|
Boron Nitride Nanosheets Supported Cu2O Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Catalytic Reduction for 4-nitrophenol
Journal of Inorganic Materials
2019, 34 (8):
817-826.
DOI: 10.15541/jim20180487
Despite excellent catalytic capability, Cu2O nanomaterial exhibits weak stability which limits its application. In this study, a novel kind of Cu2O, Cu2O/BNNSs-OH, supported catalyst with highly catalytic efficiency and stability, was facilely fabricated via a controllable liquid phase reduction of ascorbic acid and combining with an annealing process. Cu2O/BNNSs-OH catalyst was synthesized by using boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs), prepared by the “push-pull” effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and water phase change, as a supporter and spherical Cu2O nanoparticles (2-7 nm) prepared by forward titration (ascorbic acid→Cu 2+, solution with a pH 11) as active components. Morphology and structure of as-obtained samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high resolution transmission electronic microscopy (HRTEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Raman spectroscopy. The results of the synthetic method showed that spherical Cu2O nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed on the carrier surface and BNNSs displayed some stabilization effect on Cu2O which could be prevented from being oxidized into CuO. Moreover, the catalytic activity was investigated by catalytic reduction reaction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Cu2O/BNNSs-OH with high catalytic activity similar to the noble metal catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol is highly reusable for five successive cycles without significant degradation and activity loss. 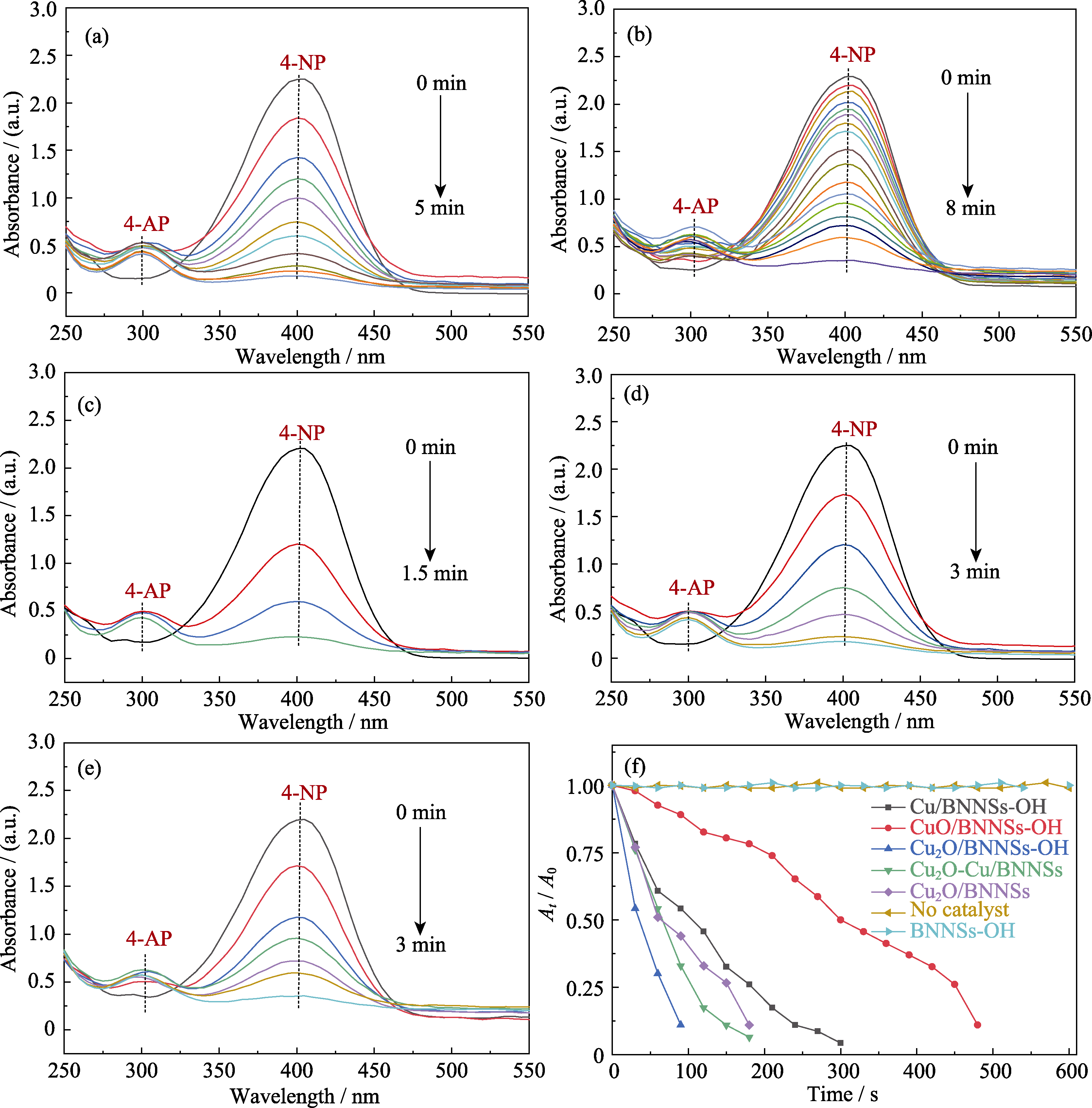
Fig. 9
UV-Vis absorption spectra of Cu/BNNSs-OH (a), CuO/BNNSs-OH (b), Cu2O/BNNSs-OH (c), Cu2O-Cu/BNNSs-OH (d), and Cu2O/BNNSs (e) in contrast to the reduction of 4-NP as a function of reaction time with excess amount of NaBH4 over various catalysts (f)
Extracts from the Article
研究以NaBH4还原对硝基苯酚反应为模型考查不同铜基催化剂的催化性能, 不同铜基和载体对还原反应进程影响的UV-Vis光谱变化情况如图9所示, 五种铜基催化剂均能催化还原4-NP。随着反应的进行, 4-NP的吸收峰逐渐下降直至几乎完全消失, 并且4-NP溶液颜色也逐渐褪去直至透明, 4-AP特征峰相应增加直至达到最高值, 表明4-NP已经完全转化为4-AP。
铜基纳米粒子的价态数、颗粒尺寸及分散程度是影响催化活性的关键因素。Cu2O/BNNSs-OH反应速率最快, 仅在1.5 min内就将4-NP完全还原为4-AP(图9(c)), 亚微米级Cu2O-Cu、Cu及CuO催化剂, 反应速率较缓慢, 分别在3、5、8 min时4-NP吸光度基本为零。Cu2O/BNNSs-OH的催化活性最高。同Cu及CuO催化剂相比, 处于中间价态的Cu2O具有较强的电子迁移能力, 还可以催化水分解产氢[30], Cu2O NPs作为电子和氢原子的中转站, 将电子和氢转移至4-NP将其快速催化还原为4-AP。
载体也是影响催化活性的一个重要因素。氮化硼纳米片中B、N的pz轨道与铜的dz2轨道重叠, 增强BNNSs与Cu2O NPs表面结合能力, 但功能化氮化硼纳米片表面的-OH同样有利于Cu2O NPs的固定。相对BNNSs而言, BNNSs-OH拥有更多的活性位点, 可作为Cu2O NPs的理想载体材料。由Cu2O/ BNNSs-OH的FT-IR图谱(图5(c))看出, 除了出现BNNSs-OH特征峰外, 在631 cm-1处有强烈的Cu-O振动, 且3400 cm-1处羟基吸收峰强度明显减弱, 表明载体表面及边缘的羟基能够充当Cu2O NPs与载体接触的活性位点。由UV-Vis光谱变化情况看出, 未功能化的氮化硼纳米片为载体(图9(e))时, 催化活性远不如BNNSs-OH。图9(f)为不同类型催化剂还原4-NP速率图, 结果表明, 单独的NaBH4和载体都不能还原4-NP, 进一步证明Cu2O/BNNSs-OH还原速率明显高于其他类型催化剂。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|