
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 1295-1302.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150206
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Yu-Jia1, ZHANG Xiao-Hong1, ZHOU Xue-Dong2, GUO Ning1, CHENG Ru-Ru1, ZHANG Tian-Xu1
Received:2015-04-29
Revised:2015-06-16
Published:2015-12-20
Online:2015-11-24
About author:CHENG Yu-Jia. E-mail: chengyujia@hrbust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHENG Yu-Jia, ZHANG Xiao-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, GUO Ning, CHENG Ru-Ru, ZHANG Tian-Xu. Effects of Cooling Methods on Dielectric Properties of MMT/LDPE[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1295-1302.
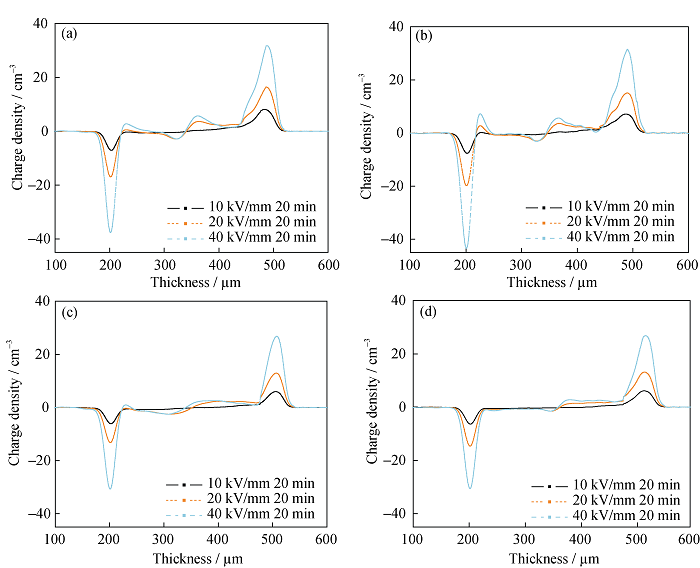
Fig. 10 Space charge distribution in MMT/LDPE samples under various electrical field. (a) Natural air cooling; (b) Rapid air cooling; (c) Water cooling; (d) Oil cooling
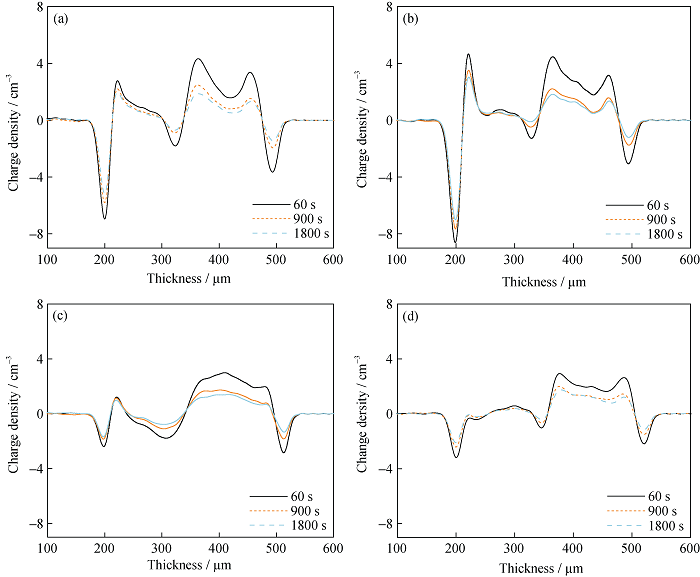
Fig. 11 Changes of space charge distribution in various samples with short-circuited time. (a) Natural air cooling; (b) Rapid air cooling; (c) Water cooling; (d) Oil cooling
| Electrical field | 10 kV/mm | 20 kV/mm | 40 kV/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural air cooling | 0.58522 | 1.74640 | 2.03929 |
| Rapid air cooling | 0.59581 | 1.79236 | 2.08940 |
| Water cooling | 0.50265 | 1.74408 | 1.67510 |
| Oil cooling | 0.34720 | 1.19120 | 1.57720 |
Table 1 Average charge density of MMT/LDPE samples under different electric field
| Electrical field | 10 kV/mm | 20 kV/mm | 40 kV/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural air cooling | 0.58522 | 1.74640 | 2.03929 |
| Rapid air cooling | 0.59581 | 1.79236 | 2.08940 |
| Water cooling | 0.50265 | 1.74408 | 1.67510 |
| Oil cooling | 0.34720 | 1.19120 | 1.57720 |
| Short circuit time | 60 s | 900 s | 1800 s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural air cooling | 1.95505 | 1.16921 | 1.01754 |
| Rapid air cooling | 1.99370 | 1.16921 | 1.01754 |
| Water cooling | 1.60711 | 0.95444 | 0.75726 |
| Oil cooling | 1.04666 | 0.65901 | 0.59119 |
Table 2 Charge density distribution of MMT/LDPE system with short-circuit time/ (C•m-3)
| Short circuit time | 60 s | 900 s | 1800 s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural air cooling | 1.95505 | 1.16921 | 1.01754 |
| Rapid air cooling | 1.99370 | 1.16921 | 1.01754 |
| Water cooling | 1.60711 | 0.95444 | 0.75726 |
| Oil cooling | 1.04666 | 0.65901 | 0.59119 |
| [1] | 杨挺, 程丽鸿, 钱丹. 我国聚乙烯发展现状及市场分析. 绝缘材料, 2013, 46(3): 33-36. |
| [2] | ALAPATI S, THOMAS M J.Electrical treeing and the associated PD characteristics in LDPE nanocomposites.IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2012, 19(2): 697-704. |
| [3] | 张金梅. PE/MMT纳米复合材料结晶形态与树枝放电特性研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学硕士学位论文, 2009. |
| [4] | 迟晓红, 高俊国, 郑杰, 等. 聚丙烯中电树枝生长机理研究. 物理学报, 2014, 63(17): 177701. |
| [5] | TOSHIKATSU TANAKA, MASAHIRO KOZAKO, NORIKAZU FUSE, et al.Proposal of a multi-core model for polymer nanocomposite dielectrics.IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2005, 12(4): 669-681. |
| [6] | 周远翔, 孙清华, 王宁花, 等. 空间电荷对低密度聚乙烯电气击穿特性的影响. 高电压技术, 2008, 34(3): 447-450. |
| [7] | 高俊国. PE/MMT纳米复合材料结构形态与电击穿性能机理研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学硕士学位论文, 2009. |
| [8] | 张晓虹, 高俊国, 郭宁, 等. 纳米蒙脱土对聚乙烯击穿和电导特性的影响. 高电压技术, 2009, 35(1): 129-134. |
| [9] | CECILIEN THOMAS, GILBERT TEYSSEDRE, CHRISTIAN LAURENT.A new method for space charge measurements under periodic stress of arbitrary waveform by the pulsed electro- acoustic method.IEEE Trans. DEI, 2008, 15(2): 554-559. |
| [10] | TTANAKA Y, CHEN G, ZHAO Y, et al.Effect of additives on morphology and space charge accumulation in low density polyethylene.IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2003, 10(1): 148-154. |
| [11] | 王霞, 吴超一, 何华琴, 等. 茂金属聚乙烯改性低密度聚乙烯中空间电荷机理的研究. 中国电机工程学报, 2006, 26(7): 158-162. |
| [12] | ZHANG XIAO-HONG, ZHANG MING-YAN, GAO JUN-GUO, et al.Investigation on Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of Polyethylene/Montmorillonite Nano-composites//2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM` 2005) :Vol 1. Kitakyus hu, Japan: IEEE Press, 2005: 235-238. |
| [13] | 莫志深, 张宏放, 张吉东. 晶态聚合物结构和X射线衍射. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 207-263. |
| [14] | CHOO W, CHEN G, SWINGLER S G.Temperature Gradient Effcet on the Conductivity of an XLPE Insulated Polymeric power cable. Solid Dielectries(ICSD), 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on, 2010. |
| [15] | 朱诚身. 聚合物结构分析. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 22-45. |
| [16] | TIAN FU-QIANG, LEI QING-QUAN, WANG XUAN, et al.Effect of deep trapping states on space charge suppression in polyethylene/ZnO nanocomposite.Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(14): 142903. |
| [17] | 张晓虹, 高俊国, 张金梅, 等. PE/MMT纳米复合材料的电击穿与耐局放性能. 高电压技术, 2008, 34(10): 2124-2128. |
| [18] | TAKEDA T, SUZUKI H, OKAMOTO T.Correlation between Space Charge Distribution under DC Voltage and Dielectric Breakdown Properties in XLPE under Impulse Voltage Superposed onto DC Voltage//Proceedings of 2001 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials.Himeji, Japan: IEEE, 2001: 493-496. |
| [19] | 王金锋, 郑晓泉, 柳立为, 等. LDPE结晶形态对水树枝老化特性的影响. 高电压技术, 2010, 3: 678-684. |
| [20] | LEI Q, WANG X, FAN Y.A new method of auto-separating thermally stimulated current.Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 72(9): 4254-4257. |
| [21] | QING QUAN L, FU QIANG T, CHUN Y, et al.Modified isothermal discharge current theory and its application in the determination of trap level distribution in polyimide films.Journal of Electrostatics, 2010, 68(3): 243-248. |
| [22] | MA D I, HUGENER T A, SIEGEL R W, et al.Influence of nanoparticle surface modification on the electrical behaviour of polyethylene nanocomposites. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16(6): 724-731. |
| [23] | 田付强. 聚乙烯基无机纳米复合电介质的陷阱特性与电性能研究. 北京: 北京交通大学博士学位论文, 2012. |
| [24] | CHEN G, TANAKA Y, TTAKADA T, et al.Effect of polyethylene interface on space charge formation.IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2004, 11(1): 113-121. |
| [25] | GREEN C D, VAUGHAN A S.Morphology and Crystallisation Kinetics of Polyethylene/Montmorillonite Nanocomposites. IEEE International Conference on Solid Dielectrics, 2007: 368-371. |
| [26] | TATSUO TAKADA, YUJI HAYASE, YASUHIRO TANAKA.Space charge trapping in electrical potential well caused by permanent and induced dipoles for LDPE/MgO nanocomposite.IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2008, 15(1): 152-160. |
| [27] | 莫志深, 张宏放, 张吉东. 晶态聚合物结构和X射线衍射. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 207-263. |
| [28] | TIAN FU-QIANG, LEI QING-QUAN, WANG XUAN, et al.Effect of deep trapping states on space charge suppression in polyethylene/ZnO nanocomposite.Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(14): 142-144. |
| [1] | WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [2] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [3] | LI Jianjun, CHEN Fangming, ZHANG Lili, WANG Lei, ZHANG Liting, CHEN Huiwen, XUE Changguo, XU Liangji. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by CoFe2O4/MgAl-LDH Catalyst for the Boosted Degradation of Antibiotic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 440-448. |
| [4] | HOU Jiaqi, CHEN Ruicong, ZENG Yaoying, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Jiaping, FU Qiangang. Thermal Shock and Ablation Resistance of SiC Coating Repaired by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 168-176. |
| [5] | LUAN Xingang, HE Dianwei, TU Jianyong, CHENG Laifei. 2D Plain and 3D Needle-punched C/SiC Composites: Low-velocity Impact Damage Behavior and Failure Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 205-214. |
| [6] | WANG Wenting, XU Jingjun, MA Ke, LI Meishuan, LI Xingchao, LI Tongqi. Oxidation Behavior at 1000-1300 ℃ in air of Ti2AlC-20TiB2 Synthesized by in-situ Reaction/Hot Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [7] | ZHANG Li, GUAN Haoyang, ZHENG Qining, HONG Zhiliang, WANG Jiaxuan, XING Ning, LI Mei, LIU Yongsheng, ZHANG Chengyu. Creep Properties and Damage Mechanisms of SiCf/SiC-SiYBC Prepared by Melt Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 23-30. |
| [8] | WEN Zhipeng, WEI Yi, HOU Xianghua, GUO Jiawen, LI Qu, ZHU Manqing, ZHANG Jiahao, PAN Kai, WU Lian. Research Progress of Bentonite-based Functional Materials in Electrochemical Energy Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1301-1315. |
| [9] | MA Yongjie, LIU Yongsheng, GUAN Kang, ZENG Qingfeng. Gas-phase Kinetic Study of Pyrolysis in the System of CH4+C2H5OH+Ar [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1235-1244. |
| [10] | DING Ningning, SUN Jianhua, WEI Xu, SUN Lixia. Monitoring Ammonia at Room Temperature of p-Aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid Modified MoO3/PPy Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1245-1253. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yunkai, DIAO Yaqi, WANG Minglei, ZHANG Yanhui, WANG Limin. First-principles Calculation Study of the Oxidation Resistance of PANI Modified Ti3C2(OH)2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [12] | WEI Xiangxia, ZHANG Xiaofei, XU Kailong, CHEN Zhangwei. Current Status and Prospects of Additive Manufacturing of Flexible Piezoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [13] | QUAN Wenxin, YU Yiping, FANG Bing, LI Wei, WANG Song. Oxidation Behavior and Meso-macro Model of Tubular C/SiC Composites in High-temperature Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [14] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [15] | YOU Bojie, LI Bo, LI Xuqin, MA Xuehan, ZHANG Yi, CHENG Laifei. Thermal Shock Damage and In-plane Shear Performance Degradation of 2D SiCf/SiC at Medium Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1367-1376. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||