无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 793-802.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240018 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240018
所属专题: 【结构材料】热障与环境障涂层(202506); 【结构材料】高熵陶瓷(202506)
收稿日期:2024-01-30
修回日期:2024-03-06
出版日期:2024-07-20
网络出版日期:2024-03-08
作者简介:李刘媛(1987-), 女, 硕士, 高级工程师. E-mail: liuyuanwuming@163.com
LI Liuyuan1( ), HUANG Kaiming1, ZHAO Xiuyi2, LIU Huichao2, WANG Chao2
), HUANG Kaiming1, ZHAO Xiuyi2, LIU Huichao2, WANG Chao2
Received:2024-01-30
Revised:2024-03-06
Published:2024-07-20
Online:2024-03-08
About author:LI Liuyuan (1987-), female, Master, senior engineer. E-mail: liuyuanwuming@163.com
摘要:
环境障涂层是高功重比航空发动机的关键技术, 其目的是阻挡燃气及环境腐蚀介质的侵蚀, 为陶瓷基复合材料热端部件提供有效保护。目前, 高熵稀土双硅酸盐((xRE1/x)2Si2O7)是最具潜力的新一代环境障涂层材料。为了进一步提升高熵稀土双硅酸盐的耐高温(1500 ℃)CMAS(CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2)腐蚀能力, 本工作设计制备了一种新型高熵(Y0.25Yb0.25Er0.25Tm0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O(RE=Yb、Y、La)复相陶瓷。结果表明, 在复相陶瓷中, RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相不仅能够包裹陶瓷晶粒, 而且能够促进稀土双硅酸盐晶粒长大, 减少晶界数量, 使CMAS熔体的渗入通道数量减少。同时, 随着RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相中稀土离子半径增大, 玻璃相更易与CMAS熔盐中的Ca2+离子反应, 生成磷灰石相, 降低CMAS熔体的活性, 抑制高温CMAS熔盐对高熵稀土双硅酸盐晶粒的侵蚀, 从而提高高熵稀土双硅酸盐的耐高温CMAS腐蚀能力。在1500 ℃腐蚀48 h后, (Y0.25Yb0.25Er0.25Tm0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷表面仍残留CMAS熔盐层, 表明该复相陶瓷具有良好的耐高温CMAS腐蚀能力。该复相陶瓷的微结构设计为增强环境障涂层材料在高温CMAS环境下的长期应用提供了一种新的思路。
中图分类号:
李刘媛, 黄开明, 赵秀艺, 刘会超, 王超. RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相对高熵稀土双硅酸盐微结构及耐CMAS腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 793-802.
LI Liuyuan, HUANG Kaiming, ZHAO Xiuyi, LIU Huichao, WANG Chao. Influence of RE-Si-Al-O Glass Phase on Microstructure and CMAS Corrosion Resistance of High Entropy Rare Earth Disilicates[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 793-802.

图1 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7陶瓷与(4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics and (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics

图2 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7陶瓷与(4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷的SEM照片及EDS谱图
Fig. 2 SEM images and EDS mappings of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics and (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics (a) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7; (b) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Yb-Si-Al-O; (c) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Y-Si-Al-O; (d) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O
| Spot | Y | Yb | Er | Tm | Si | O | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.54 | 3.55 | 3.49 | 3.40 | 19.29 | 65.73 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 2 | 4.42 | 4.31 | 5.48 | 4.09 | 18.99 | 62.71 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 3 | 4.49 | 4.19 | 4.23 | 4.06 | 19.27 | 63.76 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 4 | 5.18 | 5.69 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 21.41 | 56.94 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 5 | 4.26 | 1.84 | 2.13 | 2.11 | 17.51 | 72.15 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
表1 图2中各点的元素组成(%, 原子分数)
Table 1 Elemental composition of each point in Fig. 2 (%, in atom)
| Spot | Y | Yb | Er | Tm | Si | O | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.54 | 3.55 | 3.49 | 3.40 | 19.29 | 65.73 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 2 | 4.42 | 4.31 | 5.48 | 4.09 | 18.99 | 62.71 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 3 | 4.49 | 4.19 | 4.23 | 4.06 | 19.27 | 63.76 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 4 | 5.18 | 5.69 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 21.41 | 56.94 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
| 5 | 4.26 | 1.84 | 2.13 | 2.11 | 17.51 | 72.15 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
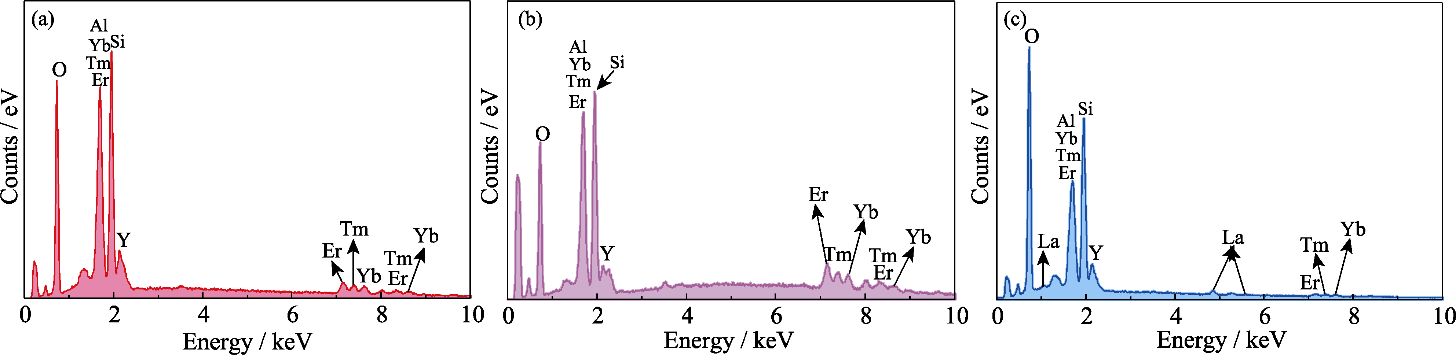
图3 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷中玻璃相的EDS谱图
Fig. 3 EDS patterns of glass phases in (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics (a) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Yb-Si-Al-O; (b) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Y-Si-Al-O; (c) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O

图4 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7陶瓷与(4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷在1300 ℃腐蚀48 h后的截面SEM照片
Fig. 4 Cross-sectional SEM images of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics and (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics after corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 48 h (a) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7; (b) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Yb-Si-Al-O; (c) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Y-Si-Al-O; (d) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | Sm | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 22.15 | 57.64 | 9.43 | 0.99 | 6.94 | CMAS | ||
| 2 | 2.85 | 2.78 | 2.67 | 2.19 | 21.16 | 52.94 | 13.05 | 2.36 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 6.06 | 5.55 | 5.23 | 3.81 | 21.75 | 57.60 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 4 | 1.91 | 1.89 | 2.02 | 1.24 | 23.55 | 58.21 | 11.18 | CMAS | ||||
| 5 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 23.43 | 58.28 | 8.82 | 0.90 | 6.42 | CMAS | ||
| 6 | 2.02 | 1.82 | 1.84 | 0.82 | 24.39 | 57.84 | 11.27 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||||
| 7 | 5.54 | 5.11 | 5.36 | 3.77 | 22.74 | 57.48 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 8 | 0.53 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 23.82 | 58.48 | 9.71 | 5.63 | Yb-Si-Al-O-Ca | |||
| 9 | 0.51 | 0.40 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 22.40 | 59.87 | 8.46 | 0.75 | 6.66 | CMAS | ||
| 10 | 1.79 | 1.90 | 1.98 | 0.95 | 23.72 | 58.85 | 10.81 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||||
| 11 | 5.98 | 4.92 | 4.89 | 3.56 | 21.68 | 58.97 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 12 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 23.14 | 59.04 | 8.50 | 0.27 | 7.74 | Y-Si-Al-O-Ca | ||
| 13 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 24.75 | 55.79 | 9.23 | 1.01 | 6.22 | 0.16 | CMAS | |
| 14 | 1.87 | 1.99 | 2.07 | 0.80 | 26.09 | 54.97 | 12.02 | 0.19 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 15 | 5.98 | 5.96 | 5.54 | 3.02 | 23.81 | 55.69 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 16 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 26.26 | 57.49 | 7.13 | 0.28 | 6.32 | 1.29 | La-Si-Al-O-Ca |
表2 图4中各点的元素组成(%, 原子分数)
Table 2 Elemental composition of each point in Fig. 4 (%, in atom)
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | Sm | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 22.15 | 57.64 | 9.43 | 0.99 | 6.94 | CMAS | ||
| 2 | 2.85 | 2.78 | 2.67 | 2.19 | 21.16 | 52.94 | 13.05 | 2.36 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 6.06 | 5.55 | 5.23 | 3.81 | 21.75 | 57.60 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 4 | 1.91 | 1.89 | 2.02 | 1.24 | 23.55 | 58.21 | 11.18 | CMAS | ||||
| 5 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 23.43 | 58.28 | 8.82 | 0.90 | 6.42 | CMAS | ||
| 6 | 2.02 | 1.82 | 1.84 | 0.82 | 24.39 | 57.84 | 11.27 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||||
| 7 | 5.54 | 5.11 | 5.36 | 3.77 | 22.74 | 57.48 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 8 | 0.53 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 23.82 | 58.48 | 9.71 | 5.63 | Yb-Si-Al-O-Ca | |||
| 9 | 0.51 | 0.40 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 22.40 | 59.87 | 8.46 | 0.75 | 6.66 | CMAS | ||
| 10 | 1.79 | 1.90 | 1.98 | 0.95 | 23.72 | 58.85 | 10.81 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||||
| 11 | 5.98 | 4.92 | 4.89 | 3.56 | 21.68 | 58.97 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 12 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 23.14 | 59.04 | 8.50 | 0.27 | 7.74 | Y-Si-Al-O-Ca | ||
| 13 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 24.75 | 55.79 | 9.23 | 1.01 | 6.22 | 0.16 | CMAS | |
| 14 | 1.87 | 1.99 | 2.07 | 0.80 | 26.09 | 54.97 | 12.02 | 0.19 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 15 | 5.98 | 5.96 | 5.54 | 3.02 | 23.81 | 55.69 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | |||||
| 16 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 26.26 | 57.49 | 7.13 | 0.28 | 6.32 | 1.29 | La-Si-Al-O-Ca |

图5 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7和RE-Si-Al-O与CMAS混合后在1300 ℃煅烧反应48 h后的XRD图谱
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 and RE-Si-Al-O mixed with CMAS after calcination at 1300 ℃ for 48 h (a) Mixture of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 and CMAS; (b) Mixture of RE-Si-Al-O and CMAS

图6 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7陶瓷与(4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷在1500 ℃腐蚀(a) 24和(b) 48 h后的XRD图谱
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics and (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics after corrosion at 1500 ℃ for (a) 24 and (b) 48 h

图7 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7陶瓷在1500 ℃腐蚀(a) 24和(b) 48 h后的截面SEM照片
Fig. 7 Cross-sectional SEM images of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics after corrosion at 1500 ℃ for (a) 24 and (b) 48 h (c) Partial enlargement of area in (b)
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.39 | 1.12 | 1.03 | 0.84 | 22.26 | 54.21 | 14.35 | 0.39 | 4.41 | CMAS | |
| 2 | 7.80 | 8.12 | 8.21 | 8.46 | 14.57 | 45.43 | 7.41 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 8.10 | 8.39 | 8.13 | 4.03 | 28.68 | 42.67 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
表3 图7中各点的元素组成(%, 原子分数)
Table 3 Elemental composition of each point in Fig. 7 (%, in atom)
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.39 | 1.12 | 1.03 | 0.84 | 22.26 | 54.21 | 14.35 | 0.39 | 4.41 | CMAS | |
| 2 | 7.80 | 8.12 | 8.21 | 8.46 | 14.57 | 45.43 | 7.41 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 8.10 | 8.39 | 8.13 | 4.03 | 28.68 | 42.67 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 |
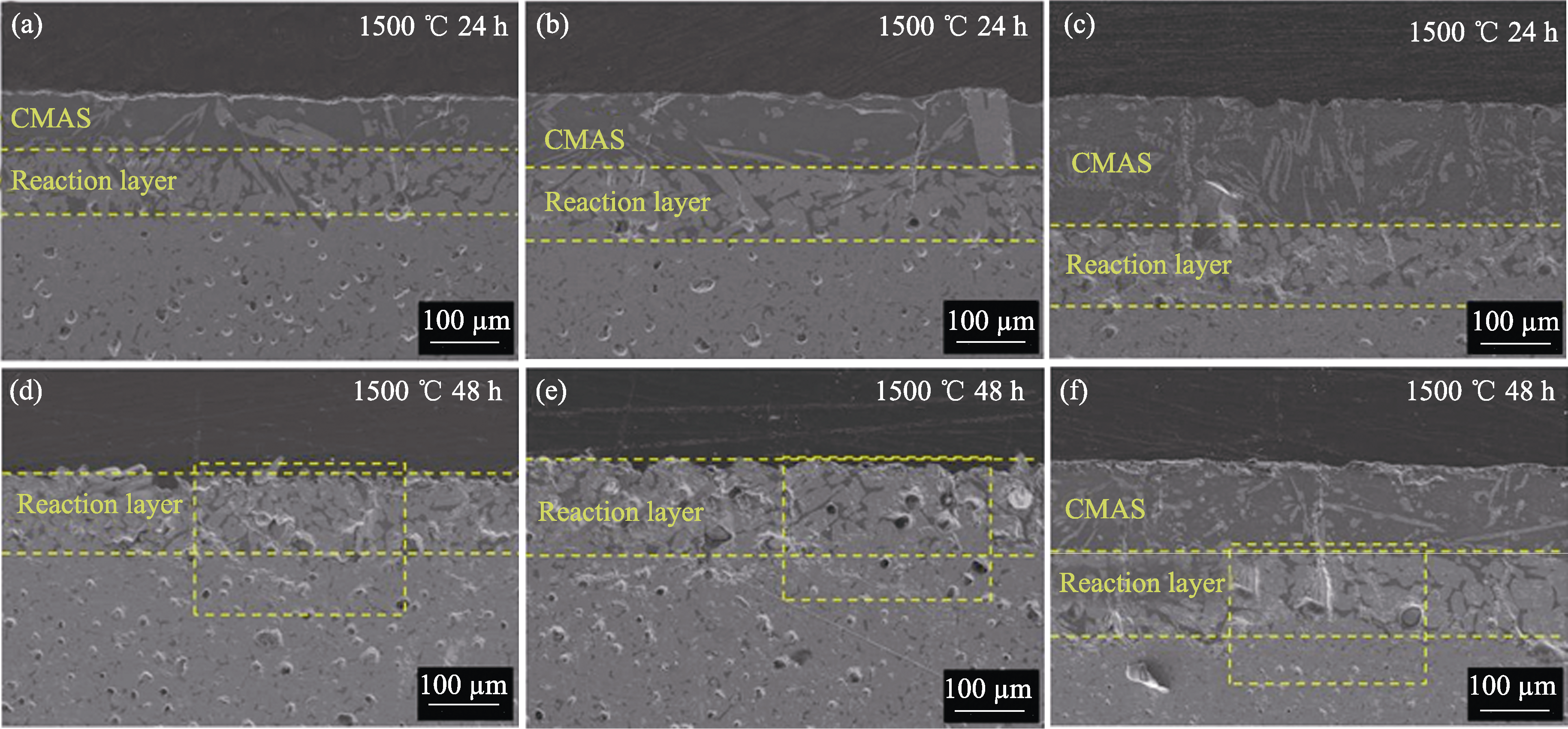
图8 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷在1500 ℃腐蚀24与48 h后的截面SEM照片
Fig. 8 Cross-sectional SEM images of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics after corrosion at 1500 ℃ for 24 and 48 h (a, d) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Yb-Si-Al-O; (b, e) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Y-Si-Al-O; (c, f) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O
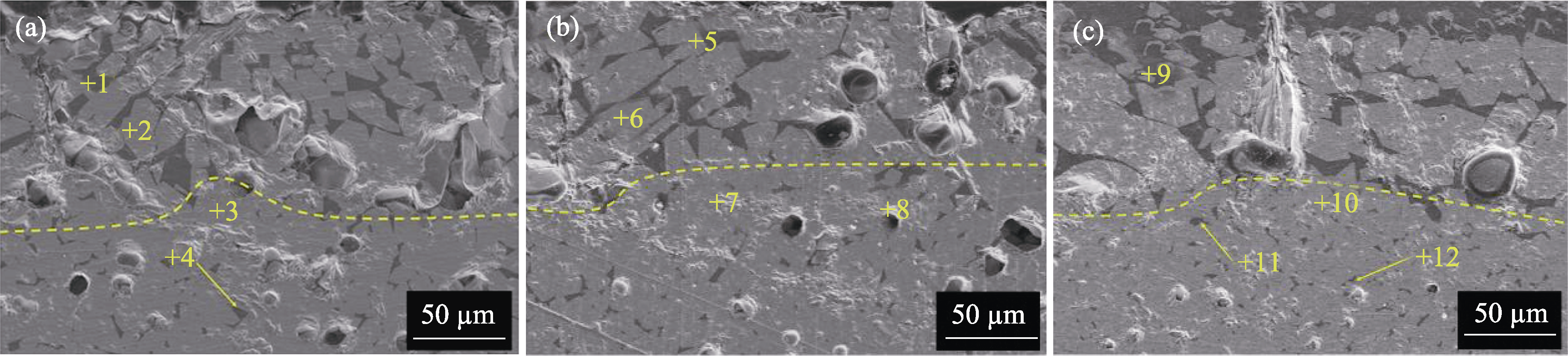
图9 (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O复相陶瓷在1500 ℃腐蚀48 h后局部放大的SEM照片
Fig. 9 Local enlarged SEM images of (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/RE-Si-Al-O multiphase ceramics after corrosion at 1500 ℃ for 48 h (a) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Yb-Si-Al-O; (b) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/Y-Si-Al-O; (c) (4RE0.25)2Si2O7/La-Si-Al-O
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.23 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 23.01 | 55.92 | 10.20 | 0.38 | 6.80 | CMAS | |
| 2 | 6.17 | 7.43 | 7.75 | 8.02 | 16.47 | 47.83 | 6.33 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 6.92 | 6.61 | 6.34 | 3.64 | 24.73 | 51.76 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 4 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 25.89 | 54.59 | 10.73 | 0.34 | 6.98 | Yb-Si-Al-O-Ca | |
| 5 | 1.01 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 24.10 | 55.69 | 9.65 | 0.22 | 6.86 | CMAS | |
| 6 | 5.92 | 6.23 | 6.52 | 6.94 | 16.85 | 52.31 | 5.23 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 7 | 5.27 | 5.35 | 5.64 | 3.77 | 23.11 | 56.86 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 8 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.41 | 24.03 | 56.45 | 9.70 | 0.43 | 6.89 | Y-Si-Al-O-Ca | |
| 9 | 5.61 | 5.82 | 6.15 | 6.43 | 15.97 | 53.99 | 5.02 | 1.01 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||
| 10 | 5.81 | 5.34 | 5.62 | 3.50 | 23.47 | 56.26 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 11 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 25.11 | 56.14 | 9.01 | 0.27 | 7.18 | 0.67 | La-Si-Al-O-Ca |
| 12 | 1.73 | 1.82 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 28.54 | 54.01 | 0.36 | 8.17 | 1.91 | La-Si-Al-O |
表4 图9中各点的元素组成(%, 原子分数)
Table 4 Elemental composition of each point in Fig. 9 (%, in atom)
| Spot | Yb | Tm | Er | Y | Si | O | Ca | Mg | Al | La | Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.23 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 23.01 | 55.92 | 10.20 | 0.38 | 6.80 | CMAS | |
| 2 | 6.17 | 7.43 | 7.75 | 8.02 | 16.47 | 47.83 | 6.33 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 3 | 6.92 | 6.61 | 6.34 | 3.64 | 24.73 | 51.76 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 4 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 25.89 | 54.59 | 10.73 | 0.34 | 6.98 | Yb-Si-Al-O-Ca | |
| 5 | 1.01 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 24.10 | 55.69 | 9.65 | 0.22 | 6.86 | CMAS | |
| 6 | 5.92 | 6.23 | 6.52 | 6.94 | 16.85 | 52.31 | 5.23 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | |||
| 7 | 5.27 | 5.35 | 5.64 | 3.77 | 23.11 | 56.86 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 8 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.41 | 24.03 | 56.45 | 9.70 | 0.43 | 6.89 | Y-Si-Al-O-Ca | |
| 9 | 5.61 | 5.82 | 6.15 | 6.43 | 15.97 | 53.99 | 5.02 | 1.01 | Ca2RE8(SiO4)6O2 | ||
| 10 | 5.81 | 5.34 | 5.62 | 3.50 | 23.47 | 56.26 | (4RE0.25)2Si2O7 | ||||
| 11 | 0.39 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 25.11 | 56.14 | 9.01 | 0.27 | 7.18 | 0.67 | La-Si-Al-O-Ca |
| 12 | 1.73 | 1.82 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 28.54 | 54.01 | 0.36 | 8.17 | 1.91 | La-Si-Al-O |
| [1] |
刘巧沐, 黄顺洲, 何爱杰. 碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料在航空发动机上的应用需求及挑战. 材料工程, 2019, 47: 1.
DOI |
| [2] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nat. Mater., 2016, 15: 804.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
刘大响. 一代新材料,一代新型发动机: 航空发动机的发展趋势及其对材料的需求. 材料工程, 2017, 45: 1.
DOI |
| [4] | ZHU S J, MIZUNO M, NAGANO Y, et al. Creep and fatigue behavior in an enhanced SiCf/SiC composite at high temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1998, 81: 2269. |
| [5] | CURTIN W A. Theory of mechanical properties of ceramic-matrix composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1991, 74: 2837. |
| [6] | 任孝旻. 高熵稀土单硅酸盐热障/环境障涂层材料的设计、制备和性能研究. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2022. |
| [7] | 黄璇璇, 郭双全, 姚改成. 航空发动机SiC/SiC复合材料环境障碍涂层研究进展. 航空维修与工程, 2017(2): 28. |
| [8] | ZHU D M. Durability and CMAS resistance of advanced environmental barrier coatings systems for SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites. J. Nucl. Mater., 2010, 8: 203. |
| [9] | POERSCHKE D L, HASS D D, EUSTIS S, et al. Stability and CMAS resistance of ytterbium-silicate/hafnate EBCs/TBC for SiC composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 98: 278. |
| [10] | WANG Y, MENG J S, LIU S Y, et al. Environmental barrier coatingschallenges and opportunities. J. Aerosp. Sci. Technol., 2018, 6: 17. |
| [11] | 周邦阳, 崔永静, 王长亮, 等. 稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层研究进展. 材料工程, 2023, 51(12): 12. |
| [12] | LEE K N, FOX D S, BANSAL N P. Rare earth silicate environmental barrier coatings for SiC/SiC composites and Si3N4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 25: 1705. |
| [13] | 王浩宇. 几种稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的制备、表征与性能研究. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2023. |
| [14] | 孙晓文. 稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层成分结构设计及高温失效机制研究. 天津: 河北工业大学硕士学位论文, 2022. |
| [15] | MAIER N, RIXECKER G, NICKEL K G. Formation and stability of Gd, Y, Yb and Lu disilicates and their solid solutions. J. Solid State Chem., 2006, 179: 1630. |
| [16] | LUO Y X, SUN L C, WANG J M, et al. Material-genome perspective towards tunable thermal expansion of rare-earth di-silicates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38: 3547. |
| [17] | 王京阳, 孙鲁超, 罗颐秀, 等. 以抗CMAS腐蚀为目标的稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层高熵化设计与性能提升. 金属学报, 2023, 59(4): 523. |
| [18] | TIAN Z L, ZHENG L Y, LI Z J, et al. Exploration of the low thermal conductivities of γ-Y2Si2O7, β-Y2Si2O7, β-Yb2Si2O7, and β-Lu2Si2O7 as novel environmental barrier coating candidates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2016, 36: 2813. |
| [19] | TIAN Z L, REN X M, LEI Y M, et al. Corrosion of RE2Si2O7 (RE=Y, Yb, and Lu) environmental barrier coating materials by molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate glass at high temperatures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39: 4245. |
| [20] | TURCER L R, SENGUPTA A, PADTURE N P. Low thermal conductivity in high-entropy rare-earth pyrosilicate solid-solutions for thermal environmental barrier coatings. Scr. Mater., 2021, 191: 40. |
| [21] | SUN L C, REN X M, LUO Y X, et al. Exploration of the mechanism of enhanced CMAS corrosion resistance at 1500 °C for multicomponent (Er0.25Tm0.25Yb0.25Lu0.25)2Si2O7 disilicate. Corros. Sci., 2022, 10: 110343. |
| [22] | GUO X T, ZHANG Y L, LI T, et al. High-entropy rare-earth disilicate (Lu0.2Yb0.2Er0.2Tm0.2Sc0.2)2Si2O7: a potential environmental barrier coating material. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 42: 3570. |
| [23] | SUN L C, LUO Y X, REN X M, et al. A multicomponent γ-type (Gd1/6Tb1/6Dy1/6Tm1/6Yb1/6Lu1/6)2Si2O7 disilicate with outstanding thermal stability. Mater. Res. Lett., 2020, 8: 424. |
| [24] | WANG X, HE Y X, WANG C, et al. Thermal performance regulation of high-entropy rare-earth disilicate for thermal environmental barrier coating materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 2: 18456. |
| [25] | WOLF M, MACK D E, GUILLON O, et al. Resistance of pure and mixed rare earth silicates against calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate (CMAS): a comparative study. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103: 7056. |
| [26] | POERSCHKE D L, JACKSON R W, LEVI C G. Silicate deposit degradation of engineered coatings in gas turbines: progress toward models and materials solutions. Annu. Rev. Mater., 2017, 47: 297. |
| [27] | DONG Y, REN K, WANG Q K, et al. Interaction of multicomponent disilicate (Yb0.2Y0.2Lu0.2Sc0.2Gd0.2)2Si2O7 with molten calcia-magnesia-aluminosilicate. J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11: 66. |
| [28] | CHEN Z Y, LIN C C, ZHENG W, et al. Investigation on improving corrosion resistance of rare earth pyrosilicates by high-entropy design with RE-doping. Corros. Sci., 2022, 199: 110217. |
| [29] | SUN L C, LUO Y X, TIAN Z L, et al. High temperature corrosion of (Er0.25Tm0.25Yb0.25Lu0.25)2Si2O7 environmental barrier coating material subjected to water vapor and molten calcium- magnesium- aluminosilicate (CMAS). Corros. Sci., 2020, 175: 108881. |
| [30] | TURCER L R, KRAUSE A R, GARCES H F, et al. Environmental-barrier coating ceramics for resistance against attack by molten calcia-magnesia-aluminosilicate (CMAS) glass: part II, β-Yb2Si2O7 and β-Sc2Si2O7. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38: 3914. |
| [31] | Ahlborg N L, ZHU D M. AHLBORG N L, ZHU D M. Calcium- magnesium aluminosilicate (CMAS) reactions and degradation mechanisms of advanced environmental barrier coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2013, 237: 79. |
| [32] | GRANT K M, KRÄMER S, LÖFVANDER J P A, et al. CMAS degradation of environmental barrier coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 202: 653. |
| [33] | WU N N, WANG Y L, TONG Y L, et al. Interaction of ytterbium monosilicate environmental barrier coating material with molten calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate (CMAS). Corros. Sci., 2023, 211: 110864. |
| [34] | WANG X, CHENG M H, XIAO G Z, et al. Preparation and corrosion resistance of high-entropy disilicate (Y0.25Yb0.25Er0.25-Sc0.25)2Si2O7 ceramics, Corros. Sci., 2021, 192: 109786. |
| [35] | HE Y X, XIAO G Z, WANG C, et al. Improved thermal properties and CMAS corrosion resistance of rare-earth monosilicates by adjusting the configuration entropy with RE-doping. Corros. Sci., 2024, 226: 11664. |
| [36] | DENG S X, HE G, YANG Z C, et al. Calcium-magnesium- alumina-silicate (CMAS) resistant high entropy ceramic (Y0.2Gd0.2-Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7 for thermal barrier coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 107: 259. |
| [37] | WEBSTER R I, OPILA E J. Viscosity of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 (CMAS) melts: experimental measurements and comparison to model calculations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids., 2022, 584: 121508. |
| [38] | SHIMIZU F, TOKUNAGA H, SAITO N, et al. Viscosity and surface tension measurements of RE2O3-MgO-SiO2 (RE=Y, Gd, Nd and La) melts. ISIJ Int., 2006, 46: 388. |
| [39] | XIAO G Z, SHEN Q Y, TIAN Y, et al. Investigation on the relation of microstructures and CMAS corrosion resistance of high entropy RE disilicates. Corros. Sci., 2024, 227: 111727. |
| [40] | HE Y X, WANG X, WANG C, et al. Significantly improved corrosion resistance of high-entropy rare-earth silicate multiphase ceramics against molten CMAS. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 106: 2744. |
| [1] | 樊文楷, 杨潇, 李宏华, 李永, 李江涛. 无压烧结制备(Y0.2Gd0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7高熵陶瓷及其高温抗CMAS腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 159-167. |
| [2] | 李捷, 罗志新, 崔阳, 张广珩, 孙鲁超, 王京阳. 大气等离子喷涂Y3Al5O12/Al2O3陶瓷涂层的CMAS腐蚀抗力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 671-680. |
| [3] | 范栋, 钟鑫, 王亚文, 张振忠, 牛亚然, 李其连, 张乐, 郑学斌. 富铝CMAS对稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 544-552. |
| [4] | 范佳锋,张小锋,周克崧,刘敏,邓畅光,邓春明,牛少鹏,邓子谦. 镀铝改性对PS-PVD 7YSZ热障涂层抗CMAS腐蚀影响机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 938-946. |
| [5] | 张小锋, 周克崧, 宋进兵, 邓春明, 牛少鹏, 邓子谦. 等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积7YSZ热障涂层沉积机理及 其CMAS腐蚀失效机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||