无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 544-552.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220532 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220532
所属专题: 【结构材料】热障与环境障涂层(202506)
范栋1,2( ), 钟鑫1(
), 钟鑫1( ), 王亚文1, 张振忠2(
), 王亚文1, 张振忠2( ), 牛亚然1, 李其连3, 张乐3, 郑学斌1
), 牛亚然1, 李其连3, 张乐3, 郑学斌1
收稿日期:2022-09-13
修回日期:2022-10-06
出版日期:2022-10-28
网络出版日期:2022-10-28
通讯作者:
钟 鑫, 助理研究员. E-mail: zhongxin@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:范 栋(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: fandong1998@126.com
基金资助:
FAN Dong1,2( ), ZHONG Xin1(
), ZHONG Xin1( ), WANG Yawen1, ZHANG Zhenzhong2(
), WANG Yawen1, ZHANG Zhenzhong2( ), NIU Yaran1, LI Qilian3, ZHANG Le3, ZHENG Xuebin1
), NIU Yaran1, LI Qilian3, ZHANG Le3, ZHENG Xuebin1
Received:2022-09-13
Revised:2022-10-06
Published:2022-10-28
Online:2022-10-28
Contact:
ZHONG Xin, assistant professor. E-mail: zhongxin@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:FAN Dong (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: fandong1998@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层(EBCs)有望应用于新一代高推重比航空发动机热端部件, 但是服役条件下的熔盐腐蚀成为限制其应用的瓶颈。CMAS组分和稀土硅酸盐的晶体结构等因素对其腐蚀行为产生显著影响。本工作以不同晶型的稀土硅酸盐涂层材料为研究对象, 采用大气等离子喷涂技术制备X1-Gd2SiO5、X2-RE2SiO5(RE=Y, Er)涂层, 并研究其在富Al2O3的CMAS熔盐环境(1400 ℃)的腐蚀行为与机制。结果表明, X2-RE2SiO5(RE=Y, Er)涂层耐蚀性能优于X1-Gd2SiO5涂层, 这与涂层材料的物相组成和晶体结构的稳定性等因素有关。经CMAS腐蚀25 h后, X1-Gd2SiO5涂层表面仅生成磷灰石相; X2-RE2SiO5涂层不仅生成磷灰石相, 涂层中的RE2O3还与CMAS中的Al2O3反应生成石榴石相。生成石榴石相可提高涂层表面CMAS中CaO、SiO2的相对含量, 促进磷灰石致密层的生成, 从而改善其耐蚀性能。
中图分类号:
范栋, 钟鑫, 王亚文, 张振忠, 牛亚然, 李其连, 张乐, 郑学斌. 富铝CMAS对稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 544-552.
FAN Dong, ZHONG Xin, WANG Yawen, ZHANG Zhenzhong, NIU Yaran, LI Qilian, ZHANG Le, ZHENG Xuebin. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Aluminum-rich CMAS on Rare-earth Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings:[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 544-552.
| Parameter | RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) |
|---|---|
| Primary Ar/(L·min-1) | 43 |
| Secondary H2/(L·min-1) | 12 |
| Carrier Ar/(L·min-1) | 2.3 |
| Spray distance/mm | 230 |
表1 等离子喷涂工艺参数
Table 1 Technical parameters used for plasma spraying
| Parameter | RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) |
|---|---|
| Primary Ar/(L·min-1) | 43 |
| Secondary H2/(L·min-1) | 12 |
| Carrier Ar/(L·min-1) | 2.3 |
| Spray distance/mm | 230 |
| XRF/(%,in mol) | CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMAS | 27.87 | 8.79 | 26.22 | 38.52 |
表2 CMAS粉体的XRF化学元素组成
Table 2 Chemical compositions of CMAS powders
| XRF/(%,in mol) | CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMAS | 27.87 | 8.79 | 26.22 | 38.52 |
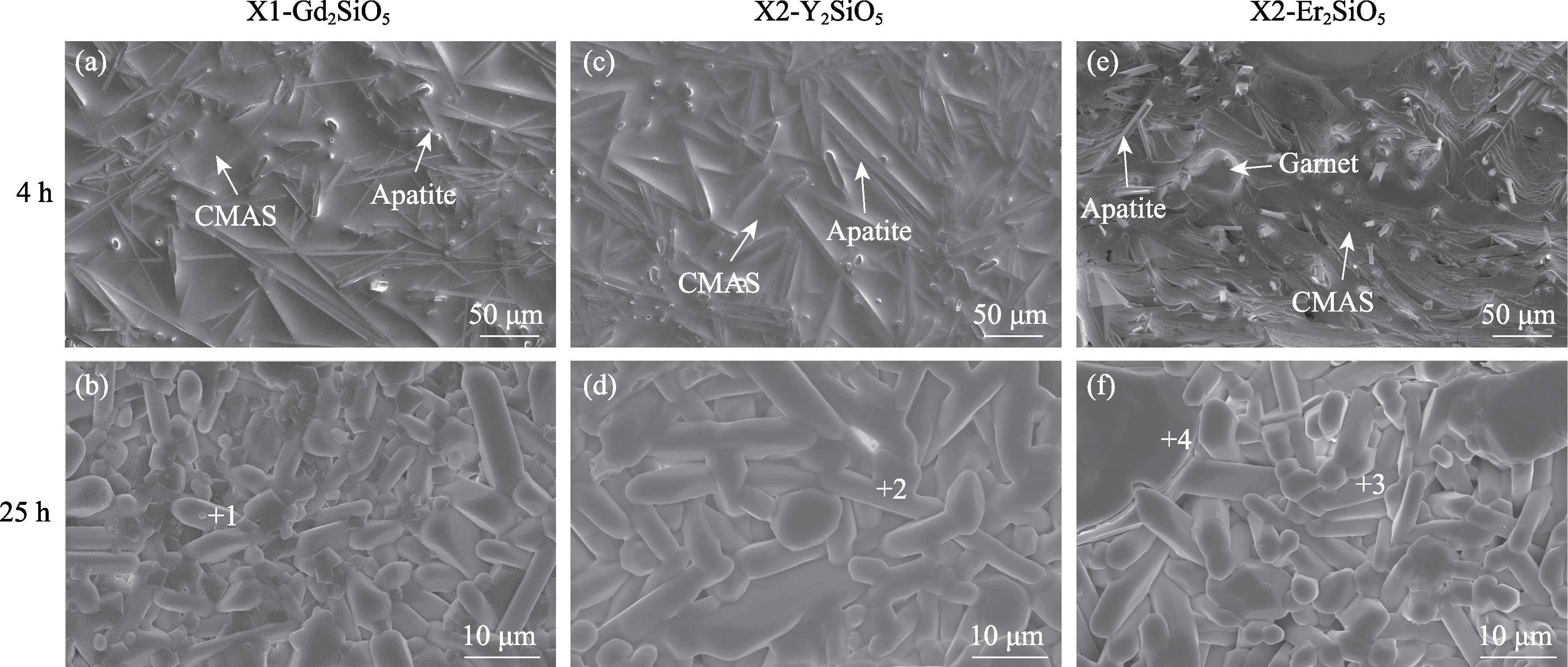
图3 涂层经CMAS腐蚀4和25 h后的表面形貌
Fig. 3 Surface microstructures of coatings after corrosion for 4 and 25 h (a-b) X1-Gd2SiO5; (c-d) X2-Y2SiO5; (e-f) X2-Er2SiO5
| EDS/ (%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 20.60 | — | — | 19.62 | 51.73 | 8.02 | — | — |
| Point 2 | — | 26.04 | — | 17.55 | 50.57 | 5.83 | — | — |
| Point 3 | — | — | 26.95 | 15.16 | 50.78 | 7.10 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 14.03 | — | 5.72 | 52.27 | 4.01 | 20.31 | 3.66 |
表3 图3中标记区域的EDS元素组成
Table 3 EDS elemental compositions of the marked regions in Fig. 3
| EDS/ (%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 20.60 | — | — | 19.62 | 51.73 | 8.02 | — | — |
| Point 2 | — | 26.04 | — | 17.55 | 50.57 | 5.83 | — | — |
| Point 3 | — | — | 26.95 | 15.16 | 50.78 | 7.10 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 14.03 | — | 5.72 | 52.27 | 4.01 | 20.31 | 3.66 |
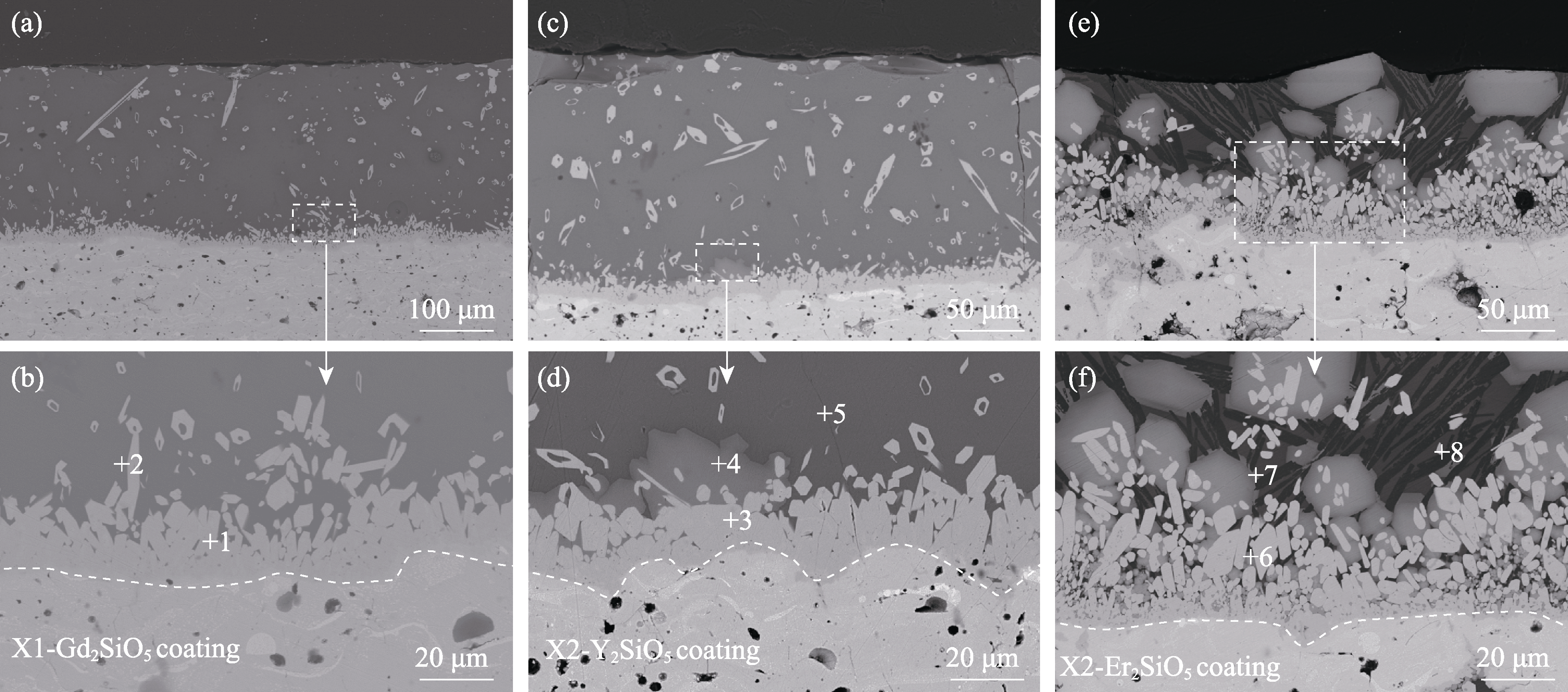
图4 涂层经CMAS腐蚀4 h后的截面形貌
Fig. 4 Cross-sectional microstructures of coatings after CMAS corrosion for 4 h (a, b) X1-Gd2SiO5; (c, d) X2-Y2SiO5; (e, f) X2-Er2SiO5
| EDS/(%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 19.21 | — | —- | 11.70 | 60.65 | 8.44 | — | — |
| Point 2 | 1.16 | — | — | 13.06 | 59.37 | 13.78 | 10.18 | 2.45 |
| Point 3 | — | 15.29 | — | 16.00 | 61.82 | 6.89 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 7.18 | — | 15.50 | 50.17 | 9.58 | 12.14 | 5.43 |
| Point 5 | — | 0.96 | — | 13.56 | 59.62 | 13.03 | 10.40 | 2.42 |
| Point 6 | — | — | 20.27 | 12.11 | 61.12 | 6.50 | — | — |
| Point 7 | — | — | 8.70 | 10.95 | 59.15 | 8.09 | 10.95 | 4.65 |
| Point 8 | — | — | 0.92 | 3.29 | 58.74 | 19.61 | 3.29 | 2.07 |
表4 中标记区域的EDS元素组成
Table 4 EDS elemental compositions of the marked regions in Fig. 4
| EDS/(%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 19.21 | — | —- | 11.70 | 60.65 | 8.44 | — | — |
| Point 2 | 1.16 | — | — | 13.06 | 59.37 | 13.78 | 10.18 | 2.45 |
| Point 3 | — | 15.29 | — | 16.00 | 61.82 | 6.89 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 7.18 | — | 15.50 | 50.17 | 9.58 | 12.14 | 5.43 |
| Point 5 | — | 0.96 | — | 13.56 | 59.62 | 13.03 | 10.40 | 2.42 |
| Point 6 | — | — | 20.27 | 12.11 | 61.12 | 6.50 | — | — |
| Point 7 | — | — | 8.70 | 10.95 | 59.15 | 8.09 | 10.95 | 4.65 |
| Point 8 | — | — | 0.92 | 3.29 | 58.74 | 19.61 | 3.29 | 2.07 |
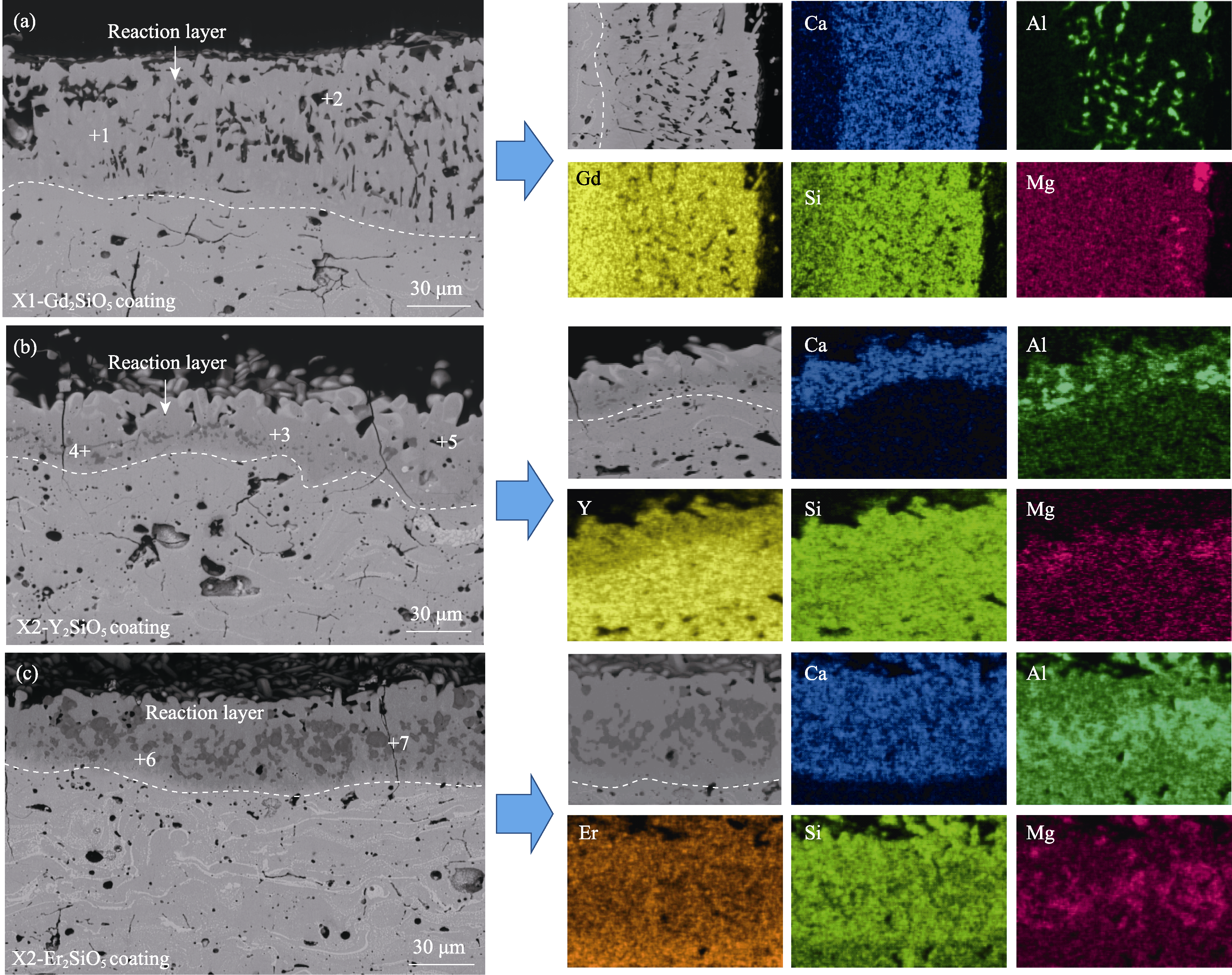
图5 X1-Gd2SiO5与X2-RE2SiO5(RE=Y, Er)涂层腐蚀25 h后的截面形貌
Fig. 5 Cross-sectional microstructures of the X1-Gd2SiO5 coating after corrosion for 25 h (a) X1-Gd2SiO5; (b) X2-Y2SiO5; (c) X2-Er2SiO5
| EDS/ (%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 24.48 | — | — | 16.22 | 51.61 | 7.68 | — | — |
| Point 2 | 1.05 | — | — | 12.62 | 59.63 | 14.25 | 9.78 | 2.66 |
| Point 3 | — | 26.70 | — | 15.78 | 50.12 | 7.40 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 17.10 | — | 8.23 | 51.25 | 2.92 | 16.41 | 4.09 |
| Point 5 | — | 0.94 | — | 14.23 | 57.36 | 13.94 | 11.98 | 1.54 |
| Point 6 | — | — | 28.80 | 12.77 | 52.22 | 6.22 | — | — |
| Point 7 | — | — | 7.12 | 13.05 | 49.26 | 7.08 | 18.26 | 5.24 |
表5 图5中标记区域的EDS元素组成
Table 5 EDS elemental compositions of the marked regions in Fig. 5
| EDS/ (%, in atom) | Gd | Y | Er | Si | O | Ca | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 24.48 | — | — | 16.22 | 51.61 | 7.68 | — | — |
| Point 2 | 1.05 | — | — | 12.62 | 59.63 | 14.25 | 9.78 | 2.66 |
| Point 3 | — | 26.70 | — | 15.78 | 50.12 | 7.40 | — | — |
| Point 4 | — | 17.10 | — | 8.23 | 51.25 | 2.92 | 16.41 | 4.09 |
| Point 5 | — | 0.94 | — | 14.23 | 57.36 | 13.94 | 11.98 | 1.54 |
| Point 6 | — | — | 28.80 | 12.77 | 52.22 | 6.22 | — | — |
| Point 7 | — | — | 7.12 | 13.05 | 49.26 | 7.08 | 18.26 | 5.24 |
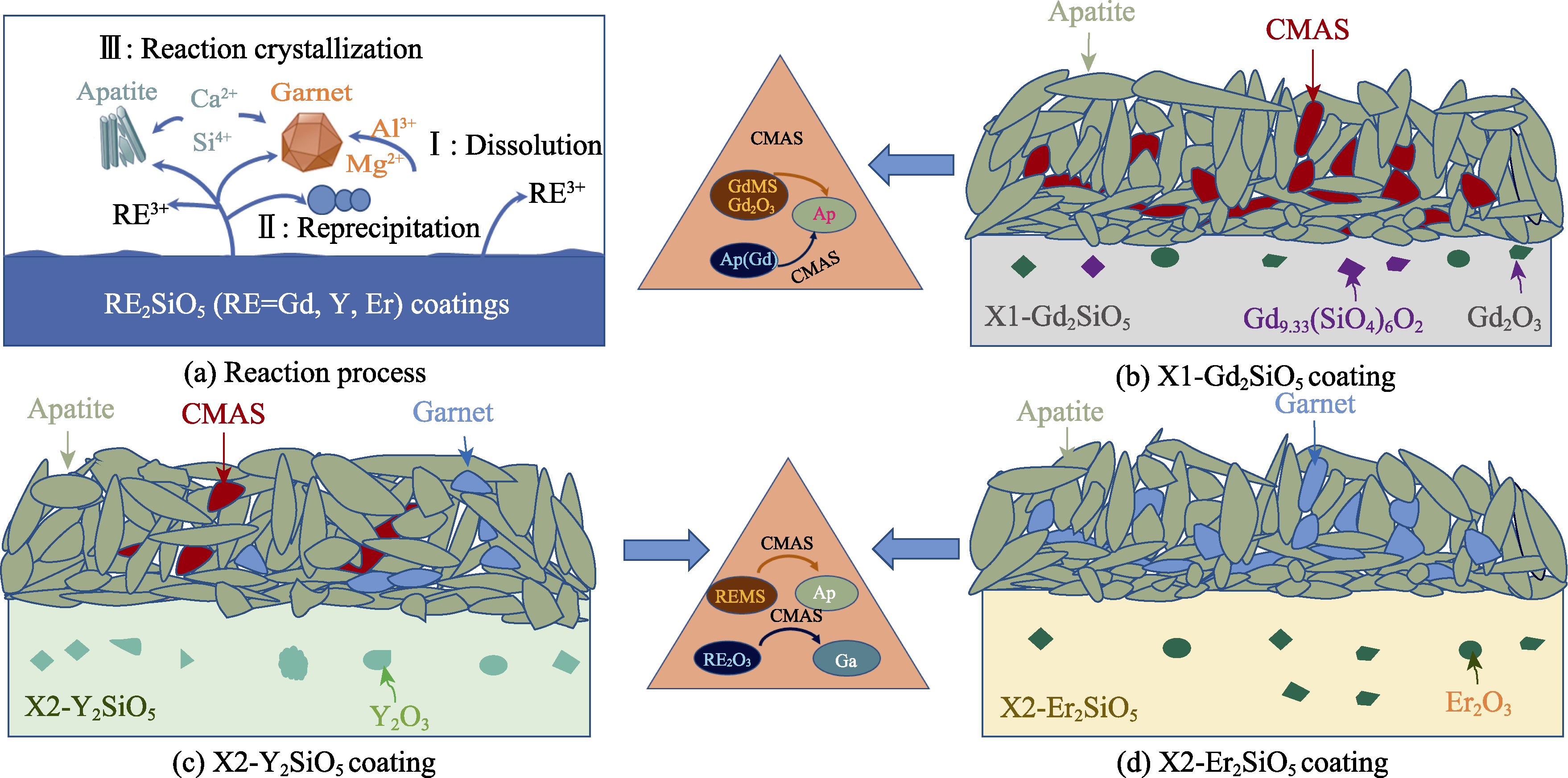
图6 不同涂层在1400 ℃下CMAS熔盐腐蚀的示意图
Fig. 6 Schematic diagrams of different coatings under CMAS molten salt corrosion at 1400 ℃ (a) Reaction process; (b) X1-Gd2SiO5; (c) X2-Y2SiO5; (d) X2-Er2SiO5
| [1] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 804.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
RAJ R. Fundamental research in structural ceramics for service near 2000 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1993, 76(9): 2147.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
EATON H E, LINSEY G D. Accelerated oxidation of SiC CMC's by water vapor and protection via environmental barrier coating approach. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(14-15): 2741.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LIU P P, ZHONG X, ZHANG L, et al. Molten salt corrosion behaviors and mechanisms of ytterbium silicate environmental barrier coating. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1267.
DOI |
| [5] |
OPILA E J. Oxidation and volatilization of silica formers in water vapor. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2003, 86(8): 1238.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG X F, SONG J B, DENG Z Q, et al. Interface evolution of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5 PS-PVD environmental barrier coatings under high temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1478.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TIAN Z L, ZHENG L Y, WANG J M, et al. Theoretical and experimental determination of the major thermo-mechanical properties of RE2SiO5 (RE= Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, and Y) for environmental and thermal barrier coating applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(1): 189.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, LIU M, et al. Preparation of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5environment barrier coating (EBC) by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD). Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 325.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SUMMERS W D, POERSCHKE D L, TAYLOR A A, et al. Reactions of molten silicate deposits with yttrium monosilicate. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(4): 2919. |
| [10] |
STOLZENBURG F, KENESEI P, ALMER J, et al. The influence of calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate deposits on internal stresses in Yb2Si2O7 multilayer environmental barrier coatings. Acta Materialia, 2016, 105: 189.
DOI URL |
| [11] | WANG C, ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, et al. Nano-composite structured environmental barrier coatings prepared by plasma spray- physical vapor deposition and their thermal cycle performance. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(11): 3455. |
| [12] |
LI G, QIN L, CAO X Q, et al. Water vapor corrosion resistance and failure mechanism of SiCf/SiC composites completely coated with plasma sprayed tri-layer EBCs. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(5): 7082.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LEE K N. Yb2Si2O7 Environmental barrier coatings with reduced bond coat oxidation rates via chemical modifications for long life. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(3): 1507.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG J G, TIAN S J, LI G B, et al. Preparation and X-ray characterization of low-temperature phases of R2SiO5 (R=rare earth elements). Materials of Research Bulletin, 2001, 36: 1855.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WOLF M, MACK D E, GUILLO O, et al. Resistance of pure and mixed rare earth silicates against calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate (CMAS): a comparative study. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(12): 7056.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIANG F R, CHENG L F, WANG Y G. Hot corrosion of RE2SiO5 with different cation substitution under calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate attack. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(12): 9019.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHONG X, WANG Y W, LIU P P, et al. Effects of microstructure on corrosion behaviors for RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) environmental barrier coatings against calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate melts. Corrosion Science, 2022, 199: 110174.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TIAN Z L, REN X M, LEI Y M, et al. Corrosion of RE2Si2O7 (RE = Y, Yb, and Lu) environmental barrier coating materials by molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate glass at high temperatures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(14): 4245.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU P P, ZHONG X, NIU Y R, et al. Reaction behaviors and mechanisms of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si environmental barrier coatings with molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate. Corrosion Science, 2022, 197: 110069.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
STOKES J L, HARDER B J, WIESNER V L, et al. Effects of crystal structure and cation size on molten silicate reactivity with environmental barrier coating materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 103(1): 622.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SUMMERS W D, POERSCHKE D L, PARK D, et al. Roles of composition and temperature in silicate deposit-induced recession of yttrium disilicate. Acta Materialia, 2018, 160: 34.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LEVI C G, JOHN W H, MARIE V S, et al. Environmental degradation of thermal barrier coatings by molten deposits. MRS Bulletin, 2012, 37: 932.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
BONDAR I A, Rare-earth silicates. Ceramics International, 1982, 8: 83.
DOI URL |
| [24] | FELSCHE J. The crystal chemistry of the rare-earth silicates. Materials Science and Chemistry, 1973, 13: 99. |
| [25] |
ZHONG X, NIU Y R, LI H, et al. Microstructure evolution and thermomechanical properties of plasma-sprayed Yb2SiO5 coating during thermal aging. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 2017, 100(5): 1896.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
POERSCHKE D L, JACKSON R W, LEVI C G. Silicate deposit degradation of engineered coatings in gas turbines: progress toward models and materials solutions. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2017, 47: 297.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI Y R, WANG J M, WANG J Y. Theoretical investigation of phonon contributions to thermal expansion coefficients for rare earth monosilicates RE2SiO5 (RE = Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu). Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(7): 2658.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 梁锐辉, 钟鑫, 洪督, 黄利平, 牛亚然, 郑学斌. Yb2O3改性硅黏结层的环境障涂层体系耐高温水氧腐蚀行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 425-432. |
| [2] | 樊文楷, 杨潇, 李宏华, 李永, 李江涛. 无压烧结制备(Y0.2Gd0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7高熵陶瓷及其高温抗CMAS腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 159-167. |
| [3] | 李刘媛, 黄开明, 赵秀艺, 刘会超, 王超. RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相对高熵稀土双硅酸盐微结构及耐CMAS腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 793-802. |
| [4] | 李捷, 罗志新, 崔阳, 张广珩, 孙鲁超, 王京阳. 大气等离子喷涂Y3Al5O12/Al2O3陶瓷涂层的CMAS腐蚀抗力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 671-680. |
| [5] | 罗淑文, 马名生, 刘峰, 刘志甫. Ca-B-Si体系LTCC材料腐蚀行为及腐蚀机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [6] | 刘平平, 钟鑫, 张乐, 李红, 牛亚然, 张翔宇, 李其连, 郑学斌. 硅酸镱环境障涂层抗熔盐腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1267-1274. |
| [7] | 孙鲁超, 任孝旻, 杜铁锋, 罗颐秀, 张洁, 王京阳. 高熵化设计: 稀土硅酸盐材料关键性能优化新策略[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 339-346. |
| [8] | 范佳锋,张小锋,周克崧,刘敏,邓畅光,邓春明,牛少鹏,邓子谦. 镀铝改性对PS-PVD 7YSZ热障涂层抗CMAS腐蚀影响机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 938-946. |
| [9] | 王鹏, 王庆雷, 张翔宇, 杨金山, 周海军, 胡建宝, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 层状硅酸钇改性SiCf/SiC复合材料湿氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 904-908. |
| [10] | 张小锋, 周克崧, 刘敏, 邓春明, 牛少鹏, 许世鸣. 等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积Si/莫来石/Yb2SiO5环境障涂层[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 325-330. |
| [11] | 张小锋, 周克崧, 宋进兵, 邓春明, 牛少鹏, 邓子谦. 等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积7YSZ热障涂层沉积机理及 其CMAS腐蚀失效机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| [12] | 关永军,夏原. 铝合金表面等离子体电解氧化陶瓷涂层在NaCl溶液中的电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 784-788. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||