
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 870-876.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160584
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Xiu-Bin1, YU Wei1, Li Jing1, JIANG Zhao-Yi2, MA Deng-Hao2, LIU Hai-Xu1
Received:2016-10-24
Revised:2016-12-27
Published:2017-08-10
Online:2017-07-19
About author:GUO Xiu-Bin. E-mail: 1067654456@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
GUO Xiu-Bin, YU Wei, Li Jing, JIANG Zhao-Yi, MA Deng-Hao, LIU Hai-Xu. Improving Microstructure and Photoelectric Performance of the Perovskite Material via Mixed Solvents[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 870-876.
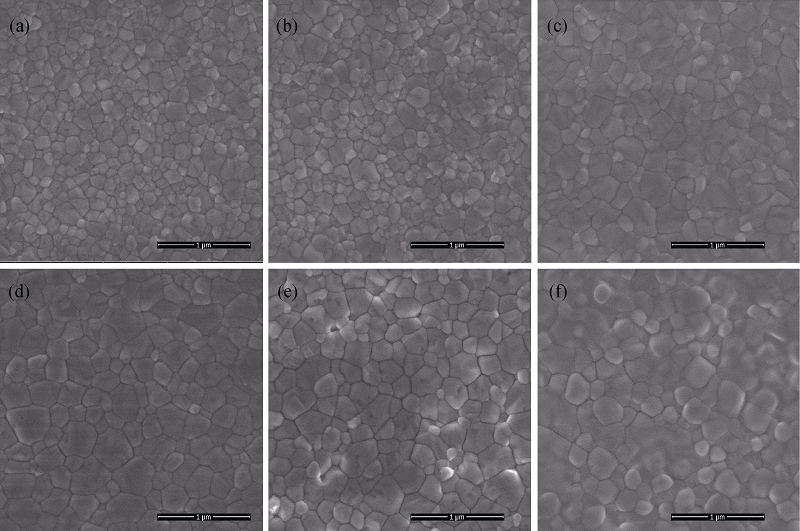
Fig. 1 Surface morphologies of perovskite films prepared by different solvents(a) Pure DMF solvent; (f) Pure DMSO solvent; (b) 15% DMSO; (c) 30% DMSO; (d) 60% DMSO; (e) 80% DMSO
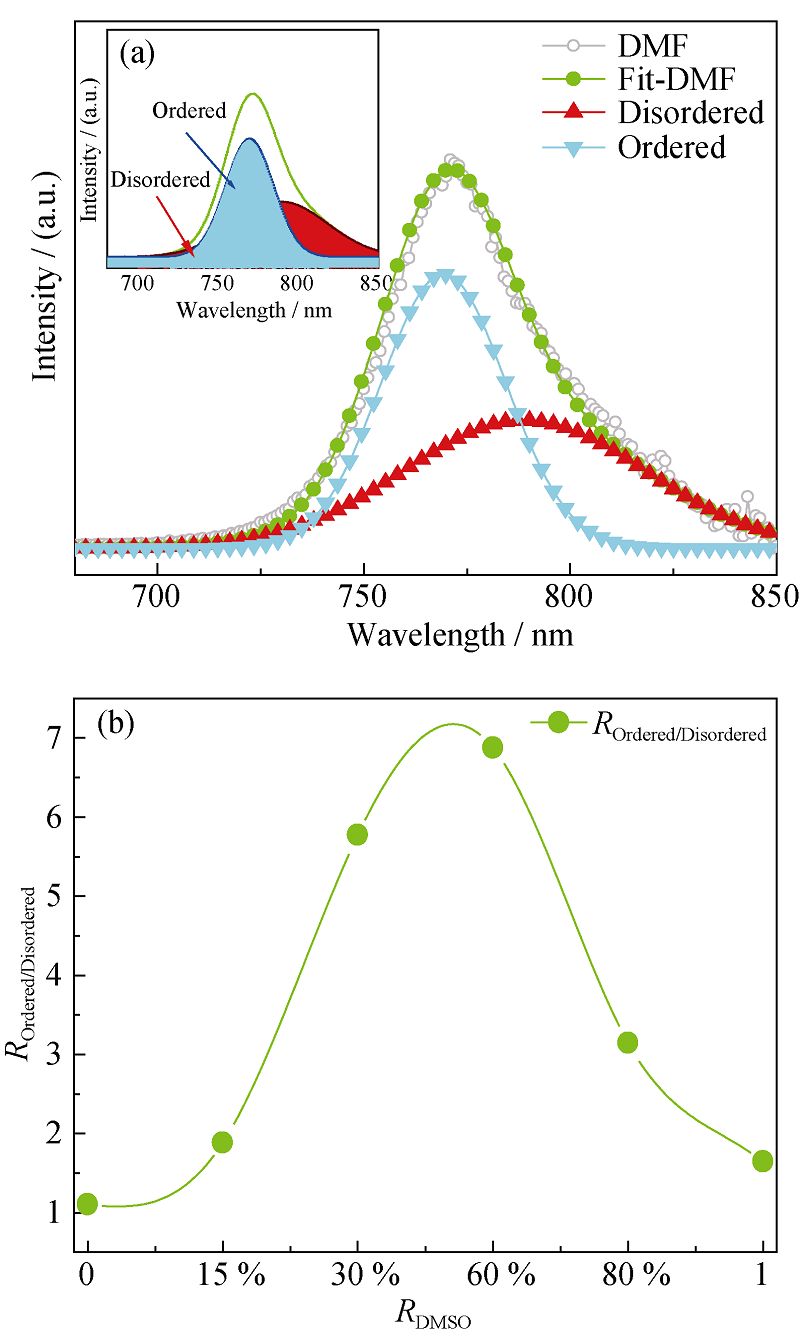
Fig. 6 Fit of PL spectrum for perovskite film based on pure DMF solvent (a); the change trend of the ratio of ordered to disordered phases with the increase of DMSO (b)
| Sample | τ1/ns | τ2/ns |
|---|---|---|
| DMF | 2.0 | 81 |
| 15% | 3.1 | 85 |
| 30% | 2.6 | 94 |
| 60% | 3.5 | 90 |
| 80% | 1.8 | 77 |
| DMSO | 1.7 | 67 |
Table 1 Carrier lifetime extracted from TR-PL decay curves
| Sample | τ1/ns | τ2/ns |
|---|---|---|
| DMF | 2.0 | 81 |
| 15% | 3.1 | 85 |
| 30% | 2.6 | 94 |
| 60% | 3.5 | 90 |
| 80% | 1.8 | 77 |
| DMSO | 1.7 | 67 |
| Devices | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | VOC/V | FF/% | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMF | 15.4 | 0.91 | 66.3 | 9.3 |
| 15% | 18.9 | 0.95 | 70.3 | 12.6 |
| 30% | 20.9 | 0.99 | 72.8 | 15.1 |
| 60% | 20.2 | 0.96 | 71.9 | 13.9 |
| 80% | 17.2 | 0.94 | 69.2 | 11.2 |
| DMSO | 14.7 | 0.91 | 63.1 | 8.4 |
Table 2 Photovoltaic parameters of devices prepared by mixed solvents with different volume ratios
| Devices | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | VOC/V | FF/% | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMF | 15.4 | 0.91 | 66.3 | 9.3 |
| 15% | 18.9 | 0.95 | 70.3 | 12.6 |
| 30% | 20.9 | 0.99 | 72.8 | 15.1 |
| 60% | 20.2 | 0.96 | 71.9 | 13.9 |
| 80% | 17.2 | 0.94 | 69.2 | 11.2 |
| DMSO | 14.7 | 0.91 | 63.1 | 8.4 |
| [1] | KOJIMA A, TESHIMA K, SHIRAI Y, et al.Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(17): 6050-6051. |
| [2] | ETGAR L, GAO P, XUE Z, et al.Mesoscopic CH3NH3PbI3/TiO2 heterojunction solar cells.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(42): 17396-17399. |
| [3] | LEE M M, TEUSCHER J, MIYASAKA T, et al.Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites.Science, 2012, 338(6107): 643-647. |
| [4] | PARK N G.Organometal perovskite light absorbers toward a 20% efficiency low-cost solid-state mesoscopic solar cell.Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(15): 2423-2429. |
| [5] | NOH J H, SANG H I, JIN H H, et al.Chemical management for colorful, efficient, and stable inorganic-organic hybrid nanostructured solar cells.Nano Letters, 2013, 13(4): 1764-1769. |
| [6] | JEON N J, NOH J H, YANG W S, et al.Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells.Nature, 2015, 517(7535): 476-480. |
| [7] | MATTEOCCI F, RAZZA S, DI G F, et al.Solid-state solar modules based on mesoscopic organometal halide perovskite: a route towards the up-scaling process.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(9): 3918-3923. |
| [8] | JENG J Y, CHIANG Y F, LEE M H, et al.CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite/fullerene planar-heterojunction hybrid solar cells.Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(27): 3727-3732. |
| [9] | IM J H, JANG I H, PELLET N, et al.Growth of CH3NH3PbI3 cuboids with controlled size for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells.Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(11): 927-932. |
| [10] | ZHAO Y, ZHU K.Solution chemistry engineering toward high-efficiency perovskite solar cells.Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2014, 5(23): 4175-4186. |
| [11] | WU Y, ISLAM A, YANG X, et al.Retarding the crystallization of PbI2 for highly reproducible planar-structured perovskite solar cells via sequential deposition.Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(9): 2934-2938. |
| [12] | WAKAMIYA A, ENDO M, SASAMORI T, et al.Reproducible fabrication of efficient perovskite-based solar cells: X-ray crystallographic studies on the formation of CH3NH3PbI3 Layer.Chemistry Letters, 2014, 43(5): 711-713. |
| [13] | TANG Z, TANAKA S, ITO S, et al.Investigating relation of photovoltaic factors with properties of perovskite films based on various solvents.Nano Energy, 2016, 21: 51-61. |
| [14] | JEON N J, NOH J H, KIM Y C, et al.Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic-organic hybrid perovskite solar cells.Nature Materials, 2014, 13(9): 897-903. |
| [15] | LI W, FAN J, LI J, et al.Controllable grain morphology of perovskite absorber film by molecular self-assembly toward efficient solar cell exceeding 17%.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(32): 10399-10405. |
| [16] | CAI B, ZHANG W H, QIU J, et al.Solvent engineering of spin-coating solutions for planar-structured high-efficiency perovskite solar cells.Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36(8): 1183-1190. |
| [17] | YANG W S, NOH J H, JEON N J, et al.High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange.Science, 2015, 348(6240): 1234-1237. |
| [18] | CHEN Q, ZHOU H, HONG Z, et al.Planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells via vapor-assisted solution process.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(2): 622-625. |
| [19] | ZHAO L, LUO D, WU J, et al.High-performance inverted planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells based on lead acetate precursor with efficiency exceeding 18%.Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(20): 3508-3514. |
| [20] | IKHMAYIES S J, AHMAD-BITAR R N. An investigation of the bandgap and Urbach tail of vacuum-evaporated SnO2 thin films.Physica Scripta, 2011, 84(5): 143-146. |
| [21] | WASSNER T A, LAUMER B, MAIER S, et al. Optical properties and structural characteristics of ZnMgO grown by plasma assisted molecular beam epitaxy. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105(2): 023505-1-6. |
| [22] | LIU F, DONG Q, WONG M K, et al. Is excess PbI2 beneficial for perovskite solar cell performance. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(7): 1502206-1-9. |
| [23] | PARK B W, JAIN S M, ZHANG X, et al.Resonance Raman and excitation energy dependent charge transfer mechanism in halide- substituted hybrid perovskite solar cells.ACS Nano, 2015, 9(2): 2088-2101. |
| [24] | PELLET N, GAO P, GREGORI G, et al.Mixed-organic-cation perovskite photovoltaics for enhanced solar-light harvesting.Angewandte Chemie, 2014, 53(12): 3151-3157. |
| [25] | CHEN Q, ZHOU H, SONG T B, et al.Controllable self-induced passivation of hybrid lead iodide perovskites toward high performance solar cells.Nano Letters, 2014, 14(7): 4158-4163. |
| [26] | XING G, MATHEWS N, SUN S, et al.Long-range balanced electron-and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3.Science, 2013, 342(6156): 344-347. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [3] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [4] | LÜ Xinyi, XIANG Hengyang, ZENG Haibo. Long-range Ordered Films Boost Efficient Perovskite Quantum Dot Light-emitting Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [5] | QU Mujing, ZHANG Shulan, ZHU Mengmeng, DING Haojie, DUAN Jiaxin, DAI Henglong, ZHOU Guohong, LI Huili. CsPbBr3@MIL-53 Nanocomposite Phosphors: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in White LEDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [6] | XIAO Zichen, HE Shihao, QIU Chengyuan, DENG Pan, ZHANG Wei, DAI Weideren, GOU Yanzhuo, LI Jinhua, YOU Jun, WANG Xianbao, LIN Liangyou. Nanofiber-modified Electron Transport Layer for Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hui, XU Zhipeng, ZHU Congtan, GUO Xueyi, YANG Ying. Progress on Large-area Organic-inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Films and Its Photovoltaic Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [8] | CHEN Tian, LUO Yuan, ZHU Liu, GUO Xueyi, YANG Ying. Organic-inorganic Co-addition to Improve Mechanical Bending and Environmental Stability of Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [9] | YU Man, GAO Rongyao, QIN Yujun, AI Xicheng. Influence of Upconversion Luminescent Nanoparticles on Hysteresis Effect and Ion Migration Kinetics in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [10] | CHEN Zhengpeng, JIN Fangjun, LI Mingfei, DONG Jiangbo, XU Renci, XU Hanzhao, XIONG Kai, RAO Muming, CHEN Chuangting, LI Xiaowei, LING Yihan. Double Perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: Preparation and Performance as Cathode Material for Intermediate-temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [11] | LIU Suolan, LUAN Fuyuan, WU Zihua, SHOU Chunhui, XIE Huaqing, YANG Songwang. In-situ Growth of Conformal SnO2 Layers for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1397-1403. |
| [12] | WANG Yu, XIONG Hao, HUANG Xiaokun, JIANG Linqin, WU Bo, LI Jiansheng, YANG Aijun. Regulation of Low-dose Stannous Iso-octanoate for Two-step Prepared Sn-Pb Alloyed Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1339-1347. |
| [13] | ZHOU Zezhu, LIANG Zihui, LI Jing, WU Congcong. Preparation of MAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells/Module via Volatile Solvents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1197-1204. |
| [14] | LI Qianyuan, LI Jiwei, ZHANG Yuhan, LIU Yankang, MENG Yang, CHU Yu, ZHU Yijia, XU Nuoyan, ZHU Liang, ZHANG Chuanxiang, TAO Haijun. Enhanced Photovoltaic Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells by PbTiO3 Modification and Polarization Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1205-1211. |
| [15] | DAI Xiaodong, ZHANG Luwei, QIAN Yicheng, REN Zhixin, CAO Huanqi, YIN Shougen. Controlling Vertical Composition Gradients in Sn-Pb Mixed Perovskite Solar Cells via Solvent Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1089-1096. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||