无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 280-287.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220642 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220642
所属专题: 【信息功能】纪念殷之文先生诞辰105周年虚拟学术专辑
齐雪君1( ), 张健1, 陈雷1, 王绍涵1, 李翔1, 杜勇1, 陈俊锋1,2(
), 张健1, 陈雷1, 王绍涵1, 李翔1, 杜勇1, 陈俊锋1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-01
修回日期:2022-12-05
出版日期:2023-03-20
网络出版日期:2023-01-11
通讯作者:
陈俊锋, 研究员. E-mail: jfchen@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:齐雪君(1969-), 女, 高级工程师. E-mail: qixuejun@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
QI Xuejun1( ), ZHANG Jian1, CHEN Lei1, WANG Shaohan1, LI Xiang1, DU Yong1, CHEN Junfeng1,2(
), ZHANG Jian1, CHEN Lei1, WANG Shaohan1, LI Xiang1, DU Yong1, CHEN Junfeng1,2( )
)
Received:2022-11-01
Revised:2022-12-05
Published:2023-03-20
Online:2023-01-11
Contact:
CHEN Junfeng, professor. E-mail: jfchen@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:QI Xuejun (1969-), female, senior engineer. E-mail: qixuejun@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
Bi12GeO20晶体是一种多功能光电材料, 在可见光范围内具有高速光折变响应, 以及良好的压电、声光、磁光, 旋光和电光等性能。目前, 提拉法生长Bi12GeO20晶体, 存在生长成本高、晶锭形状不规则、生长产率低、晶体光学质量差和有效晶体截面小等问题。本研究率先采用改进的坩埚下降法, 在铂金坩埚和空气气氛中生长大尺寸Bi12GeO20晶体。通过各种分析测试方法研究生长获得的Bi12GeO20晶体中宏观缺陷的形态、分布和成分构成, 探讨了晶体生长过程中主要宏观缺陷的形成过程和成因。坩埚下降法生长的Bi12GeO20晶体存在两种主要宏观缺陷:枝蔓状和管状包裹体。其中, 枝蔓状包裹体与铂金溶蚀后的析晶相关, 而管状包裹体与铂金析出、接种界面不稳定性和温度波动有关。本研究提出了消除坩埚下降法生长晶体中宏观缺陷的技术途径, 通过降低生长控制温度、缩短高温熔体保持时间和优选籽晶等措施, 可重复地生长光学质量良好、55 mm× 55 mm× 80 mm的大尺寸Bi12GeO20晶体, 显著提升晶体的光学透过性能。
中图分类号:
齐雪君, 张健, 陈雷, 王绍涵, 李翔, 杜勇, 陈俊锋. 坩埚下降法生长大尺寸Bi12GeO20晶体的宏观缺陷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 280-287.
QI Xuejun, ZHANG Jian, CHEN Lei, WANG Shaohan, LI Xiang, DU Yong, CHEN Junfeng. Macroscopic Defects of Large Bi12GeO20 Crystals Grown Using Vertical Bridgman Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 280-287.
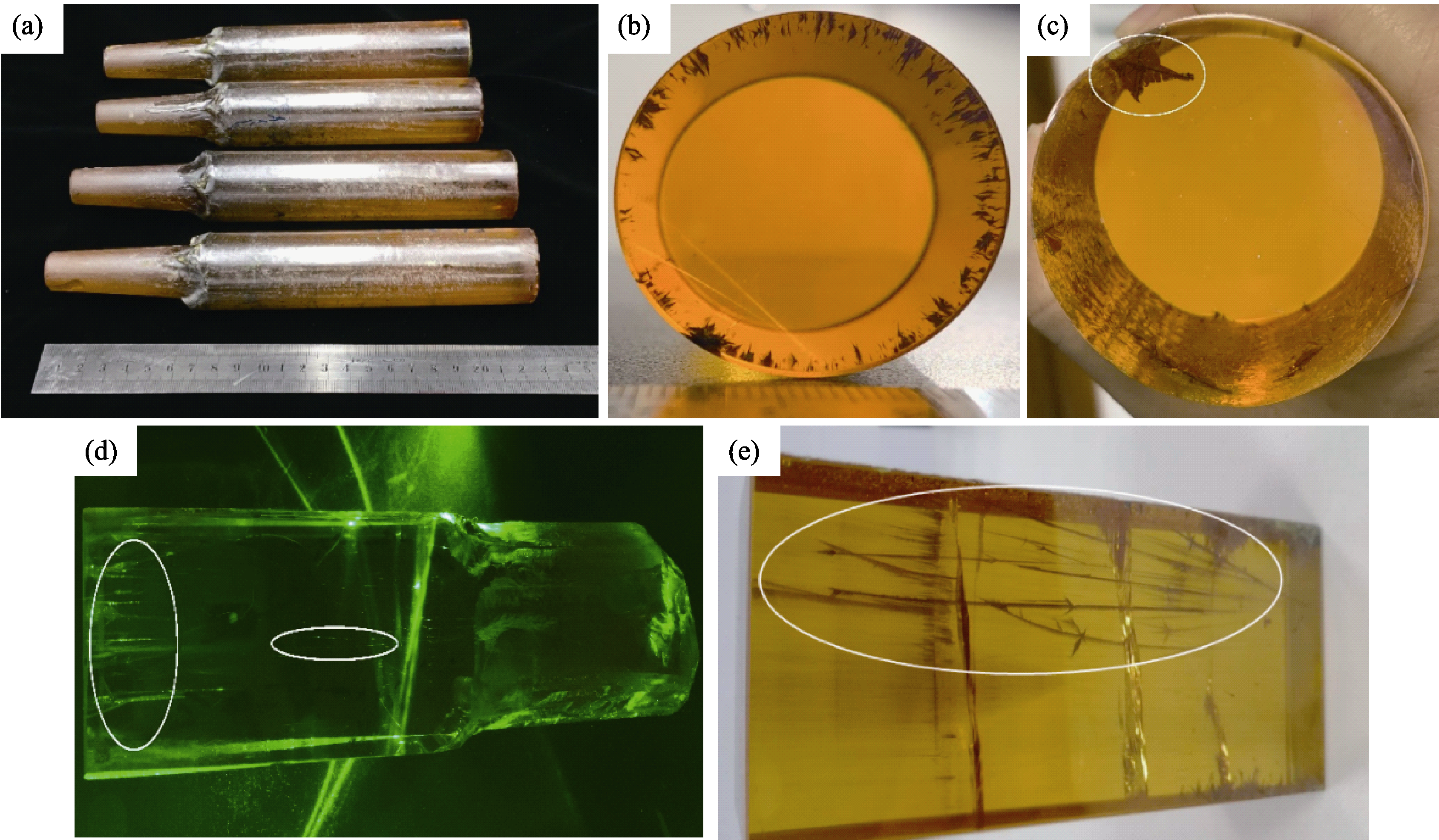
图2 Bi12GeO20晶锭中的宏观缺陷
Fig. 2 Macroscopic defects in as-grown Bi12GeO20 crystal ingots (a) As-grown Bi12GeO20 crystal ingots; (b, c) Dendritic inclusions; (d) Tubular scattering defects under the illumination of 532 nm laser light; (e) Tubular inclusions in polished crystals
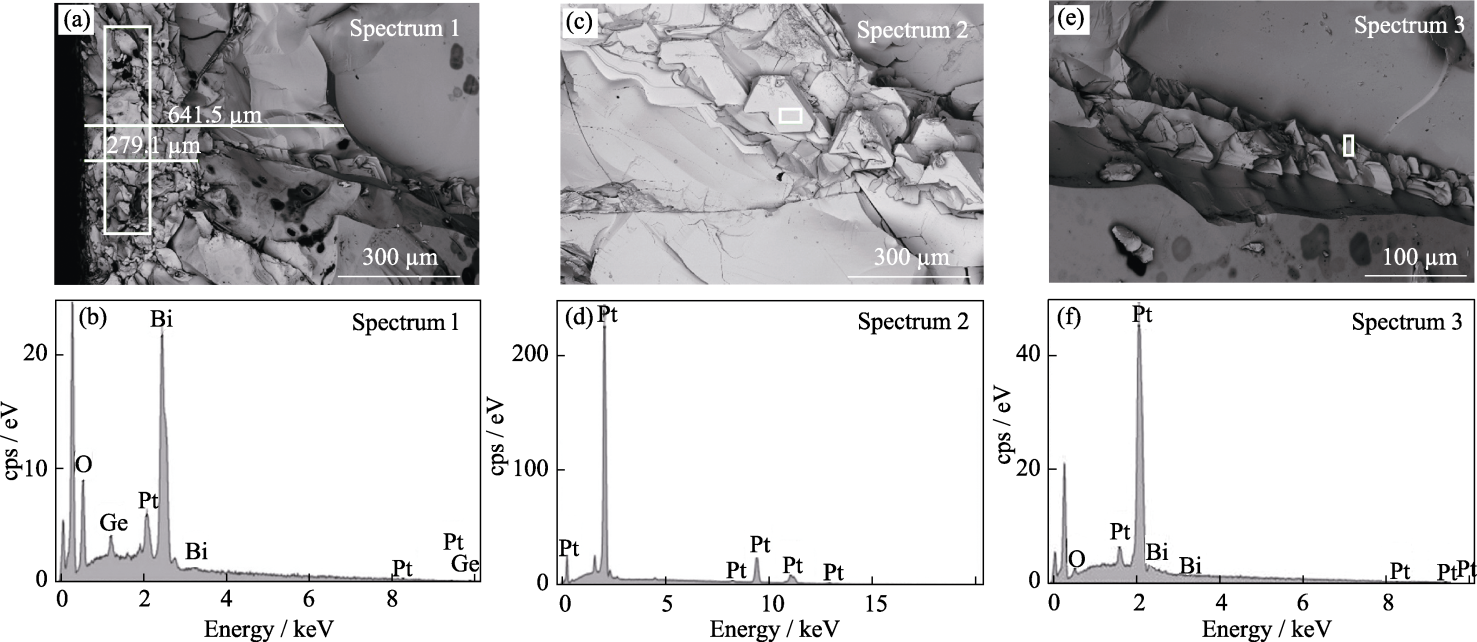
图4 Bi12GeO20晶体中枝蔓包裹体的SEM形貌(a, c, e)和EDS图谱(b, d, f)
Fig. 4 SEM images (a, c, e) and EDS spectra (b, d, f) of dendritic inclusions in Bi12GeO20 crystals
| Spectrum | Pt/% | Bi/% | Ge/% | O/% | Bi/Ge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.85 | 39.57 | 3.15 | 50.43 | 12.56 |
| 2 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 3 | 88.20 | 2.08 | 0 | 9.72 | - |
| Matrix | 0 | 36.27 | 3.11 | 60.62 | 11.66 |
表1 Bi12GeO20晶体中枝蔓包裹体的SEM-EDS成分分析结果(原子分数)
Table 1 SEM-EDS composition analysis results of dendritic inclusions in Bi12GeO20 crystal (in atomic)
| Spectrum | Pt/% | Bi/% | Ge/% | O/% | Bi/Ge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.85 | 39.57 | 3.15 | 50.43 | 12.56 |
| 2 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 3 | 88.20 | 2.08 | 0 | 9.72 | - |
| Matrix | 0 | 36.27 | 3.11 | 60.62 | 11.66 |
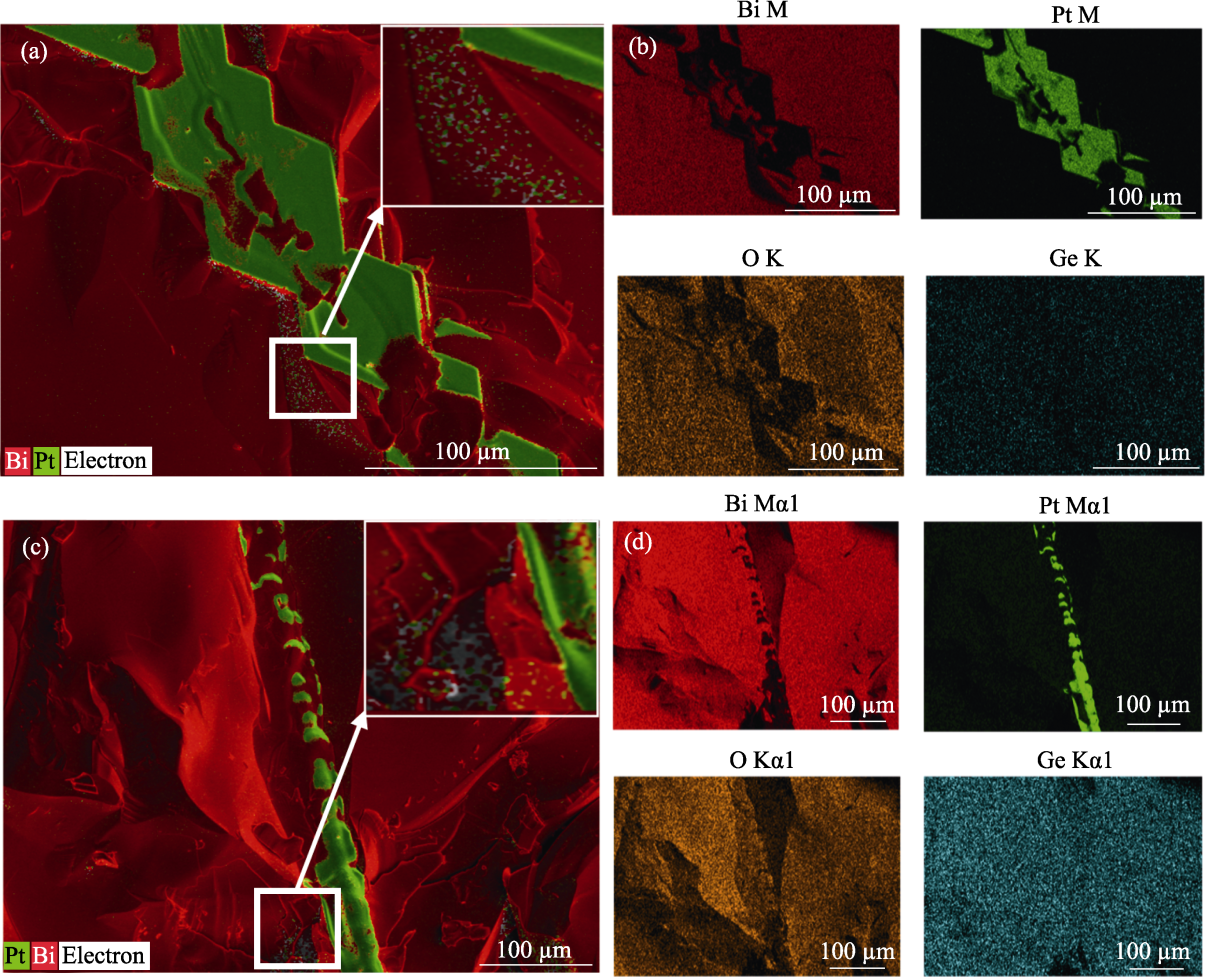
图5 Bi12GeO20晶体中枝蔓包裹体的SEM-EDS元素分布图
Fig. 5 Elemental mappings of the dendritic inclusions in Bi12GeO20 crystal at the microstructural level by scanning electron microscope (SEM) with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS) (a, c) Mappings of Bi, Pt, O, Ge; (b, d) Respective mappings of Bi, Pt, O, Ge
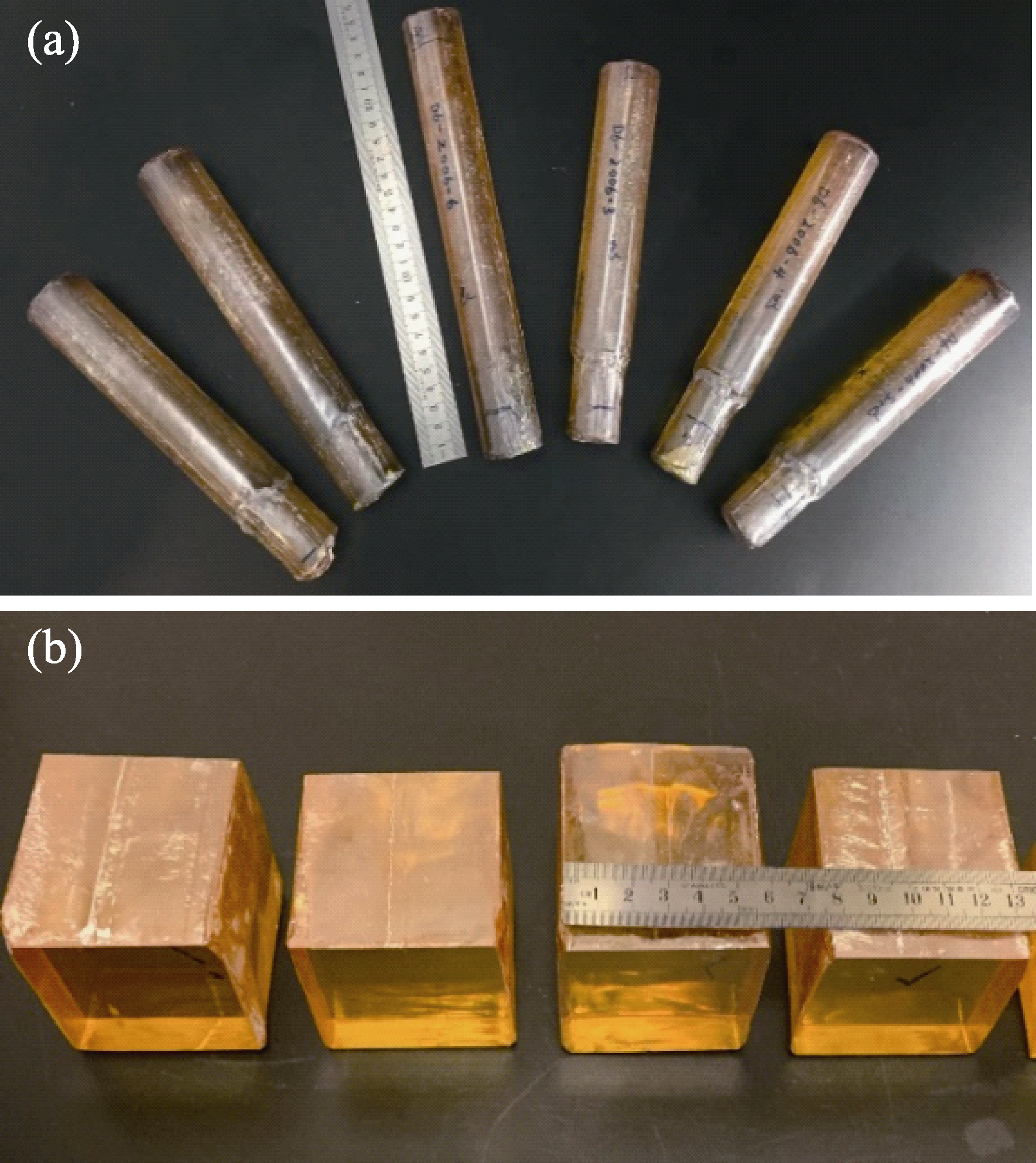
图8 ϕ35 mm (a)和55 mm×55 mm (b)截面的Bi12GeO20晶锭的照片
Fig. 8 Pictures of as-grown Bi12GeO20 crystal boules with cross-sections of ϕ35 mm (a), and 55 mm×55 mm (b)
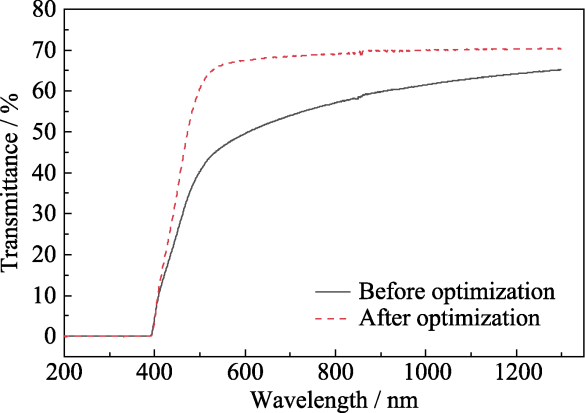
图9 工艺改进前后生长Bi12GeO20晶体的光学透过谱图
Fig. 9 Transmittance spectra of Bi12GeO20 crystals grown before and after growth parameters optimization Light path: 1 mm
| [1] |
SKORIKOV V M, KARGIN Y F, EGORYSHEVA A V, et al. Growth of sillenite-structure single crystals. Inorganic Materials, 2005, 41: S24.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DELICE S, ISIK M, GASANLY N M, et al. Structural and temperature-tuned optical characteristics of Bi12GeO20 sillenite crystals. Chinese Journal of Physics, 2020, 66: 422.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ISIK M, SURUCU G, GENCER A, et al. First principles study of Bi12GeO20: electronic, optical and thermodynamic characterizations. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 27: 102299.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LAZAREVIC Z Z, MIHAILOVIC, et al. Determination of magneto-optical quality and refractive index of bismuth germanium oxide single crystals grown by Czochralski technique. Optical Materials, 2012, 34: 1849.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BERMÚDEZ V, BUDENKOVA O N, YUFEREV V S, et al. Effect of the shouldering angle on the shape of the solid-liquid interface and temperature fields in sillenite-type crystals growth. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 279(1/2): 82.
DOI URL |
| [6] | WANG X, PANG C, HU S. Growth of large Bi12GeO20 crystals with plano-interfaces. Piezoelectrics & Acoustooptics, 1984(1): 24. |
| [7] |
SHLEGEL V N, PANTSURKIN D S. Growth of Bi12Ge20 and Bi12SiO20crystals by the low-thermal gradient Czochralski technique. Crystallography Reports, 2011, 56(2): 339.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SANTOS M T, ARIZMENDI L, BRAVO D, et al. Analysis of the core in Bi12SiO20 and Bi12GeO20 crystals grown by the Czochralski method. Materials Research Bulletin, 1996, 31(4): 389.
DOI URL |
| [9] | LI M, QIANG L, XU Y, et al. Growth and properties of Bi12GeO20 crystal. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 1992, 21(4): 349. |
| [10] |
BUDENKOVA O N, VASILIEV M G, SHLEGEL V N, et al. Comparative analysis of the heat transfer processes during growth of Bi12GeO20 and Bi4Ge3O12 crystals by the low-thermal-gradient Czochralski technique. Crystallography Reports, 2005, 50(1): S100.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHANG Y, LIU Y, JIANG W, et al. Vertical Bridgman growth of Bi12SiO20crystal with axial vibration. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310: 5432.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
UEDA T, HIGUCHI M, KODAIRA K. Growth of Bi12GeO20 single crystals by the pulling-down method with a continuous powder feed system. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2001, 109(7): 627.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
XU X W, LIAO J Y, SHEN B F, et al. Bi12SiO20 single-crystal growth by the Bridgman method. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1993, 133(3/4): 267.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHANG A, XU J, FAN S. Bridgman growth and platinum-related defects of Bi12SiO20 crystals. Chemical Research, 2004, 15(3): 5. |
| [15] |
CORSMIT G, VAN DRIEL M A, ELSENAAR R J, et al. Thermal analysis of bismuth germanate compounds. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1986, 75(3): 551.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KAPLUN A B, MESHALKIN A B. Stable and metastable phase equilibrium in system Bi2O3-GeO2. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1996, 167(1/2): 171.
DOI URL |
| [17] | COYA C, FIERRO J, ZALDO C. Thermal reduction of sillenite and eulite single crystals. Journal of Physics & Chemistry of Solids, 1997, 58(9): 1461. |
| [18] | YIN Z W, XUE Z L, HU G Q, et al. Studies on the macro-defects in BGO single crystals. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1991, 6(4): 391. |
| [19] | YAO D, QI X, SONG G, et al. Defects and performances of Bi4Ge3O12crystal-(1) defects and its formation. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2004, 33(6): 940. |
| [20] |
JACKSON K A. Constitutional supercooling surface roughening. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 264(4): 519.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
BORISOV A, DANYUSHEVSKY L. The effect of silica contents on Pd, Pt and Rh solubilities in silicate melts: an experimental study. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2011, 23(3): 355.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SANZ O, HARO-PONIATOWSKI E, GONZALO J, et al. Influence of the melting conditions of heavy metal oxide glasses containing bismuth oxide on their optical absorption. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006, 352(8): 761.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
DENISOV V M, PODKOPAEV O I, DENISOVA L T, et al. Contact interaction of the Bi12GeO20, Bi12SiO20, and Bi4Ge3O12melts with noble metals. Russian Metallurgy (Metally), 2014, 2014(2): 97.
DOI URL |
| [24] | DENISOVA L T, PASTUKHOV E A, ISTOMIN S A, et al. Wetting of noble metals by Bi2O3-based melts. Russian Metallurgy Metally C/c of Izvestiia Akademiia Nauk Sssr Metally, 2014, 2014(8): 647. |
| [25] |
YUAN L Y, NI H H, CHEN J F, et al. Experimental verification of vacancy defects and their vital role on reddish Bi4Ge3O12 single crystals. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2022, 61(SB): SB1017.
DOI |
| [26] | ZHONG W, LUO H, CAO H, et al. Formation of dendrite growth related with the growth units of anion coordination polyhedra. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2002, 31(3): 5. |
| [27] |
NIE Y Z, XIE Y Q, PENG H J, et al. Ab initio thermodynamics of metals: Pt and Ru. Physica B-Condensed Matter, 2007, 395(1/2): 121.
DOI URL |
| [28] | HU Z, LV G, WANG X. Study of [100] orientation bismuth germanate single crystals for electroacoustics. Piezoelectrics & Acoustooptics, 1979(3): 14. |
| [29] |
ABRAHAMS S C, JAMIESON P B, BERNSTEIN J L. Crystal structure of piezoelectric bismuth germanium oxide Bi12GeO20. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1967, 47(10): 4034.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MOSQUERA E, KATIYAR R S, MARIN C. Vibrational study of the liquid structure of molten bismuth germanate (Bi12GeO20). Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2019, 100: 191.
DOI URL |
| [31] | SERGIO A S, FARIAS J B L M. Bonding and electronic structure of sillenites. Chemical Physics Letters, 2012, 533: 4. |
| [32] | ZHONG W, HUA S. Crystal habits of bismuth silicon oxide and their growth forms. Journal of the Chinese Ceramics Society, 1995, 23(2): 201. |
| [1] | 李宪珂, 张超逸, 黄林, 孙鹏, 刘波, 徐军, 唐慧丽. 高质量铟掺杂氧化镓单晶浮区法生长研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1384-1390. |
| [2] | 蔡豪, 汪琦航, 邹朝勇. 镁离子调控无定形碳酸钙制备一水碳酸钙结晶过程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1275-1282. |
| [3] | 郝永鑫, 秦娟, 孙军, 杨金凤, 李清连, 黄贵军, 许京军. 坩埚底角形状对提拉法生长同成分铌酸锂晶体的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1167-1174. |
| [4] | 秦娟, 梁丹丹, 孙军, 杨金凤, 郝永鑫, 李清连, 张玲, 许京军. 提拉法生长平肩同成分铌酸锂晶体的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 978-986. |
| [5] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [6] | 杨佳雪, 李雯, 王燕, 朱昭捷, 游振宇, 李坚富, 涂朝阳. Dy3+: Y3Al5O12晶体的光谱与黄色激光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 350-356. |
| [7] | 穆宏赫, 王鹏飞, 施宇峰, 张中晗, 武安华, 苏良碧. 热交换坩埚下降法制备大尺寸氟化铈晶体的热场设计与优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 288-295. |
| [8] | 吴振, 李慧芳, 张中晗, 张振, 李阳, 蓝江河, 苏良碧, 武安华. 面向磁光应用的CeF3晶体生长与性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 296-302. |
| [9] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [10] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [11] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [12] | 王海东, 王燕, 朱昭捷, 李坚富, LAKSHMINARAYANA Gandham, 涂朝阳. Dy3+掺杂SrGdGa3O7晶体的晶体生长, 结构、光学和可见光荧光特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1475-1482. |
| [13] | 金敏, 白旭东, 赵素, 张如林, 陈玉奇, 周丽娜. 坩埚下降法生长SnSe单晶及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 313-318. |
| [14] | 徐家跃, 李志超, 潘芸芳, 周鼎, 温丰, 马文军. 超化学计量比氧化铀晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1183-1192. |
| [15] | 李荣辉, 郏义征, 胡楠楠. 三维层级花状活性氧化铝纳米材料的制备及其除砷性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 553-559. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||