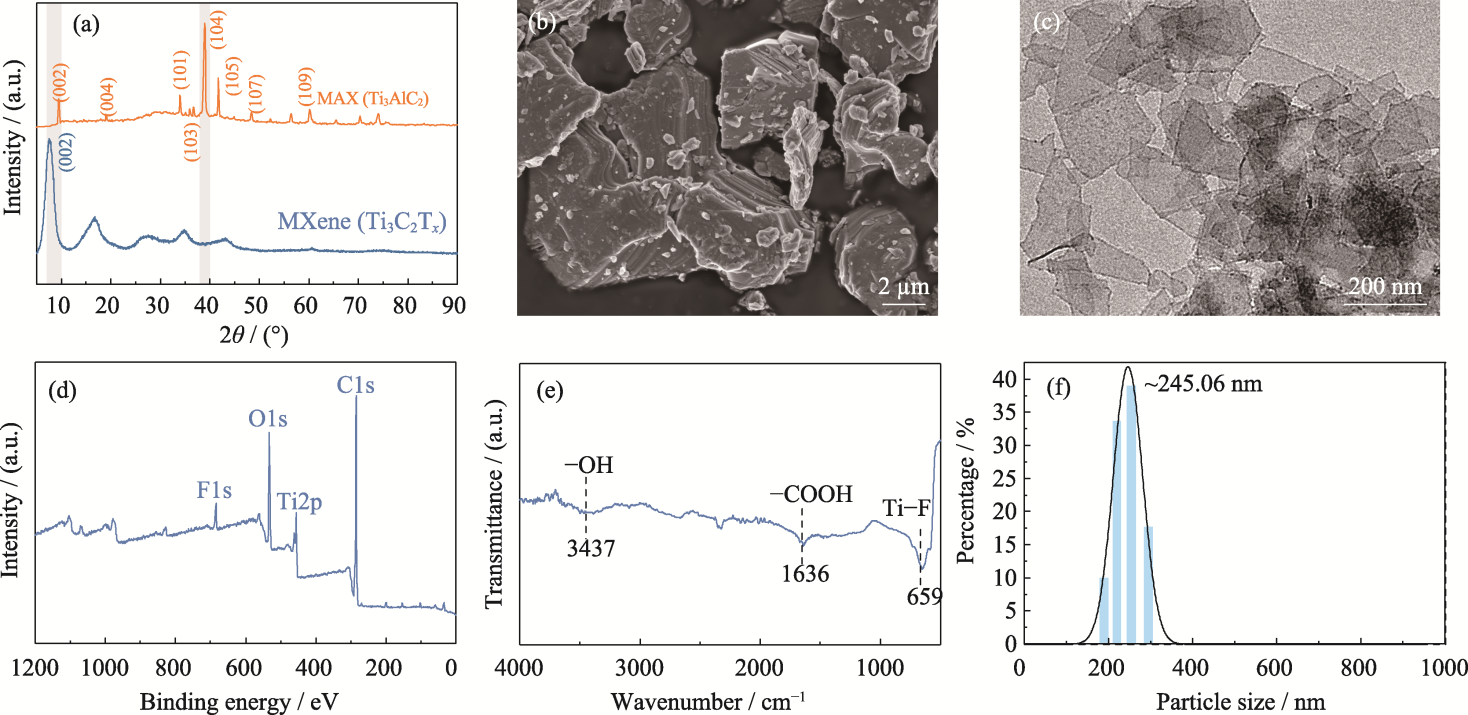
图1 Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片的合成和表征
Fig. 1 Synthesis and characterization of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets (a) XRD patterns of MAX and MXene nanosheets; (b) SEM image of MAX; (c) TEM image, (d) XPS spectrum, (e) FT-IR spectrum and (f) particle size of MXene
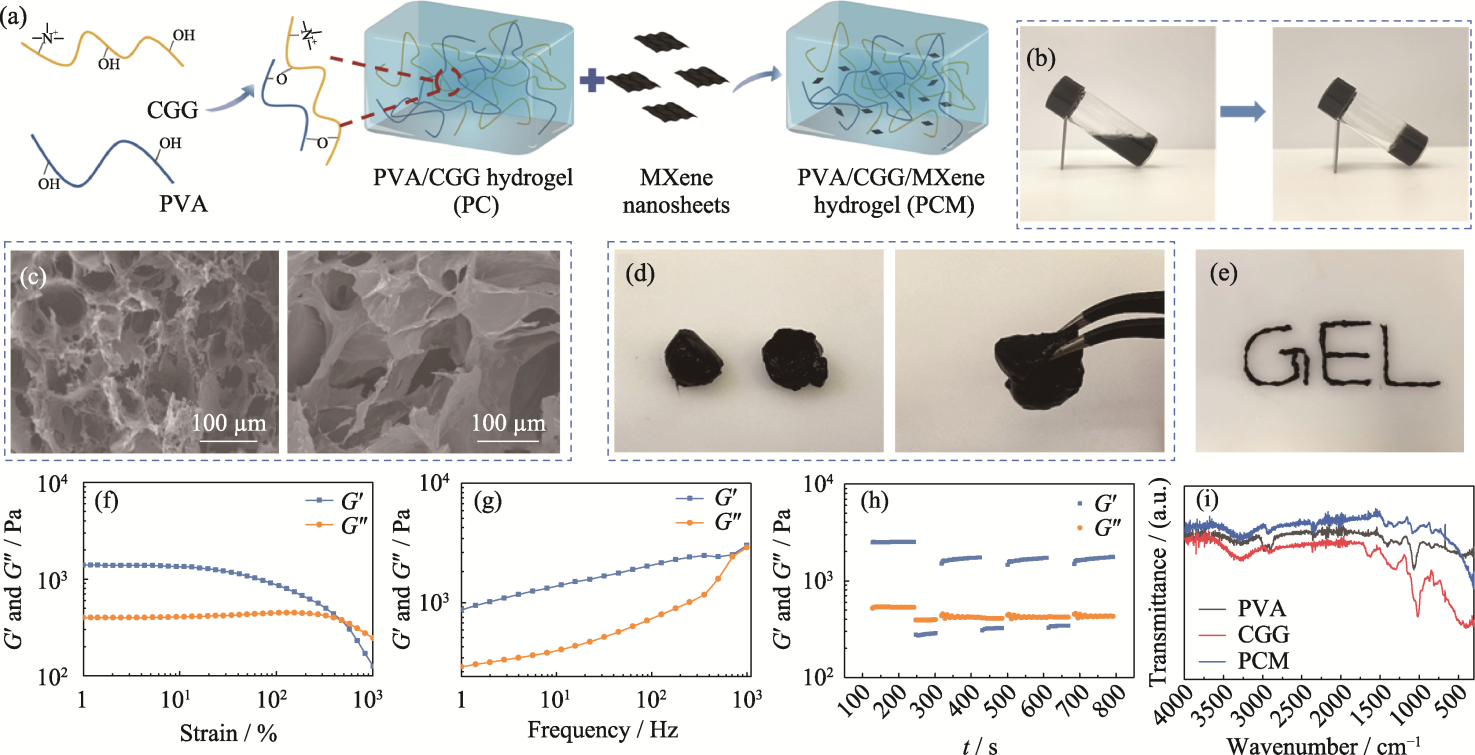
图2 PCM水凝胶的制备和表征
Fig. 2 Preparation and characterization of PCM composite hydrogel (a) Schematic representation of preparation of the PCM hydrogel; (b) Optical image depicting transition of the PCM hydrogel from sol state to gel state; (c) SEM images of the PC (left) and the PCM (right) hydrogels; (d) Self-healing and (e) injectable properties of the PCM hydrogel; (f-h) Rheological properties of the PCM hydrogel: (f) strain scan, (g) frequency scan, (h) cyclic strain scan, and (i) FT-IR spectra of hydrogels. Colorful figures are available on website
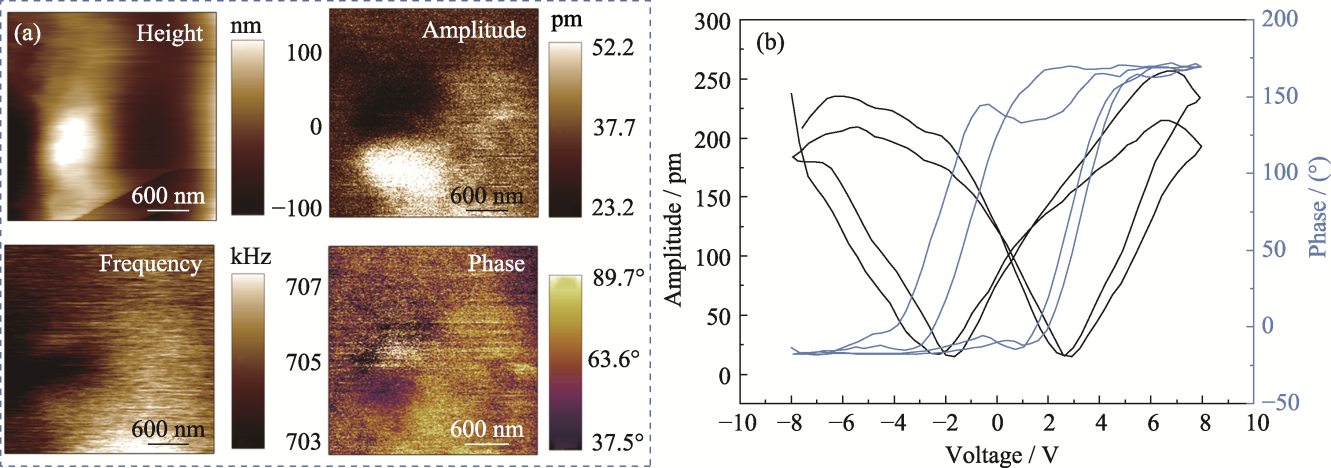
图4 PCM水凝胶的压电性能
Fig. 4 Piezoelectric properties of PCM hydrogel (a) Surface topography, phase, frequency, and phase liner plots; (b) Butterfly pressure-amplitude curves and hysteresis loops
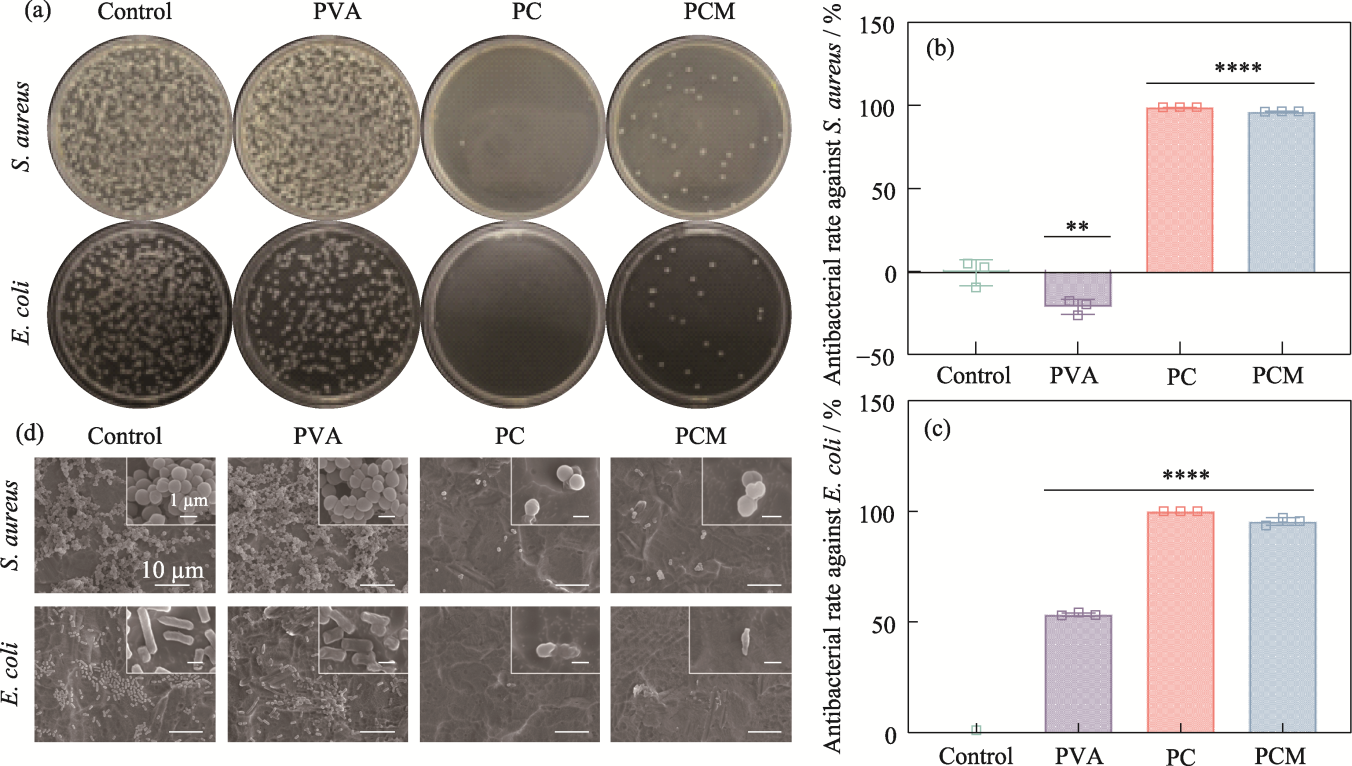
图6 水凝胶的抗菌性能
Fig. 6 Antimicrobial properties of the hydrogels (a) Agar plate images; (b, c) Antibacterial rates against (b) S. aureus and (c) E. coli, n=3, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001; (d) SEM images of S. aureus and E. coli from hydrogels
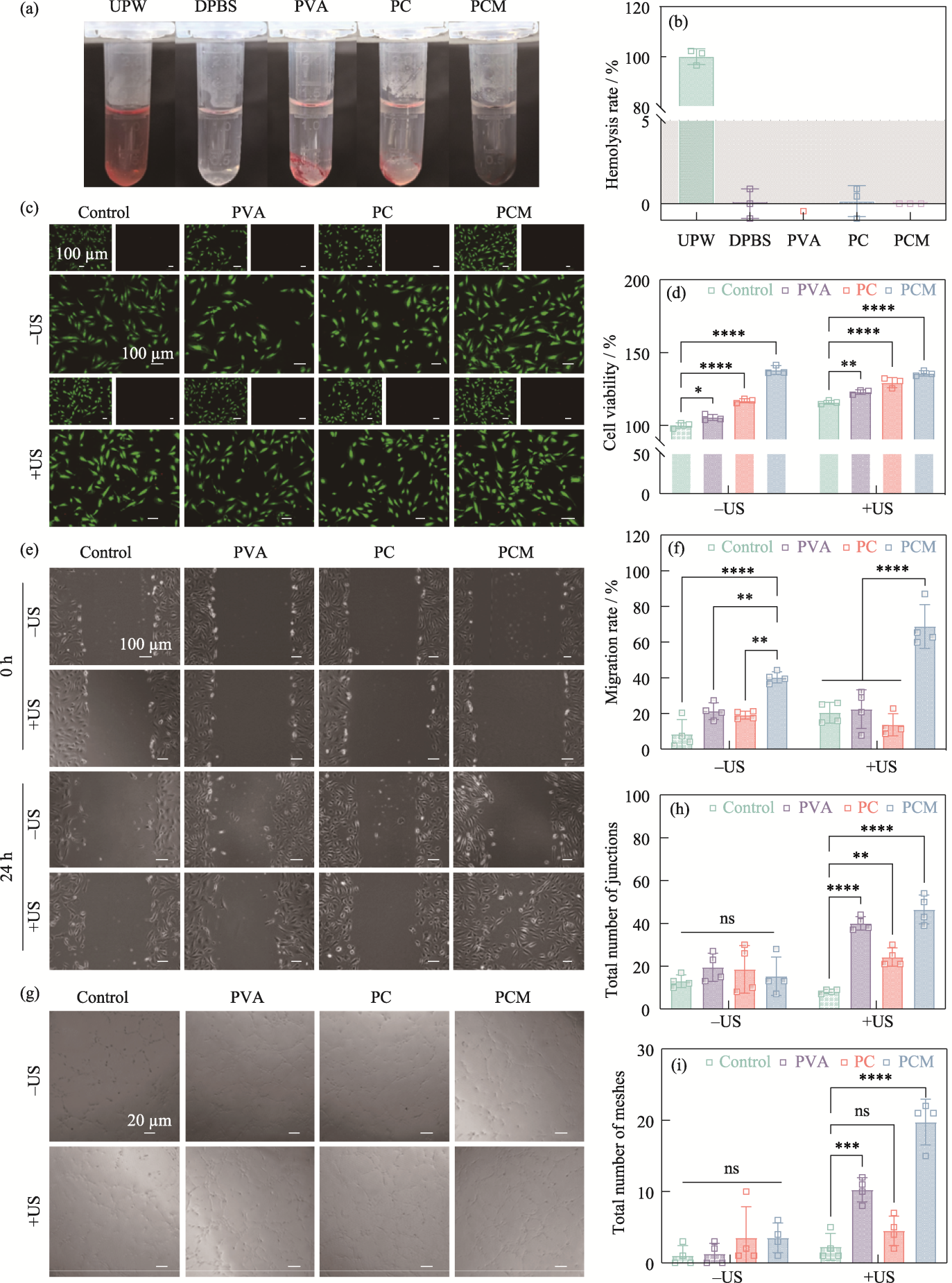
图7 水凝胶的生物相容性及细胞行为调控
Fig. 7 Biocompatibility and regulation of cellular behaviors of the hydrogels (a) Optical images of the hemolysis experiments; (b) Hemolysis rates of UPW, DPBS, PVA, PC, and PCM hydrogels; (c) Live/dead staining fluorescent images and (d) cell viability of HUVECs from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation; (e) Cell migration images of HUVECs from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation and (f) corresponding migration rate; (g) Images of tube formation assay at 0 and 24 h from the control, PVA, PC, and PCM groups with or without ultrasound stimulation and corresponding total number of (h) junctions and (i) meshes n=3, **p< 0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
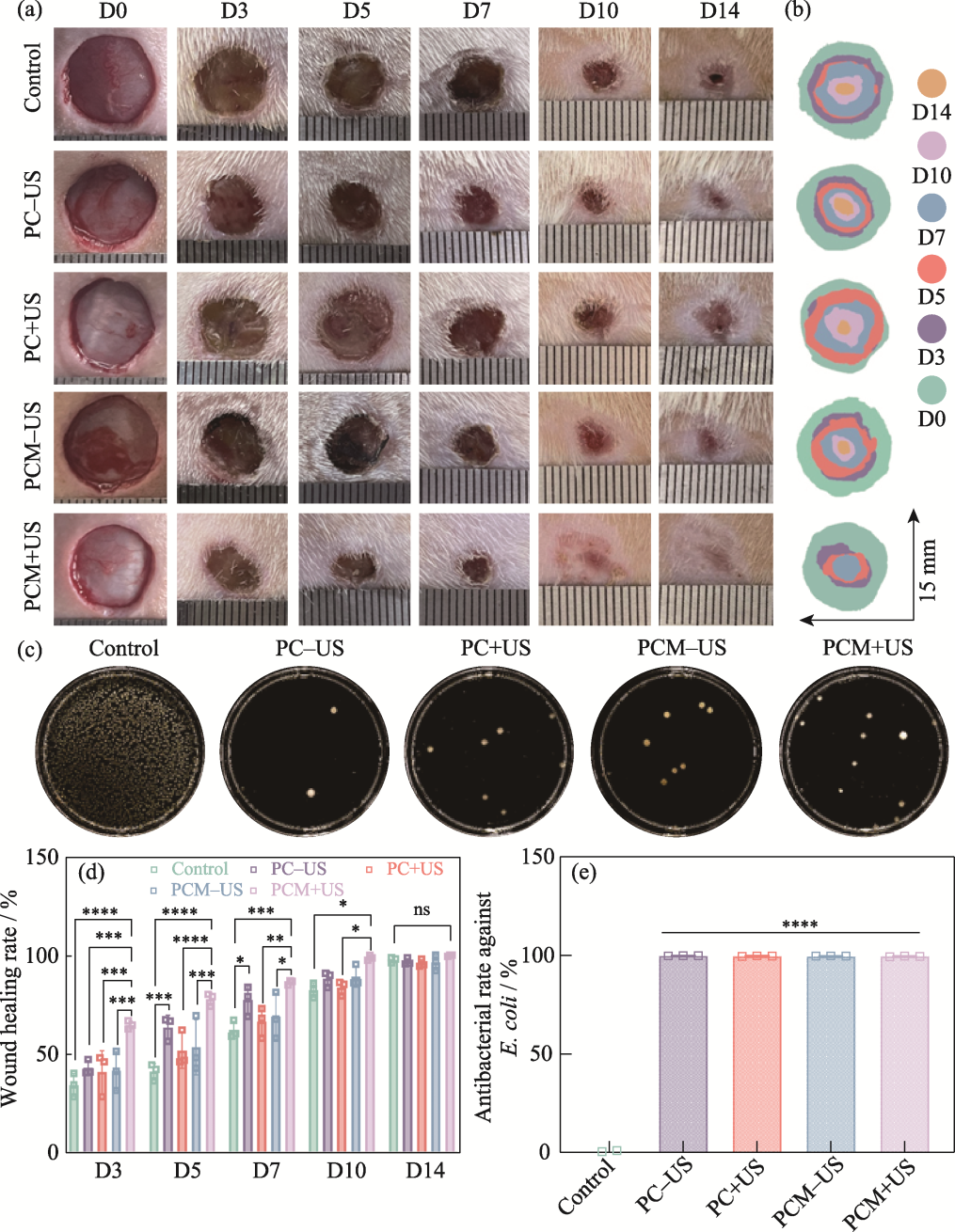
图8 水凝胶的体内治疗效果评价
Fig. 8 Evaluation of in vivo therapeutic effect of the hydrogels (a) Representative digital photographs of skin wounds on 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 d; (b) Schematic diagram of the wounds treated with different groups for 14 d; (c) Agar plate images of E. coli from the control, PC-US, PC+US, PCM-US, and PCM+US groups; (d) Quantitative analysis of the wound healing rates in various groups on 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 d; (e) Antibacterial rates of the control, PC-US, PC+US, PCM-US, and PCM+US groups against E. coli n=3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
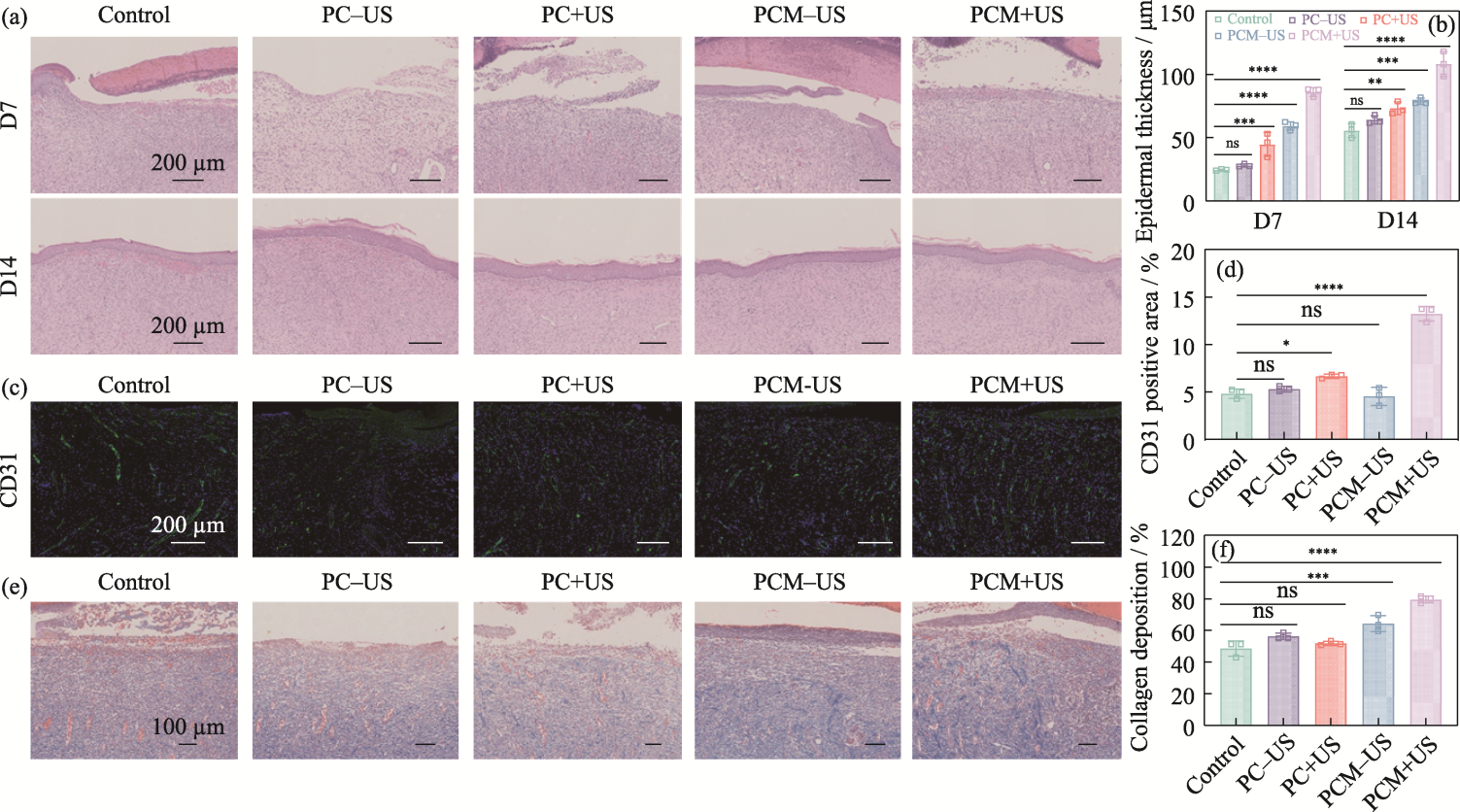
图9 水凝胶的体内疗效组织学评价
Fig. 9 Histologic evaluation of in vivo efficacy of the hydrogels (a) H&E staining of wound tissues on 7 and 14 d; (b) Epidermal thickness of skin tissues on 7 and 14 d; (c) CD31 staining of wound tissues on 7 d; (d) Area proportion of CD31-positive skin tissue on 7 d; (e) Masson staining of wound tissues on 7 d;(f) Proportion of collagen deposition from skin tissues on 7 d n=3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Colorful figures are available on website
| Component | PVA/(mg·mL-1) | CGG/(mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 |
| PC1 | 52.5 | 10 |
| PC2 | 52.5 | 20 |
| PC3 | 52.5 | 30 |
| PC4 | 52.5 | 40 |
| PC5 | 52.5 | 50 |
| PC6 | 52.5 | 60 |
表S1 PCx水凝胶中各组分的浓度
Table S1 Volume of each component in PCx hydrogels
| Component | PVA/(mg·mL-1) | CGG/(mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 |
| PC1 | 52.5 | 10 |
| PC2 | 52.5 | 20 |
| PC3 | 52.5 | 30 |
| PC4 | 52.5 | 40 |
| PC5 | 52.5 | 50 |
| PC6 | 52.5 | 60 |
| Component | PVA/ (mg·mL-1) | CGG/ (mg·mL-1) | MXene/ (mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PC | 52.5 | 40 | 0 |
| PCM1 | 52.5 | 40 | 1 |
| PCM2 | 52.5 | 40 | 2 |
| PCM3 | 52.5 | 40 | 3 |
| PCM4 | 52.5 | 40 | 4 |
| PCM5 | 52.5 | 40 | 5 |
表S2 PCMx水凝胶中各组分的浓度
Table S2 Volume of each component in PCMx hydrogels
| Component | PVA/ (mg·mL-1) | CGG/ (mg·mL-1) | MXene/ (mg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | 52.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PC | 52.5 | 40 | 0 |
| PCM1 | 52.5 | 40 | 1 |
| PCM2 | 52.5 | 40 | 2 |
| PCM3 | 52.5 | 40 | 3 |
| PCM4 | 52.5 | 40 | 4 |
| PCM5 | 52.5 | 40 | 5 |
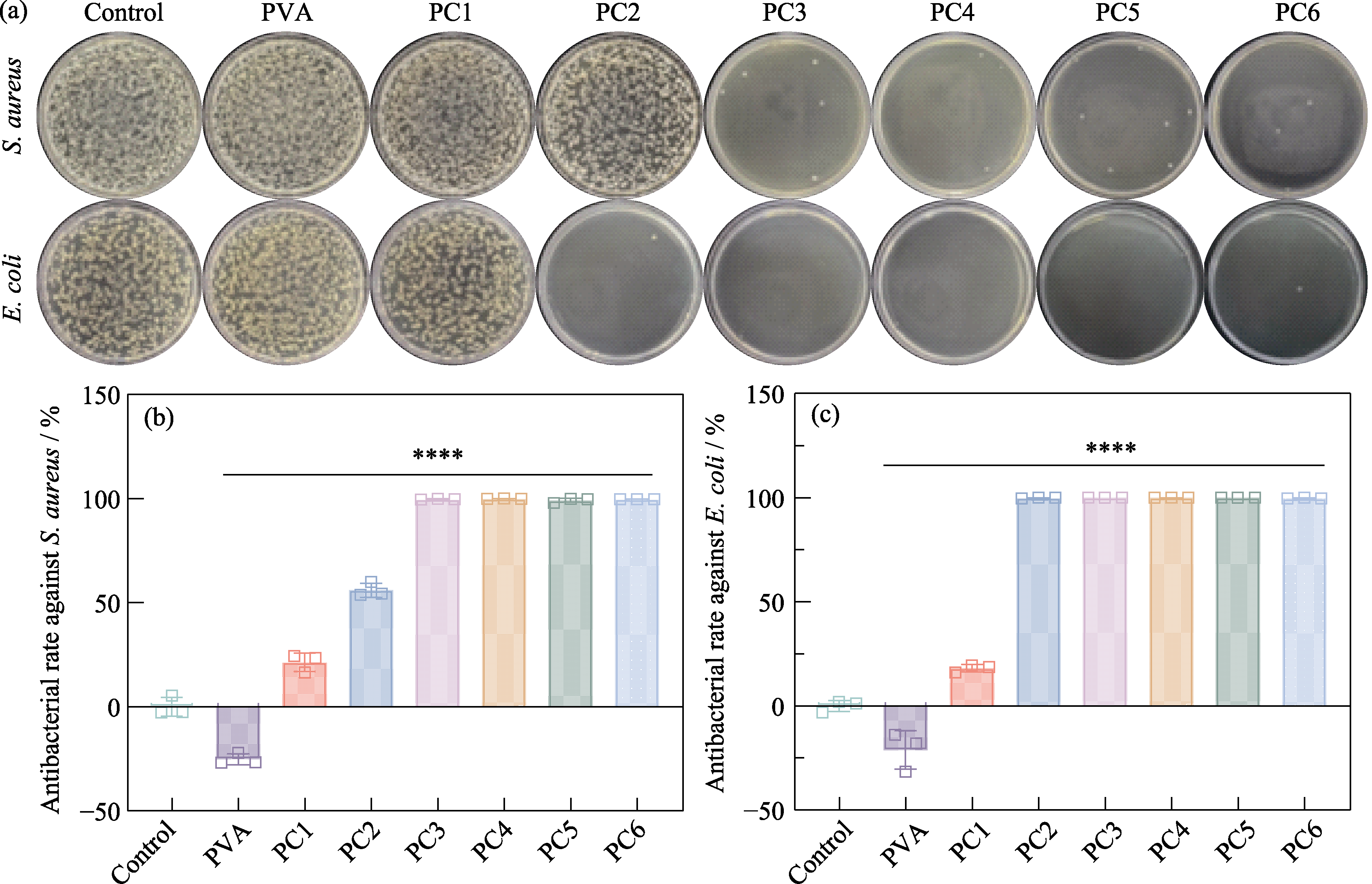
图S5 PCx水凝胶的抗菌性能测试
Fig. S5 Antibacterial performance testing of PCx hydrogels (a) Agar plate images of S. aureus and E. coli from control, PVA, PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, PC5, and PC6 groups, respectively, and corresponding antibacterial rates against (b) S. aureus and (c) E. coli

图S6 水凝胶成胶时间对比
Fig. S6 Comparison of gelation time for hydrogels After 30 min of freezing, the PC4 hydrogel (left) has formed a gel, while the PC3 hydrogel (right) is still in a thick, soluble state after 1 h of freezing
| [1] |
GÜIZA-ARGÜELLO V R, SOLARTE-DAVID V A, PINZÓN- MORA A V, et al. Current advances in the development of hydrogel-based wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Polymers, 2022, 14(14): 2764.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GONZALEZ A C D O, COSTA T F, ANDRADE Z D A, et al. Wound healing-a literature review. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia, 2016, 91(5): 614. |
| [3] |
TAVAKOLI S, KLAR A S. Advanced hydrogels as wound dressings. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(8): 1169.
DOI URL |
| [4] | WANG Y, WU Y, LONG L, et al. Inflammation-responsive drug-loaded hydrogels with sequential hemostasis, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory behavior for chronically infected diabetic wound treatment. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(28): 33584. |
| [5] |
LEAPER D, ASSADIAN O, EDMISTON C E. Approach to chronic wound infections. British Journal of Dermatology, 2015, 173(2): 351.
DOI URL |
| [6] | METCALF D G, BOWLER P G. Biofilm delays wound healing: a review of the evidence. Burns & Trauma, 2013, 1(1): 5. |
| [7] |
LINDLEY L E, STOJADINOVIC O, PASTAR I, et al. Biology and biomarkers for wound healing. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2016, 138(3S): 18S.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
UBEROI A, MCCREADY-VANGI A, GRICE E A. The wound microbiota: microbial mechanisms of impaired wound healing and infection. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024, 22(8): 507.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
MIZELLE R M. Diabetes, race, and amputations. The Lancet, 2021, 397(10281): 1256.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ARMSTRONG D G, TAN T, BOULTON A J M, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers: a review. Journal of the American Medical Association, 2023, 330(1): 62. |
| [11] |
SEN C K. Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates. Advances in Wound Care, 2019, 8(2): 39.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
SEN C K. Human wound and its burden: updated 2020 compendium of estimates. Advances in Wound Care, 2021, 10(5): 281.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DENG L, DU C, SONG P, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic wound healing. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 2021(1): 8852759.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PIETRAMAGGIORI G, SCHERER S S, MATHEWS J C, et al. Healing modulation induced by freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma and micronized allogenic dermis in a diabetic wound model. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2008, 16(2): 218.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | MEYER M, MÜLLER A K, YANG J, et al. The role of chronic inflammation in cutaneous fibrosis:fibroblast growth factor receptor deficiency in keratinocytes as an example. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 2011, 15(1): 48. |
| [16] |
TANAKA Y, SUTARLIE L, SU X. Detecting bacterial infections in wounds: a review of biosensors and wearable sensors in comparison with conventional laboratory methods. Analyst, 2022, 147(9): 1756.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DENG Y, BOON C, CHEN S, et al. Cis-2-dodecenoic acid signal modulates virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through interference with quorum sensing systems and T3SS. BMC Microbiology, 2013, 13: 231.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
JACOBS M R, FELMINGHAM D, APPELBAUM P C, et al. The Alexander project 1998-2000: susceptibility of pathogens isolated from community-acquired respiratory tract infection to commonly used antimicrobial agents. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2003, 52(2): 229.
PMID |
| [19] |
YAGUPSKY P. Selection of antibiotic-resistant pathogens in the community. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 2006, 25(10): 974.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FALAGAS M E, MAVROUDIS A D, VARDAKAS K Z. The antibiotic pipeline for multi-drug resistant gram negative bacteria: what can we expect? Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy, 2016, 14(8): 747.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CHEN S, WANG H, SU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-laden, personalized 3D scaffolds with controlled structure and fiber alignment promote diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomaterialia, 2020, 108: 153.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
LEE K, SILVA E A, MOONEY D J. Growth factor delivery-based tissue engineering: general approaches and a review of recent developments. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2011, 8(55): 153.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | CHENG B, YAN Y, QI J, et al. Cooperative assembly of a peptide gelator and silk fibroin afford an injectable hydrogel for tissue engineering. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(15): 12474. |
| [24] |
ZAREI F, SOLEIMANINEJAD M. Role of growth factors and biomaterials in wound healing. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 2018, 46(sup1): 906.
DOI |
| [25] |
NUCCITELLI R. A role for endogenous electric fields in wound healing. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 2003, 58(2): 1.
PMID |
| [26] |
THRIVIKRAMAN G, BODA S K, BASU B. Unraveling the mechanistic effects of electric field stimulation towards directing stem cell fate and function: a tissue engineering perspective. Biomaterials, 2018, 150: 60.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
SNYDER A R, PEROTTI A L, LAM K C, et al. The influence of high-voltage electrical stimulation on edema formation after acute injury: a systematic review. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2010, 19(4): 436.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
SEBASTIAN A, SYED F, PERRY D, et al. Acceleration of cutaneous healing by electrical stimulation: degenerate electrical waveform down-regulates inflammation, up-regulates angiogenesis and advances remodeling in temporal punch biopsies in a human volunteer study. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2011, 19(6): 693.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | GUO Z, SAW P E, JON S. Non-invasive physical stimulation to modulate the tumor microenvironment: unveiling a new frontier in cancer therapy. BIO Integration, 2024, 5(1): 986. |
| [30] |
SALATINO J W, LUDWIG K A, KOZAI T D, et al. Glial responses to implanted electrodes in the brain. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1(11): 862.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
HUANG D, CHENG Y, CHEN G, et al. 3D-printed Janus piezoelectric patches for sonodynamic bacteria elimination and wound healing. Research, 2023, 6: 0022.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
ZHANG Y, RUAN K, GU J. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small, 2021, 17(42): 2101951.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZENG Z, WANG C, SIQUEIRA G, et al. Nanocellulose-MXene biomimetic aerogels with orientation-tunable electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(15): 2000979.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHANG Y, HU Y, XIE B, et al. Hoffmeister effect optimized hydrogel electrodes with enhanced electrical and mechanical properties for nerve conduction studies. Research, 2024, 7: 0453.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
ZHOU H, CHEN L, HUANG C, et al. Endogenous electric field coupling MXene sponge for diabetic wound management: haemostatic, antibacterial, and healing. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 530.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
DONG S, ZHANG Y, MEI Y, et al. Researching progress on bio-reactive electrogenic materials with electrophysiological activity for enhanced bone regeneration. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 921284.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [2] | 赵丽华, 王言帅, 尹昕妩, 毛叶琼, 牛德超. 负载硫化铋纳米簇的硅基杂化胶束的制备及其光热抗菌性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [3] | 张博, 付一敏, 陈政, 石澳, 朱敏. 近红外光响应的双相抗菌介孔生物活性玻璃复合支架的制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1137-1144. |
| [4] | 王月月, 黄佳慧, 孔红星, 李怀珠, 姚晓红. 载银放射状介孔二氧化硅的制备及其在牙科树脂中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [5] | 李承瑜, 丁自友, 韩颖超. 锰掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的体外抗菌-促成骨性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [6] | 张志民, 葛敏, 林翰, 施剑林. 新型磁电催化纳米粒子的活性氮释放与抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1114-1124. |
| [7] | 张淑敏, 奚晓雯, 孙磊, 孙平, 王德强, 魏杰. 基于声动力和类酶活性的铌基涂层: 抗菌及促进细胞增殖与分化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1125-1134. |
| [8] | 冒爱琴, 陆文宇, 贾洋刚, 王冉冉, 孙静. 柔性压电器件及其可穿戴应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 717-730. |
| [9] | 谢家晔, 李力文, 朱强. 三种临床盖髓剂的抗菌性及生物相容性对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [10] | 杜佳恒, 范鑫丽, 肖东琴, 尹一然, 李忠, 贺葵, 段可. 电泳沉积制备微弧氧化钛表面氧化镁涂层及其生物学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1441-1448. |
| [11] | 吴雪彤, 张若飞, 阎锡蕴, 范克龙. 纳米酶: 一种抗微生物感染新方法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 43-54. |
| [12] | 盛丽丽, 常江. 光/磁热Fe2SiO4/Fe3O4双相生物陶瓷及其复合电纺丝膜制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 983-990. |
| [13] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [14] | 吴爱军, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 含铜硅酸钙纳米棒复合水凝胶用于肿瘤治疗和皮肤伤口愈合性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216. |
| [15] | 黄田, 赵运超, 李琳琳. 压电半导体纳米材料在声动力疗法中的应用进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1170-1180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||