
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 393-400.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150402
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai
Received:2015-08-27
Revised:2015-11-16
Published:2016-04-20
Online:2016-03-25
About author:YUAN Qin. E-mail: yinzi863@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai. Effects of Al and O Content on Transformation from SiAlCO to Si(Al)C Fibers after High Temperature Treatment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 393-400.
| Sample | Oxidation temperature before EB/℃ | Si/wt% | C/wt% | Al/wt% | O/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | - | 57.27 | 36.71 | 0.24 | 5.78 | 1.496 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 160 | 55.88 | 35.08 | 0.20 | 8.84 | 1.465 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 190 | 54.16 | 32.21 | 0.22 | 13.41 | 1.388 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | - | 55.20 | 36.93 | 0.33 | 7.54 | 1.561 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 160 | 54.77 | 35.42 | 0.33 | 9.48 | 1.509 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 190 | 53.63 | 33.02 | 0.36 | 12.94 | 1.437 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | - | 55.77 | 36.27 | 0.62 | 7.36 | 1.517 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 160 | 54.69 | 35.03 | 0.57 | 9.71 | 1.495 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 190 | 54.10 | 32.69 | 0.53 | 12.68 | 1.410 |
Table1 Chemical compositions of SiAlCO fibers
| Sample | Oxidation temperature before EB/℃ | Si/wt% | C/wt% | Al/wt% | O/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | - | 57.27 | 36.71 | 0.24 | 5.78 | 1.496 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 160 | 55.88 | 35.08 | 0.20 | 8.84 | 1.465 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 190 | 54.16 | 32.21 | 0.22 | 13.41 | 1.388 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | - | 55.20 | 36.93 | 0.33 | 7.54 | 1.561 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 160 | 54.77 | 35.42 | 0.33 | 9.48 | 1.509 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 190 | 53.63 | 33.02 | 0.36 | 12.94 | 1.437 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | - | 55.77 | 36.27 | 0.62 | 7.36 | 1.517 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 160 | 54.69 | 35.03 | 0.57 | 9.71 | 1.495 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 190 | 54.10 | 32.69 | 0.53 | 12.68 | 1.410 |
| Sample | Si/wt% | C/wt% | O/wt% | Al/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | 62.53 | 37.27 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 65.72 | 33.80 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 1.200 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 68.73 | 31.07 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 1.060 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | 62.31 | 37.36 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 1.406 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 63.33 | 36.34 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 1.345 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 66.97 | 32.70 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 1.145 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | 62.03 | 37.11 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 63.02 | 36.06 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 1.335 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 65.55 | 33.50 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.222 |
| Tyranno SA(edge)[ | 68.00 | 31.30 | - | 0.50 | 1.080 |
| Tyranno SA(core)[ | 62.90 | 36.10 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 1.340 |
Table2 Chemical compositions of SiAlCO fibers after heat-treatment at 1700℃
| Sample | Si/wt% | C/wt% | O/wt% | Al/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | 62.53 | 37.27 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 65.72 | 33.80 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 1.200 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 68.73 | 31.07 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 1.060 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | 62.31 | 37.36 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 1.406 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 63.33 | 36.34 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 1.345 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 66.97 | 32.70 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 1.145 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | 62.03 | 37.11 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 63.02 | 36.06 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 1.335 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 65.55 | 33.50 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.222 |
| Tyranno SA(edge)[ | 68.00 | 31.30 | - | 0.50 | 1.080 |
| Tyranno SA(core)[ | 62.90 | 36.10 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 1.340 |
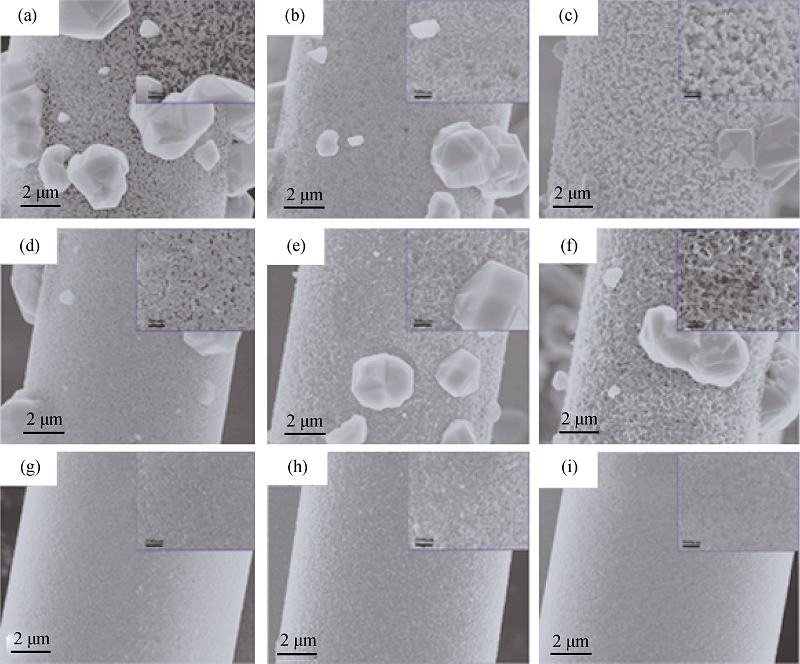
Fig. 7 Surface morphologies of SiAlCO fibers after heat-treatment at 1700℃ (a)-(c) SiAlCO2-6~SiAlCO2-13, (d)-(f) SiAlCO3-6~SiAlCO3-13, (g)-(i) SiAlCO6-6~SiAlCO6-13
| [1] | DONG S, KATOH Y, KOHYAMA A.Preparation of SiC/SiC composites by hot-pressing, using Tyranno-SA fiber as reinforcement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2003, 86(1): 26-32. |
| [2] | WANG DE-YIN,MAO XIAN-HE,SONG YONG-CAI, et al.Preparation and properties of SiC fiber with a stable excess carbon layer on the surface.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1209-1213. |
| [3] | KATOH Y, OZAWA K, SHIH C, et al.Continuous SiC fiber, CVI SiC matrix composites for nuclear applications: properties and irradiation effects. J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, 448(1/2/3): 448-476. |
| [4] | ABE T, KISHIMOTO H, NAKAZATO N, et al.SiC/SiC composite heater for IFMIF.Fusion. Eng. Des., 2012, 87(7/8): 1258-1260. |
| [5] | WANG DE-YIN,MAO XIAN-HE,SONG YONG-CAI, et al.Preparation and properties of SiC fiber with a stable excess carbon layer on the surface.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1209-1213. |
| [6] | WANG DE-YIN, SONG YONG-CAI, JIAN KE.Effect of structure and composition on the specific resistivity of continuous silicon carbide fibers.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(2): 162-168. |
| [7] | BUNSELL A, PIANT A.A review of the development of the three generations of small diameter silicon carbide fibers.J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(3): 823-839. |
| [8] | ISHIKAWA T.Advances in inorganic fibers.Adv. Polym. Sci., 2005, 178: 109-144. |
| [9] | ZHAO DA-FANG,WANG HAI-ZHE,LI XIAO-DONG.Development of polymer-derived SiC fiber.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1097-1104. |
| [10] | ISHIKAWA T, KOHTOKU Y, KUMAGAWA K, et al.High-strength alkali-resistant sintered SiC fibre stable to 2200℃.Nature, 1998, 391(6669): 773-775. |
| [11] | ISHIKAWA T, KAJII S, MATSUNAGA K, et al.A tough, thermally conductive silicon carbide composite with high strength up to 1600℃ in air. Science, 1998, 282(5392): 1295-1297. |
| [12] | DONG S M, CHOLLON G, LABRUGERE C, et al.Characterizaiton of nearly stoichiometric SiC ceramic fibres.J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36(10): 2371-2381. |
| [13] | CAO F, KIM D P, LI X D, et al.Synthesis of polyaluminocarbosilane and reaction mechanism study.J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 85(13): 2787-2792. |
| [14] | YU Y, TAI J, TANG X, et al.Continuous Si-C-O-Al fiber derived from aluminum-containing polycarbosilane precursor.Compos. Part A-Appl. S., 2008, 39(7): 1101-1105. |
| [15] | MORISHITA K, OCHIAI S, OKUDA H, et al.Fracture toughness of a crystalline silicon carbide fiber Tyranno-SA3. J. Am Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(8): 2571-2576. |
| [16] | CHEN L, ZHANG L, CAI Z, et al, Effects of oxidation curing and sintering additives on the formation of polymer-derived near-stoichiometric silicon carbide fibers.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 9(2): 428-436. |
| [17] | TAKEDA M, IMAI Y, ICHIKAWA H, et al.Thermal stability of SiC fiber prepared by an irradiation-curing process.Compos. Sci. Technol., 1999, 59(6): 793-799. |
| [18] | SUGIMOTO M, SHIMOO T, OKAMURA K, et al.Reaction mechanisms of silicon carbide fiber synthesis by heat treatment of polycarbosilane fibers cured by radiation: I, Evolved gas analysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1995, 78(8): 1013-1017. |
| [19] | CHOLLON G, PAILLER R, NASLAIN R, et al.Thermal stability of a PCS-derived SiC fibre with a low oxygen content (Hi-Nicalon). J. Mater. Sci., 1997, 32(2): 327-347. |
| [20] | LY H Q, TAYLOR R, DAY J, et al.Conversion of polycarbosilane (PCS) to SiC-based ceramic Part Ⅱ pyrolysis and characterisation.J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36(16): 4045-4057. |
| [21] | PORTE L, SARTRE A.Evidence for a silicon oxycarbide phase in the Nicalon silicon carbide fibre.J. Mater. Sci., 1989, 24(1): 271-275. |
| [22] | LAFFON C, FLANK A M, LAGARDE P, et al.Study of Nicalon-based ceramic fibres and powders by EXAFS spectrometry, X-ray diffractometry and some additional methods.J. Mater. Sci., 1989, 24(4): 1503-1512. |
| [23] | COUSTUMER L P, MONTHIOUX M, OBERLIN A.Understanding Nicalon fiber.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 1993, 11(2): 95-103. |
| [24] | SHIMOO T, CHEN H, OKAMURA K.High-temperature stability of Nicalon under Ar or O2 atmosphere.J. Mater. Sci., 1994, 29(2): 456-463. |
| [25] | ORTIZ A L, SANCHEZ B F, CUMBRERA F L, et al.X-ray powder diffraction analysis of a silicon carbide-based ceramic.Mater. Lett., 2001, 49(2): 137-145. |
| [26] | JACOBSON N S, KLINE S E.A thermoanalytical study of the conversion of amorphous Si-Ti-C-O fibers to SiC.Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2012, 9(4): 816-822. |
| [27] | SHIMOO T, OKAMURA K, TSUKADA I, et al.Thermal stability of low-oxygen SiC fibers fired under different conditions.J. Mater. Sci., 1999, 34(22): 5623-5631. |
| [28] | RAHAMAN M N.Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd edition. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 2003: 591-592. |
| [1] | WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [2] | CUI Ning, ZHANG Yuxin, WANG Lujie, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, TANG Huaguo, QIAO Zhuhui. Single-phase Formation Process and Carbon Vacancy Regulation of (TiVNbMoW)Cx High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [3] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [4] | HE Zongbei, CHEN Fang, LIU Dianguang, LI Tongye, ZENG Qiang. Sintering Behavior of Simulating Core FCM Fuel via Hot Oscillatory Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 501-508. |
| [5] | YANG Yong, GUO Xiaotian, TANG Jie, CHANG Haotian, HUANG Zhengren, HU Xiulan. Research Progress and Prospects of Non-oxide Ceramic in Stereolithography Additive Manufacturing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 267-277. |
| [6] | Zhui WANG, Jian-Jun HAN, Jian-Qiang LI, Xiao-Yu LI, Jiang-Tao LI, Gang HE, Jun XIE. Plastic Sintering Behavior of Large-sized La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2 Amorphous Bulk [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 433-438. |
| [7] | NIE Lan-Jian, GU Zhen-An, WANG Yu-Fen, XIANG Zai-Kui, ZHANG Chen-Yang, RAO Chuan-Dong. SiO2 Soot Body at Vacuum Sintering Process: Densification and Transparency Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1060-1066. |
| [8] | GUO Sheng-Qiang, WANG Hao, TU Bing-Tian, WANG Bin, XU Peng-Yu, WANG Wei-Min, FU Zheng-Yi. Fabrication and Property of Fine-grained MgO·1.44Al2O3 Spinel Transparent Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1067-1071. |
| [9] | LI Ren-Yi, LI Xiao-Yu, LI Jian-Qiang, ZHAO Jian-Ling, MA Xiao-Guang, HE Gang, LI Jiang-Tao. Large-sized La2O3-TiO2-SiO2 Amorphous Oxide Fabricated by Hot Press Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 851-856. |
| [10] | WANG Jun-Kai, ZHANG Yuan-Zhuo, LI Jun-Yi, ZHANG Hai-Jun, LI Fa-Liang, HAN Lei, SONG Shu-Peng. Low Temperature Catalytic Synthesis of β-SiC Powders via Microwave Heating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 725-730. |
| [11] | YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai. Effect of SiCxOy Decomposition on Densification of SiCO(Al) Fibers during Sintering Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1320-1326. |
| [12] | LI Hai-Tao, LI Qian, YAN Yan-Fu, XU Rong-Hui. Effect of ZnO-doping on Sinterability and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [13] | LI Yan, CUI Hong, ZHANG Hua-Kun, JI A-Lin, JIE Yu-Jie. Densification Behavior of Thermal Gradient CVI of Large-scale C/C Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(2): 153-158. |
| [14] | DU Xian-Wu, ZHANG Zhi-Xiao, WANG Wei-Min, FU Zheng-Yi, WANG Hao. Effect of Particle Size on Densification and Mechanical Properties of Hot-pressed Boron Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(10): 1062-1066. |
| [15] | ZHANG Guo-Jun, ZOU Ji, NI De-Wei, LIU Hai-Tao, KAN Yan-Mei. Boride Ceramics: Densification, Microstructure Tailoring and Properties Improvement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(3): 225-233. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||