无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 262-272.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250113 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250113
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
李浩1,2( ), 齐源1,2, 高相东2(
), 齐源1,2, 高相东2( ), 张星星2, 王金敏1(
), 张星星2, 王金敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-18
修回日期:2025-04-21
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-27
通讯作者:
高相东, 研究员. E-mail: xdgao@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:李 浩(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 769718909@qq.com
LI Hao1,2( ), QI Yuan1,2, GAO Xiangdong2(
), QI Yuan1,2, GAO Xiangdong2( ), ZHANG Xingxing2, WANG Jinmin1(
), ZHANG Xingxing2, WANG Jinmin1( )
)
Received:2025-03-18
Revised:2025-04-21
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-04-27
Contact:
GAO Xiangdong, professor. E-mail: xdgao@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:LI Hao (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 769718909@qq.com
摘要:
二氧化硅气凝胶因低密度、低导热系数和良好的高温稳定性, 广泛应用于高温隔热领域, 但由于其固有的材料特性, 当工作温度超过600 ℃, 其孔结构将逐渐塌缩, 从而使隔热性能大幅度衰减, 同时在高温下红外辐射的遮蔽效果也较差。本研究旨在探讨通过钙掺杂提高二氧化硅气凝胶的高温稳定性及红外遮蔽能力。以水玻璃和无水氯化钙为前驱体, 以三甲基氯硅烷(TMCS)为疏水改性剂, 通过溶胶-凝胶、水热和常压干燥(APD)技术制备了耐高温的钙掺杂二氧化硅气凝胶(CSA)粉体。研究了前驱体中Ca/Si摩尔比和水热条件(温度和pH)对CSA结晶特性、微观形貌和孔结构的影响。结果表明, 在400~1000 ℃范围内, Ca/Si摩尔比和水热处理对CSA的微观结构和耐热性有显著影响。1000 ℃烧结的样品具有较高的比表面积(100.1 m2/g)和孔容(0.8705 cm3/g), 表明CSA具有良好的耐高温性能。温度高达600 ℃的单面隔热测试表明, Ca/Si摩尔比为1的样品隔热性能最好, 冷表面温度为450 ℃, 比纯二氧化硅气凝胶低27 ℃。
中图分类号:
李浩, 齐源, 高相东, 张星星, 王金敏. 溶胶凝胶水热法制备耐高温、隔热增强钙掺杂二氧化硅气凝胶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 262-272.
LI Hao, QI Yuan, GAO Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingxing, WANG Jinmin. High Temperature Resistant Calcium-doped Silica Aerogels with Enhanced Thermal Insulation via Sol-Gel Hydrothermal Route[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 262-272.
| Sample | Ca/Si molar ratio | Temperature/℃ | pH* |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSA | 0 | - | - |
| HPSA | 0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| CSA-0.4 | 0.4 | - | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.4 | 0.4 | 120 | 5-6 |
| 0.4 | 140 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 160 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 180 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 200 | 5-6 | |
| HCSA-0.6 | 0.6 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.8 | 0.8 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.0 | 1.0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| 1.0 | 180 | 7-8 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 9-10 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 12-13 | |
| HCSA-1.2 | 1.2 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.5 | 1.5 | 180 | 5-6 |
Table 1 Experimental parameters of the aerogel powders
| Sample | Ca/Si molar ratio | Temperature/℃ | pH* |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSA | 0 | - | - |
| HPSA | 0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| CSA-0.4 | 0.4 | - | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.4 | 0.4 | 120 | 5-6 |
| 0.4 | 140 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 160 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 180 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 200 | 5-6 | |
| HCSA-0.6 | 0.6 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.8 | 0.8 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.0 | 1.0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| 1.0 | 180 | 7-8 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 9-10 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 12-13 | |
| HCSA-1.2 | 1.2 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.5 | 1.5 | 180 | 5-6 |
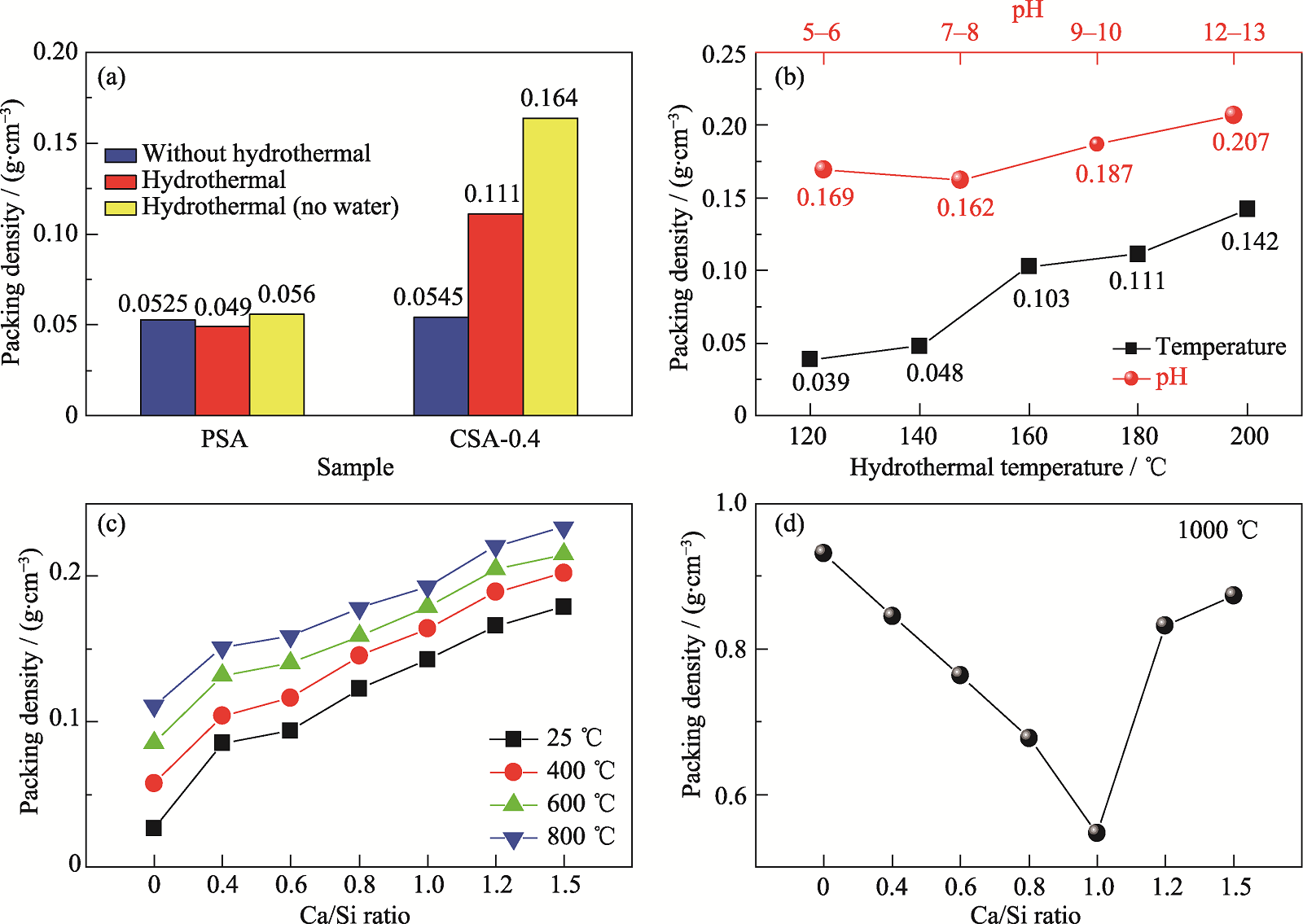
Fig. 2 Packing densities of different samples (a) PSA and CSA-0.4 under different hydrothermal conditions; (b) HCSA-0.4 at different hydrothermal temperatures and HCSA-1.0 at different hydrothermal pH; (c, d) HCSA sintered at different temperatures for 2 h
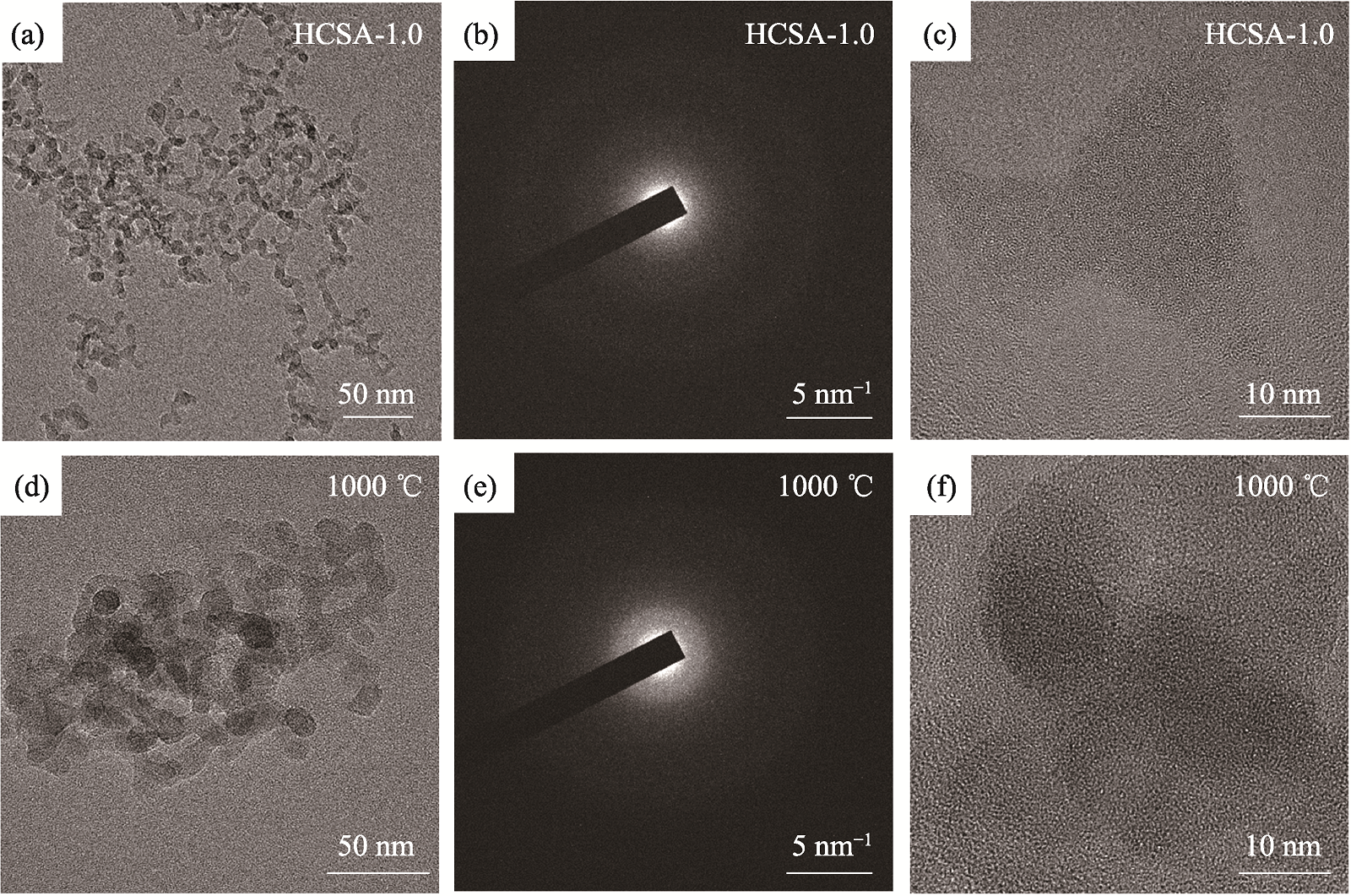
Fig. 5 (a) TEM image, (b) SAED pattern and (c) HRTEM image of the as-prepared HCSA-1.0; (d) TEM image, (e) SAED pattern and (f) HRTEM image of HCSA-1.0 sintered at 1000 ℃ for 2 h
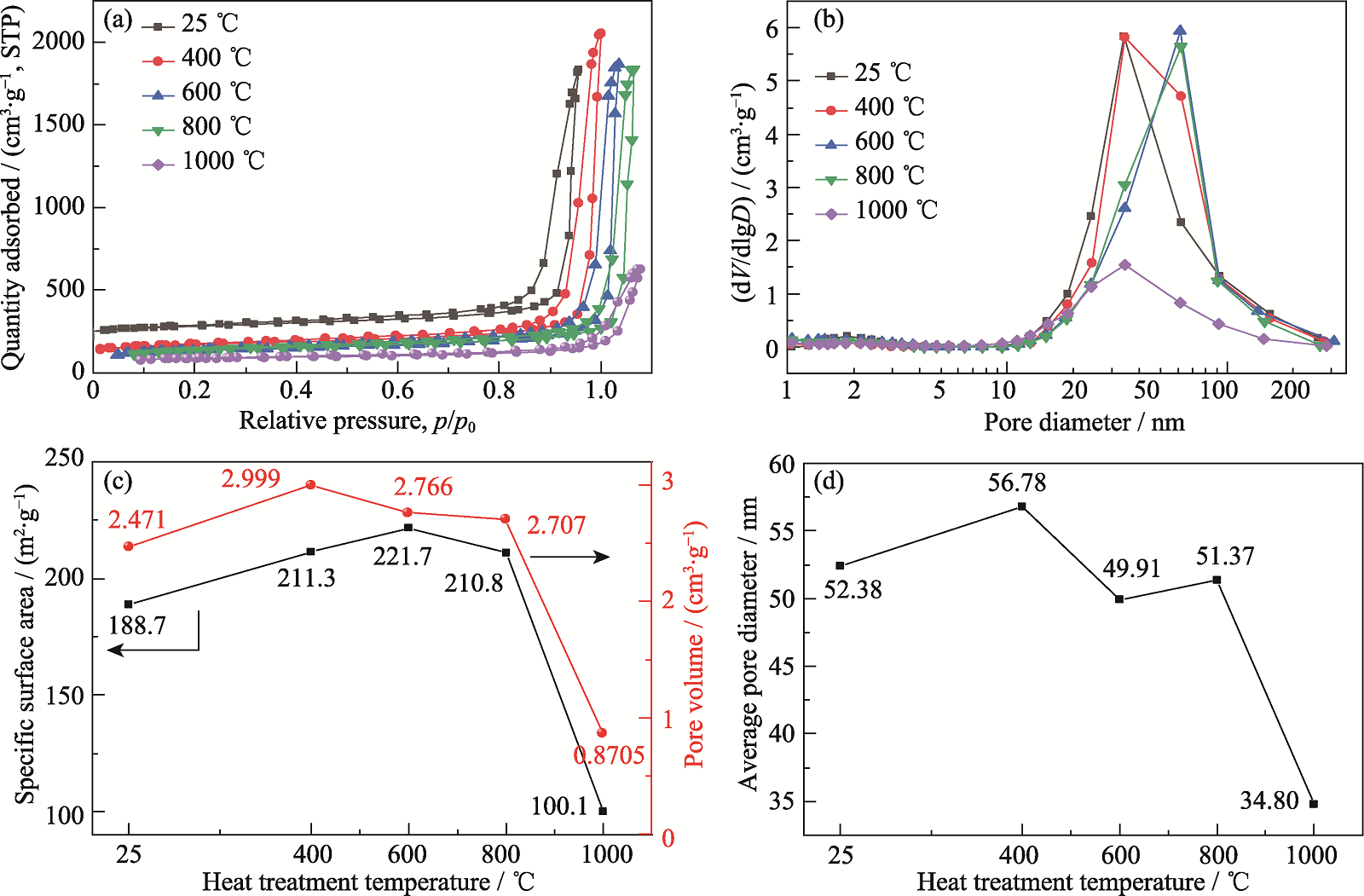
Fig. 6 Pore structure of HCSA-1.0 sintered at different temperatures (a) Adsorption-desorption isotherms; (b) Pore size distributions (evaluated from desorption isotherm); (c) Specific surface area and pore volume; (d) Average pore size
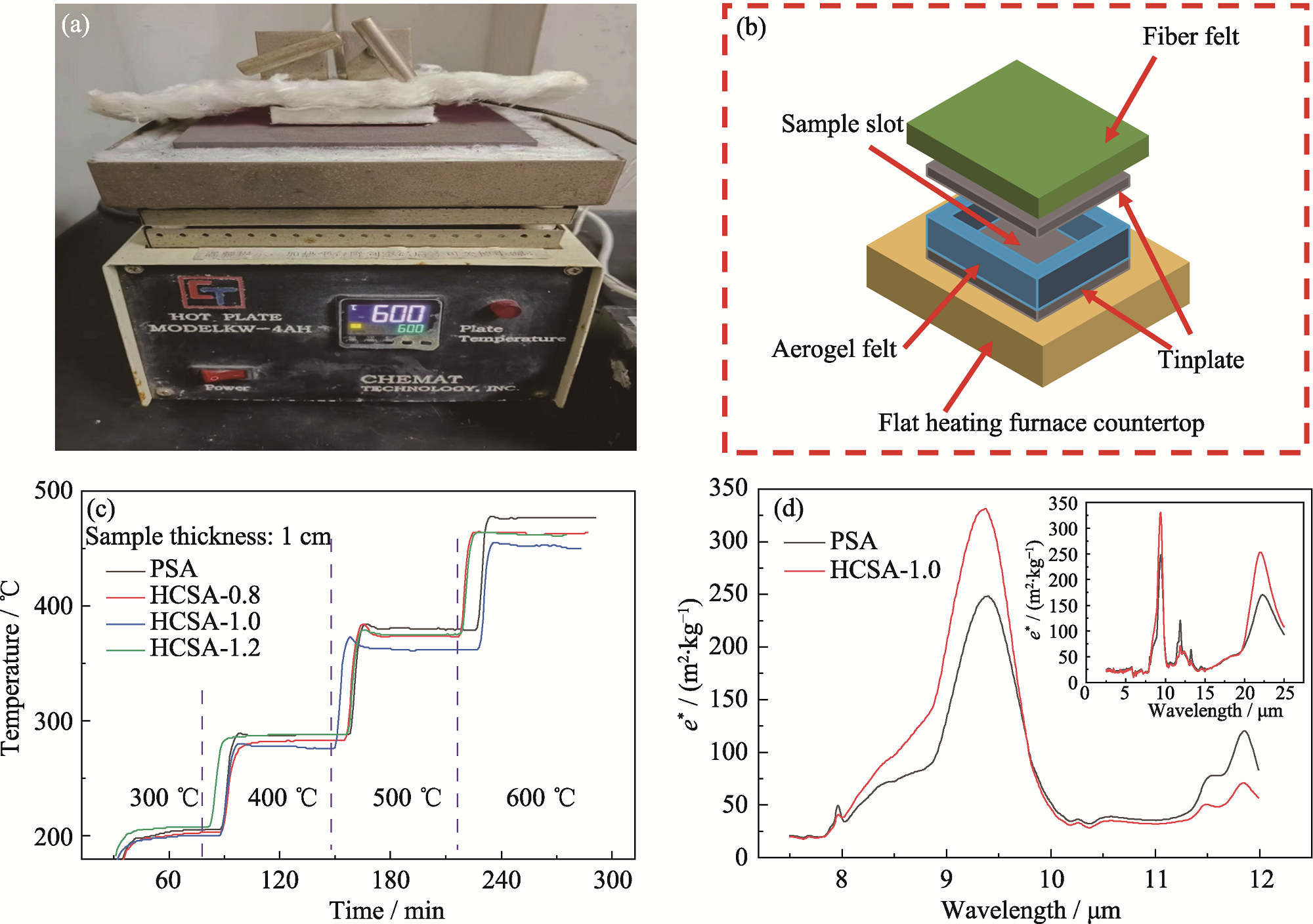
Fig. 9 (a) Flat heating furnace test device; (b) Schematic diagram of a home-made device for measuring thermal insulation properties; (c) Plots of temperature variation of the flat heating furnace test; (d) Specific extinction coefficients of PSA and HCSA-1.0 in infrared band Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
AHMAD S, AHMAD S, SHEIKH J N. Silica centered aerogels as advanced functional material and their applications: a review. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2023, 611: 122322.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
PENG F, JIANG Y, FENG J, et al. Research proggress on alumina aerogel composites for high-temperature thermal insulation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 673.
DOI |
| [3] | LI F P, CHU J B, QIU H B, et al. Compression resilience mechanism of silica fiber aerogel. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 981. |
| [4] |
LUO Y, XIA S, NIU B, et al. Preparation and high temperature inorganic transformation of flexible silicon aerogel. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1281.
DOI |
| [5] |
AKHTER F, SOOMRO S A, INGLEZAKIS V J. Silica aerogels; a review of synthesis, applications and fabrication of hybrid composites. Journal of Porous Materials, 2021, 28(5): 1387.
DOI |
| [6] |
LIU Z H, DING Y D, WANG F, et al. Thermal insulation material based on SiO2 aerogel. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 122: 548.
DOI URL |
| [7] | EL RASSY H, MAURY S, BUISSON P, et al. Hydrophobic silica aerogel-lipase biocatalysts. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2004, 350: 23. |
| [8] |
RAO A V, HEGDE N D, HIRASHIMA H. Absorption and desorption of organic liquids in elastic superhydrophobic silica aerogels. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 305(1): 124.
PMID |
| [9] |
MALEKI H, DURAES L, GARCIA-GONZALEZ C A, et al. Synthesis and biomedical applications of aerogels: possibilities and challenges. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 236: 1.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | LAMY-MENDES A, PONTINHA A D R, ALVES P, et al. Progress in silica aerogel-containing materials for buildings’ thermal insulation. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 286: 122815. |
| [11] |
ALMEIDA C M R, GHICA M E, DURÃES L. An overview on alumina-silica-based aerogels. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 282: 102189.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WALKER R C, POTOCHNIAK A E, HYER A P, et al. Zirconia aerogels for thermal management: review of synthesis, processing, and properties information architecture. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 295: 102464.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KIM Y N, SHAO G N, JEON S J, et al. Sol-Gel synthesis of sodium silicate and titanium oxychloride based TiO2-SiO2aerogels and their photocatalytic property under UV irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 231: 502.
DOI URL |
| [14] | GAO S, YANG T, LIU S N, et al. Preparation of high-temperature resistant aluminum-doped silica aerogel from aluminum sol source by ambient pressure drying. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2023, 109(1): 162. |
| [15] |
WU Y, WANG X D, SHEN J. Metal oxide aerogels for high- temperature applications. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2022, 106(2): 360.
DOI |
| [16] |
GAO S, CAO Z Q, LIU K, et al. Preparation of high-temperature resistant aerogels by incorporating aluminum sol into composite silica sources using ambient pressure drying. Polymers, 2024, 16(16): 2296.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG X X, GAO X D, DONG Y B, et al. Nanoporous Mg-doped SiO2 nanoparticles with tunable infrared emissivity toward effective radiative cooling coatings. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 940: 168905.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZU G Q, SHEN J, ZOU L P, et al. Highly thermally stable zirconia/silica composite aerogels prepared by supercritical deposition. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 238: 90.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TU F, YU Y X, WANG Y, et al. Preparation of SiO2/Fe2O3 composite aerogels for thermal insulation enhancement. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(2): 2976.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
IKIZLER B K, YAPC E, YÜCEL S, et al. Production and characterization of calcium silica aerogel powder as a food additive. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(12): 11479.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
ZHU M Y, LI G Y, GONG W B, et al. Calcium-doped boron nitride aerogel enables infrared stealth at high temperature up to 1300 ℃. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 14(1): 18.
DOI |
| [22] |
YANG J X, ZHANG Y W, HONG Z L, et al. Preparations of TiO2 nanocrystal coating layers with various morphologies on mullite fibers for infrared opacifier application. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(7): 2651.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
FENG J P, CHEN D P, NI W, et al. Study of IR absorption properties of fumed silica-opacifier composites. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2010, 356(9/10): 480.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG X D, SUN D, DUAN Y Y, et al. Radiative characteristics of opacifier-loaded silica aerogel composites. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2013, 375: 31.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WEI G S, LIU Y S, ZHANG X X, et al. Thermal conductivities study on silica aerogel and its composite insulation materials. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 54(11/12): 2355.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YOU J G, XING H P, XUE J, et al. Preparation of rigid cross- linked PVC foam with excellent thermal insulation through adding high-reflectivity IR opacifier. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 203: 108566.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHI T Q, GAO X D, WU Y Q, et al. Ba/Sn induced high temperature phase and microstructure evolution of silica aerogel via co-precursor Sol-Gel method. Chemical Physics, 2021, 545: 111161.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
YAO J Q, GAO X D, WU Y Q, et al. High-temperature resistant ambient pressure-dried aluminum doped silica aerogel from inorganic silicon and aluminum sources. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(11): 15006.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BHAGAT S D, RAO A V. Surface chemical modification of TEOS based silica aerogels synthesized by two step (acid-base) Sol-Gel process. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 252(12): 4289.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BHAGAT S D, KIM Y H, AHN Y S, et al. Rapid synthesis of water-glass based aerogels by in situ surface modification of the hydrogels. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(6): 3231.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 冯关正, 杨健, 周渡, 陈啟明, 许文涛, 周有福. 水热-碳热合成AlN纳米粉体的机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [2] | 肖文艳, 付艳, 杨书镔, 朱洁, 程照阳, 温小煦, 唐嘉繁, 于亮, 张骞. 自支撑非晶Ce-FeHPi/NF电极的电解海水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1348-1356. |
| [3] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [4] | 徐州, 刘宇轩, 池俊霖, 张婷婷, 王姝越, 李伟, 马春慧, 罗沙, 刘守新. 双模板-水热炭化制备马蹄形中空多孔炭及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 954-962. |
| [5] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟. S型异质结Bi4O5Br2/CeO2的制备及其光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [6] | 牛海滨, 黄佳慧, 李倩文, 马董云, 王金敏. 多孔NiMoO4纳米片薄膜的直接水热生长及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [7] | 姚仪帅, 郭瑞华, 安胜利, 张捷宇, 周国治, 张国芳, 黄雅荣, 潘高飞. 原位负载Pt-Co高指数晶面催化剂的制备及其电催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [8] | 张弦, 张策, 姜文君, 冯德强, 姚伟. 四元BiMnVO5的合成、电子结构与可见光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | 王婷婷, 史书梅, 柳晨媛, 朱万诚, 张恒. 多级多孔硅酸镍微球的合成及其对碱性品红的高效吸附[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [10] | 宋可可, 黄浩, 鲁梦婕, 杨安春, 翁杰, 段可. 水热制备锌、硅、镁、铁等元素掺杂羟基磷灰石及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [11] | 肖昱旻, 李彬, 覃礼钊, 林华, 李庆, 廖斌. 用CuCl2为铜源高效制备形貌可控CuGeO3的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| [12] | 王举汉,文雄,刘成超,张煜华,赵燕熹,李金林. 多级孔Co/Al-SiO2催化剂制备及其费-托合成催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 999-1004. |
| [13] | 张东硕,蔡昊,高凯茵,马子川. Zn2SiO4-ZnO-生物炭复合物的制备及其可见光催化H2O2降解甲硝唑[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 923-930. |
| [14] | 王志虎,张菊梅,白力静,张国君. AZ31镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层表面Mg(OH)2膜层的制备及耐蚀性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [15] | 张志宾, 周润泽, 董志敏, 曹小红, 刘云海. 偕胺肟水热碳对U(VI)-CO3/Ca-U(VI)-CO3的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 352-358. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||