
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 1303-1309.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150184
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Xue-Tong1, REN Lu-Lu1, LIAO Rui-Jin1, LI Jian-Ying2, WANG Fei-Peng1
Received:2015-04-14
Revised:2015-07-09
Published:2015-12-20
Online:2015-11-24
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHAO Xue-Tong, REN Lu-Lu, LIAO Rui-Jin, LI Jian-Ying, WANG Fei-Peng. Effect of the Oxidizing Atmosphere on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1303-1309.
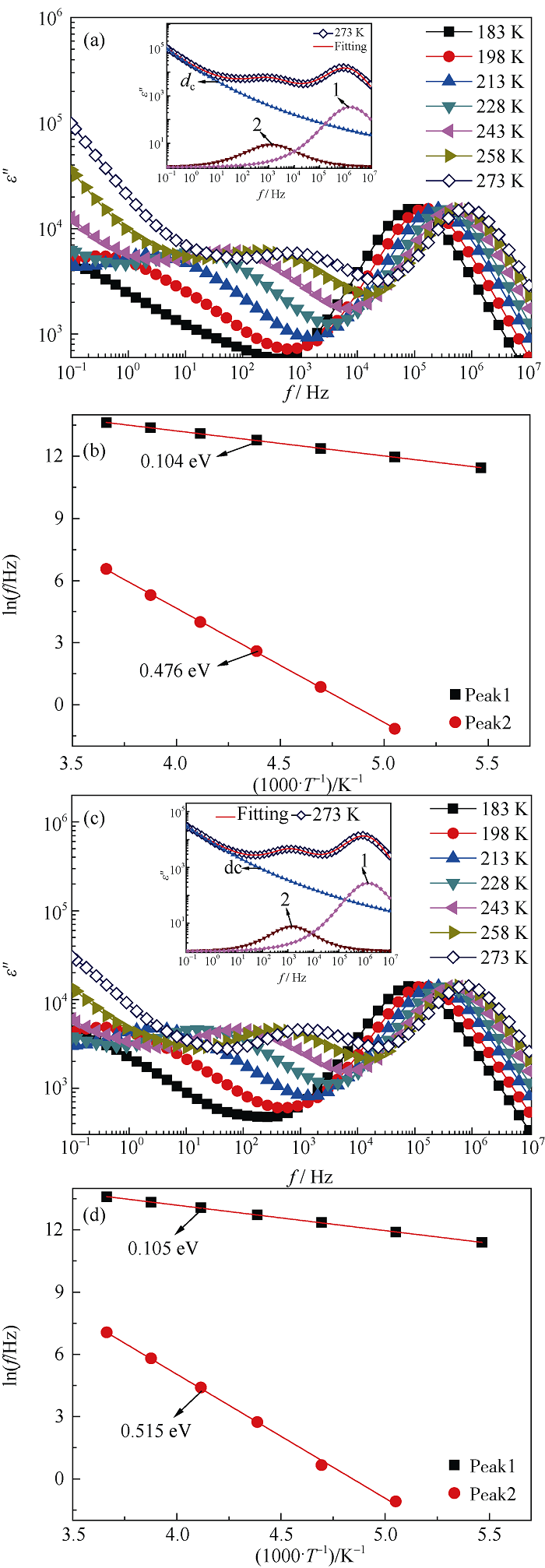
Fig. 4 Dielectric frequency spectra of CCTO samples measured in 183-273 K and the calculation of the activation energy for the relaxation peaks. The fitting results of dielectric loss at 273 K in the inset of (a) and (c). (a, b) CCTO-A; (c, d) CCTO-B
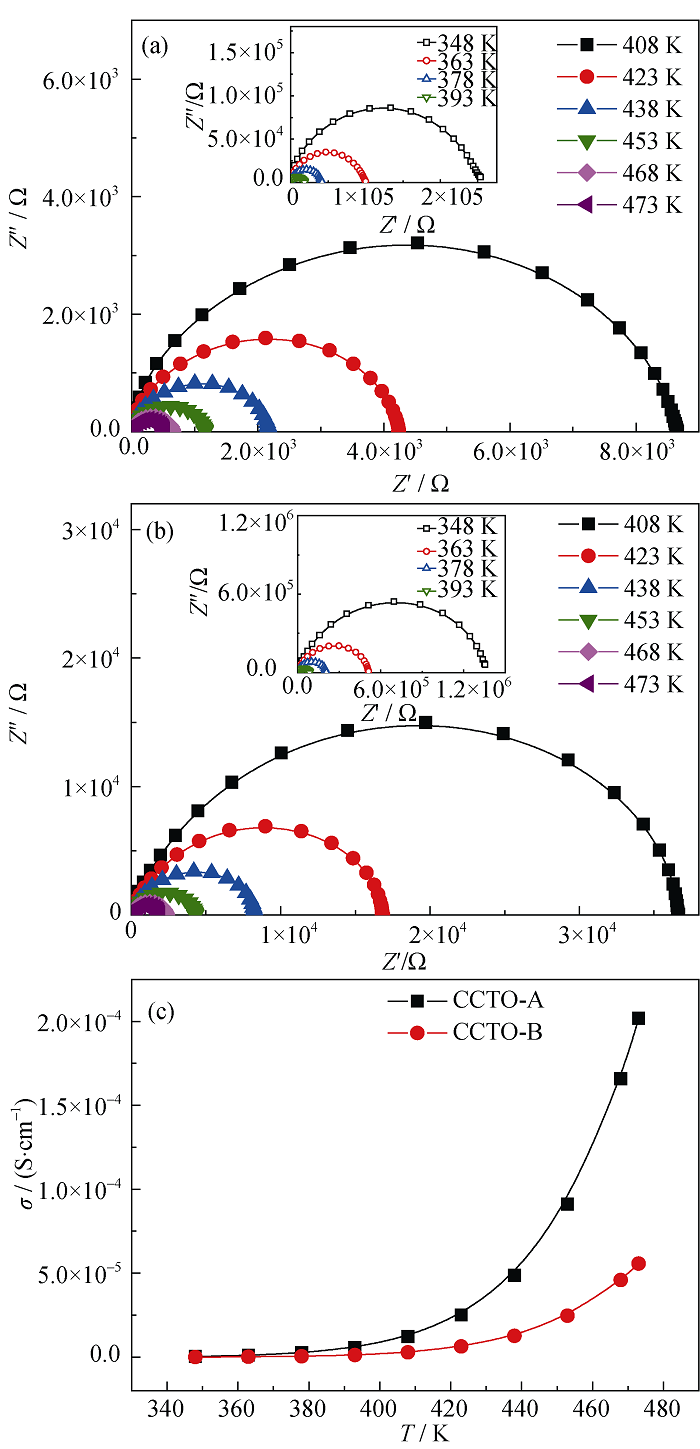
Fig. 6 Complex impedance plane measured in 348-473 K for CCTO-A (a) and CCTO-B (b), and the variation of the conductivity for the samples (c) with increasing temperature
| [1] | SUBRAMANIAN M A, LI D, DUAN N, et al.High dielectric constant in ACu3Ti4O12 and ACu3Ti3FeO12 phases.J. Solid State Chem., 2000, 151(2): 323-325. |
| [2] | HOMES C C, VOGT T, SHAPIRO S M, et al.Optical response of high-dielectric-constant perovskite-related oxide.Science, 2001, 293(5530): 673-676. |
| [3] | LIU Y, WITHERS R L, WEI X Y. Structurally frustrated relaxor ferroelectric behavior in CaCu3Ti4O12. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 72(13): 134104-1-4. |
| [4] | HE L, NEATON J B, COHEN M H, et al. First-principles study of the structure and lattice dielectric response of CaCu3Ti4O12. Phys. Rev. B, 2002, 65(21): 214112-1-11. |
| [5] | COHEN M H, NEATON J B, HE L, et al.Extrinsic models for the dielectric response of CaCu3Ti4O12.J. Appl. Phys., 2003, 94(5): 3299-3306. |
| [6] | SINCLAIR D C, ADAMS T B, MORRISON F D.CaCu3Ti4O12: one-step internal barrier layer capacitor.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 80(12): 2153-2155. |
| [7] | HAO W T, ZHANG J L, TAN Y Q, et al.Origin of giant dielectric permittivity in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.J. Inorg. Mater., 2011, 26(10): 1058-1062. |
| [8] | BÄRNER K, LUO X J, SONG X P, et al. Correlation between the trap state spectra and dielectric behavior of CaCu3Ti4O12.J. Mater. Res., 2011, 26(1): 36-44. |
| [9] | LUO X J, YANG C P, SONG X P, et al.Dielectric and impedance performances of giant dielectric constant oxide CaCu3Ti4O12. Acta Phys. Sin., 2012, 59(5): 3516-3522. |
| [10] | LI J Y, ZHAO X T, GU F, et al. Defects and dc electrical degradation in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics: Role of oxygen vacancy migration. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 100(22): 202905-1-4. |
| [11] | ZHAO X T, LI J Y, LI H, et al. Intrinsic and extrinsic defect relaxation behavior of ZnO ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 111(12): 124106-1-8. |
| [12] | ZHAO X T, LIAO R J, LIANG N C, et al. Role of defects in determining the electrical properties of ZnO ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 116(1): 014103-1-10. |
| [13] | ZANG G Z, ZHANG J L, ZHENG P J.Grain boundary effect on the dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics.J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2005, 38(11): 1824-1827. |
| [14] | FANG T T, MEI L T, HO H F.Effects of Cu stoichiometry on the micro structures, barrier-layer structures, electrical conduction, dielectric responses, and stability of CaCu3Ti4O12.Acta Mater., 2006, 54(10): 2867-2875. |
| [15] | VANGCHANGYIA S, SWATSITANG E, THONGBAI P, et al.Very low loss tangent and high dielectric permittivity in pure- CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by a modified Sol-Gel process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 95(5): 1497-1500. |
| [16] | YU R, XUE H, CAO Z L, CHEN L, et al.Effect of oxygen sintering atmosphere on the electrical behavior of CCTO ceramics.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 32(6): 1245-1249. |
| [17] | 陈季丹, 刘子玉. 电介质物理学. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1982: 155-160. |
| [18] | ADAMS T B, SINCLAIR D C, WEST A R. Characterization of grain boundary impedances in fine- and coarse-grained CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 73(9): 094124-1-9. |
| [19] | ZHANG J L, ZHENG P, WANG C L, et al. Dielectric dispersion of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics at high temperatures. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, 87(14): 142901-1-3. |
| [20] | SINCLAIR D C, WEST A R.Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of semiconducting BaTiO3 showing positive temperature- coefficient of resistance.J. Appl. Phys., 1989, 66(8): 3850-3856. |
| [21] | DENG G C, LI G R, DING A L, et al. Evidence for oxygen vacancy inducing spontaneous normal-relaxor transition in complex perovskite ferroelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, 87(19): 192905-1-3. |
| [22] | WHANGBO M H, SUBRAMANIAN M A.Structural model of planar defects in CaCu3Ti4O12 exhibiting a giant dielectric constant.Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(14): 3257-3260. |
| [23] | 张美蓉. ZnO压敏陶瓷老化机理的研究. 西安: 西安交通大学博士学位论文, 1991. |
| [24] | YANG Z, ZHANG Y, ZHANG K, et al.Effect of grain-boundary behavior on the dc electric conduction in Rb-doped CaCu3Ti4O12,J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2013, 24: 1063-1067. |
| [25] | 成鹏飞. 稀土氧化物对ZnO-Bi2O3系压敏陶瓷晶界结构和电气性能的影响. 西安: 西安交通大学博士学位论文, 2008. |
| [1] | WEI Tingting, XU Huarui, ZHU Guisheng, LONG Shenfeng, ZHANG Xiuyun, ZHAO Yunyun, JIANG Xupeng, SONG Jinjie, GUO Ningjie, GONG Yipeng. Preparation and Properties of BaTiO3 Ceramics by Low Temperature Cold Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 903-910. |
| [2] | YAO Xiaogang, PENG Haiyi, GU Zhongyuan, HE Fei, ZHAO Xiangyu, LIN Huixing. Polyphenylene Oxide/Ca0.7La0.2TiO3 Microwave Composite Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 493-498. |
| [3] | Gang JIAN, Mei-Rui LIU, Chen ZHANG, Hui SHAO. Preparation of Fully-coated Ag@TiO2 Particle Fillers for High-k Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 641-645. |
| [4] | HAN Lin-Cai, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, HUANG Long, ZHANG Xiao-Yun, XIONG Zhong. ZBAS on the Structure and Dielectric Property of BaAl2Si2O8 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 883-888. |
| [5] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, LIU Fei, YUAN Chang-Lai, CHEN Guo-Hua, HUANG Xian-Pei. Heat-treatment on Crystallization and Dielecty Property of Mg-Al-Si-Ti-B Glass-ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(12): 1309-1315. |
| [6] | LIU Fei, HUANG Xian-Pei, YUAN Chang-Lai, CHEN Guo-Hua. Influence of Sintering Temperature and CaTiO3 Doping on Structure and Dielectric Properties for Instability Layered Can+1TinO3n+1 (n = 1) Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 489-494. |
| [7] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, SONG Xiao-Hui, YUAN Chang-Lai, LIU Fei. B-site Substitution by (Mg1/3Ta2/3)4+ on Structures and Dielectric Properties of New Sr-based (Sr, Nd, Ca)TiO3 Microwave Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 293-298. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yao, DING Shi-Hua, LIU Yang-Qiong, DUAN Shao-Ying, XIAO Peng, HAN Lin-Cai. Crystal Structure and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 91-95. |
| [9] | SUN Qing-Lei, ZHOU Hong-Qing, QIAN-Lei, WANG Ya-Zhou, ZHU Hai-Kui, YUE Zhen-Xing. Effects of MgO, SrO and La2O3 Co-doping on Structure and Properties of (Zr0.8Sn0.2)TiO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 812-818. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kang, LI Wei, LIN Hui-Xin. Effect of MgO/ Eu2O3 Co-doping on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of Al2O3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 984-988. |
| [11] | XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling. Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 882-886. |
| [12] | XIE Hui-Dong, XI Hai-Hong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao. Microwave Dielectric Properties of BiMg2VO6 Ceramic with Low Sintering Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(2): 202-206. |
| [13] | QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, JING Ben-Qin, LIU Fei, YUAN Chang-Lai. Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Property of (1-x)(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)TiO3-xNd(Ti0.5Mg0.5)O3 Ceramics with High Quality Factor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(11): 1213-1217. |
| [14] | LI Jian-Ying, HOU Lin-Lin, JIA Ran, GAO Lu, WU Kang-Ning, LI Sheng-Tao. Influences of CuAl2O4 Doping on the Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1056-1062. |
| [15] | LI Wei, XIONG Zhao-Xian, XUE Hao. Preparation and Electrical Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Thin Ceramic Sheets via Water-based Tape Casting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(11): 1228-1232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||