
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 1070-1076.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240136
WANG Hao1,2, LIU Xuechao1( ), ZHENG Zhong3, PAN Xiuhong1, XU Jintao1, ZHU Xinfeng1,2, CHEN Kun1, DENG Weijie1, TANG Meibo1, GUO Hui3, GAO Pan4
), ZHENG Zhong3, PAN Xiuhong1, XU Jintao1, ZHU Xinfeng1,2, CHEN Kun1, DENG Weijie1, TANG Meibo1, GUO Hui3, GAO Pan4
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-04-10
Published:2024-09-20
Online:2024-04-19
Contact:
LIU Xuechao, professor. E-mail: xcliu@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:WANG Hao (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wanghao218@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Hao, LIU Xuechao, ZHENG Zhong, PAN Xiuhong, XU Jintao, ZHU Xinfeng, CHEN Kun, DENG Weijie, TANG Meibo, GUO Hui, GAO Pan. Performance of Lateral 4H-SiC Photoconductive Semiconductor Switches by Extrinsic Backside Trigger[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1070-1076.

Fig. 5 Electrode damage microscope images of SiC2_Ni PCSS after FSI and BSI single trigger tests (a) Anode FSI; (b) Cathode FSI; (c) Cathode BSI; (d) Anode BSI
| Element | SiC1/(μg·g-1) | SiC2/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| B | 3.2 | 3.0 |
| Al | 41 | 22 |
| V | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Table 1 GDMS results of SiC1 and SiC2
| Element | SiC1/(μg·g-1) | SiC2/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| B | 3.2 | 3.0 |
| Al | 41 | 22 |
| V | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Element | Residual metal/(%, in atom) | Ablation/(%, in atom) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 53.41 | 55.91 |
| O | BDL | 1.31 |
| Si | 13.85 | 42.42 |
| Ti | 2.03 | BDL |
| Ni | 11.14 | 0.25 |
| W | 7.41 | BDL |
| Au | 12.17 | 0.10 |
Table 2 EDS results of SiC1_Ni PCSS
| Element | Residual metal/(%, in atom) | Ablation/(%, in atom) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 53.41 | 55.91 |
| O | BDL | 1.31 |
| Si | 13.85 | 42.42 |
| Ti | 2.03 | BDL |
| Ni | 11.14 | 0.25 |
| W | 7.41 | BDL |
| Au | 12.17 | 0.10 |
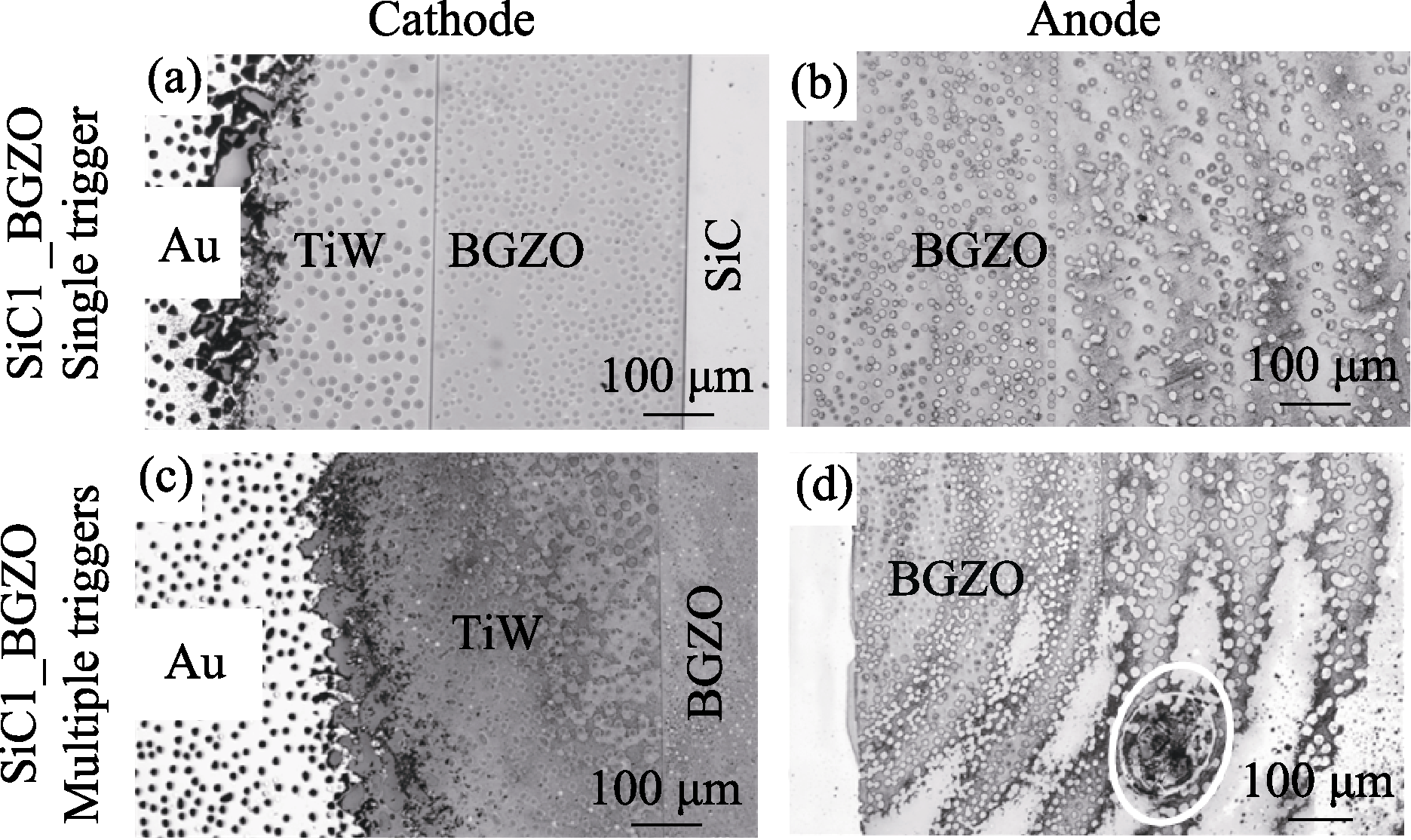
Fig. 8 Microscope images on electrode damage of SiC1_BGZO PCSS after trigger tests (a) Cathode and (b) anode after a single trigger test; (c) Cathode and (d) anode after multiple triggers
| [1] | CHANG S H, LIU X C, HUANG W, et al. Preparation and properties of lateral contact structure SiC photoconductive semiconductor switches. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1058. |
| [2] | BRAGG J W, SULLIVAN W W, MAUCH D, et al. All solid-state high power microwave source with high repetition frequency. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(5): 054703. |
| [3] | HARRIS J R, BLACKFIELD D, CAPORASO G J, et al. Vacuum insulator development for the dielectric wall accelerator. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(2): 023301. |
| [4] |
ZHANG D, XU Z, CHENG G, et al. Strongly enhanced THz generation enabled by a graphene hot-carrier fast lane. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 6404.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | YAN C F, SHI E W, CHEN Z Z, et al. Super fast and high power SiC photoconductive semiconductor switches. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(3): 425. |
| [6] | MAJDA-ZDANCEWICZ E, SUPRONIUK M, PAWŁOWSKI M, et al. Current state of photoconductive semiconductor switch engineering. Opto-Electronics Review, 2018, 26(2): 92. |
| [7] | CHOWDHURY A R, NESS R, JOSHI R P. Assessing lock-on physics in semi-insulating GaAs and InP photoconductive switches triggered by subbandgap excitation. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2018, 65(9): 3922. |
| [8] | XU M, WANG Y, LIU C, et al. Photoexcited carrier dynamics in a GaAs photoconductive switch under nJ excitation. Plasma Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 075503. |
| [9] | JAMES C, HETTLER C, DICKENS J. Design and evaluation of a compact silicon carbide photoconductive semiconductor switch. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2011, 58(2): 508. |
| [10] | YANG F, WANG Z, LIANG Z, et al. Electrical performance advancement in SiC power module package design with kelvin drain connection and low parasitic inductance. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2019, 7(1): 84. |
| [11] | CHU X, LIU J, XUN T, et al. MHz repetition frequency, hundreds kilowatt, and sub-nanosecond agile pulse generation based on linear 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2022, 69(2): 597. |
| [12] | SULLIVAN J S, STANLEY J R. 6H-SiC photoconductive switches triggered at below bandgap wavelengths. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2007, 14(4): 980. |
| [13] | HETTLER C, SULLIVAN W W, DICKENS J, et al. Performance and optimization of a 50 kV silicon carbide photoconductive semiconductor switch for pulsed power applications. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference, San Diego, 2012. |
| [14] | HUANG J, HU L, MA Z, et al. Study on photoelectric efficiency and failure mechanism of high purity 4H-SiC PCSS. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(11): 5762. |
| [15] | ZHU K, DOGAN S, MOON Y T, et al. Effect of n+-GaN subcontact layer on 4H-SiC high-power photoconductive switch. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(26): 261108. |
| [16] | XIAO L, YANG X, DUAN P, et al. Effect of electron avalanche break-down on a high-purity semi-insulating 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch under intrinsic absorption. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(11): 2804. |
| [17] | MAUCH D, SULLIVAN W, BULLICK A, et al. High power lateral silicon carbide photoconductive semiconductor switches and investigation of degradation mechanisms. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2015, 43(6): 2021. |
| [18] | ZHENG Z, HUANG W, HAN W W, et al. Analyzing the effects of aluminum-doped ZnO and Ag layers for the transparent electrode vertical PCSS. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(6): 2414. |
| [19] | ZHOU T Y, LIU X C, HUANG W, et al. Application of an Al-doped zinc oxide subcontact layer on vanadium-compensated 6H-SiC photoconductive switches. Chinese Physics B, 2015, 24(4): 044209. |
| [20] | WANG B, WANG L, NIU X, et al. Breakdown behavior of SiC photoconductive switch with transparent electrode. AIP Advances, 2022, 12(8): 085210. |
| [21] | CHOWDHURY A R, MAUCH D, JOSHI R P, et al. Contact extensions over a high-k dielectric layer for surface field mitigation in high power 4H-SiC photoconductive switches. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2016, 63(8): 1. |
| [22] | FENG Z, LUAN C, XIAO L, et al. Performance of a novel rear-triggered 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(2): 627. |
| [23] | FU W, WANG L, WANG B, et al. Investigation on the photocurrent tail of vanadium-compensated 4H-SiC for microwave application. AIP Advances, 2022, 12(9): 095121. |
| [24] | ZHAI Z, ZHANG R, TANG A, et al. Fabrication of microstructure on C/SiC surface via femtosecond laser diffraction. Materials Letters, 2021, 293: 293711. |
| [25] | KIM I W, DOH S J, KIM C C, et al. Effect of evaporation on surface morphology of epitaxial ZnO films during postdeposition annealing. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 241(1): 179. |
| [1] | WANG Lujie, ZHANG Yuxin, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, REN Pengwei, WANG Jianzhang, TANG Huaguo, YAO Xiumin, HUANG Yihua, LIU Xuejian, QIAO Zhuhui. Corrosion and Wear Behavior of Silicon Carbide Ceramic in Deep-sea Service Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [2] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [3] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [4] | XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 923-930. |
| [5] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [6] | GU Xuesu, YIN Jie, WANG Kanglong, CUI Chong, MEI Hui, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Particle Grading on Properties of Silicon Carbide Ceramics by Binder Jetting Printing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1373-1378. |
| [7] | OUYANG Qin, WANG Yanfei, XU Jian, LI Yinsheng, PEI Xueliang, MO Gaoming, LI Mian, LI Peng, ZHOU Xiaobing, GE Fangfang, ZHANG Chonghong, HE Liu, YANG Lei, HUANG Zhengren, CHAI Zhifang, ZHAN Wenlong, HUANG Qing. Research Progress of SiC Fiber Reinforced SiC Composites for Nuclear Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [8] | RUAN Jing, YANG Jinshan, YAN Jingyi, YOU Xiao, WANG Mengmeng, HU Jianbao, ZHANG Xiangyu, DING Yusheng, DONG Shaoming. Porous SiC Ceramic Matrix Composite Reinforced by SiC Nanowires with High Strength and Low Thermal Conductivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [9] | LUO Qing,YUAN Qing,JIANG Qian-Qin,YU Nai-Sen. Cu-SSZ-13/SiC-waste Composite: Synthesis and Application for NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 953-960. |
| [10] | HE Fei, LI Ya, LUO Jin, FANG Min-Han, HE Xiao-Dong. Development of SiO2/C and SiC/C Composites Featuring Aerogel Structures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [11] | YU Jie-Yi, HUANG Hao, GAO Jian, ZHOU Lei, GAO Song, DONG Xing-Long, QUAN Xie. Synthesis and Catalytic Performances of SiC Nanoparticles by DC Arc-discharge Plasma [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 351-356. |
| [12] | ZHUO Shi-Yi, LIU Xi, GAO Pan, YAN Cheng-Feng, SHI Er-Wei. Luminescence of Donor-acceptor-pair in Fluorescent 4H-SiC Doped with Nitrogen, Boron and Aluminum [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 51-55. |
| [13] | WANG Feng, GAO Zhao-Fen, XU Jia-Qiang, ZENG Yu-Ping. Porous SiC Ceramics with Multiple Pore Structure Fabricated via Gelcasting and Solid State Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 305-310. |
| [14] | YANG Xiao, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren, LIU Gui-Ling, YAO Xiu-Min. Effects of Vickers Cracks on the Mechanical Properties of Solid-phase-sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(9): 965-969. |
| [15] | ZHU Ming-Xing, SHI Biao, CHEN Yi, LIU Xue-Chao, SHI Er-Wei. High-speed Homoepitaxial Growth of 4H-SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(8): 785-789. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||