无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 37-44.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250146 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250146
收稿日期:2025-04-07
修回日期:2025-05-10
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-05-22
通讯作者:
陈继新, 副教授. E-mail: jxchen@imr.ac.cn作者简介:张永恒(1994-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: yhzhang18s@imr.ac.cn
ZHANG Yongheng1,2( ), CHEN Jixin1(
), CHEN Jixin1( )
)
Received:2025-04-07
Revised:2025-05-10
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-05-22
Contact:
CHEN Jixin, associate professor. E-mail: jxchen@imr.ac.cnAbout author:ZHANG Yongheng (1994-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: yhzhang18s@imr.ac.cn
摘要:
六方氮化硼(h-BN)陶瓷在工业领域具有重要地位, 但由于其特殊的层状结构, h-BN的强度和硬度相对较低, 限制了其应用。本研究同时引入镱铝硅酸盐(YbAS)玻璃和硬质颗粒SiC作为增强相, 通过原位反应热压烧结的方法制备了一系列h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料, 其中YbAS玻璃含量固定为30%(体积分数), 在此基础上研究了SiC含量对复合材料性能的影响。研究表明, YbAS玻璃和SiC协同作用能够显著提升h-BN基复合材料的强度和韧性。当SiC体积分数为30%时, 复合材料的室温力学性能达到最佳, 其弯曲强度、压缩强度、断裂韧性、维氏硬度和弹性模量分别为(462±5) MPa、(1465±58) MPa、(5.5±0.3) MPa·m1/2、(4.7±0.3) GPa和140 GPa。其强化机制在于: 当SiC含量达到一定比例后, 其在复合材料中起到支撑作用, 能够有效承担外部载荷, 从而增强复合材料。同时, SiC在烧结过程中可以有效抑制h-BN晶粒长大, 实现细晶强化。此外, 复合材料具有良好的高温力学性能和较低的热导率, 其热膨胀系数与h-BN的结构和YbAS玻璃的转变温度有关。本研究为h-BN陶瓷材料的强韧化提供了一种有效途径。
中图分类号:
张永恒, 陈继新. 镱铝硅酸盐玻璃和SiC改性h-BN基复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 37-44.
ZHANG Yongheng, CHEN Jixin. Preparation and Properties of Ytterbium Aluminosilicate Glass and SiC Modified h-BN-based Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 37-44.
| Sample | SiC/ % (in volume) | YbAS glass/ % (in volume) | h-BN/ % (in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYbSi5 | 5 | 30 | 65 |
| BYbSi10 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| BYbSi20 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| BYbSi30 | 30 | 30 | 40 |
表1 原料粉的样品符号和组成
Table 1 Sample notations and compositions of raw powders
| Sample | SiC/ % (in volume) | YbAS glass/ % (in volume) | h-BN/ % (in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYbSi5 | 5 | 30 | 65 |
| BYbSi10 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| BYbSi20 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| BYbSi30 | 30 | 30 | 40 |
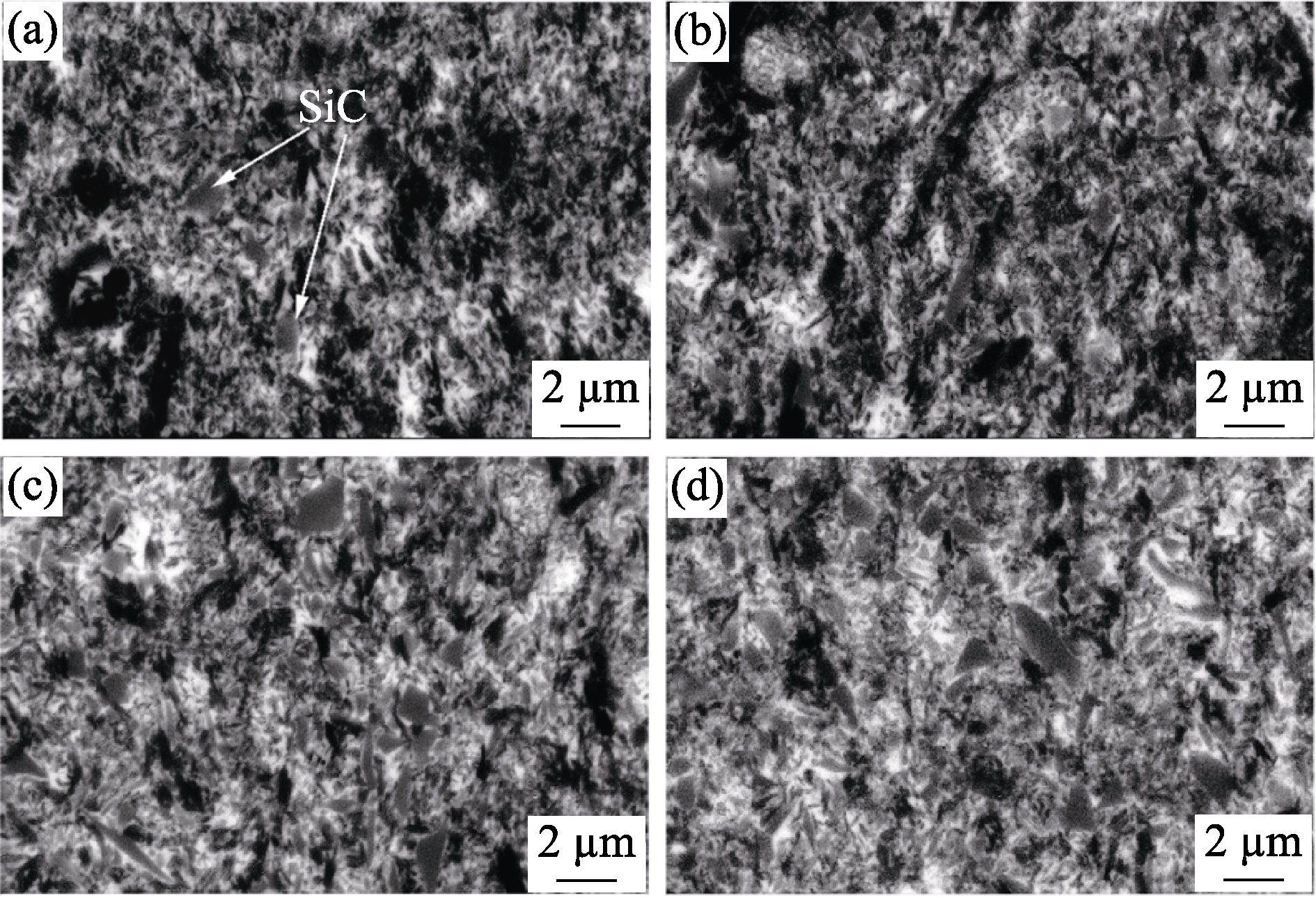
图2 不同SiC含量h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of the h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites with varying contents of SiC (a) BYbSi5; (b) BYbSi10; (c) BYbSi20; (d) BYbSi30

图3 BYbSi30复合材料的微观结构和元素分布图
Fig. 3 Microstructure and element mappings of the BYbSi30 composite (a) Bright field image; (b) HAADF image; (c-e) Diffraction patterns of h-BN (c), SiC (d) and YbAS glass (e); (f-l) Distributions of B, N, Yb, Al, O, Si and C elements in Fig. (b); (m, n) High-resolution images of area A (m) and area B (n) in Fig. (a)
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 2.763 | 2.813 | 2.910 | 3.015 |
| Relative density/% | 96.12 | 96.30 | 96.55 | 97.04 |
表2 h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料的密度和相对密度
Table 2 Densities and relative densities of the h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 2.763 | 2.813 | 2.910 | 3.015 |
| Relative density/% | 96.12 | 96.30 | 96.55 | 97.04 |
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength/MPa | 377±41 | 348±29 | 447±10 | 462±5 |
| Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | 4.9±0.2 | 5.1±0.1 | 5.3±0.1 | 5.5±0.3 |
| Compressive strength/MPa | 1067±55 | 1046±91 | 1288±64 | 1465±58 |
| Elasticity modulus/GPa | 104 | 108 | 125 | 140 |
| Vickers hardness/GPa | 2.5±0.1 | 2.8±0.3 | 3.3±0.2 | 4.7±0.3 |
表3 h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料的室温力学性能
Table 3 Room-temperature mechanical properties of the h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength/MPa | 377±41 | 348±29 | 447±10 | 462±5 |
| Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | 4.9±0.2 | 5.1±0.1 | 5.3±0.1 | 5.5±0.3 |
| Compressive strength/MPa | 1067±55 | 1046±91 | 1288±64 | 1465±58 |
| Elasticity modulus/GPa | 104 | 108 | 125 | 140 |
| Vickers hardness/GPa | 2.5±0.1 | 2.8±0.3 | 3.3±0.2 | 4.7±0.3 |
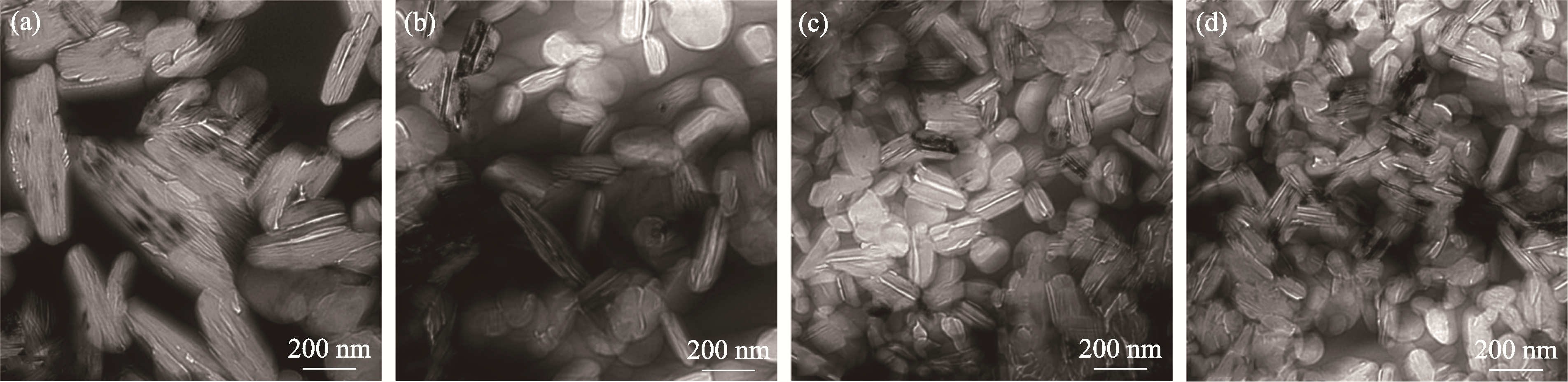
图4 不同SiC含量h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料中h-BN的SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of h-BN in h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites with different SiC contents (a) BYbSi5; (b) BYbSi10; (c) BYbSi20; (d) BYbSi30
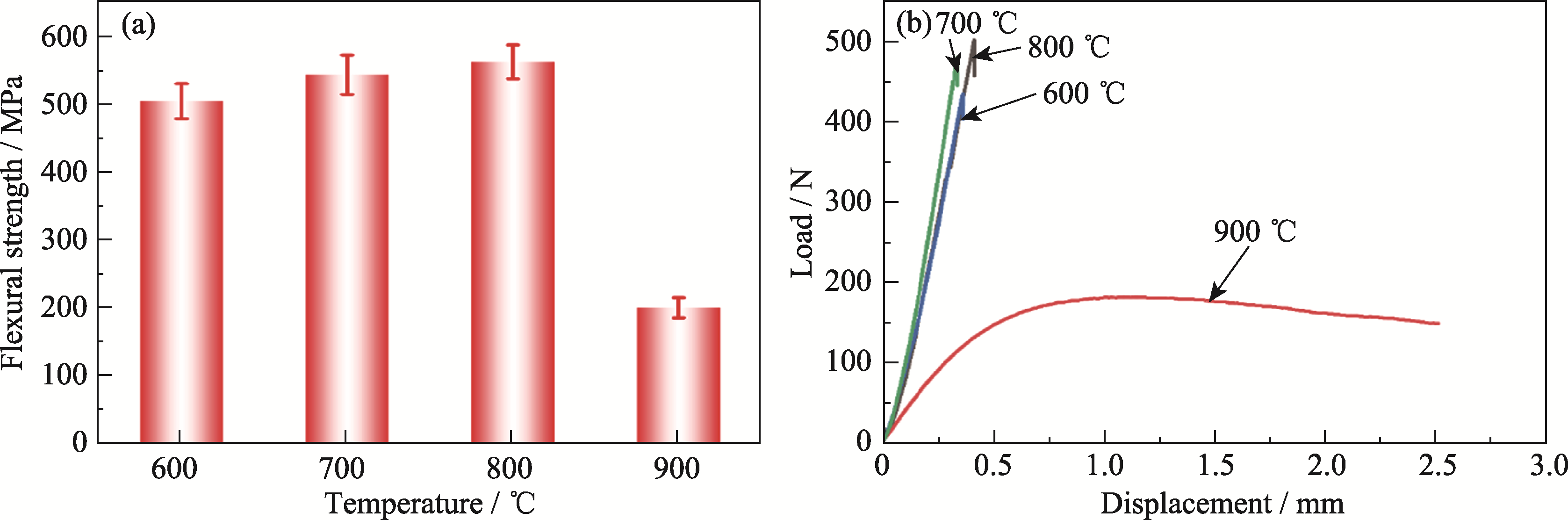
图6 BYbSi30复合材料(a)在不同温度下的弯曲强度和(b)高温弯曲强度测试时的载荷-位移曲线
Fig. 6 (a) Flexural strength of the BYbSi30 composite at different temperatures and (b) load-displacement curves for testing flexural strength at elevated temperature
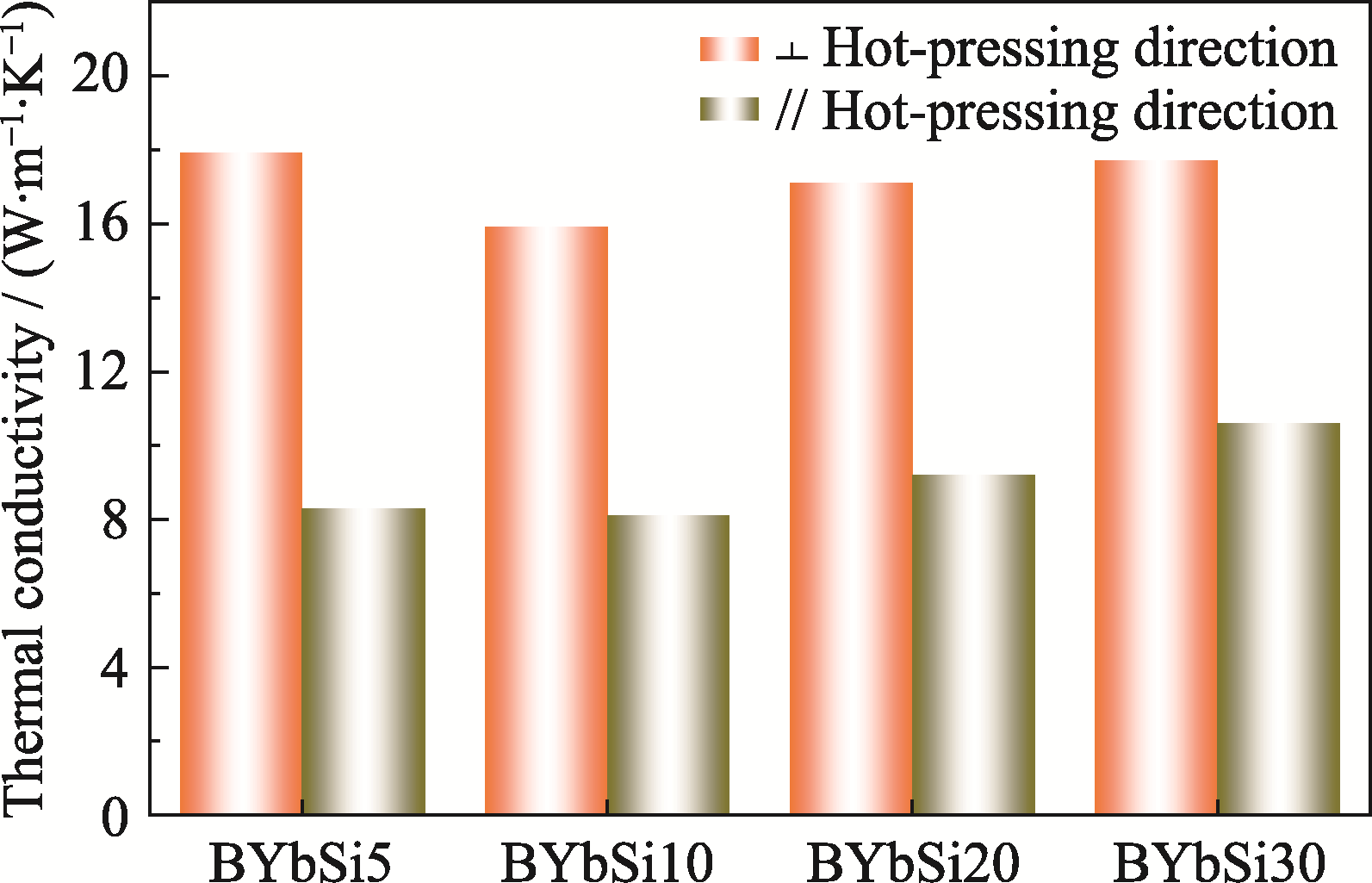
图7 h-BN/YbAS/SiC复合材料垂直和平行热压方向的热导率
Fig. 7 Thermal conductivities of h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites in the directions perpendicular and parallel to hot pressing

图8 BYbSi30复合材料在不同方向的热膨胀曲线
Fig. 8 Thermal expansion curves of BYbSi30 composites in different directions (a) Perpendicular to hot pressing; (b) Parallel to hot pressing
| [1] |
LIPP A, SCHWETZ K A, HUNOLD K. Hexagonal boron nitride fabrication, properties and applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1989, 5(1): 3.
DOI URL |
| [2] | HAUBNER R, WILHELM M, WEISSENBACHER R, et al. Boron nitrides properties, synthesis and applications. Structure and Bonding, 2002, 102: 14. |
| [3] | RUSANOVA L N, ROMASHLN A G, KULLKOVA G I, et al. Boron nitride ceramics: problems and development perspectives. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1988, 1: 23. |
| [4] |
QIAO W, YANG J, QIAO J, et al. Pressureless-sintered boron nitride nanosheets/glass composite ceramics for excellent mechanical, dielectric and thermo-conductive performances. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(9): 3998.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FREDERIKSE H P R, KAHN A H, DRAGOO A L, et al. Electrical resistivity and microwave transmission of hexagonal boron nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1985, 68(3): 131.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SINCLAIR W, SIMMONS H. Microstructure and thermal-shock behavior of BN composites. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1987, 6(6): 627.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TAHARA H, IMANAKA K, YUGE S. Effects of channel wall material on thrust performance and plasma characteristics of Hall-effect thrusters. Vacuum, 2006, 80(11/12): 1216.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
EICHLER J, LESNIAK C, CHRISTOPH L. Boron nitride (BN) and BN composites for high-temperature applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(5): 1105.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
RIZAKHANOV R N B, IVANOV A A, IVLIEVA A V, et al. Ceramic composite based on boron nitride with enhanced resistance to ion bombardment for application in hall thruster. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 2015, 6(2): 156.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI Y L, QIAO G J, JIN Z H. Machinable Al2O3/BN composite ceramics with strong mechanical properties. Materials Research Bulletin, 2002, 37(8): 1401.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DUAN X M, JIA D C, ZHOU Y, et al. Mechanical properties and plasma erosion resistance of BNp/Al2O3-SiO2 composite ceramics. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(6): 1462.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TIAN Z, DUAN X M, YANG Z, et al. Ablation mechanism and properties of in-situ SiAlON reinforced BN-SiO2 ceramic composite under an oxyacetylene torch environment. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(7): 11149.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG X, CHEN J X, LI X C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of h-BN/Y2SiO5 composites. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1): 1279.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CAI D, YANG Z, DUAN X M, et al. A novel BN-MAS system composite ceramics with greatly improved mechanical properties prepared by low temperature hot-pressing. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 633: 194.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN J J, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of h-BN/Yb4Si2O7N2 composites. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2018, 7(4): 317.
DOI |
| [16] |
ZHANG X, ZHANG R, CHEN G, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of hot-pressed ZrO2(3Y)-BN composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 497(1/2): 195.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHEN L, HUANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Effect of ZrO2 content on microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of (ZrB2+3Y-ZrO2)/BN composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 573: 106.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN L, WANG Y, SHEN H, et al. Effect of SiC content on mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of BN-ZrO2-SiC composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 590: 346.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHAI F R, LI S, SUN J L, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock behavior of h-BN-SiC ceramic composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(2): 2413.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J, LU D, XUAN W, et al. Boron nitride microribbons strengthened and toughened alumina composite ceramics with excellent mechanical, dielectric, and thermal conductivity properties. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(4): 496.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WEN G, WU G L, LEI T Q, et al. Co-enhanced SiO2-BN ceramics for high-temperature dielectric applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(12): 1923.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHEN J J, CHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of h-BN based composites containing dual glass phases. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(9): 3210.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
QIU B F, DUAN X M, ZHANG Z, et al. Microstructure and room/elevated-temperature mechanical properties of hot-pressed h-BN composite ceramics with La2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 addition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(6): 2260.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG Y H, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Hexagonal boron nitride ceramic reinforced with a dispersed glass phase and microdomain-extruded glass fibers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025 45(10): 117362.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHANG Y H, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Bulk ytterbium aluminosilicate glass with excellent mechanical properties and plasma etching resistance. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2024, 642: 123159.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 李文新, 李文辉. 常压烧结碳化硅陶瓷的力学性能与质密度. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2002, 7: 80. |
| [27] |
LI Z, BRADT R C. Thermal expansion of the hexagonal (6H) polytype of silicon carbide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 69(12): 863.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 武安华, 曹文斌, 李江涛, 等. 固相烧结SiC陶瓷. 材料工程, 2001, 4: 3. |
| [29] |
PEASE R S. An X-ray study of boron nitride. Acta Crystallographica, 1952, 5(3): 356.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SIMPSON A, STUCKES A D. The thermal conductivity of highly oriented pyrolytic boron nitride. Journal of Physics Part C Solid State Physics, 1971, 4(13): 1710. |
| [31] | WANG F F, ZENG X L, YAO Y M, et al. Silver nanoparticle- deposited boron nitride nanosheets as fillers for polymeric composites with high thermal conductivity. Scientific Report, 2016, 6: 19394. |
| [1] | 袁旺, 胡建宝, 周亮, 阚艳梅, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 氩气气氛热处理对Shicolon-II SiC纤维机械性能和微观结构演变的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 119-128. |
| [2] | 徐锦涛, 高攀, 何唯一, 蒋圣楠, 潘秀红, 汤美波, 陈锟, 刘学超. 3C-SiC晶体制备研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | 陈斌, 任科, 王一光. Mini-SiCf/SiC复合材料长时间高温下的力学性能演变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 971-980. |
| [4] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [5] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [6] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 王堋人. 烧结条件对制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [7] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [8] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [9] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [10] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [11] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [12] | 侯佳琪, 陈睿聪, 曾耀莹, 周磊, 张佳平, 付前刚. 气相渗硅法修复SiC涂层及其抗热震和烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 168-176. |
| [13] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [14] | 李勇锋, 顾玉萍, 师广照, 胡九林, 雷萌, 彭晖, 曾宇平, 李驰麟. NASICON型陶瓷固态电池的电化学电位界面调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1201-1211. |
| [15] | 林元伟, 景昭, 陈鹤拓, 李佳恒, 覃显鹏, 周国红, 王士维. SiCp掺杂Cf/Li2O-Al2O3-SiO2复合材料耐烧蚀性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1153-1162. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||