无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 245-256.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200220 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20200220
张晓山1( ), 王兵1, 吴楠2, 韩成1, 吴纯治1, 王应德1(
), 王兵1, 吴楠2, 韩成1, 吴纯治1, 王应德1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-26
修回日期:2020-06-09
出版日期:2021-03-20
网络出版日期:2020-09-09
通讯作者:
王应德, 教授. E-mail: wangyingde@nudt.edu.cn
作者简介:张晓山(1991-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: zhangxiaoshan15@nudt.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Xiaoshan1( ), WANG Bing1, WU Nan2, HAN Cheng1, WU Chunzhi1, WANG Yingde1(
), WANG Bing1, WU Nan2, HAN Cheng1, WU Chunzhi1, WANG Yingde1( )
)
Received:2020-04-26
Revised:2020-06-09
Published:2021-03-20
Online:2020-09-09
Contact:
WANG Yingde, professor. E-mail: wangyingde@nudt.edu.cn
About author:ZHANG Xiaoshan(1991-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhangxiaoshan15@nudt.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
陶瓷纤维具有密度低、强度高、耐高温、抗氧化和耐机械震动性能好等优点, 是空天飞行器、核能发电和化工冶金等热防护领域所需的关键高温隔热材料。传统陶瓷纤维直径粗(?>5 μm)、脆性大、热导率高, 在实际隔热领域应用中受到了极大限制。减小纤维直径, 制备微纳陶瓷纤维, 不仅有利于提高纤维力学性能, 还有望改善其高温隔热性能, 近年来引起了研究者的广泛关注。从微纳陶瓷纤维中影响热传输(气体热传导、固体热传导和辐射传热)的本征因素出发, 有针对地进行组成和结构优化, 进而改善其高温隔热性能, 是当前微纳陶瓷隔热纤维研究的重点方向。本文结合国内外研究现状, 在介绍微纳陶瓷纤维隔热机理的基础上, 按照纤维的组成和结构特点将目前微纳陶瓷隔热纤维分为三类, 即微纳陶瓷纤维气凝胶、中空/多孔微纳陶瓷纤维和复合微纳陶瓷纤维。对这三类不同特点的微纳陶瓷隔热纤维最新研究进展进行综述, 并展望了微纳陶瓷隔热纤维的未来发展方向。
中图分类号:
张晓山, 王兵, 吴楠, 韩成, 吴纯治, 王应德. 高温隔热用微纳陶瓷纤维研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 245-256.
ZHANG Xiaoshan, WANG Bing, WU Nan, HAN Cheng, WU Chunzhi, WANG Yingde. Micro-nano Ceramic Fibers for High Temperature Thermal Insulation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 245-256.
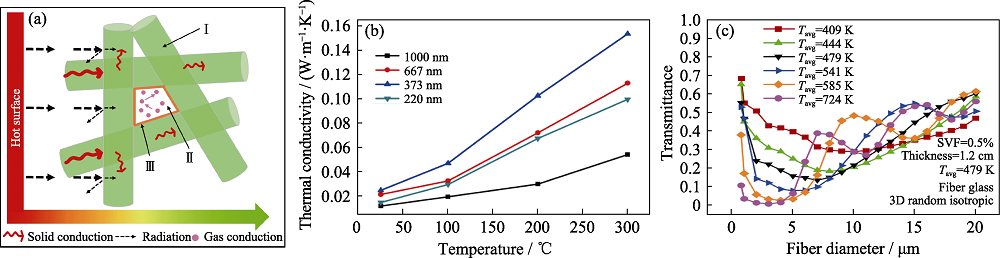
图2 微纳陶瓷纤维热传导示意图(a), 不同温度下直径对碳纳米纤维热导率的影响(b)和不同温度条件下不同直径纤维红外透过率(c)[13,21]
Fig. 2 Schematic of micro-nano fiber heat conduction (a), effect of fiber diameter on thermal conductivity of carbon nanofiber at different testing temperatures (b), and transmittance values for fibers with different fiber diameters at different operating temperatures (c)[13,21]
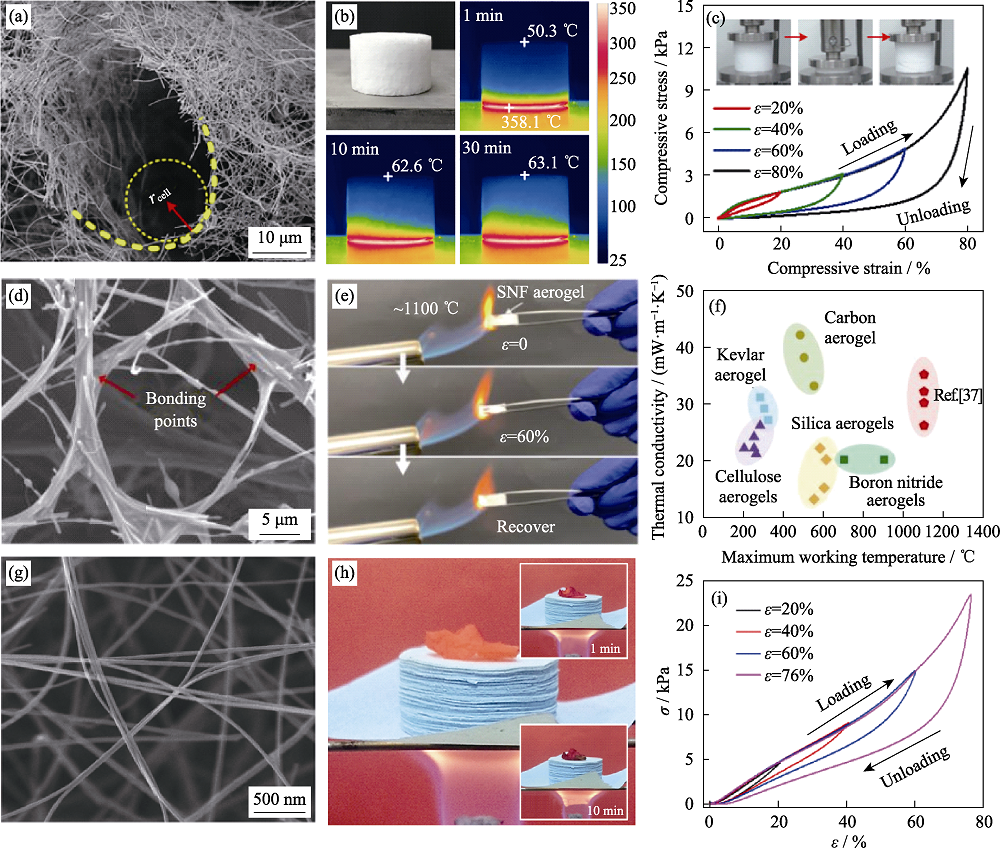
图3 SiO2和SiC纳米纤维气凝胶[7-8,37] (a)SEM照片; (b)隔热性能测试红外成像照片; (c)压缩应力应变图; SiO2纳米纤维气凝胶的(d)SEM照片, (e)高温条件下压缩性能测试图和(f)热导率对比图; (g)SiC纳米纤维气凝胶的SEM照片, (h)隔热性能测试光学照片和(i)压缩应力应变曲线
Fig. 3 SiO2 and SiC nanofiber aerogel[7-8,37] (a,d) SEM images of SiO2 nanofiber aerogel; (b) Infrared thermal image; (c) Compression stress-strain; (e) Compression test under high temperature; (f) Thermal conductivity comparison; (g) SEM image of SiC nanofiber aerogel; (h) Optical photo of thermal insulation performance of SiC nanofiber aerogel; (i) Compression stress-strain of SiC nanofiber aerogel

图5 中空微纳陶瓷纤维[44,48] (a)中空ZrO2纤维表面和截面SEM照片; (b)中空ZrO2纤维与传统实芯ZrO2纤维热导率对比; (c)中空Al2O3纤维表面和截面SEM照片; (d)中空Al2O3纤维气凝胶与其他材料热导率对比
Fig. 5 Hollow micro-nano ceramic fiber[44,48] (a) Surface and cross section SEM images of hollow ZrO2 fiber; (b) Comparison of thermal conductivity between hollow ZrO2 fiber and traditional ZrO2 fiber; (c) Surface and cross section SEM images of hollow Al2O3 fiber; (d) Thermal conductivity comparison among hollow Al2O3 fiber aerogel and other materials
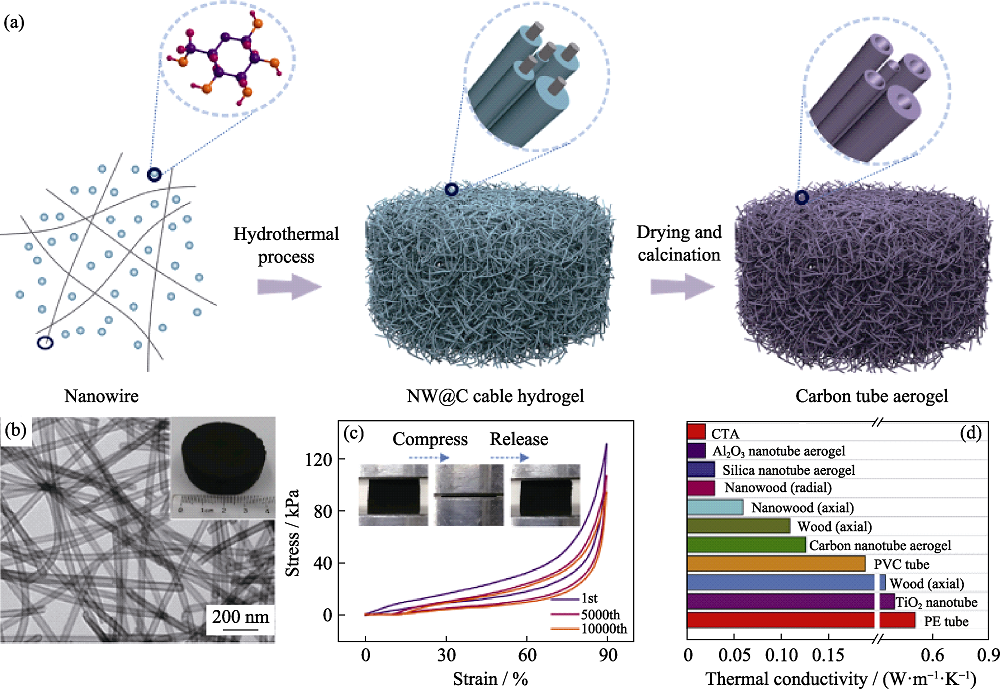
图6 中空碳纳米纤维气凝胶[49] (a)制备流程示意图; (b)TEM照片; (c)中空碳纳米纤维气凝胶经10000次压缩应力应变曲线及压缩测试图; (d)中空碳纳米纤维气凝胶与其他中空材料热导率比较
Fig. 6 Hollow carbon micro-nano fiber aerogel[49] (a) Schematic illustration of the fabrication processes; (b) TEM image; (c) Stress-strain curves for 10000 cycles; (d) Thermal conductivity comparison among different hollow-structured thermally insulating materials
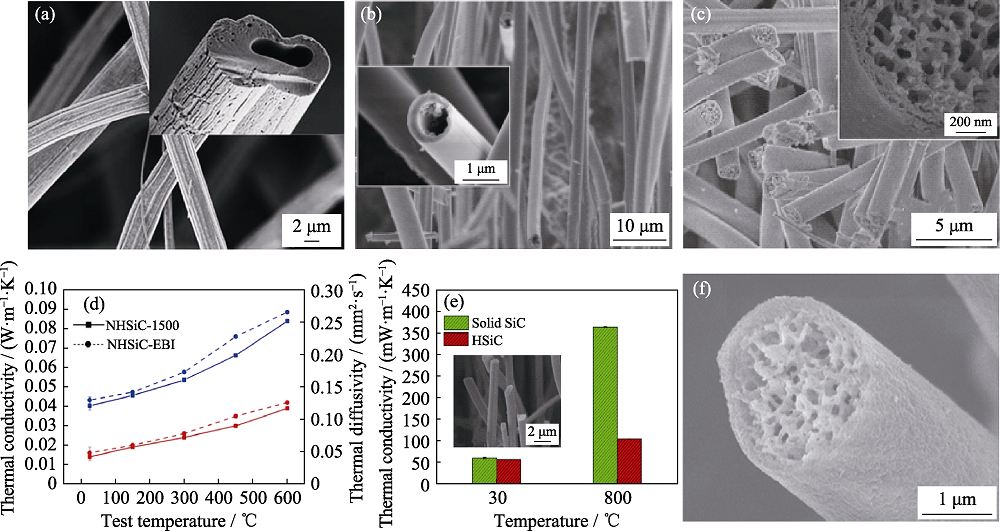
图7 中空和多空微纳纤维[51-52,54] (a)氮掺杂中空SiC纤维SEM照片; (b)中空SiC纤维SEM照片; (c)多孔SiO2-TiO2纤维SEM照片; (d)氮掺杂中空SiC纤维热导率和热扩散系数; (e)中空和实芯SiC纤维热导率; (f)多孔SiO2-ZrO2纤维SEM照片
Fig. 7 Hollow and porous micro-nano fiber[51-52,54] (a) SEM image of N-doped hollow SiC fiber; (b) SEM image of hollow SiC fiber; (c)SEM image of porous SiO2-TiO2 fiber; (d) Thermal conductivities and thermal diffusivities of N-doped hollow SiC fiber; (e) Thermal conductivities of solid SiC fiber and hollow SiC fiber; (f) SEM image of SiO2-ZrO2 fiber
| Fiber | Method | Infrared reflectance layer | Coating thickness/μm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | Dip-coating | TiO2, TiO2/SiO2/TiO2, TiO2-Pt | - | [64] |
| SiO2 | Dip-coating | ITO, ITO/Ag/ITO | ~0.2 | [60,65] |
| ZrO2 | Hydrothermal | CeO2 | 52-214 | [66] |
| Mullite | Hydrothermal | TiO2 | - | [67] |
| ZrO2 | Hydrothermal | TiO2 | 89-236 | [68] |
| Mullite | Dip-coating | SiC | ~0.8 | [69] |
表1 高反射率涂层纤维制备方法及涂层种类
Table 1 Preparation method and coating types of high-reflectivity coated fiber
| Fiber | Method | Infrared reflectance layer | Coating thickness/μm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | Dip-coating | TiO2, TiO2/SiO2/TiO2, TiO2-Pt | - | [64] |
| SiO2 | Dip-coating | ITO, ITO/Ag/ITO | ~0.2 | [60,65] |
| ZrO2 | Hydrothermal | CeO2 | 52-214 | [66] |
| Mullite | Hydrothermal | TiO2 | - | [67] |
| ZrO2 | Hydrothermal | TiO2 | 89-236 | [68] |
| Mullite | Dip-coating | SiC | ~0.8 | [69] |
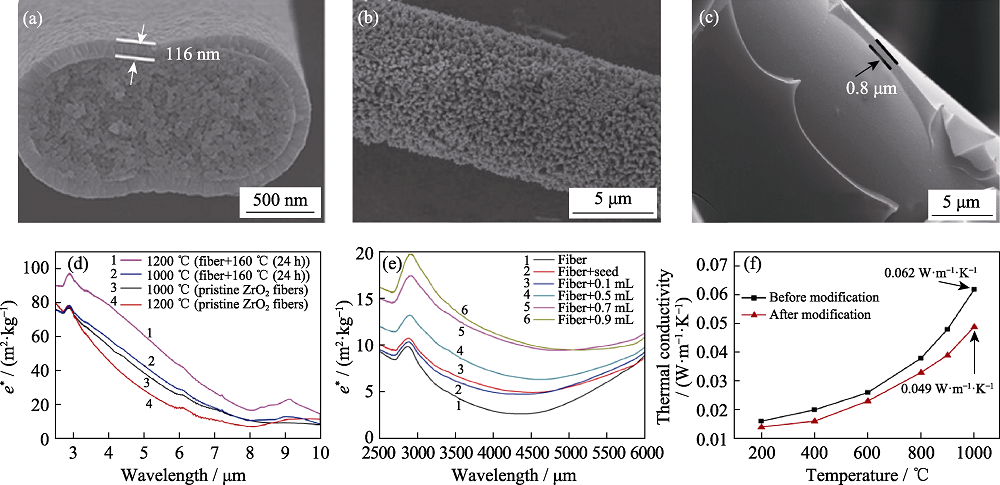
图9 高反射率涂层纤维[66-67,69] (a)CeO2/ZrO2纤维SEM照片; (b)TiO2/莫来石纤维SEM照片; (c)SiC/莫来石纤维表面SEM照片; (d)ZrO2纤维和CeO2/ZrO2纤维的比消光系数对比; (e)莫来石纤维和TiO2/莫来石纤维比消光系数对比; (f)莫来石纤维和SiC/莫来石纤维增强气凝胶复合材料热导率对比
Fig. 9 High-reflectivity coated fiber[66-67,69] (a) SEM image of ZrO2 fiber with CeO2 coating; (b) SEM image of mullite fiber with TiO2 coating; (c) SEM image of mullite fiber with SiC coating; (d) Specific extinction coefficients comparison of ZrO2 fiber and CeO2/ZrO2 fiber; (e) Specific extinction coefficients comparison of mullite fiber and TiO2/mullite fiber; (f) Thermal conductivity comparison of mullite fiber and SiC/mullite fiber reinforced aerogel composite

图10 复相微纳陶瓷纤维[14,70] (a)ZrO2/SiC纤维制备示意图; (b) ZrO2/SiC纤维TEM照片; (c) SiZrOC纤维SEM照片; (d) SiZrOC纤维热导率对比; (e) SiZrOC纤维隔热机理示意图
Fig. 10 Composite micro-nano ceramic fiber[14,70] (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation of ZrO2/SiC fiber; (b) TEM images of ZrO2/SiC fiber; (c) SEM images of SiZrOC fiber; (d) Thermal conductivity comparison of SiZrOC fiber with other ceramic fibers; (e) Schematic illustration of thermal insulation mechanisms of SiZrOC fibers
| [1] | CHEN Y F, HONG C Q, HU C L, et al. Ceramic-based thermal protection materials for aerospace vehicle. Advanced Ceramics, 2017,38(5):311-390. |
| [2] | BEHRENS B, MULLER M. Technologies for thermal protection systems applied on reusable launcher. Acta Astronautica, 2004,55(3-9):529-536 |
| [3] | WANG C A, LANG Y, HU L F, et al. Research progress on lightweight and high strength heat-insulating porous ceramics. Journal of Ceramics, 2017,38(6):287-296. |
| [4] | TERESA L, MARIA T P A, LUISA D. Silica aerogel composites with embedded fibres: a review on their preparation, properties and applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7:22768-22802. |
| [5] | LUO Y, JIANG Y G, FENG J Z, et al. Progress on the preparation of SiO2 aerogel composites by ambient pressure drying technique. Materials Review, 2018,32(5):780-787. |
| [6] |
XU X, ZHANG Q, HAO M, et al. Double-negative-index ceramic aerogels for thermal superinsulation. Science, 2019,363(6428):723-727.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
SI Y, WANG X, DOU L, et al. Ultralight and fire-resistant ceramic nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity. Science Advances, 2018, 4(4): eaas8925.
URL PMID |
| [8] |
SU L, WANG H, NIU M, et al. Ultralight, recoverable, and high-temperature-resistant SiC nanowire aerogel. ACS Nano, 2018,12(4):3103-3111.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | SABETZADEH N, BAHRAMBEYGI H, RABBI A, et al. Thermal conductivity of polyacrylonitrile nanofibre web in various nanofibre diameters and surface densities. Micro & Nano Letters, 2012,7(7):662-666. |
| [10] | YAN J, HAN Y, XIA S, et al. Polymer template synthesis of flexible BaTiO3 Crystal nanofibers. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019,29(51):1907919. |
| [11] |
YAN J, ZHAO Y, WANG X, et al. Polymer template synthesis of soft, light, and robust oxide ceramic films. iScience, 2019,15:185-195.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | ARAMBAKAM R, TAFRESHI H V, POURDEYHIMI B. A simple simulation method for designing fibrous insulation materials. Materials & Design, 2013,44:99-106. |
| [13] | ARAMBAKAM R, TAFRESHI H V, POURDEYHIMI B. Dual-scale 3-D approach for modeling radiative heat transfer in fibrous insulations. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013,64:1109-1117. |
| [14] | ZHANG X S, WANG B, WU N, et al. Flexible and thermal-stable SiZrOC nanofiber membranes with low thermal conductivity at high-temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020,40(5):1877-1885. |
| [15] | DARYABEUGI K, CUNNINGTON G R, KNUTSON J R. Heat transfer modeling for rigid high-temperature fibrous insulation. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2013,27(3):414-421. |
| [16] | HU F, WU S, SUN Y. Hollow structured materials for thermal insulation. Advanced Materials, 2019,31(38):1801001. |
| [17] | MACHADO H A. Modeling heat transfer with micro-scale natural convection in fibrous insulation. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2014,36(4):847-857. |
| [18] | DARYABEUGI K, CUNNINGTON G R, KNUTSON J R. Combined heat transfer in high-porosity high-temperature fibrous insulation: theory and experimental validation. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2011,25(4):536-546. |
| [19] | SHIN S, WANG Q, LUO J, et al. Advanced materials for high- temperature thermal transport. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020,30:1904815. |
| [20] | GIBSON P W, LEE C, KO F, et al. Application of nanofiber technology to nonwoven thermal insulation. Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics, 2007,2(2):32-40. |
| [21] | WANG B, WANG Y D. Effect of fiber diameter on thermal conductivity of the electrospun carbon nanofiber mats. Advanced Materials Research, 2011,332:672-677. |
| [22] | YAN J, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Transformation of oxide ceramic textiles from insulation to conduction at room temperature. Science Advances, 2020, 6(6): eaay8538. |
| [23] | ZHU W, GUO A, XUE Y, et al. Mechanical evaluations of mullite fibrous ceramics processed by filtration and in situ pyrolysis of organic precursor. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019,39(4):1329-1335. |
| [24] | HE F, LI W, ZKOU L, et al. Preparation and characterization of the three-dimensional network mullite porous fibrous materials by pressure and freeze-casting method. Ceramics International, 2019,45(3):3954-3960. |
| [25] |
XUE J, WU T, DAI Y, et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2019,119(8):5298-5415.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | WU N, WANG B, WANG Y D. Enhanced mechanical properties of amorphous SiOC nanofibrous membrane through in situ embedding nanoparticles. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(10):4763-4772. |
| [27] | SI Y, MAO X, ZHENG H, et al. Silica nanofibrous membranes with ultra-softness and enhanced tensile strength for thermal insulation. RSC Advances, 2015,5(8):6027-6032. |
| [28] | MAO X, BAI Y, YU J, et al. Flexible and highly temperature resistant polynanocrystalline zirconia nanofibrous membranes designed for air filtration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016,99(8):2760-2768. |
| [29] | ZHANG P, CHEN D, JIAO X. Fabrication of flexible α-alumina fibers composed of nanosheets. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2012,2012(26):4167-4173. |
| [30] | LI W, ZHAO X M, WANG Y F, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of flexible gamma-Al2O3 nanofibrous membranes. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2017,38(6):915-921. |
| [31] | YUAN K, WANG X, LIU H, et al. Formation of barium zirconate fibers for high-temperature thermal insulation applications. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016,99(9):2913-2919. |
| [32] | SHI S, YUAN K, XU C, et al. Electrospun fabrication, excellent high-temperature thermal insulation and alkali resistance performance of calcium zirconate fiber. Ceramics International, 2018,44(12):14013-14019. |
| [33] | XIE Y, WANG L, LIU B, et al. Flexible, controllable, and high-strength near-infrared reflective Y2O3 nanofiber membrane by electrospinning a polyacetylacetone-yttrium precursor. Materials & Design, 2018,160:918-925. |
| [34] | SI Y, YU J, TANG X, et al. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nature Communications, 2014,5(1):1-9. |
| [35] | DOU L, CHENG X, ZHANG X, et al. Temperature-invariant superelastic, fatigue resistant, and binary-network structured silica nanofibrous aerogels for thermal superinsulation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020,32(2):1904331. |
| [36] |
DOU L, ZHANG X, CHENG X, et al. Hierarchical cellular structured ceramic nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity for thermal insulation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019,11(32):29056-29064.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
WANG F, DOU L, DAI J, et al. In situ synthesis of biomimetic silica nanofibrous aerogels with temperature-invariant superelasticity over one million compressions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020,59(21):8285-8292.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] | XIAN L, ZHANG Y, WU Y, et al. Microstructural evolution of mullite nanofibrous aerogels with different ice crystal growth inhibitors. Ceramics International, 2020,46(2):1869-1875. |
| [39] | YU Z L, QIN B, MA Z Y, et al. Superelastic hard carbon nanofiber aerogels. Advanced Materials, 2019,31(23):1900651. |
| [40] | LI C, DING Y W, HU B C, et al. Temperature-invariant superelastic and fatigue resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels. Advanced Materials, 2020,32(2):1904331. |
| [41] | ZHANG J, LI B, LI L, et al. Ultralight, compressible and multifunctional carbon aerogels based on natural tubular cellulose. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016,4(6):2069-2074. |
| [42] | RUCKDESCHEL P, PHILIPP A, RETSCH M. Understanding thermal insulation in porous, particulate materials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017,27(38):1702256. |
| [43] | BRENDEL H, SEIFERT G, RARTHER F. Heat transfer properties of hollow-fiber insulation materials at high temperatures. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2017,31(2):463-472. |
| [44] | WANG T C, ZHANG Z, DAI C, et al. Amorphous silicon and silicates-stabilized ZrO2 hollow fiber with low thermal conductivity and high phase stability derived from a cogon template. Ceramics International, 2019,45(6):7120-7126. |
| [45] |
WANG T C, KONG S, CHANG L, et al. Preparation and heat-insulating property of the bio-inspired ZrO2 fibers based on the silk template. Ceramics International, 2012,38(8):6783-6788.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
WANG T C, YU Q, KONG J, et al. Synthesis and heat-insulating properties of yttria-stabilized ZrO2 hollow fibers derived from a ceiba template. Ceramics International, 2017,43(12):9296-9302.
DOI URL |
| [47] | WANG T C, YU Q, KONG J. Preparation and heat-insulating properties of biomorphic ZrO2 hollow fibers derived from a cotton template. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2018,15(2):472-478. |
| [48] | XU C, WANG H, SONG J, et al. Ultralight and resilient Al2O3 nanotube aerogels with low thermal conductivity. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(4):1677-1683. |
| [49] |
ZHAN H J, WU K J, HU Y L, et al. Biomimetic carbon tube aerogel enables super-elasticity and thermal insulation. Chem, 2019,5(7):1871-1882.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
DU A, WANG H, ZHOU B, et al. Multifunctional silica nanotube aerogels inspired by polar bear hair for light management and thermal insulation. Chemistry of Materials, 2018,30(19):6849-6857.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
LIU Y, LIU Y, CHOI W C, et al. Highly flexible, erosion resistant and nitrogen doped hollow SiC fibrous mats for high temperature thermal insulators. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(6):2664-2672.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
TIAN Q, WU N, WANG B, et al. Fabrication of hollow SiC ultrafine fibers by single-nozzle electrospinning for high-temperature thermal insulation application. Materials Letters, 2019,239:109-112.
DOI URL |
| [53] | GBEWONYO S, CARPENTER A W, GAUSE C B, et al. Low thermal conductivity carbon fibrous composite nanomaterial enabled by multi-scale porous structure. Materials & Design, 2017,134:218-225. |
| [54] | WANG Y D, HUANG H, ZHAO Y, et al. Self-assembly of ultralight and compressible inorganic sponges with hierarchical porosity by electrospinning. Ceramics International, 2020,46(1):768-774. |
| [55] |
LIU Z, LYU J, FANG D, et al. Nanofibrous Kevlar aerogel threads for thermal insulation in harsh environments. ACS Nano, 2019,13(5):5703-5711.
DOI URL PMID |
| [56] | ZHOU J, HSIEH Y L. Nanocellulose aerogel-based porous coaxial fibers for thermal insulation. Nano Energy, 2020,68:104305. |
| [57] |
YANG H, WANG Z, LIU Z, et al. Continuous, strong, porous silk firoin-based aerogel fibers toward textile thermal insulation. Polymers, 2019,11(11):1899.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
YANG J, WU H, WANG M, et al. Prediction and optimization of radiative thermal properties of ultrafine fibrous insulations. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016,104:394-402.
DOI URL |
| [59] | YANG L L, GE D, WEI H, et al. Morphology and characterization of ITO-Ag-ITO films on fibers by layer-by-layer method. Applied Surface Science, 2009,255(19):8197-8201. |
| [60] | WANG X D, SUN D, DUAN Y Y, et al. Radiative characteristics of opacifier-loaded silica aerogel composites. Journal of Non-crystalline Solids, 2013,375:31-39. |
| [61] |
LEE S C, CUNNINGTON G R. Conduction and radiation heat transfer in high-porosity fiber thermal insulation. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2000,14(2):121-136.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
TONG T W, SWATHI P S, CUNNINGTON JR G R. Examination of the radiative properties of coated silica fibers. Journal of Thermal Insulation, 1987,11(1):7-31.
DOI URL |
| [63] | TONG T W, SWATHI P S, CUNNINGTON JR G R. Reduction of radiative heat transfer in thermal insulations by use of dielectric coated fibers. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 1989,16(6):851-860. |
| [64] | HASS D D, PRASDA B D, GLASS D E, et al. Reflective Coating on Fibrous Insulation for Reduced Heat Transfer. NASA Contractor Report 201733, 1997. |
| [65] |
YANG L L, HE X, HE F. ITO coated quartz fibers for heat radiative applications. Materials Letters, 2008,62(30):4539-4541.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
GAN X, YU Z, YUAN K, et al. Preparation of a CeO2-nanoparticle thermal radiation shield coating on ZrO2 fibers via a hydrothermal method. Ceramics International, 2017,43(16):14183-14191.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
YANG J, ZHANG Y, HONG Z, et al. Preparations of TiO2 nanocrystal coating layers with various morphologies on mullite fibers for infrared opacifier application. Thin Solid Films, 2012,520(7):2651-2655.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
MA D, ZHU L, LIU B. Hydrothermally grown uniform TiO2 coatings on ZrO2 fibers and their infrared reflective and thermal conductive properties. Ceramics International, 2020,46(3):3400-3405.
DOI URL |
| [69] | XU L, JIANG Y, FENG J, et al. Infrared-opacified Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel composites reinforced by SiC-coated mullite fibers for thermal insulations. Ceramics International, 2015,41(1):437-442. |
| [70] |
WANG Y D, HAN C, ZHENG D, et al. Large-scale, flexible and high-temperature resistant ZrO2/SiC ultrafine fibers with a radial gradient composition. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,2(25):9607-9612.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||