
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 776-780.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2014.14148
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Feng1,2, SUN Tuan-Wei2, QI Chao2, WU Jin2, CUI Da-Xiang1, ZHU Ying-Jie2
Received:2014-03-27
Published:2014-07-20
Online:2014-06-20
About author:CHEN Feng (1981–), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: fchen@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Feng, SUN Tuan-Wei, QI Chao, WU Jin, CUI Da-Xiang, ZHU Ying-Jie. Microwave-assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Microspheres and Polyhedra[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 776-780.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
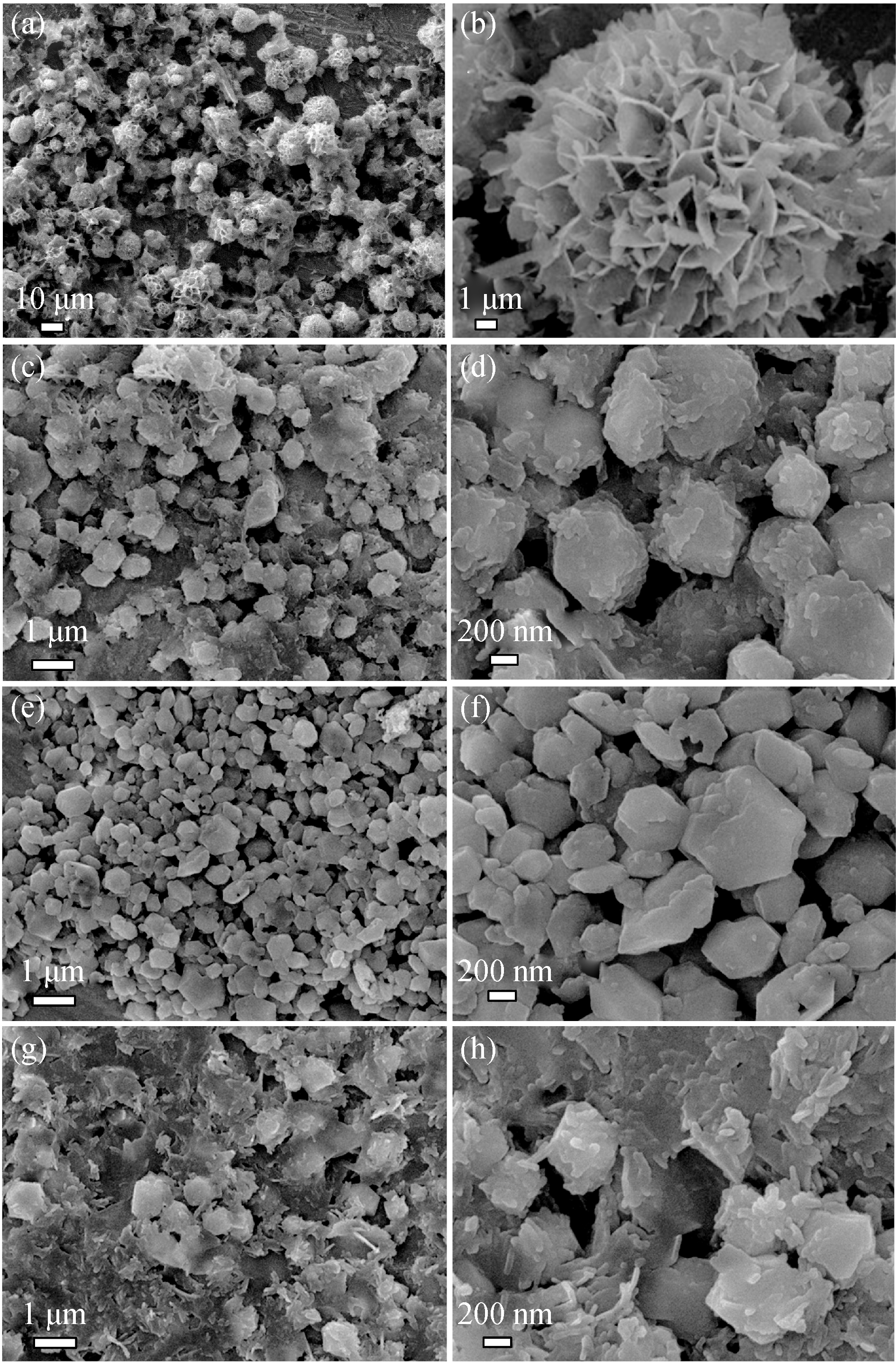

Fig. 1 SEM images of CaP products prepared using Ca (CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and EG by the microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min The volume of EG: (a,b) 0 mL; (c,d) 10 mL; (e,f) 15 mL; (g,h) 20 mL
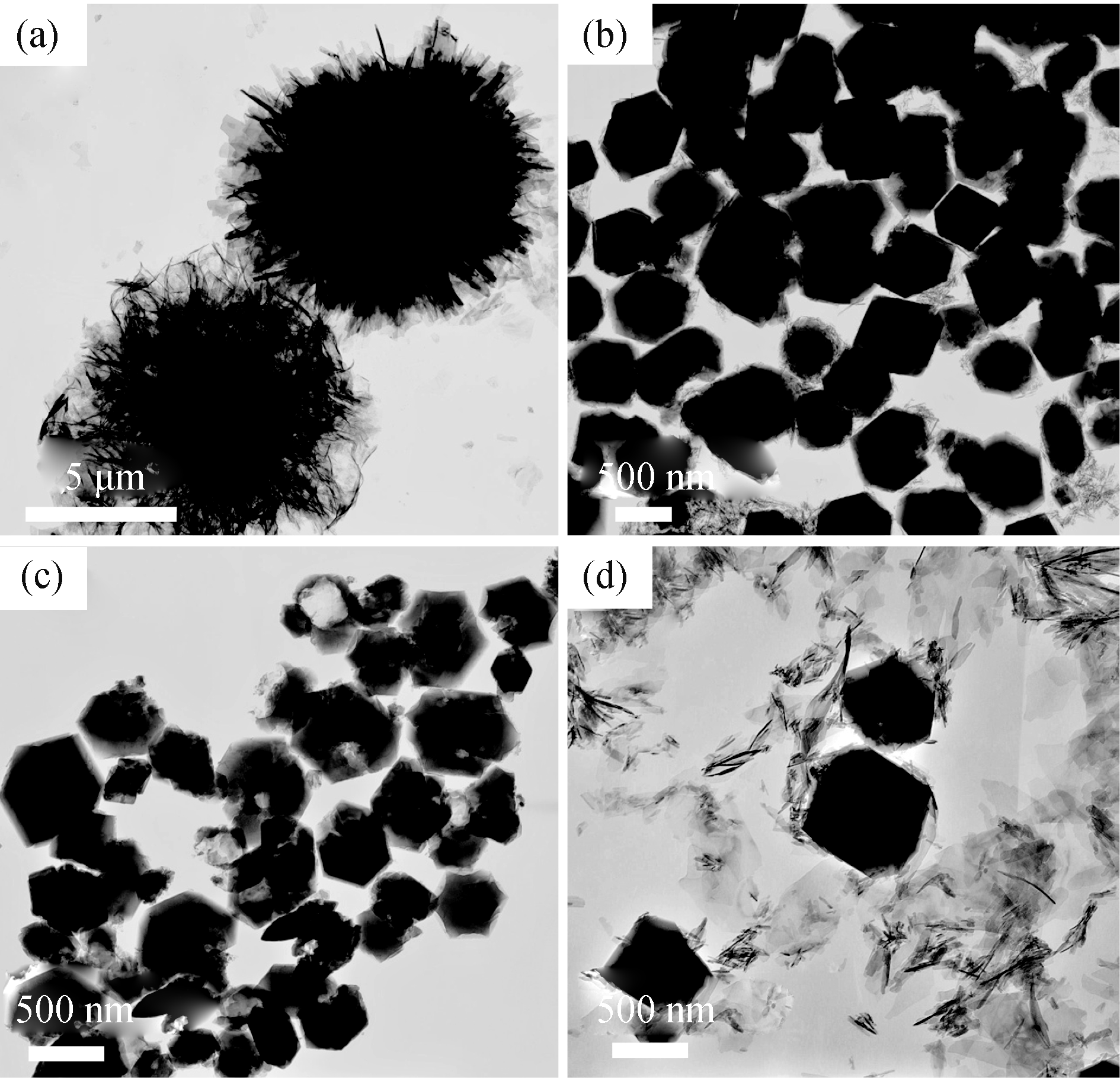
Fig. 2 TEM micrographs (a)-(d) of the CaP products prepared using Ca(CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and EG by the microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min The volume of EG: (a) 0 mL; (b) 10 mL; (c) 15 mL; (d) 20 mL
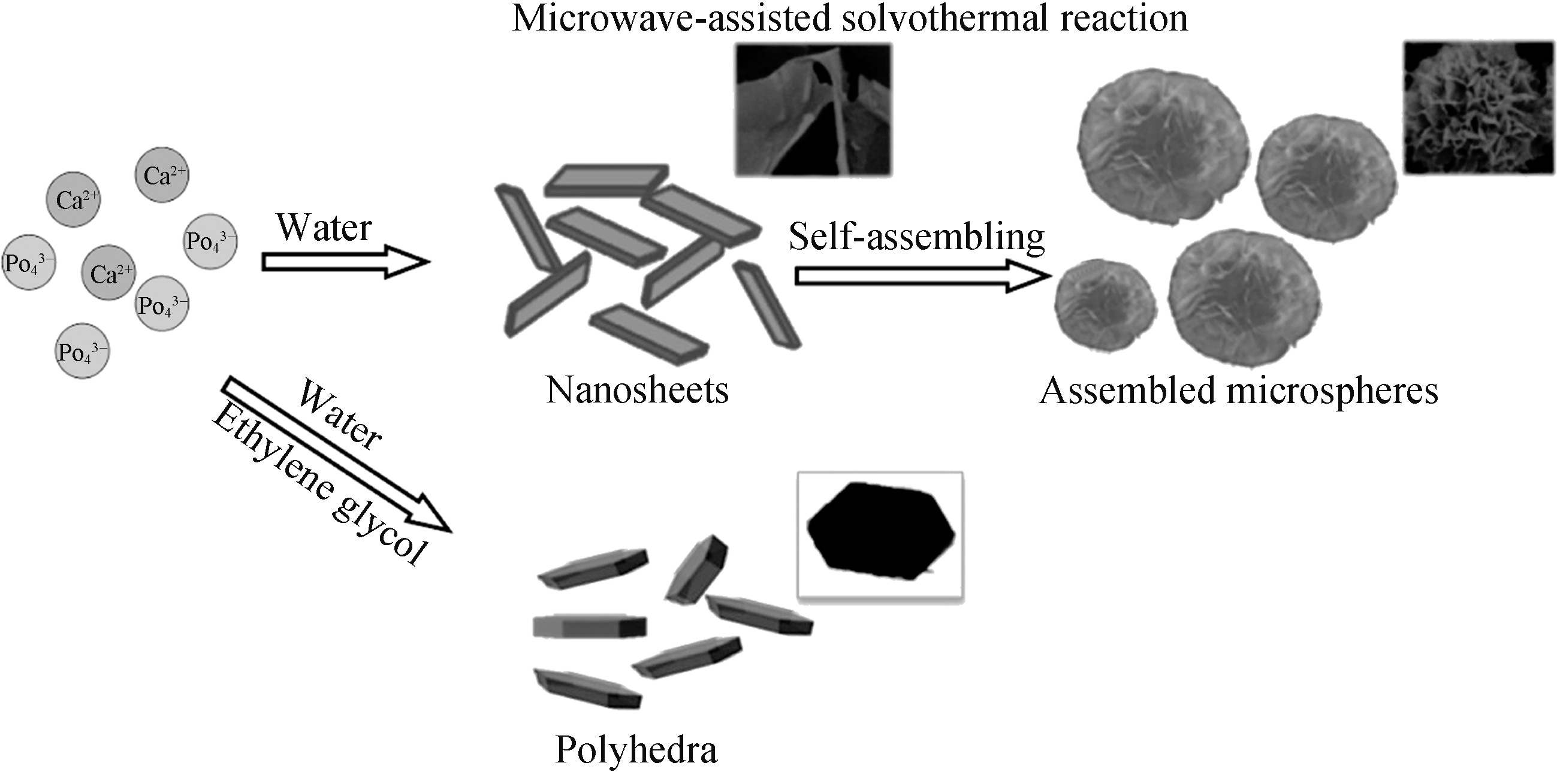
Fig. 3 Schematic illustration of the formation process of the CaP microspheres and polyhedra by the microwave-assisted hydrothermal/solvothermal methods
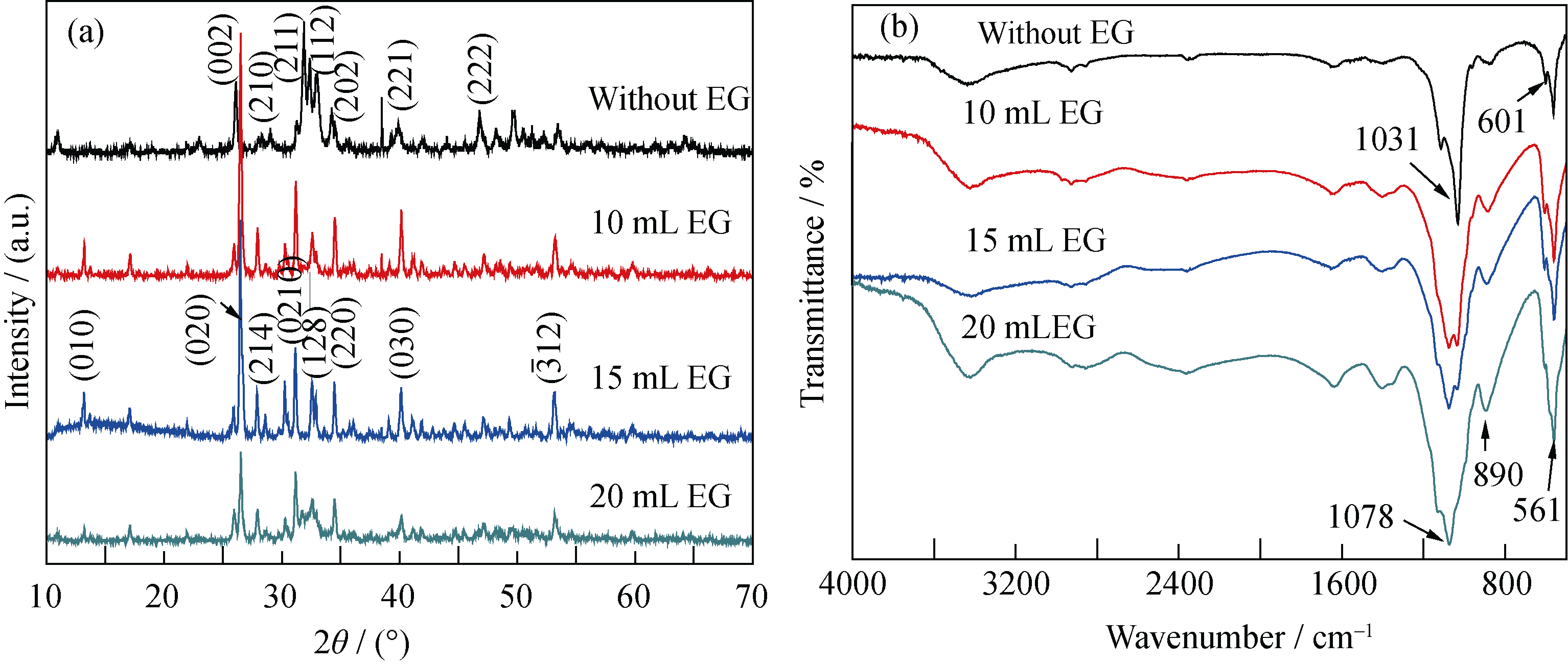
Fig. 4 XRD patterns (a) and FTIR spectra (b) of the products prepared using Ca(CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and EG with different volumes of EG by the microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min
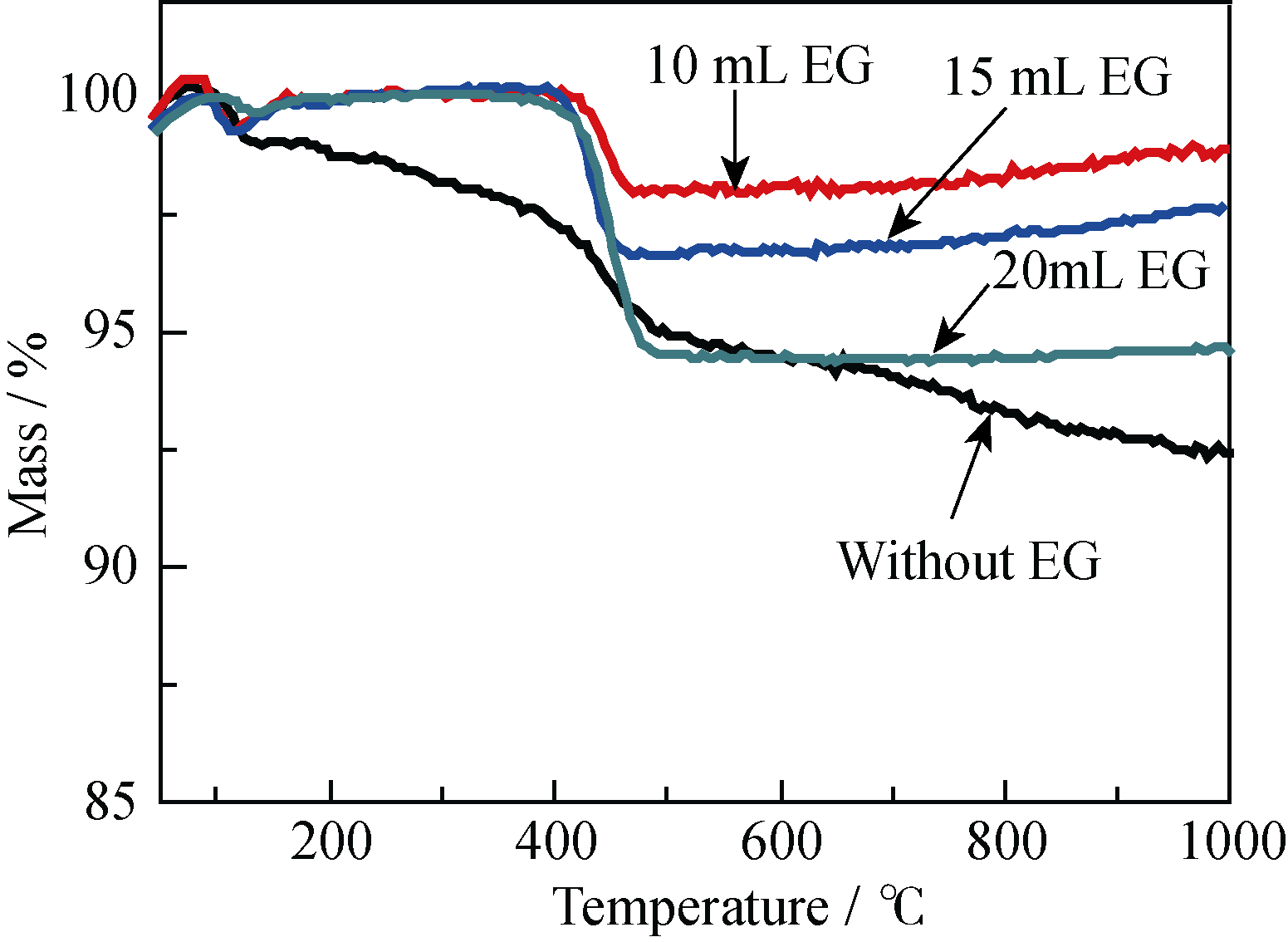
Fig. 5 TG curves of the products prepared using Ca (CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and EG with different volumes of EG by the microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min
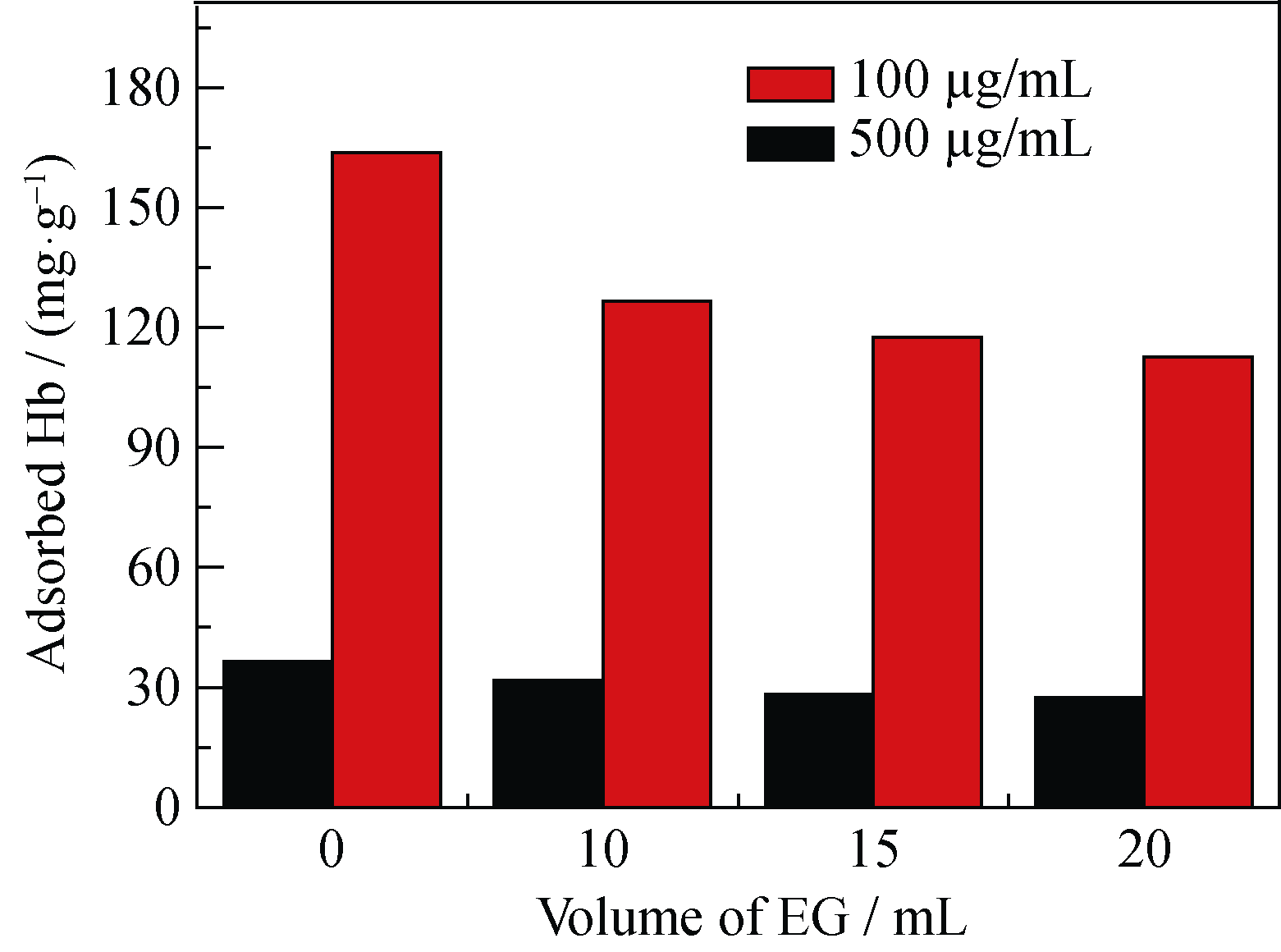
Fig. 6 Hb protein adsorption properties of the products prepared using Ca(CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and EG with different volumes of EG by the microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min
| [1] | FRATZL P, GUPTA H S, PASCHALIS E P, et al. Structure and mechanical quality of the collagen-mineral nano-composite in bone. J. Mater. Chem., 2004, 14(14): 2115-2123. |
| [2] | TZAPHLIDOU M. Bone architecture: collagen structure and calcium/ phosphorus maps. J. Biol. Phys., 2008, 34(1/2): 39-49. |
| [3] | ONG J L, CHAN D C N. Hydroxyapatite and their use as coatings in dental implants: a review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2000, 28(5/6): 667a-707a. |
| [4] | YANG S B,WANG J, LIU C S. Research on calcium phosphate cement bone adhesive. J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(1): 85-90. |
| [5] | CHEN X Q, CHEN X N, ZHU X D, et al. Effect of surface topography of hydroxyapatite on human osteosarcoma MG-63 cell. J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(8): 901-906. |
| [6] | LAI C, TANG S Q, WANG Y J, et al. Formation of calcium phosphate nanoparticles in reverse microemulsions. Mater. Lett., 2005, 59(2/3): 210-214. |
| [7] | LIN KL, CHANG J, ZHU Y J, et al. A facile one-step surfactant- free and low-temperature hydrothermal method to prepare uniform 3D structured carbonated apatite flowers. Cryst. Growth Des., 2009, 9(1): 177-181. |
| [8] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J, WANG K W, et al. Surfactant-free solvothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanowire/nanotube ordered arrays with biomimetic structures. CrystEngComm, 2011, 13(6): 1858-1863. |
| [9] | CHEN F, TANG Q L, ZHU Y J, et al. Hydroxyapatite nanorods/poly(vinyl pyrolidone) composite nanofibers, arrays and three-dimensional fabrics: Electrospun preparation and transformation to hydroxyapatite nanostructures. Acta Biomater., 2010, 6(8): 3013-3020. |
| [10] | CHEN X, TANG Q L, ZHU Y J, et al. Synthesis and antibacterial property of zinc loaded hydroxyapatite nanorods. Mater. Lett., 2012, 89: 233-235. |
| [11] | LUO H T, ZHI W, LU X, et al. Research on preparation and biological properties of dense hydroxyapatite spheres. J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(1): 40-44. |
| [12] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J, WU J, et al. Nanostructured calcium phosphates: preparation and their application in biomedicine. Nano. Biomed. Eng., 2012, 4(1): 41-49. |
| [13] | WANG K F, ZHOU C C, HONG Y L, et al. Review article: a review of protein adsorption on bioceramics. Interface Focus, 2012, 2(3): 259-277. |
| [14] | ZENG H, CHITTUR K K, LACEFIELD W R. Analysis of bovine serum albumin adsorption on calcium phosphate and titanium surfaces. Biomaterials, 1999, 20(4): 377-384. |
| [15] | WASSELL D T H, HALL R C, EMBERY G. Adsorption of bovine serum albumin onto hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials, 1995, 16(9): 697-702. |
| [16] | BAGHBANZADEH M, CARBONE L, COZZOLI P D, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of colloidal inorganic nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit., 2011, 50(48): 11312-11359. |
| [17] | GEDYE R, SMITH F, WESTAWAY K, et al. The use of microwave-ovens for rapid organic-synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett., 1986, 27(3): 279-282. |
| [18] | GIGUERE R J, BRAY T L, DUNCAN S M, et al. Application of commercial microwave-ovens to organic-synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett., 1986, 27(41): 4945-4948. |
| [19] | ZHU Y J, WANG W W, QI R J, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of single-crystalline tellurium nanorods and nanowires in ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit., 2004, 43(11): 1410-1414. |
| [20] | ZHAO J, ZHU Y J, ZHENG J Q, et al. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal preparation using adenosine 5'-triphosphate disodium salt as a phosphate source and characterization of zinc-doped amorphous calcium phosphate mesoporous microspheres. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2013, 180: 79-85. |
| [21] | ZHAO X Y, ZHU Y J, QI C, et al. Hierarchical hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis by using pyridoxal-5 '-phosphate as a phosphorus source and application in drug delivery. Chem. Asian J., 2013, 8(6): 1313-1320. |
| [22] | QI C, ZHU Y J, LU B Q, CHEN F, et al. Hydroxyapatite hierarchically nanostructured porous hollow microspheres: rapid, sustainable microwave-hydrothermal synthesis by using creatine phosphate as an organic phosphorus source and application in drug delivery and protein adsorption. Chem. Eur. J., 2013, 19(17): 5332-5341. |
| [23] | QI C, ZHU Y J, ZHAO X Y, et al. Highly stable amorphous calcium phosphate porous nanospheres: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis using ATP as phosphorus source and stabilizer, and their application in anticancer drug delivery. Chem. Eur. J., 2013, 19(3): 981-987. |
| [24] | CHEN F, HUANG P, ZHU Y J, et al. The photoluminescence, drug delivery and imaging properties of multifunctional Eu3+/Gd3+ dual-doped hydroxyapatite nanorods. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(34): 9031-9039. |
| [25] | WANG K W, ZHU Y J, CHEN X Y, et al. Flower-like hierarchically nanostructured hydroxyapatite hollow spheres: facile preparation and application in anticancer drug cellular delivery. Chem. Asian J., 2010, 5(12): 2477-2482. |
| [1] | TANG Xinli, DING Ziyou, CHEN Junrui, ZHAO Gang, HAN Yingchao. In vivo Distribution and Metabolism of Calcium Phosphate Nanomaterials Based on Fluorescent Labeling with Rare Earth Europium Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | LI Wenyuan, XU Jianan, DENG Han'ao, CHANG Aimin, ZHANG Bo. Effect of V5+ Substitution on Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaTaO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [4] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [5] | TANG Ying, LI Jie, XIANG Huaicheng, FANG Weishuang, LIN Huixing, YANG Junfeng, FANG Liang. Rattling Effect: A New Mechanism Affecting the Resonant Frequency Temperature Coefficient of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [6] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [7] | YIN Changzhi, CHENG Mingfei, LEI Weicheng, CAI Yiyang, SONG Xiaoqiang, FU Ming, LÜ Wenzhong, LEI Wen. Effect of Ga3+ Doping on Crystal Structure Evolution and Microwave Dielectric Properties of SrAl2Si2O8 Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [8] | XIONG Siyu, MO Chen, ZHU Xiaowei, ZHU Guobin, CHEN Deqin, LIU Laijun, SHI Xiaodong, LI Chunchun. Low-temperature Sintering of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics with Ultra-low Permittivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [9] | CHEN Xi, YUAN Yuan, TAN Yeqiang, LIU Changsheng. Strategic Study on the Development of Inorganic Non-metallic Biomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 449-456. |
| [10] | XIN Zhenyu, GUO Ruihua, WUREN Tuoya, WANG Yan, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Pt-Fe/GO Nanocatalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance on Ethanol Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [11] | LIU Wenlong, ZHAO Jin, LIU Juan, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Microwave Drying of Spontaneous-Coagulation-Cast Wet Alumina Green Body [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 461-468. |
| [12] | CHEN Yongqiang, WANG Yixue, ZHANG Fan, LI Hongxia, DONG Binbin, MIN Zhiyu, ZHANG Rui. Preparation of Special Ceramics by Microwave Heating: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 841-852. |
| [13] | YAO Xiaogang, PENG Haiyi, GU Zhongyuan, HE Fei, ZHAO Xiangyu, LIN Huixing. Polyphenylene Oxide/Ca0.7La0.2TiO3 Microwave Composite Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 493-498. |
| [14] | ZHANG Hang, HAN Kunyuan, DONG Lanlan, LI Xiang. Preparation and Characterization of β-tricalcium Phosphate/Nano Clay Composite Scaffolds via Digital Light Processing Printing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1116-1122. |
| [15] | FU Yukun, ZENG Min, RAO Xianfa, ZHONG Shengwen, ZHANG Huijuan, YAO Wenli. Microwave-assisted Synthesis and Co, Al Co-modification of Ni-rich LiNi0.8Mn0.2O2 Materials for Li-ion Battery Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 718-724. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||