
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 1178-1184.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200748
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Ruihong1( ), WEI Xin2, LU Zhanhui1, AI Yuejie3(
), WEI Xin2, LU Zhanhui1, AI Yuejie3( )
)
Received:2020-12-31
Revised:2021-04-15
Published:2021-11-20
Online:2021-06-01
Contact:
AI Yuejie, associate professor. E-mail: aiyuejie@ncepu.edu.cn
About author:ZHANG Ruihong(1996-), femal, Master candidate. E-mail: zhangruihong@ncepu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Ruihong, WEI Xin, LU Zhanhui, AI Yuejie. Training Model for Predicting Adsorption Energy of Metal Ions Based on Machine Learning[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184.
| No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charge | 8 | Ionic radius | 15 | CV (Cal/mol-K) |
| 2 | Spin | 9 | Melting point | 16 | S(Cal/mol-K) |
| 3 | Atomic radius | 10 | Boiling point | 17 | Zero-point vibrational energy/(kCal·mol-1) |
| 4 | Atomic number | 11 | First ionization energy | 18 | Molecular mass |
| 5 | Atomic weight | 12 | Electronegativity | 19 | Mulliken charges |
| 6 | Density/(g·cm-3) | 13 | M-O (bond length) | 20 | APT charges |
| 7 | Atomic volume | 14 | E(Thermal)/(kCal·mol-1) | 21 | Dipole moment/D |
Table 1 21 feature descriptors calculated based on DFT
| No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charge | 8 | Ionic radius | 15 | CV (Cal/mol-K) |
| 2 | Spin | 9 | Melting point | 16 | S(Cal/mol-K) |
| 3 | Atomic radius | 10 | Boiling point | 17 | Zero-point vibrational energy/(kCal·mol-1) |
| 4 | Atomic number | 11 | First ionization energy | 18 | Molecular mass |
| 5 | Atomic weight | 12 | Electronegativity | 19 | Mulliken charges |
| 6 | Density/(g·cm-3) | 13 | M-O (bond length) | 20 | APT charges |
| 7 | Atomic volume | 14 | E(Thermal)/(kCal·mol-1) | 21 | Dipole moment/D |
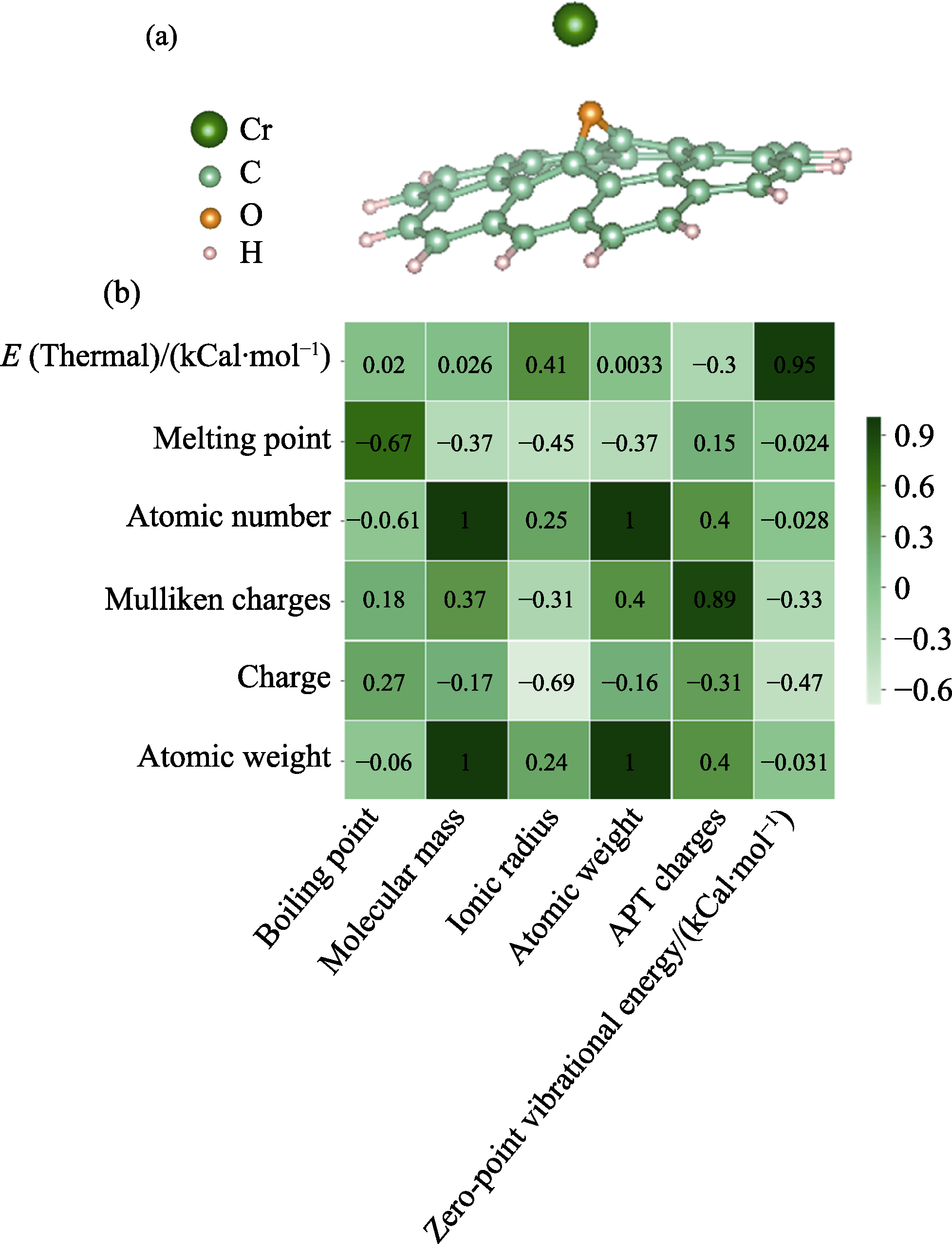
Fig. 1 (a) Thermal map of correlation between features with correlation coefficient>0.6, and (b) example of adsorption structure of GO adsorbing Cr3+ Note: 1 Cal=4.104 J
| Category | Method | Optimal hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel | Support vector regression (SVR) | C = 2, kernel=“ rbf ” |
| Ridge regression | Alpha = 30 | |
| Random forest | Random forest (RF) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 6, max_features = 2 |
| Extremely randomized trees (ERT) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 7, random_state = 1 | |
| Boosting | Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 2, min_child_weight = 13, learning_rate =.32 |
| Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) | n_estimators =17, objective = ‘regression’, num_leaves = 31, learning_ rate = 0.32 |
Table 2 Optimal hyperparameters of six machine learning methods
| Category | Method | Optimal hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel | Support vector regression (SVR) | C = 2, kernel=“ rbf ” |
| Ridge regression | Alpha = 30 | |
| Random forest | Random forest (RF) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 6, max_features = 2 |
| Extremely randomized trees (ERT) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 7, random_state = 1 | |
| Boosting | Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 2, min_child_weight = 13, learning_rate =.32 |
| Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) | n_estimators =17, objective = ‘regression’, num_leaves = 31, learning_ rate = 0.32 |
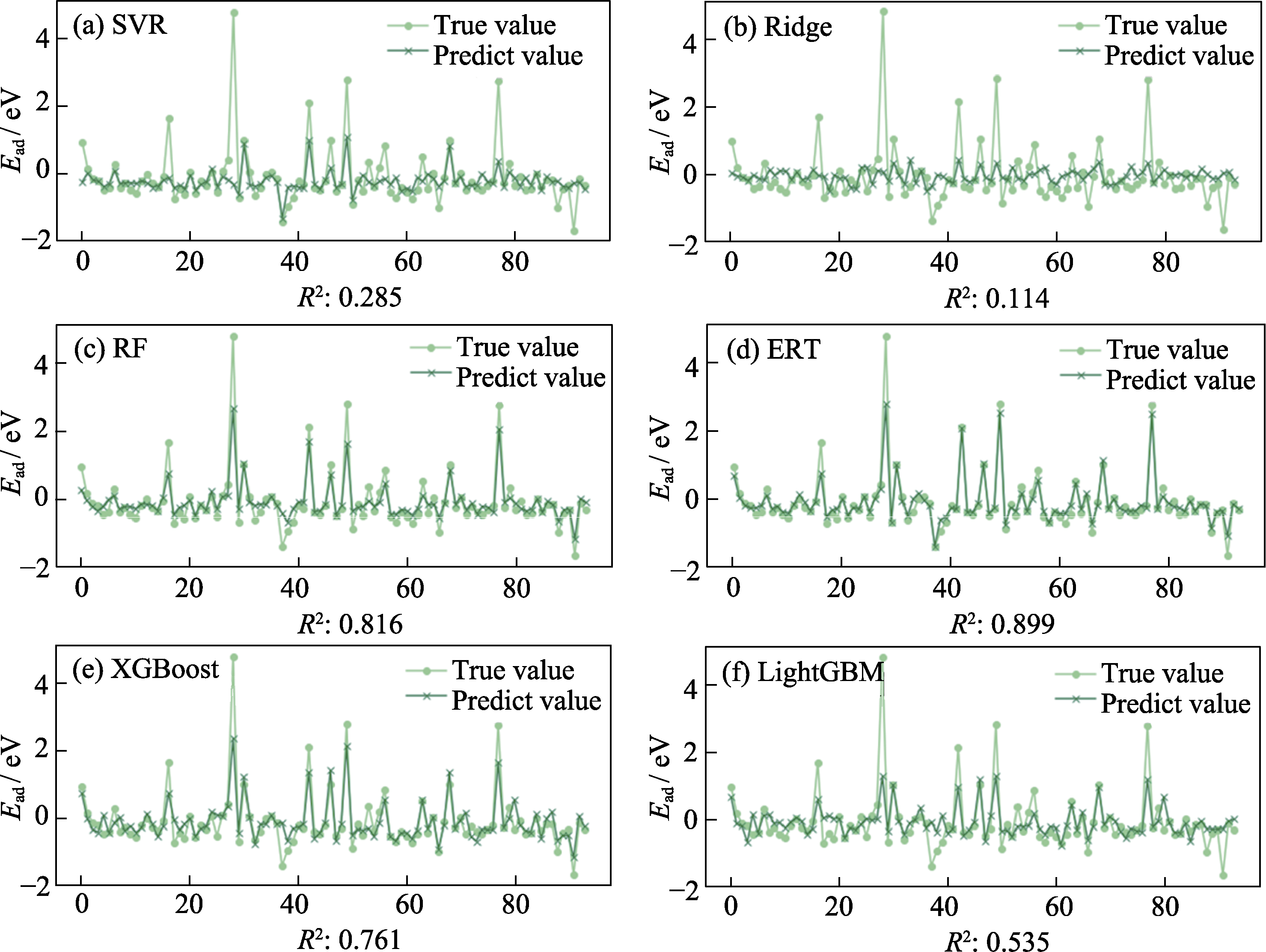
Fig. 3 Fitting effect diagram and score of six machine learning methods. (a) Support vector regression (SVR); (b) Ridge regression (Ridge); (c) Random forest (RF); (d) Extremely randomized trees (ERT); (e) Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost); (f) Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM)
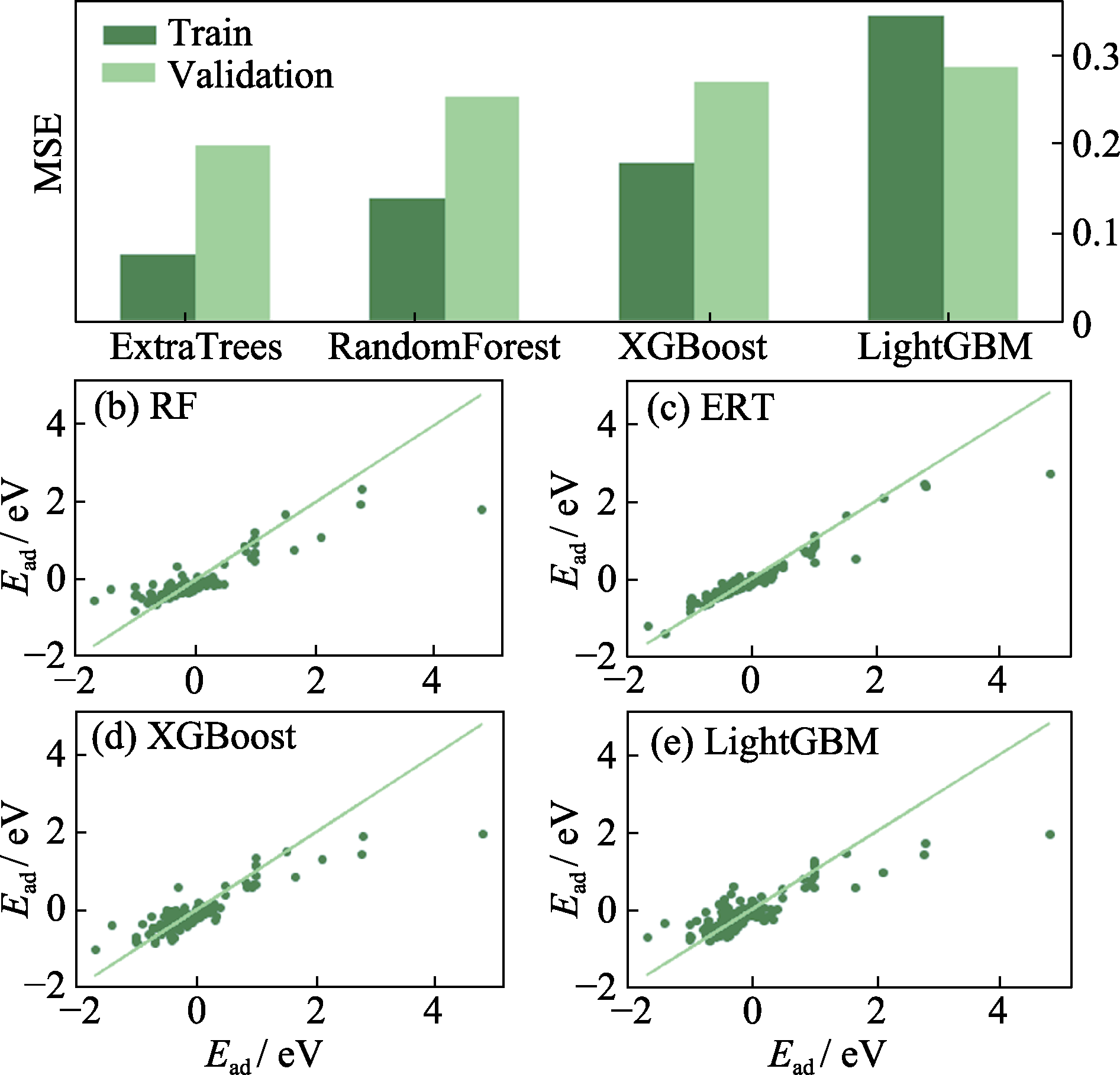
Fig. 4 (a) Mean square error (MSE) of the four ensemble methods, and (b-e) correlation graphs of the true and predicted values of the four ensemble methods (b) Random forest (RF); (c) Extremely randomized trees (ERT); (d) Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost); (e) Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM)
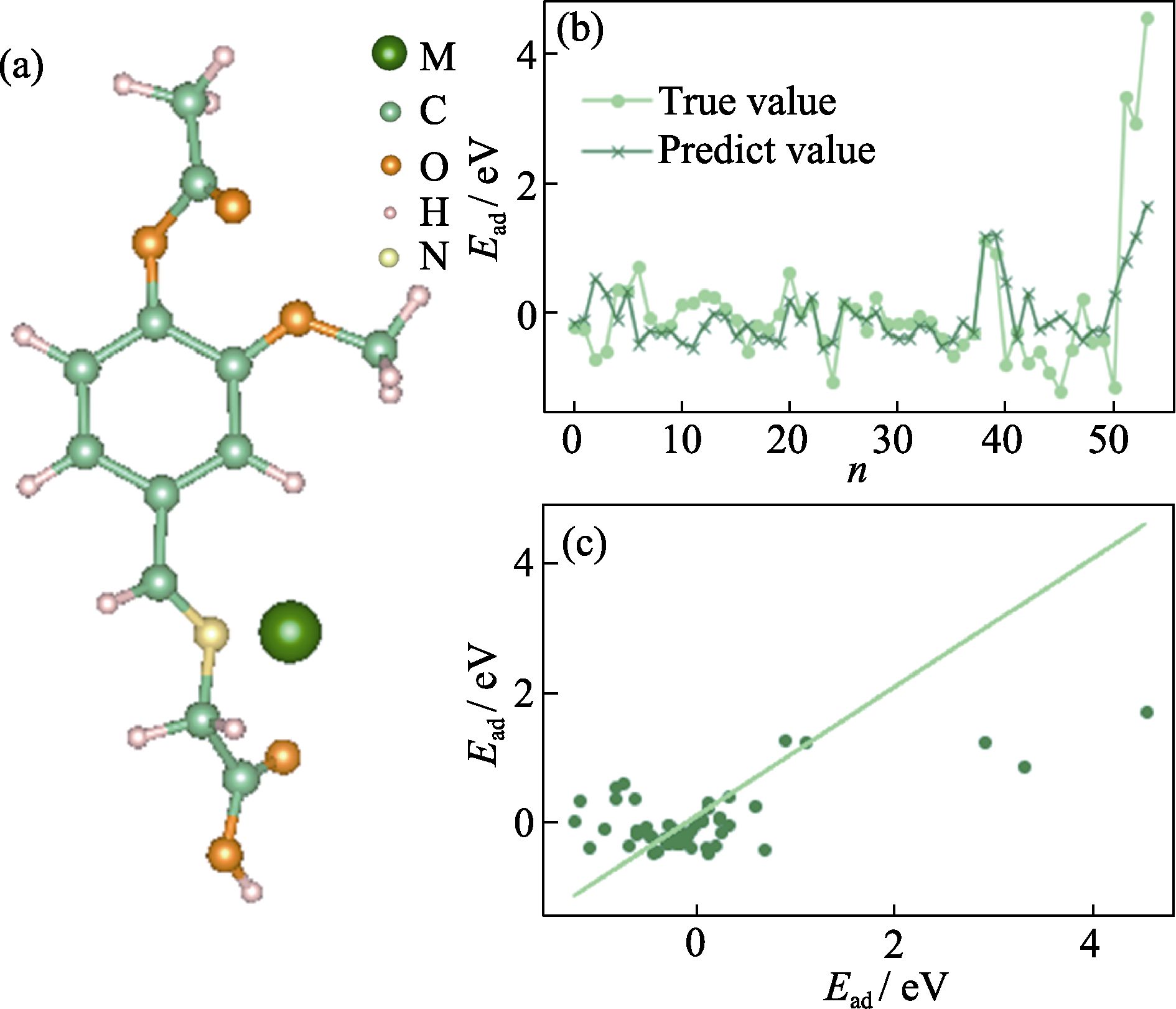
Fig. 5 (a) Example of the structure of vanillin monomer adsorbing metal ions; (b) Fitting effect graph of Extremely Randomized Trees (ERT) for VMA-Mn+ adsorption energy; (c) Correlation diagram of ERT for VMA-Mn+ adsorption energy
| [1] |
PENG W J, LI H Q, LIU Y Y, et al. A review on heavy metalions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 230:496-504.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AHMAD S Z N, SALLEH W N W, ISMAIL A F, et al. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions using graphene-based nanomaterials: toxicity, roles of functional groups and mechanisms. Chemosphere, 2020, 248:126008.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIU Y, ZHAO C F, ZHANG A R, et al. Theoretical study on the removal of uranyl by nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur doped graphene materials. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2019, 49(1):91-102.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PENG X J, WANG Y F. Efficient stochastic simulation algorithm for chemically reacting systems based on support vector regression. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2009, 22(5):502-510.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CAI C, LI L, DENG X, et al. Machine learning and high- throughput computational screening of metal-organic framework for separation of methane/ethane/propane. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(5):427.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ORUPATTUR N V, MUSHRIF S H, PRASAD V. Catalytic materials and chemistry development using a synergistic combination of machine learning and ab initio methods. Computational Materials Science, 2020, 174:109497-16.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI X, XI L L, YANG J. First principles high-throughput research on thermoelectric materials: a review. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3):236-246.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MENG Y, WANG X, YANG J, et al. Research on machine learning based model for predicting the impact status of laminated glass. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1):61-68.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FENG C, SHARMAN E, YE S, et al. A neural network protocol for predicting molecular bond energy. Sci. China Chem., 2019, 62(12):1698-1703.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LU S, ZHOU Q, OUYANG Y, et al. Accelerated discovery of stable lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites via machine learning. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):3405.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TEHRANI A M, OLIYNYK A O, PARRY M, et al. Machine learning directed search for ultraincompressible, superhard materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(31):9844-9853.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KANG Y, LI L, LI B. Recent progress on discovery and properties prediction of energy materials: simple machine learning meets complex quantum chemistry. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 54:72-88.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BROCKHERDE F, VOGT L, LI L, et al. By-passing the Kohn-Sham equations with machine learning. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1):872.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XIAO Y, MIARA L J, WANG Y, et al. Computational screening of cathode coatings for solid-state batteries. Joule, 2019, 3(5):1252-1275.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PANAPITIYA G, AVENDANO-FRANCO G, REN P, et al. Machine learning prediction of CO adsorption in thiolated, Ag alloyed Au nanoclusters. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(50):17508-17514.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PARDAKHTI M, MOHARRERI E, WANIK D, et al. Machine learning using combined structural and chemical descriptors for prediction of methane adsorption performance of metal organic frameworks (MOFs). ACS Combinatorial Science, 2017, 19(10):640-645.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SI Y, SAMULSKIE T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(6):1679-1682.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN D, FENG H, LI J. Graphene oxide: preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(11):6027-6053.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHENG Z H, SHAO L, CHEN J J, et al. Catalyst free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(6):4350-4358.
DOI URL |
| [20] | MAURIZIO C, VICENZO B, MICHAEL A R. A direct procedure for the evaluation of solvent effects in MC-SCF calculations. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 111(12):5295-5302. |
| [21] | BRAND M. Incremental Singular Value Decomposition of Uncertain Data with Missing Values. Computer Vision-ECCV 2002, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002: 707-720. |
| [22] | NEELAKANTAN A, VILNIS L, LEQ V, et al. Adding gradiant noise improves learning for very deep networks. arXiv: Machine Learning, 2015, 1511:06807. |
| [23] | 迪安J A, 魏俊发. 兰氏化学手册, 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 1-1579. |
| [24] |
FRIEDMAN J H, JAO S. Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(5):1189-1232.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LIASHCHYNSKYI P, LIASHCHYNSKYI P. Grid search, random search, genetic algorithm: a big comparison for NAS. arXiv: Learning, 2019, 1912:06059. |
| [26] | MARTENS H A, DARDENNE P J, CSYSTEMS I L. Validation and verification of regression in small data sets. ChemomERTics & Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1998, 44(1/2):99-121. |
| [27] |
FRIEDMAN J H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2002, 38(4):367-378.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SMOLA A J, SCHOLKOPF B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3):199-222.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
RUPP M. Machine learning for quantum mechanics in a nutshell. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2015, 115(16):1058-1073.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SVETNIK V. Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2003, 43(6):1947-1958. |
| [31] | GEURTS P, ERNST D, WEHENKEL L. Extremely randomized trees. Machine Learning, 2006, 63(1):3-42. |
| [32] | DRUCKER H. Improving regressors using boosting techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1997: 107-115. |
| [33] | FRANLLIN J. The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. The Mathematical Intelligencer, 2005, 27(2):83-85. |
| [34] | SANTOS R I H, REIS D T, PEREIRA D H. A DFT based analysis of adsorption of Cd2+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+, on vanillin monomer: a study of the removal of metalions from effluents. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2019, 25(9):267. |
| [1] | LIU Lei, GUO Ruihua, WANG Li, WANG Yan, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Pt3Co High-index Facets by Density Functional Theory [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 39-46. |
| [2] | LI Honglan, ZHANG Junmiao, SONG Erhong, YANG Xinglin. Mo/S Co-doped Graphene for Ammonia Synthesis: a Density Functional Theory Study [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 561-568. |
| [3] | WU Guangyu, SHU Song, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jianjun. Enhanced Styrene Adsorption by Grafted Lactone-based Activated Carbon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [4] | XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [5] | WANG Peng, JIN Zunlong, CHEN Ningguang, LIU Yonghao. Theoretical Investigation of Mo Doped α-MnO2 Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 541-546. |
| [6] | JIAO Zhixiang, JIA Fanhao, WANG Yongchen, CHEN Jianguo, REN Wei, CHENG Jinrong. Curie Temperature Prediction of BiFeO3-PbTiO3-BaTiO3 Solid Solution Based on Machine Learning [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1321-1328. |
| [7] | SHI Siqi, SUN Shiyu, MA Shuchang, ZOU Xinxin, QIAN Quan, LIU Yue. Detection Method on Data Accuracy Incorporating Materials Domain Knowledge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1311-1320. |
| [8] | WU Jing, YU Libing, LIU Shuaishuai, HUANG Qiuyan, JIANG Shanshan, ANTON Matveev, WANG Lianli, SONG Erhong, XIAO Beibei. NiN4/Cr Embedded Graphene for Electrochemical Nitrogen Fixation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1141-1148. |
| [9] | HE Junlong, SONG Erhong, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. DFT Calculation of NO Adsorption on Cr Doped Graphene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| [10] | MENG Yanran, WANG Xinger, YANG Jian, XU Han, YUE Feng. Research on Machine Learning Based Model for Predicting the Impact Status of Laminated Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 61-68. |
| [11] | WANG Xiangxue, LI Xing, WANG Jiaqi, ZHU Hongtao. Recent Advances in Carbon Nitride-based Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 260-270. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zihang, WANG Qun, GE Xiang, LI Zhaoyang. Strontium Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Simulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| [13] | QI Xin-Xin, SONG Guang-Ping, YIN Wei-Long, WANG Ming-Fu, HE Xiao-Dong, ZHENG Yong-Ting, WANG Rong-Guo, BAI Yue-Lei. Analysis on Phase Stability and Mechanical Property of Newly-discovered Ternary Layered Boride Cr4AlB4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 53-60. |
| [14] | WANG Jun-Kai, ZHANG Yuan-Zhuo, LI Jun-Yi, ZHANG Hai-Jun, LI Fa-Liang, HAN Lei, SONG Shu-Peng. Low Temperature Catalytic Synthesis of β-SiC Powders via Microwave Heating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 725-730. |
| [15] | CHEN Hai-Tao, HUANG Xue-Fei, HUANG Wei-Gang. Influence of N Doping on the Electronic Structure and Absorption Spectrum of Ca2SiO4: Eu2+ Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 443-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||