无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 731-740.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210535 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20210535
王晓俊1( ), 许文2, 刘润路1, 潘辉1,3(
), 许文2, 刘润路1, 潘辉1,3( ), 朱申敏1(
), 朱申敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-27
修回日期:2022-01-24
出版日期:2022-07-20
网络出版日期:2022-02-21
通讯作者:
朱申敏, 教授. E-mail: smzhu@sjtu.edu.cn;作者简介:王晓俊(1999-), 男, 学士. E-mail: chunyu@sjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Xiaojun1( ), XU Wen2, LIU Runlu1, PAN Hui1,3(
), XU Wen2, LIU Runlu1, PAN Hui1,3( ), ZHU Shenmin1(
), ZHU Shenmin1( )
)
Received:2021-08-27
Revised:2022-01-24
Published:2022-07-20
Online:2022-02-21
Contact:
ZHU Shenmin, professor. E-mail: smzhu@sjtu.edu.cn;About author:WANG Xiaojun (1999-), male, Bachelor. E-mail: chunyu@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)具有独特的二维平面结构和半导体能带结构, 广泛应用于光催化。但其又存在光生电子空穴对复合过快、可见光利用效率低、在水中分散性差等问题, 阻碍了其实际应用。本研究以海藻酸钠制备的水凝胶为基体, 通过与负载银纳米颗粒(AgNPs)的g-C3N4复合, 提升光生电子-空穴的分离效率, 同时解决催化剂在水中的分散性问题, 改善其光催化性能。首先, 采用热聚合法合成g-C3N4, 结合超声的高能量使其剥离成纳米片; 然后采用溶液法在g-C3N4表面原位生成银纳米颗粒, 制备得到负载银纳米颗粒的g-C3N4(Ag@C3N4); 最后以海藻酸钠(SA)为前驱体通过钙离子交联的方法得到负载有Ag@C3N4的水凝胶(SA/Ag@C3N4)。通过不同手段表征SA/Ag@C3N4的形貌、微观结构和相组成; 以甲基橙为模型物, SA/Ag@C3N4的光催化降解速率是Ag@C3N4的2.5倍。通过光致发光谱、时间分辨光致发光谱、电子顺磁共振波谱等表征手段对材料的催化机理进行探究。结果显示, 体系中银纳米颗粒表面等离子体共振效应与海藻酸钠水凝胶的多孔结构及传质通道发挥协同效应, 促进了光催化性能的提升。
中图分类号:
王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740.
WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740.
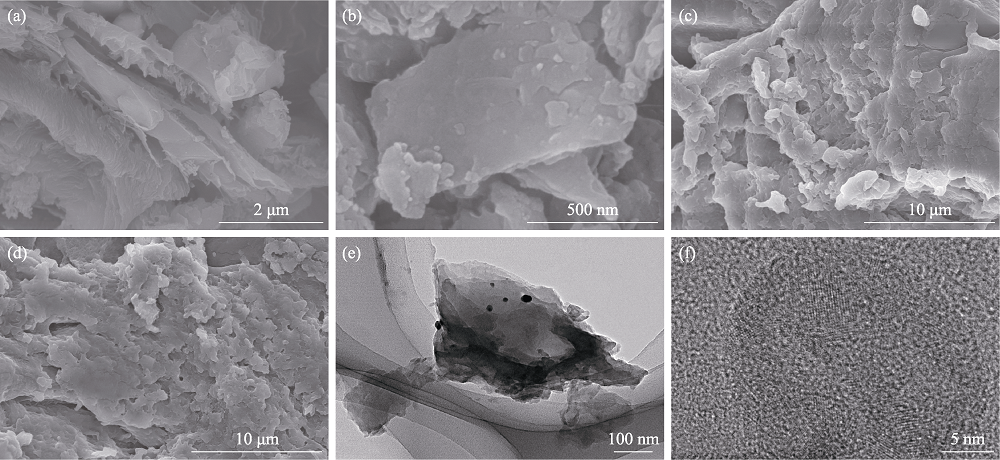
图2 C3N4 (a), Ag@C3N4 (b), SA/Ag@C3N4 (c, d)的SEM照片; Ag@C3N4的TEM (e)和HRTEM(f)照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of C3N4 (a), Ag@C3N4 (b) and SA/Ag@C3N4 (c, d), TEM (e) and HRTEM (f) images of Ag@C3N4
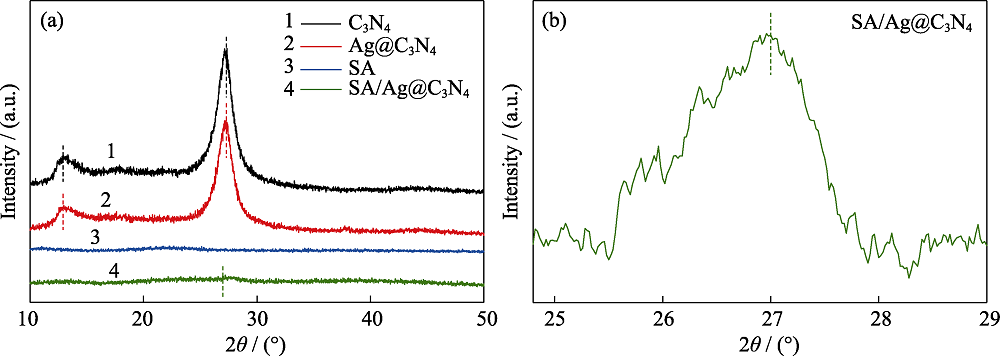
图4 C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA, SA/Ag@C3N4的XRD图谱(a); SA/Ag@C3N4的XRD放大图谱(b)
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA and SA/Ag@C3N4 (a), and magnified XRD patterns of SA/Ag@C3N4(b) Colorful figures are available on the website
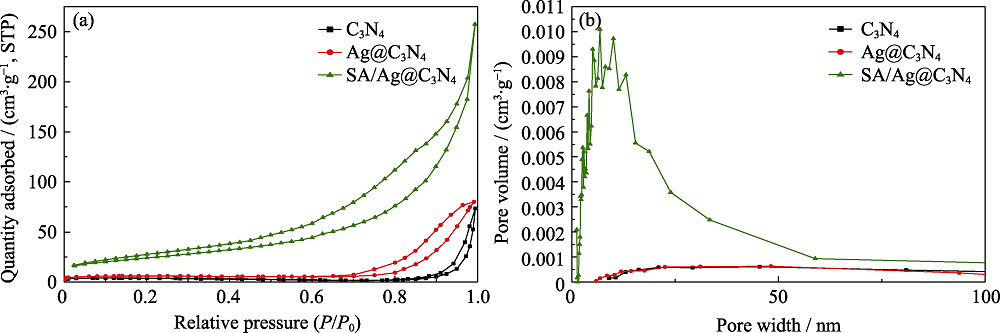
图5 C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA/Ag@C3N4的氮气吸附-脱附曲线(a)和孔径分布曲线(b)
Fig. 5 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms (a) and pore size distribution curves (b) of C3N4, Ag@C3N4 and SA/Ag@C3N4 Colorful figures are available on the website
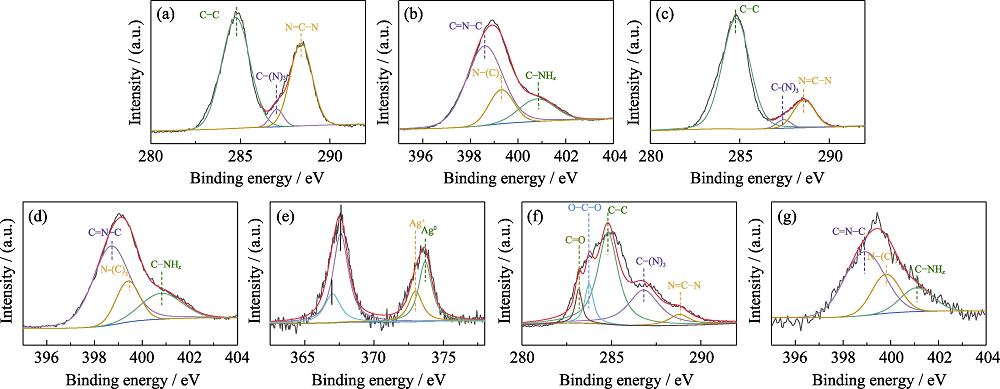
图7 C3N4 (a, b), Ag@C3N4 (c, d), SA/Ag@C3N4 (e~g)的X射线光电子能谱
Fig. 7 XPS spectra of C3N4 (a, b), Ag@C3N4 (c, d) and SA/Ag@C3N4 (e-g) (a, c, e) C1s; (b, d, f) N1s; (g) Ag3d
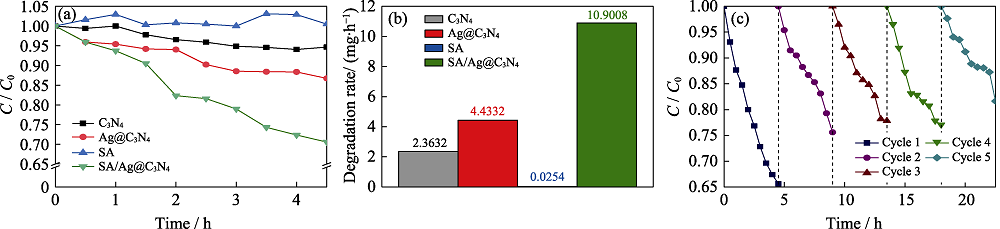
图8 C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA, SA/Ag@C3N4对甲基橙的光降解曲线 (a)、光降解速率 (b)以及SA/Ag@C3N4的循环稳定性 (c)
Fig. 8 Methyl orange degradation curves (a), degradation rates (b) of C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA, and SA/Ag@C3N4, and cyclic stability(c) of SA/Ag@C3N4 Colorful figures are available on the website
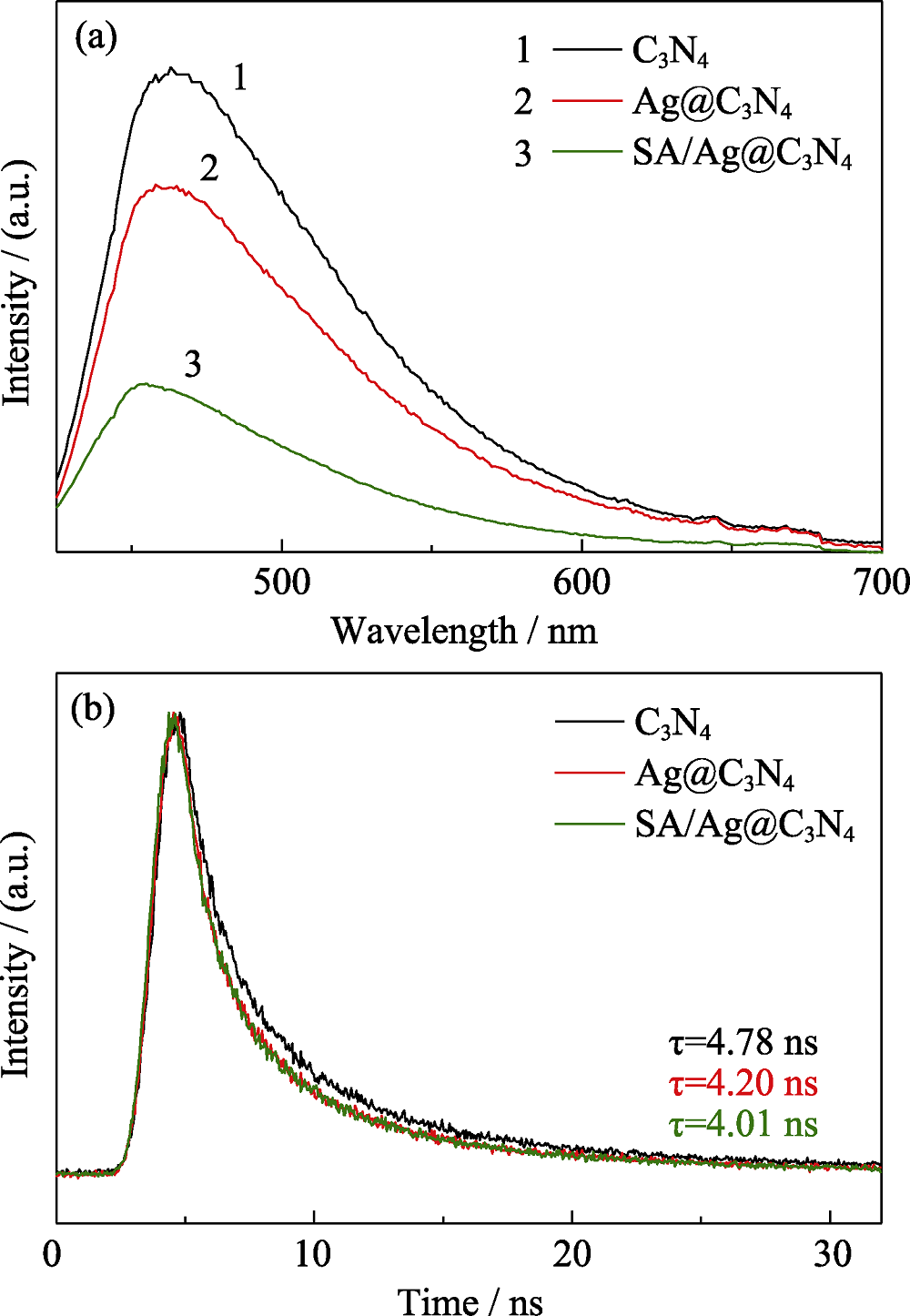
图9 C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA/Ag@C3N4的PL光谱(a)和TRPL光谱(b)
Fig. 9 PL (a) and TRPL (b) spectra of C3N4, Ag@C3N4 and SA/Ag@C3N4 Colorful figures are available on the website
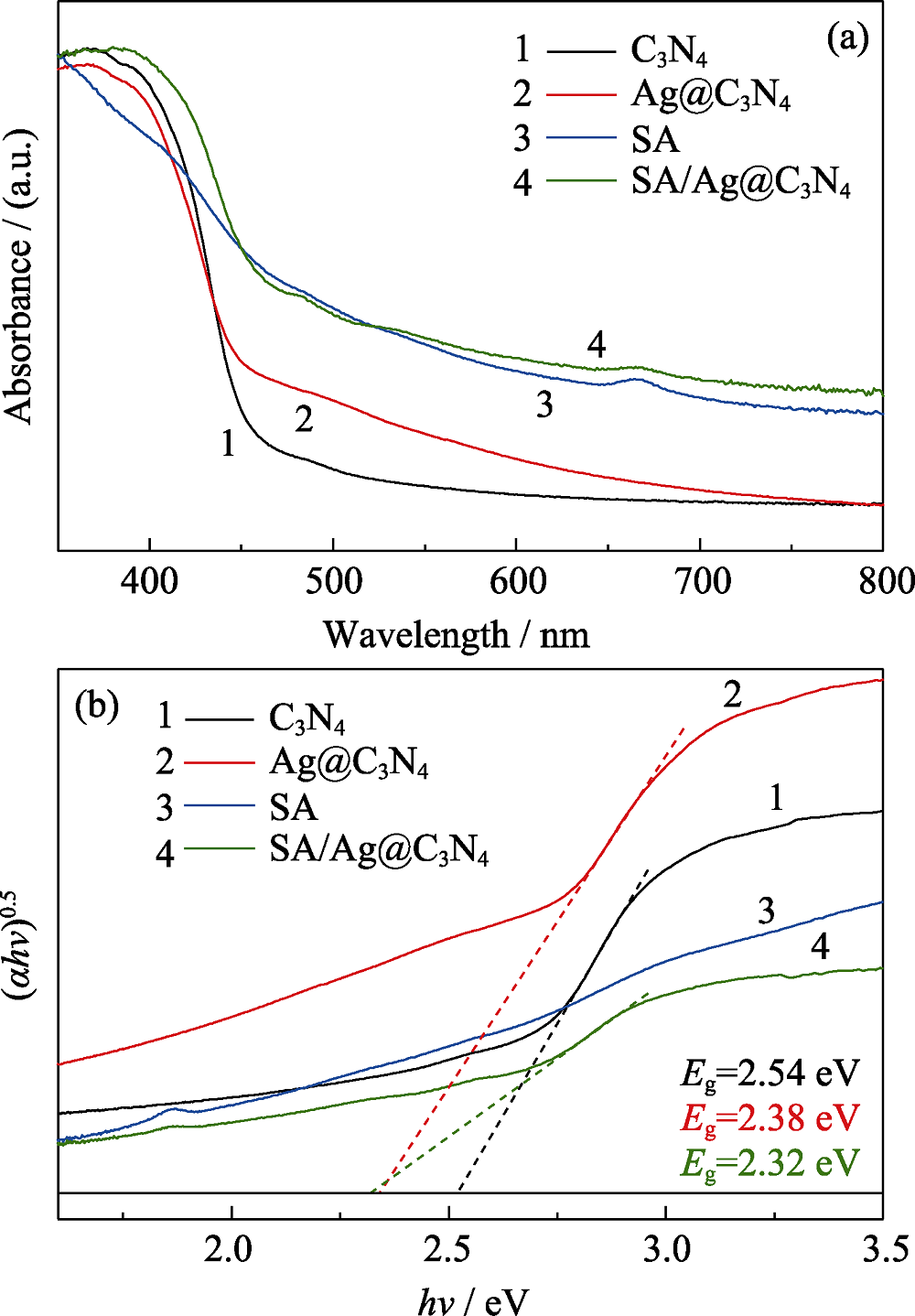
图10 C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA, SA/Ag@C3N4的(a)紫外-可见漫反射光谱和(b) (αhν)0.5随hν的变化曲线
Fig. 10 (a) UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectra and (b) (αhν)0.5 vs hν curves of C3N4, Ag@C3N4, SA and SA/Ag@C3N4 Colorful figures are available on the website
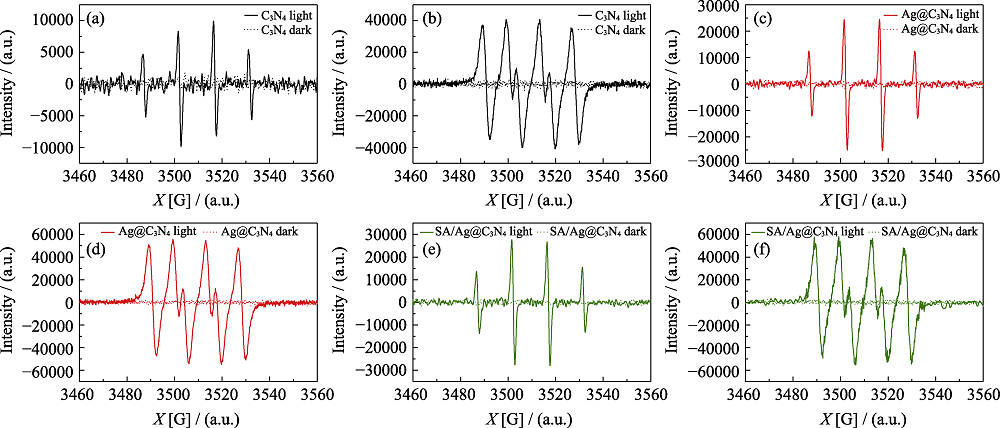
图11 (a, b) C3N4, (c, d) Ag@C3N4, (e, f) SA/Ag@C3N4的EPR曲线
Fig. 11 EPR spectra of C3N4 (a, b), Ag@C3N4 (c, d) and SA/Ag@C3N4 (e, f) during detecting ·OH (a, c, e) and ·O2- (b, d, f) Colorful figures are available on the website
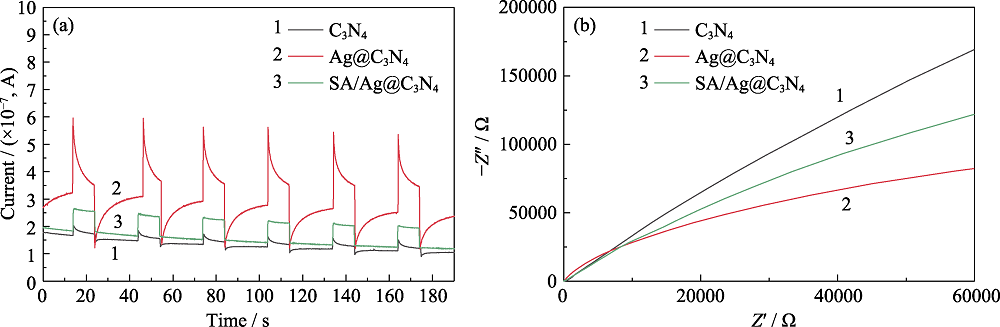
图12 C3N4, Ag@C3N4的光电流曲线(a)和EIS曲线(b)
Fig. 12 Transient photocurrent curves (a) and EIS curves (b) of C3N4 and Ag@C3N4 Colorful figures are available on the website
| [1] | 陈思, 李侃, 徐云兰, 等. N、F掺杂的TiO2膜电极在可见光条件下光电催化氧化诱惑红脱色效果的研究. 净水技术, 2009, 28(4): 55-59. |
| [2] | 任南琪, 周显娇, 郭婉茜, 等. 染料废水处理技术研究进展. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 84-94. |
| [3] |
CHEN Q H, XIN Y J, ZHU X W. Au-Pd nanoparticles-decorated TiO2 nanobelts for photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic levofloxacin in aqueous solution. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 186: 34-42.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
MARDAREV D, TEODORESCU V, IANCULESCU A, et al. Thermal behavior study of some Sol-Gel TiO2 based materials. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2008, 92(1): 7-13.
DOI URL |
| [5] | XIN G, MENG Y. Pyrolysis synthesized g-C3N4 for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 2013: 1-5. |
| [6] |
JI H, CHANG F, HU X, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol over g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 218: 183-190.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI X H, ZHANG J, CHEN X, et al. Condensed graphitic carbon nitride nanorods by nanoconfinement: promotion of crystallinity on photocatalytic conversion. Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(19): 4344-4348.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JORGE A B, MARTIN D J, DHANOA M T S, et al. H2 and O2 evolution from water half-splitting reactions by graphitic carbon nitride materials. Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(14): 7178-7185.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN Q, LI S, XU H, et al. Co-MOF as an electron donor for promoting visible-light photoactivities of g-C3N4 nanosheets for CO2 reduction. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 41(3): 514-523.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HAN C Q, LI J, MA Z Y, et al. Black phosphorus quantum dot/g-C3N4composites for enhanced CO2 photoreduction to CO. Science China Materials, 2018, 61(9): 1159-1166.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 张家晶, 郑永杰, 金春雪, 等. g-C3N4基光催化剂改性的研究进展. 现代化工, 2021, 3: 42-47. |
| [12] |
ZHANG J S, CHEN X F, TAKANABE K, et al. Synthesis of a carbon nitride structure for visible-light catalysis by copolymerization. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(2): 441-444.
DOI URL |
| [13] | MENG J C, WANG X Y, LIU Y Q, et al. Acid-induced molecule self-assembly synthesis of Z-scheme WO3/g-C3N4 heterojunctions for robust photocatalysis against phenolic pollutants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126354. |
| [14] |
KREIBIG U. Electronic properties of small silver particles: the optical constants and their temperature dependence. Journal of Physics F: Metal Physics, 1974, 4: 999-1014.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 刘兵, 周益民, 吴清珍, 等. 纤维素水凝胶包覆Fe3O4类Fenton纳米催化剂的制备及其催化降解性能. 材料科学与工程学报, 2017, 35(1): 119-124. |
| [16] | 冯华伟, 薛长国, 林秀玲. 海藻酸钠-碳材料复合凝胶吸附水中污染物的研究进展. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(3): 241-244. |
| [17] | 李莉, 郭伊荇, 周萍, 等. 孔道结构H3PW12O40/TiO2的制备及其可见光光催化降解水溶性染料的性能. 催化学报, 2005, 3: 209-215. |
| [18] | 张晨宇, 王利强. 添加LDH-ZnO的海藻酸钠基抗菌复合材料研究综述. 包装工程, 2020, 41(23): 76-82. |
| [19] |
KHAN S B, AHMAD S, KAMAL T, et al. Metal nanoparticles decorated sodium alginatecarbon nitride composite beads as effective catalyst for the reduction of organic pollutants. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 164: 1087-1098.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BARRETT E P, JOYNER L G, HALENDA P P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1951, 73(1): 373-380.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
BRUNAUER S, EMMETT P H, TELLER E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1938, 60(2): 309-319.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHENG Y, LIN L, YE X, et al. Helical graphitic carbon nitrides with photocatalytic and optical activities. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53: 11926-11930.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WATERHOUSE G, BOWMAKER G A, METSON J B. The thermal decomposition of silver (I, Ⅲ) oxide: A combined XRD, FT-IR and Raman spectroscopic study. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2001, 3(17): 3838-3845.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
FAN J C, SHI Z X, LIAN M, et al. Mechanically strong graphene oxide/sodium alginate/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel with improved dye adsorption capacity. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(25): 7433-7443.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ITHIARA D, BIANCA C S, ALVARO L M, et al. Formulation and optimization of a novel TiO2/calcium alginate floating photocatalyst. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 137: 992-1001.
DOI URL |
| [26] | MOHSIN N, ALAMGIR A K, ABID H, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-TiO2/sodium alginate 3-dimensional structure aerogel for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere, 2020, 261: 127702. |
| [27] |
MOHSIN N, MOKREMA M, JIHO K, et al. Photodegradation of microcystin-LR using graphene-TiO2/sodium alginate aerogels. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 199: 109-118.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 樊新, 黄可龙, 刘素琴, 等. 化学还原法制备纳米银粒子及其表征. 功能材料, 2007, 38(6): 996-999. |
| [29] |
WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal- free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nature Materials, 2009, 8: 76-80.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 金瑞瑞, 游继光, 张倩, 等. Fe掺杂g-C3N4的制备及其可见光催化性能. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(9): 1706-1712. |
| [31] | YU X, HU C W, HAO D N, et al. Tubular carbon nitride with hierarchical network: localized charge carrier generation and reduced charge recombination for high-performance photocatalysis of H2 and H2O2 production. Solar RRL, 2020, 5(5): 566-571. |
| [32] | 查莉, 王璐瑶, 郑雅慧, 等. 纤维素/海藻酸钠复合气凝胶的表面功能化与仿生矿化. 功能高分子学报, 2020, 33(4): 382-389. |
| [33] |
TONG Q, DONG Y M, YAN L, et al. High-efficient synthesis and photo catalytic properties of Ag/AgBr/TiO2monolithic photocatalysts using sodium alginate as substrate. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 637-642.
DOI URL |
| [34] | JING H, LI W, ZHOU H M, et al. Metallic MoO2-modified graphitic carbon nitride boosting photocatalytic CO2 reduction via Schottky junction. Solar RRL, 2020, 4(8): 841-848. |
| [35] | ZHANG Y Z, HUANG Z X, SHI J W, et al. Maleic hydrazide- based molecule doping in three-dimensional lettuce-like graphite carbon nitride towards highly effiffifficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 119009. |
| [36] | CHENG L, YIN H, CAI C, et al. Single Ni atoms anchored on porous few-layer g-C3N4 for photocatalytic CO2 reduction: the role of edge confinement. Small, 2020, 16: 986-996. |
| [37] | SUBHAJYOTI S, RAJKUMAR Y, ABHINAV K, et al. Surface modifified C, O co-doped polymeric g-C3N4 as an efficient photocatalyst for visible light assisted CO2 reduction and H2O2 production. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 259: 118054. |
| [38] |
ZENG Z X, YU H T, QUAN X, et al. Structuring phase junction between tri-s-triazine and triazine crystalline C3N4 for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 227: 153-160.
DOI URL |
| [39] | FRANZ URBACH. The long-wavelength edge of photographic sensitivity and of the electronic absorption of solids. Physical Review, 1953, 92(5): 1324. |
| [40] |
CUSHING S K, LI J, MENG F, et al. Photocatalytic activity enhanced by plasmonic resonant energy transfer from metal to semiconductor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(36): 15033-15041.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ALBERTO A, DI W. Photoelectrochemical properties of graphene and its derivatives. Nanomaterials, 2013, 3: 325-356.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈莉波, 盛盈, 伍明, 宋季岭, 蹇建, 宋二红. Na和O元素共掺杂氮化碳高效光催化制氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 552-562. |
| [2] | 范小暄, 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心, 王绩伟. 基于富氧空位LiYScGeO4: Bi3+长余辉光催化剂的自激活余辉驱动有机污染物芬顿降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [3] | 贾相华, 张辉霞, 刘艳凤, 左桂鸿. 湿化学法制备Cu2O/Cu空心球异质结光催化剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [4] | 马彬彬, 钟婉菱, 韩涧, 陈椋煜, 孙婧婧, 雷彩霞. ZIF-8/TiO2复合介观晶体的制备及光催化活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [5] | 曹青青, 陈翔宇, 吴健豪, 王筱卓, 王乙炫, 王禹涵, 李春颜, 茹菲, 李兰, 陈智. SiO2增强自敏性氮化碳微球可见光降解盐酸四环素的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [6] | 王兆阳, 秦鹏, 蒋胤, 冯小波, 杨培志, 黄富强. 三明治结构钌插层二氧化钛光催化四环素降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [7] | 叶茂森, 王耀, 许冰, 王康康, 张胜楠, 冯建情. II/Z型Bi2MoO6/Ag2O/Bi2O3异质结可见光催化降解四环素[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 321-329. |
| [8] | 李秋实, 殷广明, 吕伟超, 王怀尧, 李婧琳, 杨红光, 关芳芳. Na+/g-C3N4材料的制备及光催化降解亚甲基蓝机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1143-1150. |
| [9] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟. S型异质结Bi4O5Br2/CeO2的制备及其光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [10] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [11] | 凌洁, 周安宁, 王文珍, 贾忻宇, 马梦丹. Cu/Mg比对Cu/Mg-MOF-74的CO2吸附性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [12] | 孙晨, 赵昆峰, 易志国. 甲烷完全催化氧化研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [13] | 贾鑫, 李晋宇, 丁世豪, 申倩倩, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Pd纳米颗粒协同氧空位增强TiO2光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1301-1308. |
| [14] | 马润东, 郭雄, 施凯旋, 安胜利, 王瑞芬, 郭瑞华. MoS2/g-C3N4 S型异质结的构建及光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1176-1182. |
| [15] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||