
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 656-666.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240529
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Ying1( ), LI Jie1(
), LI Jie1( ), XIANG Huaicheng1, FANG Weishuang1,2, LIN Huixing2, YANG Junfeng3, FANG Liang1(
), XIANG Huaicheng1, FANG Weishuang1,2, LIN Huixing2, YANG Junfeng3, FANG Liang1( )
)
Received:2024-12-18
Revised:2025-02-07
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-02-13
Contact:
LI Jie, associate professor. E-mail: jielee@glut.edu.cn;About author:TANG Ying (1988-), female, professor. E-mail: tangyinggl001@aliyun.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TANG Ying, LI Jie, XIANG Huaicheng, FANG Weishuang, LIN Huixing, YANG Junfeng, FANG Liang. Rattling Effect: A New Mechanism Affecting the Resonant Frequency Temperature Coefficient of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 656-666.
| Sample | Bond type of A site | Bond valence parameter | Bond valence | Measured εr | Theoretical εth | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Y2Ge3O12 | Ca-O | 1.967 | 1.88 | 10.8 | 9.33 | 97126 | -40.6 |
| Mg3Y2Ge3O12 | Y-O Mg-O | 2.014 1.693 | 2.97 1.25 | 14.1 | 9.79 | 12600 | +120.5 |
Table 1 Bond lengths, bond valences and microwave dielectric properties of Ca3Y2Ge3O12 and Mg3Y2Ge3O12 ceramics
| Sample | Bond type of A site | Bond valence parameter | Bond valence | Measured εr | Theoretical εth | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Y2Ge3O12 | Ca-O | 1.967 | 1.88 | 10.8 | 9.33 | 97126 | -40.6 |
| Mg3Y2Ge3O12 | Y-O Mg-O | 2.014 1.693 | 2.97 1.25 | 14.1 | 9.79 | 12600 | +120.5 |
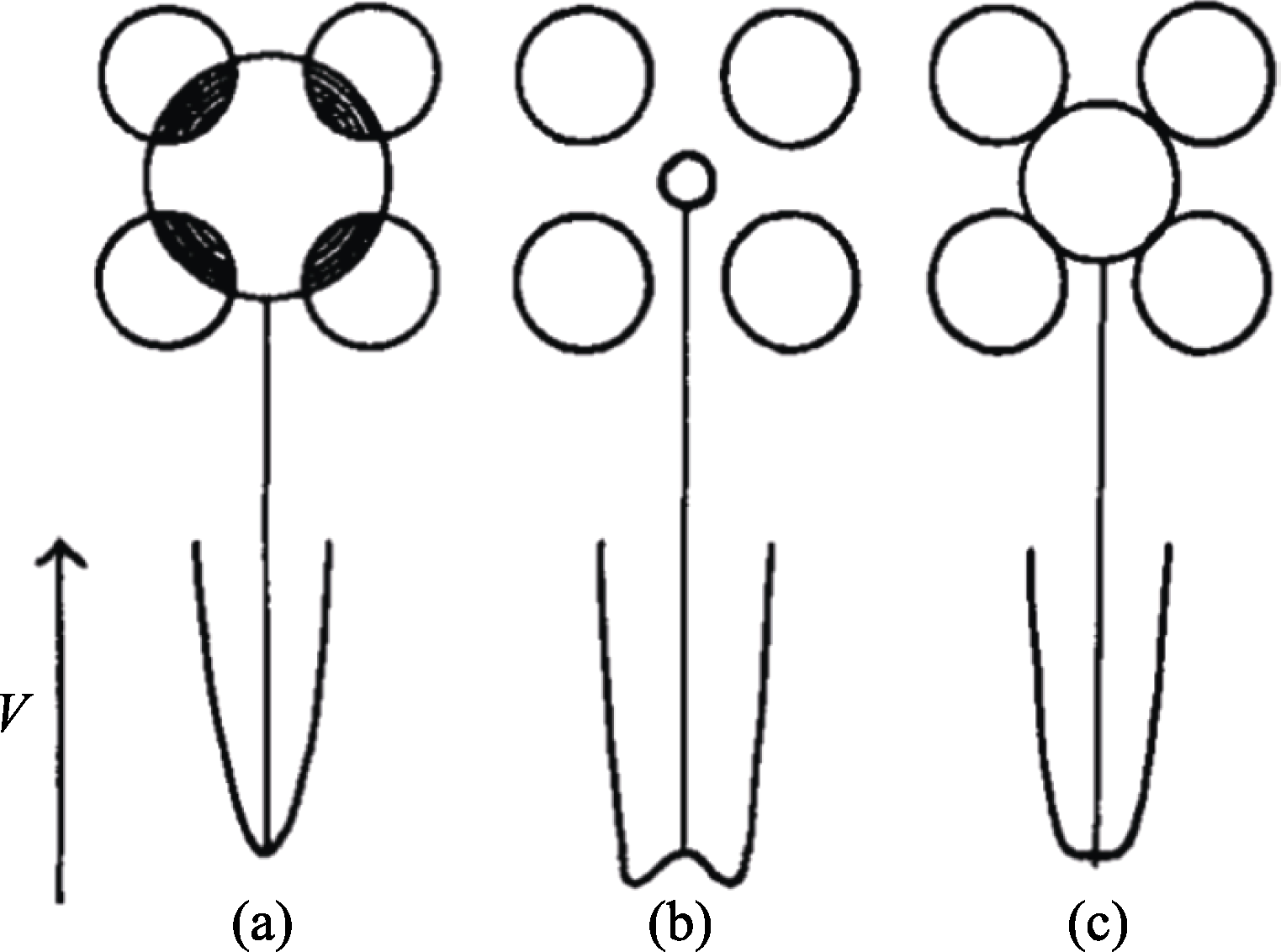
Fig. 1 Variation of potential energy with displacement of a metal ion from the center of a fixed oxide octahedron (shown in two dimensions for clarity)[6] (a) Large ion; (b) Small ion; (c) Ion of intermediate size
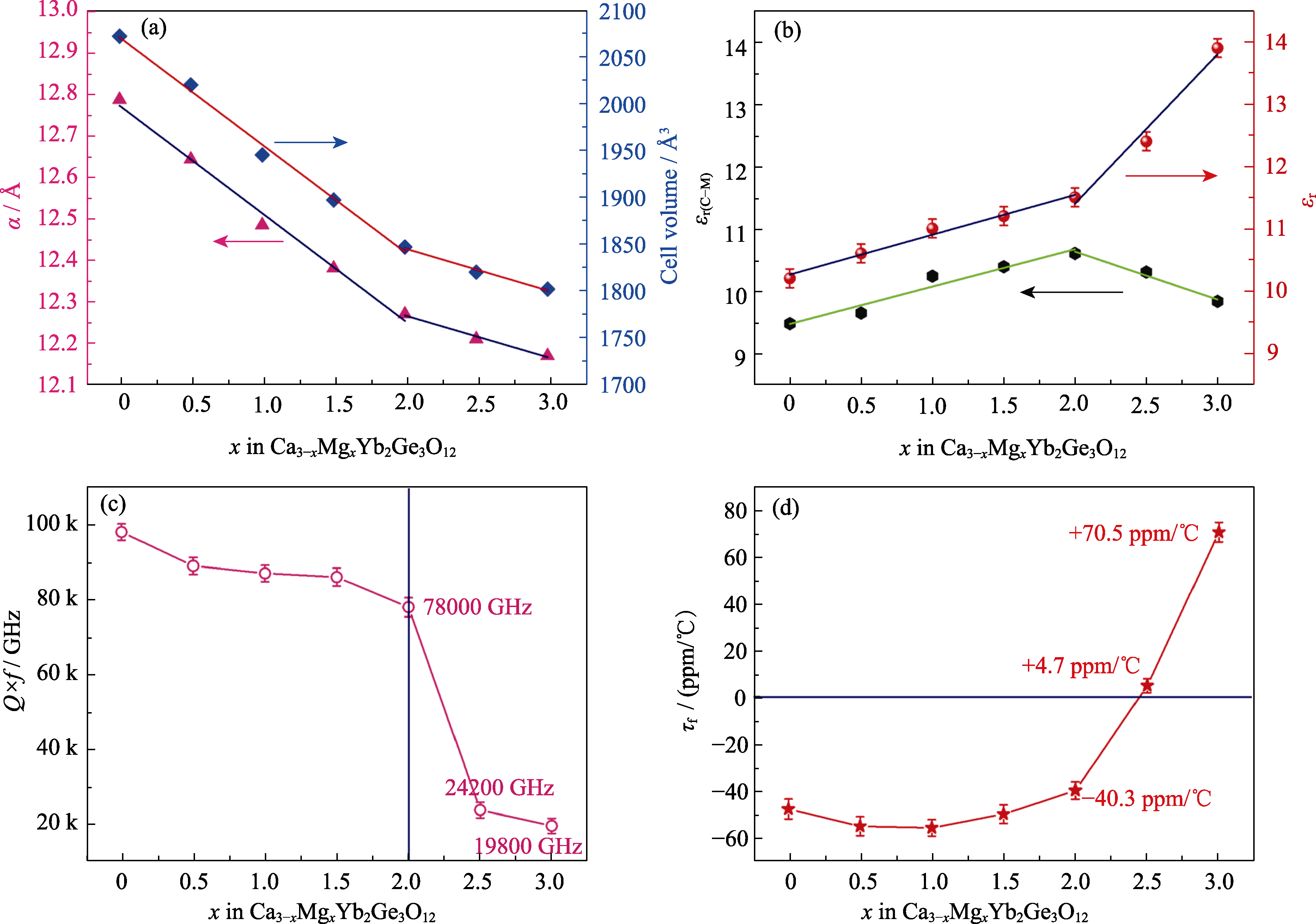
Fig. 2 Microwave dielectric properties of Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12 (0≤x≤3) ceramics[57] (a) Unit cell parameters and volumes; (b) Theoretical and measured permittivity; (c) Q×f; (d) τf. 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
| x | Ceramic | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | ταm/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ca3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1360 | 10.3 | 98000 | -48.2 | +50.64 |
| 0.5 | Ca2.5Mg0.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1380 | 10.6 | 89000 | -55.6 | +53.97 |
| 1.0 | Ca2MgYb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.0 | 87000 | -56.3 | +53.49 |
| 1.5 | Ca1.5Mg1.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.2 | 86000 | -50.4 | +50.16 |
| 2.0 | CaMg2Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.8 | 78000 | -40.3 | +44.40 |
| 2.5 | Ca0.5Mg2.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1420 | 12.4 | 24000 | +4.7 | +23.34 |
| 3.0 | Mg3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1440 | 13.5 | 19800 | +70.5 | -3.66 |
Table 2 Optimum sintering temperature (ST), microwave dielectric properties and ταm of Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12 (0≤x≤3) ceramics
| x | Ceramic | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | ταm/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ca3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1360 | 10.3 | 98000 | -48.2 | +50.64 |
| 0.5 | Ca2.5Mg0.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1380 | 10.6 | 89000 | -55.6 | +53.97 |
| 1.0 | Ca2MgYb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.0 | 87000 | -56.3 | +53.49 |
| 1.5 | Ca1.5Mg1.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.2 | 86000 | -50.4 | +50.16 |
| 2.0 | CaMg2Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.8 | 78000 | -40.3 | +44.40 |
| 2.5 | Ca0.5Mg2.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1420 | 12.4 | 24000 | +4.7 | +23.34 |
| 3.0 | Mg3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1440 | 13.5 | 19800 | +70.5 | -3.66 |
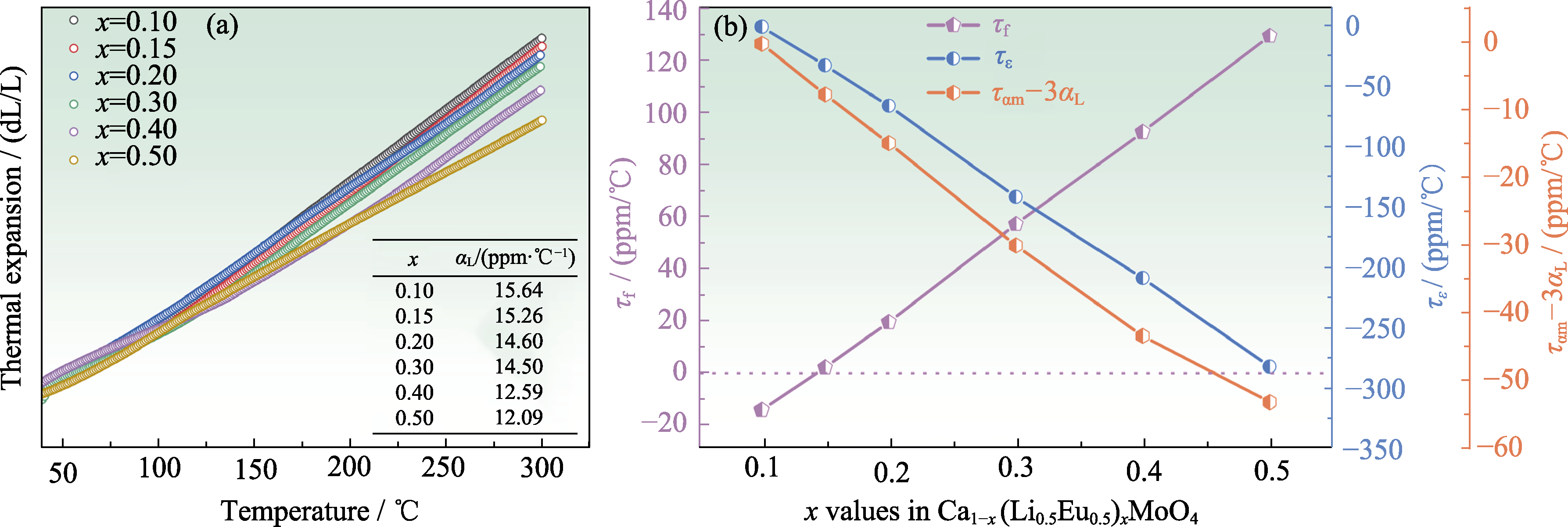
Fig. 4 (a) Thermal expansion data (50-300 ℃)and (b) τε, τf and ταm-3αL for Ca1-x(Li0.5Eu0.5)xMoO4 ceramics[62] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
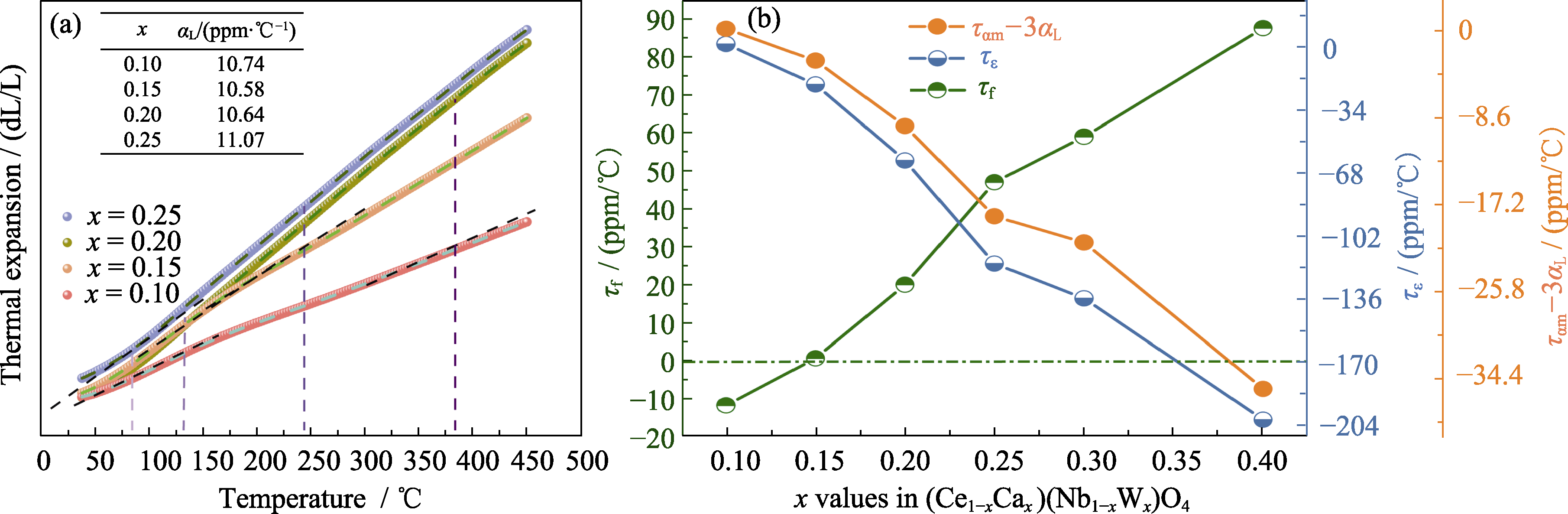
Fig. 5 (a) Thermal expansion data (40-100 ℃) and (b) τε, τf and ταm-3αL for (Ce1-xCax)(Nb1-xWx)O4 ceramics[63] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
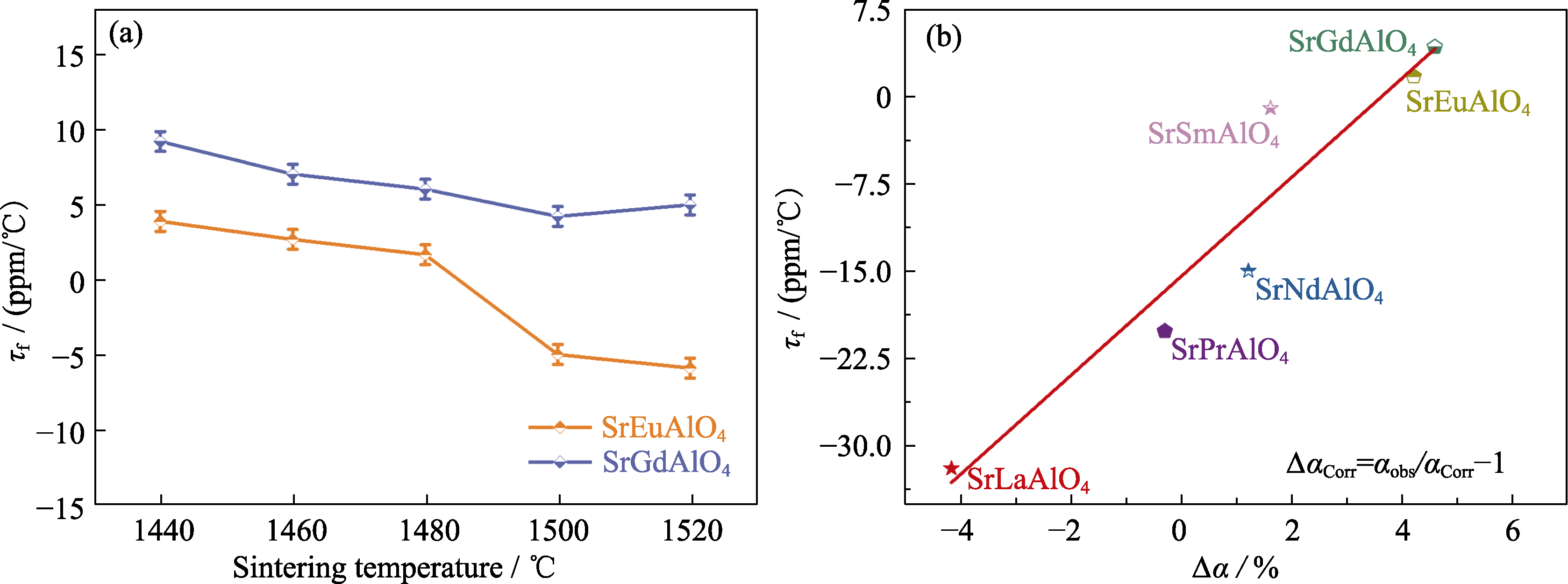
Fig. 6 (a) τf of SrEuAlO4 and SrGdAlO4 ceramics; (b) τf and Δα in SrLnAlO4 (Ln= La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, and Gd) ceramics[64] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
| [1] |
周济, 李龙土, 熊小雨. 我国电子陶瓷技术发展的战略思考. 中国工程科学, 2020, 22(5): 20.
DOI |
| [2] | DING Y H, LIU L, YANG Z J, et al. Structure and microwave dielectric characteristics of Hf1-xTixO2 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(2): 1127. |
| [3] | 闻立群, 王亦菲, 李晖, 等. 主要国家和地区5G发展战略举措及对我国的启示. 通信世界, 2021, 8: 28. |
| [4] | HILL M D, CRUICKSHANK D B, MACFARLANE I A. Perspective on ceramic materials for 5G wireless communication systems. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(12): 120501. |
| [5] | ZURMÜHLEN R, PETZELT J, KAMBA S, et al. Dielectric- spectroscopy of Ba(B'1/2B''1/2)O3 complex perovskite ceramics- correlations between ionic parameters and microwave dielectric properties. I. Infrared reflectivity study (1012-1014 Hz). Journal of Applied Physics, 1995, 77(10): 5341. |
| [6] | BOSMAN A J, HAVINGA E E. Temperature dependence of dielectric constants of cubic ionic compounds. Physical Review, 1963, 129(4): 1593. |
| [7] | REANEY I M, IDDLES D. Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7): 2063. |
| [8] | HARROP P J. Temperature coefficients of capacitance of solids. Journal of Materials Science, 1969, 4: 370. |
| [9] | COCKBAIN A G, HARROP P J. The temperature coefficient of capacitance. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 1968, 1(9): 1109. |
| [10] | WISE P L, REANEY I M, LEE W E, et al. Tunability of τf in perovskites and related compounds. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(8): 2033. |
| [11] | XIAO Y, CHEN X M, LIU X Q. Microstructures and microwave dielectric characteristics of CaRAlO4 (R = Nd, Sm, Y) ceramics with tetragonal K2NiF4 structure. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 87(11): 2143. |
| [12] | FAN X C, CHEN X M, LIU X Q. Structural dependence of microwave dielectric properties of SrRAlO4 (R = Sm, Nd, La) ceramics: crystal structure refinement and infrared reflectivity study. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(12): 4092. |
| [13] | LIU B, LI L, LIU X Q, et al. Structural evolution of SrLaAl1-x(Zn0.5Ti0.5)xO4 ceramics and effects on their microwave dielectric properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(21): 4684. |
| [14] | COLLA E L, REANEY I M, SETTER N. Effect of structural changes in complex perovskites on the temperature coefficient of the relative permittivity. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(5): 3414. |
| [15] | REANEY I M, COLLA E L, SETTER N. Dielectric and structural characteristics of Ba-and Sr-based complex perovskites as a function of tolerance factor. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 33(7R): 3984. |
| [16] | REANEY I M, WISE P L, UBIC R, et al. On the temperature coefficient of resonant frequency in microwave dielectrics. Philosophical Magazine A, 2001, 81(2): 501. |
| [17] | WISE P L, REANEY I M, LEE W E, et al. Structure-microwave property relations in (SrxCa1-x)n+1TinO3n+1. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(10/11): 1723. |
| [18] | ZHOU D, RANDALL C A, WANG H, et al. Ultra-low firing high-k scheelite structures based on [(Li0.5Bi0.5)xBi1-x][MoxV1-x]O4 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(8): 2147. |
| [19] | DU K, YIN C Z, GUO Y B, et al. Phase transition and permittivity stability against temperature of CaSn1-xTixGeO5 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(1): 147. |
| [20] | WU F F, ZHOU D, DU C, et al. Design of a sub-6 GHz dielectric resonator antenna with novel temperature-stabilized (Sm1-xBix) NbO4 (x = 0-0.15) microwave dielectric ceramics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(5): 7030. |
| [21] | CHENG K, LI C C, YIN C Z, et al. Effects of Sr2+ substitution on the crystal structure, Raman spectra, bond valence and microwave dielectric properties of Ba3-xSrx(VO4)2 solid solutions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3738. |
| [22] | YIN C Z, YIN Y H, DU K, et al. Fabrication of high-efficiency dielectric patch antennas from temperature-stable Sr3-xCaxV2O8 microwave dielectric ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(4): 1492. |
| [23] | LEE H J, HONG K S, KIM S J, et al. Dielectric properties of MNb2O6 compounds (where M = Ca, Mn, Co, Ni, OR Zn). Materials Research Bulletin, 1997, 32(7): 847. |
| [24] | LEI W, ZOU Z Y, CHEN Z H, et al. Controllable τf value of barium silicate microwave dielectric ceramics with different Ba/Si ratios. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(1): 25. |
| [25] | KIM E S, CHOI W. Effect of phase transition on the microwave dielectric properties of BiNbO4. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10/11): 1761. |
| [26] | JO H J, KIM J S, KIM E S. Microwave dielectric properties of MgTiO3-based ceramics. Ceramics International, 2015, 41: S530. |
| [27] | CHEN J Q, FANG W S, AO L Y, et al. Structure and chemical bond characteristics of two low-εr microwave dielectric ceramics LiBO2 (B = Ga, In) with opposite τf. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3452. |
| [28] | ZHANG J Y, LI J, SUN Y H, et al. Densification, microwave dielectric properties and rattling effect of LiYbO2 ceramics with low εr and anomalous positive τf. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(16): 7455. |
| [29] | KANG D H, KIM E S. Microwave dielectric properties of rutile (Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.40(Ti1-xSnx)0.60O2 (0.15≤x≤0.30) ceramics. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(4): 889. |
| [30] | KIM E S, KANG D H. Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn1/3B2/35+)xTi1-xO2 (B5+ = Nb, Ta) ceramics. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(4): 883. |
| [31] | KIM E S, KANG D H. Microwave dielectric properties of (A2+1/3B5+2/3)0.5Ti0.5O2 (A2+ = Zn, Mg, B5+= Nb, Ta) ceramics. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2008, 55(5): 1069. |
| [32] | CHOI J W, VAN DOVER R B. Correlation between temperature coefficient of resonant frequency and tetragonality ratio. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(3): 1144. |
| [33] | LIAO Q W, LI L X, REN X, et al. New low-loss microwave dielectric material ZnTiNbTaO8. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(10): 3237. |
| [34] | RAMARAO S D, MURTHY V R K. Crystal structure refinement and microwave dielectric properties of new low dielectric loss AZrNb2O8 (A: Mn, Zn, Mg and Co) ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(3): 274. |
| [35] | LIAO Q W, LI L X. Structural dependence of microwave dielectric properties of ixiolite structured ZnTiNb2O8 materials: crystal structure refinement and Raman spectra study. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41(23): 6963. |
| [36] | XIA W S, LI L X, NING P F, et al. Relationship between bond ionicity, lattice energy, and microwave dielectric properties of Zn(Ta1-xNbx)2O6 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(8): 2587. |
| [37] | MA X M, ZHOU X, TIAN H R, et al. Effect of (Zn1/3Nb2/3)4+ co-substitution on the microwave dielectric properties of Ce2Zr3(MoO4)9 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(6): 7441. |
| [38] | LI H, CHEN X Q, XIANG Q Y, et al. Structure, bond characteristics and Raman spectra of CaMg1-xMnxSi2O6 microwave dielectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(11): 14160. |
| [39] | PASCHOAL C W A, MOREIRA R L, SURENDRAN K P, et al. Infrared reflectivity and intrinsic dielectric behavior of RETiTaO6 (RE = Y, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, and Yb) microwave ceramics. Journal of Materials Research, 2005, 20(5): 1164. |
| [40] | PARK H S, YOON K H, KIM E S. Relationship between the bond valence and the temperature coefficient of the resonant frequency in the complex perovskite (Pb1-xCax)[Fe0.5(Nb1-yTay)0.5]O3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(1): 99. |
| [41] | YOON K H, KIM W S, KIM E S. Dependence of the octahedral bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of Ca1-xSm2x/3TiO3 ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2003, (1/2/3): 112. |
| [42] | PARK H S, YOON K H, KIM E S. Effect of bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of complex perovskite ceramics. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 79(2/3): 181. |
| [43] | CHO Y S, YOON K H, LEE B D, et al. Understanding microwave dielectric properties of Pb-based complex perovskite ceramics via bond valence. Ceramics International, 2004, 30(8): 2247. |
| [44] | LUFASO M W. Crystal structures, modeling, and dielectric property relationships of 2 : 1 ordered Ba3MM'2O9 (M = Mg, Ni, Zn; M' = Nb, Ta) perovskites. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(11): 2148. |
| [45] | ZHANG H, FANG L, DRONSKOWSKI R, et al. Some A6B5O18 cation-deficient perovskites in the BaO-La2O3-TiO2-Nb2O5 system. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2004, 177(11): 4007. |
| [46] | ZHANG H, FANG L, ELSEBROCK R, et al. Crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of a new A6B5O18-type cation-deficient perovskite Ba3La3Ti4NbO18. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 93(2/3): 450. |
| [47] | KIM E S, CHUN B S, FREER R, et al. Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+B6+O4 (A2+: Ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(7): 1731. |
| [48] | KIM E S, JEON C J, CLEM P G. Effects of crystal structure on the microwave dielectric properties of ABO4 (A=Ni, Mg, Zn and B= Mo, W) ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(9): 2934. |
| [49] | YOON S H, KIM D W, CHO S Y, et al. Investigation of the relations between structure and microwave dielectric properties of divalent metal tungstate compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10/11): 2051. |
| [50] | CHOI G K, KIM J R, YOON S H, et al. Microwave dielectric properties of scheelite (A=Ca, Sr, Ba) and wolframite (A=Mg, Zn, Mn) AMoO4 compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(8/9): 3063. |
| [51] | 严康, 高兆芬, 卞建江. 钨酸盐类陶瓷微波介电性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2006, 34(2): 251. |
| [52] | NEELAKANTAN U A, KALATHIL S E, RATHEESH R. Structure and microwave dielectric properties of ultralow-temperature cofirable BaV2O6 ceramics. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 2015(2): 305. |
| [53] | TANG Y, ZHANG Z W, LI J, et al. A3Y2Ge3O12 (A=Ca, Mg): two novel microwave dielectric ceramics with contrasting τf and Q×f. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12): 3989. |
| [54] | DUNITZ J D, ORGEL L E. Stereochemistry of ionic solids. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry, 1960, 2: 1. |
| [55] | SHANNON R D. Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 73(1): 348. |
| [56] | 唐莹. 石榴石型低介电常数微波介质陶瓷制备与性能. 北京: 北京科技大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [57] | 唐莹, 相怀成, 李洁, 等. Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12(0≤x≤3)石榴石的A位Rattling效应与微波介电性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2023, 51(4): 872. |
| [58] | TANG Y, LI H, LI J, et al. Relationship between Rattling Mg2+ ions and anomalous microwave dielectric behavior in Ca3-xMg1+xLiV3O12 ceramics with garnet structure. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7697. |
| [59] | LIU M X, LI J, TANG Y, et al. Tunability of τf in garnet-structured Y3Ga5O12 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7711. |
| [60] | YANG Y, ZHAI Y F, XIANG H C, et al. Rattling effects on microwave dielectric properties of Ca3TiBGe3O12 (B = Mg, Zn) garnets. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(11): 4566. |
| [61] | YANG Y, TANG Y, LI J, et al. Effects of ionic coordination bonding on microwave dielectric properties of Y2CaBGa4O12 (B = Zr, Sn) garnets. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2022, 4(7): 3512. |
| [62] | GU X L, TANG Y, CHEN J Q, et al. Tuning microwave dielectric properties of low-temperature sintered Ca1-x(Li0.5Eu0.5)xMoO4 (0.1≤x≤0.5) ceramics by the strong rattling effect of Li+. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(5): 117149. |
| [63] | XU L, FANG W S, TANG Y, et al. Crystal structure evolution, bond characteristics and tunable microwave dielectric properties of (Ce1-xCax)(Nb1-xWx)O4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(7): 4657. |
| [64] | WANG S J, FANG W S, WU D F, et al. Two K20 microwave dielectric ceramics SrLnAlO4 (Ln=Eu, Gd) with near-zero τf and contrasting Q×f. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(11): 6470. |
| [65] | MENG K Y, WU D F, WANG S J, et al. Tuning εr and τf by the combined effects of rattling RE3+ and compressed Ca2+ at the A-site in microwave dielectric ceramics CaREAlO4 (RE=Eu, Ho, Er, Yb). Ceramics International, 2024, 50(15): 26792. |
| [66] | LI F H, TANG Y, LI J, et al. Effect of A-site cation on crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of AGe4O9 (A=Ba, Sr) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 4153. |
| [67] | SUN Y, XIANG H C, TANG Y, et al. Constructing the cationic rattling effect to realize the adjustability of the temperature coefficient in Nd2-xSmxO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(5): 2859. |
| [68] | SUN Y, WU J T, TANG Y, et al. Effects of ion polarizability and oxygen vacancy on microwave dielectric properties of fluorite- structured Ce1-xCaxO2-x. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(2): 1148. |
| [69] | JIA Y Q, LUO W K, LI L, et al. MSO4 (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) microwave dielectric ceramics with low dielectric constant. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(2): 1250. |
| [70] | WANG X, ZHU X L, LI L, et al. Structure evolution and adjustment of τf in (Ba, Sr)HfO3 and (Sr, Ca)HfO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(1): 285. |
| [71] | JIANG Y, WU G F, MAO M M, et al. Deeper insights into dodecahedron distortion and microwave dielectric properties of Y3-xRxAl(Oct)2Al(Tet)3-xSixO12 (x = 0.1-0.5; R = Mg, Ca) garnet-type ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(14): 23334. |
| [1] | YIN Changzhi, CHENG Mingfei, LEI Weicheng, CAI Yiyang, SONG Xiaoqiang, FU Ming, LÜ Wenzhong, LEI Wen. Effect of Ga3+ Doping on Crystal Structure Evolution and Microwave Dielectric Properties of SrAl2Si2O8 Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [2] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [3] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [4] | LI Wenyuan, XU Jianan, DENG Han'ao, CHANG Aimin, ZHANG Bo. Effect of V5+ Substitution on Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaTaO4 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [5] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [6] | LI Hai-Tao, LI Qian, YAN Yan-Fu, XU Rong-Hui. Effect of ZnO-doping on Sinterability and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [7] | LIU Lin, FANG You-Wei, DENG Xin-Feng, ZHUANG Wen-Dong, TANG Bin, ZHANG Shu-Ren. Crystal Structures and Microwave Dielectric Properties of (Ba1-xSrx)La4Ti4O15 (x=0.8-0.95) Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(3): 281-284. |
| [8] | YAO Xiao-Gang, LIN Hui-Xing, JIANG Shao-Hu, CHEN Wei, LUO Lan. Effects of Al2O3-doping on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(12): 1266-1270. |
| [9] | LIU Hao, SHEN Chun-Ying, LU Zheng-Dong, QIU Tai. Microwave Dielectric Properties of the (1-x)(Mg0.9Co0.1)TiO3-x(Ca0.61La0.26)TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 664-668. |
| [10] | YAO Guo-Guang,LIU Peng. Effects of V5+ Substitution on the Dielectric Properties of Mg(SbNb1-xV xO9 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(5): 877-880. |
| [11] | ZHOU Dong-Xiang,YU Xiao-Hua,WANG He,ZHAO Jun. Sintering Characters and Phase Composition of BaO-CeO2-TiO2 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(6): 1197-1200. |
| [12] | YANG Qiu-Hong,KIM Eung-Soo,XU Jun. Effect of A-site Substitution by Nd~3+ on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of (Pb0.5Ca0.5)(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(5): 1051-1056. |
| [13] | WANG Ning,ZHAO Mei-Yu,YIN Zhi-Wen. Low-Temperature Firing in Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(5): 915-924. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||