无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (9): 1053-1058.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190573 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190573
王东海1( ),侯文涛1,李纳1,李东振2,徐晓东2,徐军1(
),侯文涛1,李纳1,李东振2,徐晓东2,徐军1( ),王庆国1(
),王庆国1( ),唐慧丽1
),唐慧丽1
收稿日期:2019-11-11
修回日期:2019-12-25
出版日期:2020-09-20
网络出版日期:2020-04-05
作者简介:王东海(1982–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail:
WANG Donghai1( ),HOU Wentao1,LI Na1,LI Dongzhen2,XU Xiaodong2,XU Jun1(
),HOU Wentao1,LI Na1,LI Dongzhen2,XU Xiaodong2,XU Jun1( ),WANG Qingguo1(
),WANG Qingguo1( ),TANG Huili1
),TANG Huili1
Received:2019-11-11
Revised:2019-12-25
Published:2020-09-20
Online:2020-04-05
摘要:
通过导模法(EFG)成功生长了蓝宝石单晶光纤(直径400~1000 μm, 长度500 mm)。光纤的横截面大致为圆形, 侧面无明显的小面, 直径变化小于40 μm。本研究对晶体缺陷, 例如微气泡, 包裹物和生长条纹等进行观察与分析, 得出: 大多数微气泡是球状的, 且存在于光纤的外侧缘; 在蓝宝石光纤外侧面也观察到少量的钼包裹物元素; 新模具在前几次使用中往往会产生更多的钼夹杂物, 在多次使用后降低。通过对熔体膜流体流动的实验和数值模拟, 研究蓝宝石光纤中微气泡尺寸和分布, 实验和数值模拟的结果显示出良好的一致性。微气泡的分布取决于熔体膜处的流体流动模式, 流体流动的涡流使微气泡在热毛细对流作用下移动到蓝宝石光纤外侧缘。633 nm处的吸收损耗为9 dB/m, 包裹物和表面不规则性会增加散射损耗。
中图分类号:
王东海,侯文涛,李纳,李东振,徐晓东,徐军,王庆国,唐慧丽. 导模法生长蓝宝石单晶光纤的缺陷和光学特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1053-1058.
WANG Donghai,HOU Wentao,LI Na,LI Dongzhen,XU Xiaodong,XU Jun,WANG Qingguo,TANG Huili. Defects and Optical Property of Single-crystal Sapphire Fibers Grown by Edge-defined Film-fed Growth Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1053-1058.
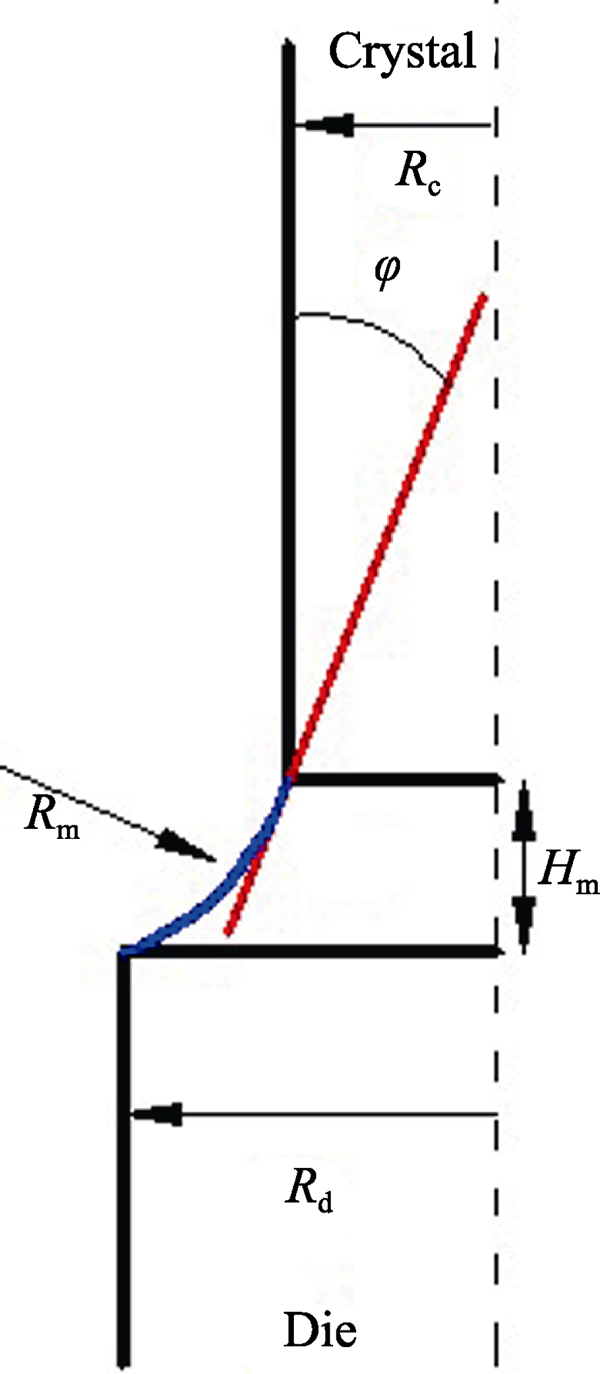
Fig. 6 Principles of capillary shaping for EFG fiber growth method Rm-Vertical curvature of the meniscus; Rd-Die radius; Rc-Radius of the crystal; Hm-Meniscus height
| Materials | Orientation | φo /(o) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si | [111] | 11 | [10] |
| YAG | [100] | 11 | [11] |
| Sapphire | [0001] | 17 | [12] |
| Sapphire | $[10\bar{1}0]$ | 35 | [12] |
Table 1 Parameter φo for different crystals
| Materials | Orientation | φo /(o) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si | [111] | 11 | [10] |
| YAG | [100] | 11 | [11] |
| Sapphire | [0001] | 17 | [12] |
| Sapphire | $[10\bar{1}0]$ | 35 | [12] |
| [1] |
LABELLE JR H E. EFG, the invention and application to sapphire growth. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1980,50(1):8-17.
DOI URL |
| [2] | WILSON B A, PETRIE C M, BLUE T E. High temperature effects on the light transmission through sapphire optical fiber. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(8):3452-3459. |
| [3] |
COULTER A H. Sapphire fibers for erbium: YAG continue to evolve. Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine and Surgery, 1995,13(3):227-228.
URL PMID |
| [4] | KURLOV V N, STRYUKOV D O, SHIKUNOVA I A. Growth of sapphire and oxide eutectic fibers by the EFG technique. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016,673(1):012017. |
| [5] | BERA S, NIE C D, SOSKIND M G,et al. Growth and lasing of single crystal YAG fibers with different Ho3+ concentrations. Optical Materials, 2018,75:44-48. |
| [6] | LEBBOU K. Single crystals fiber technology design. Optical Materials, 2017,63:13-18. |
| [7] | KURLOV V N, MILEIKO S T, KOLCHIN A A,et al. Growth of oxide fibers by the internal crystallization method. Crystallography Reports, 2002,47(1):S53-S62. |
| [8] | KURLOV V N, KIIKO V M, KOLCHIN A A,et al. Sapphire fibres grown by a modified internal crystallisation method Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999,204(4):499-504. |
| [9] | FITZGIBBON J J, COLLINS J M. High-volume production of low-loss sapphire optical fibers by Saphikon EFG (edge-defined, film-fed growth) method. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1998,3262:135-141. |
| [10] |
SUREK T. Theory of shape stability in crystal growth from the melt. Journal of Applied Physics, 1976,47(10):4384-4393.
DOI URL |
| [11] | RUDOLPH P, FUKUDA T. Fiber crystal growth from the melt. crystal research and technology. Journal of Experimental and Industrial Crystallography, 1999,34(1):3-40. |
| [12] | KAMADA K, MURAKAMI R, KOCHURIKHIN V V,et al. Single crystal growth of submillimeter diameter sapphire tube by the micro- pulling down method. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2018,492:45-49. |
| [13] | ZHDANOV A V, SATUNKIN G A, TATARCHENKO V A,et al. Cylindrical pores in a growing crystal. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1980,49(4):659-664. |
| [14] | TATARCHENKO V A, YALOVETS T N, SATUNKIN G A,et al. Defects in shaped sapphire crystals. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1980,50(1):335-340. |
| [15] | BUNOIU O, NICOARA I, SANTAILLER J L,et al. Fluid flow and solute segregation in EFG crystal growth process. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005,275(1/2):e799-e805. |
| [16] |
NUBLING R K, HARRINGTON J A. Optical properties of single- crystal sapphire fibers. Applied Optics, 1997,36(24):5934-5940.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 汤新丽, 丁自友, 陈俊锐, 赵刚, 韩颖超. 基于稀土铕离子荧光标记的磷酸钙纳米材料体内分布与代谢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [5] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [6] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [10] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [11] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [12] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [13] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [14] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [15] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||