|
Boron Nitride Nanosheets Supported Cu2O Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Catalytic Reduction for 4-nitrophenol
Journal of Inorganic Materials
2019, 34 (8):
817-826.
DOI: 10.15541/jim20180487
Despite excellent catalytic capability, Cu2O nanomaterial exhibits weak stability which limits its application. In this study, a novel kind of Cu2O, Cu2O/BNNSs-OH, supported catalyst with highly catalytic efficiency and stability, was facilely fabricated via a controllable liquid phase reduction of ascorbic acid and combining with an annealing process. Cu2O/BNNSs-OH catalyst was synthesized by using boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs), prepared by the “push-pull” effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and water phase change, as a supporter and spherical Cu2O nanoparticles (2-7 nm) prepared by forward titration (ascorbic acid→Cu 2+, solution with a pH 11) as active components. Morphology and structure of as-obtained samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high resolution transmission electronic microscopy (HRTEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Raman spectroscopy. The results of the synthetic method showed that spherical Cu2O nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed on the carrier surface and BNNSs displayed some stabilization effect on Cu2O which could be prevented from being oxidized into CuO. Moreover, the catalytic activity was investigated by catalytic reduction reaction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Cu2O/BNNSs-OH with high catalytic activity similar to the noble metal catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol is highly reusable for five successive cycles without significant degradation and activity loss. 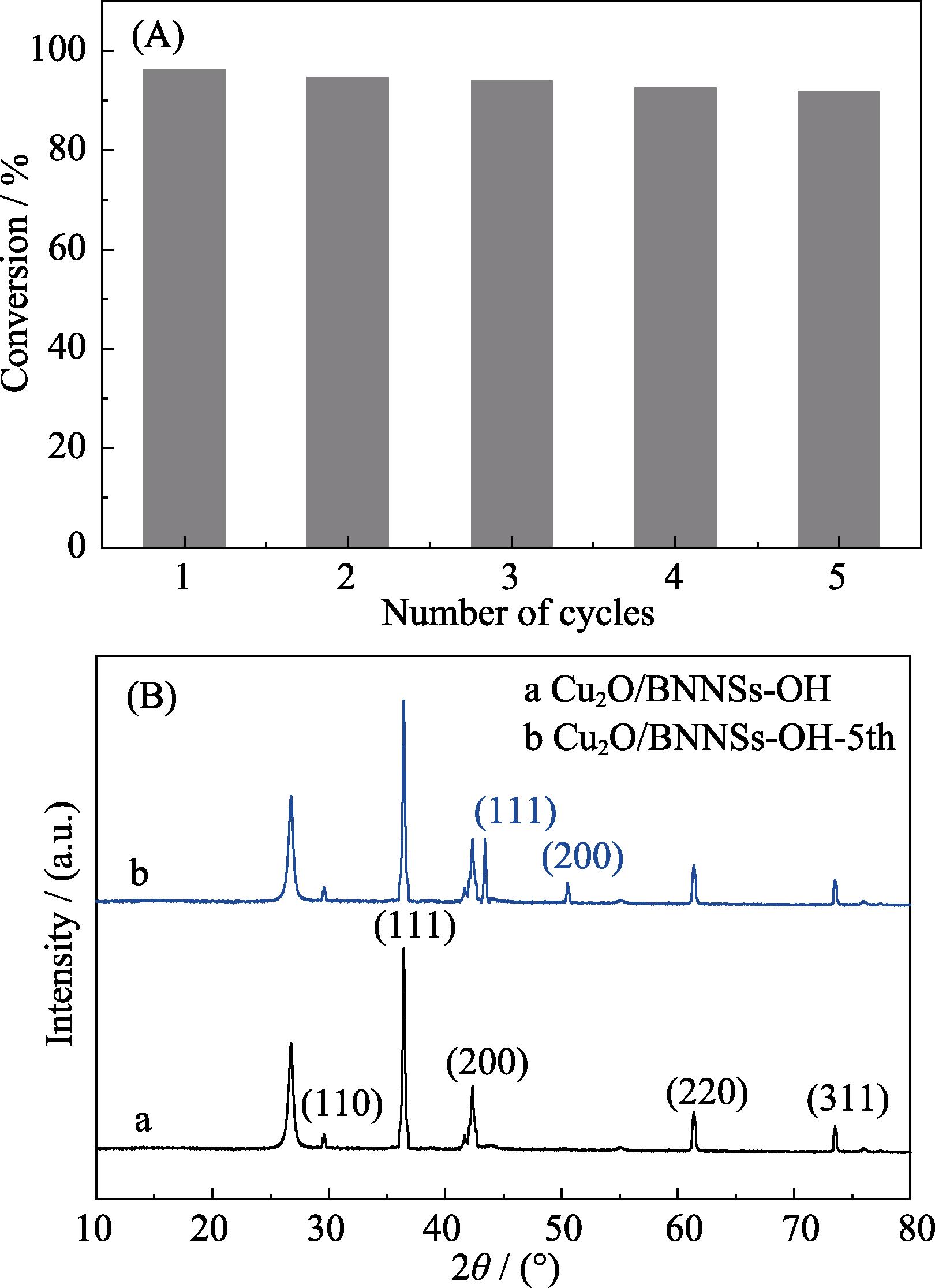
Fig. 11
Reusability of Cu2O/BNNSs-OH catalyst for the reduction of 4-NP with NaBH4 (A), XRD patterns of Cu2O/BNNSs- OH catalyst before and after five usages (B)
Extracts from the Article
图7(a)为功能化氮化硼纳米片的SEM照片, 可以清晰地看出 BNNSs-OH 为平滑交错的片状结构。前驱体阶段(混合溶液pH=11)制备的CuO/ BNNSs-OH由大量细小的CuO颗粒构成, 其粒径相对较大, 且紧紧团聚在一起(图7(b))。抗坏血酸还原阶段, 不同pH下制备的铜基催化剂SEM照片如 图7(c~g)所示。当反应体系pH在3~7时, Cu颗粒粒径随着pH增加逐渐减小, 最终变为球形颗粒 (图7(c~e))。当反应体系pH升高至9时, 在亚微米级Cu颗粒的表面开始产生纳米级颗粒, 对应上述XRD结果可知, 新生的Cu2O NPs附着在原来的Cu颗粒上(图7(f))。高分辨TEM图说明反应体系pH为11时, 产物全部为2~7 nm左右的Cu2O球形纳米粒子, 高度分散于氮化硼纳米片的表面, 且Cu2O NPs具有清晰的晶格, 层间距为0.24 nm, 对应立方相Cu2O的(111)晶面[29](图7(h~i))。
催化剂循环稳定性在工业生产应用中至关重要, Cu2O/BNNSs-OH催化剂的重复性测试结果如 图11(a)所示。随着循环次数的增加, 催化剂对4-NP的还原活性没有明显降低, 转化率仍保持在90%以上, 表明催化剂具有优异的循环稳定性。由5次重复降解前后催化剂的XRD图谱(图11(b))可以看出, 5次循环后, Cu2O仍为主要物相, 但出现了极少单质Cu的特征峰, 表明极少Cu2O NPs被反应体系中过量NaBH4还原为Cu NPs。此时, 催化剂主要活性组份变为Cu-Cu2O NPs, 由于在催化剂中引入原位生成的Cu NPs, 促进Cu和Cu2O之间的界面电荷转移, 使得 Cu2O/Cu NPs同样展现优异的催化性能。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|