
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1163-1174.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250017
WAN Xinyi1, WANG Wenqi1, LI Jiacheng1, ZHAO Junliang2, MA Dongyun1, WANG Jinmin1( )
)
Received:2025-01-13
Revised:2025-03-03
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-04-09
Contact:
WANG Jinmin, professor. E-mail: jmwang@usst.edu.cn.About author:WAN Xinyi (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 222143048@st.usst.edu.cn
CLC Number:
WAN Xinyi, WANG Wenqi, LI Jiacheng, ZHAO Junliang, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Colorless/Black Switching Electrochromic Device Based on WO3·xH2O and Reversible Metal Electrodeposition[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1163-1174.
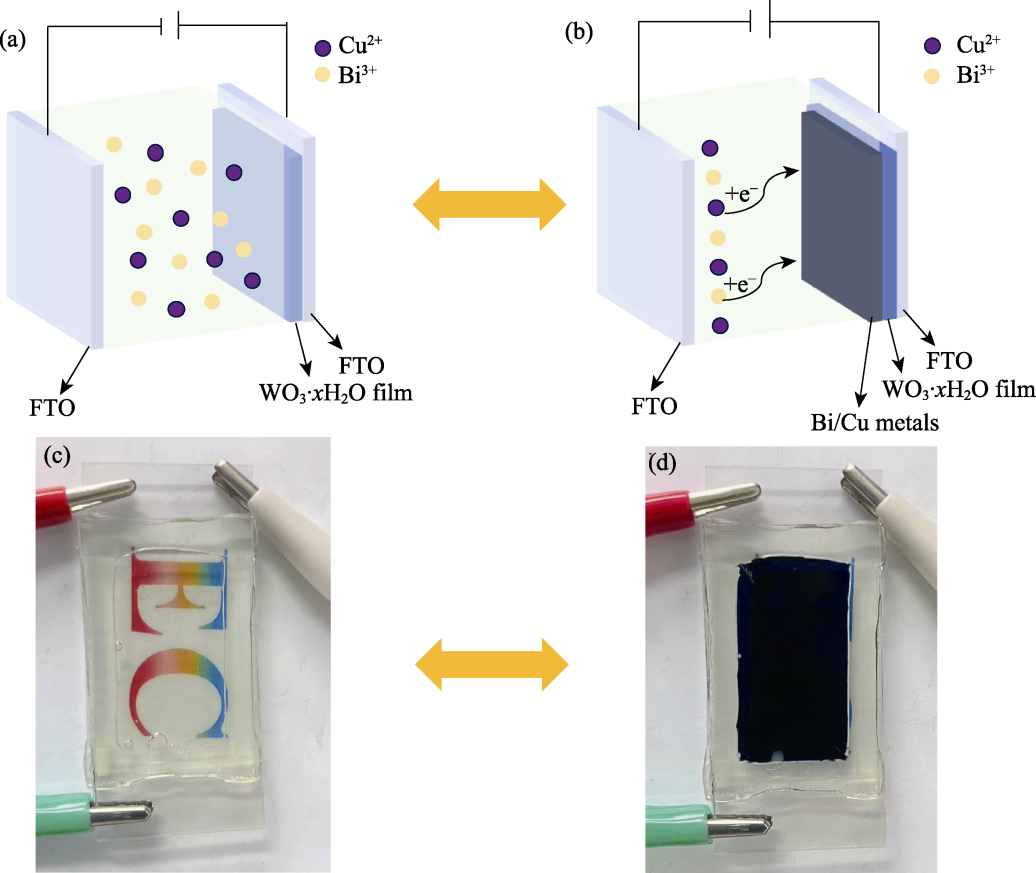
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration and photos of the RMED (a, b) Schematic diagrams of the RMED in the (a) bleached state and (b) colored state; (c, d) Photos of the RMED (c) after 40 s of metal stripping at 1.0 V and (d) after 30 s of metal electrodeposition at -3.0 V
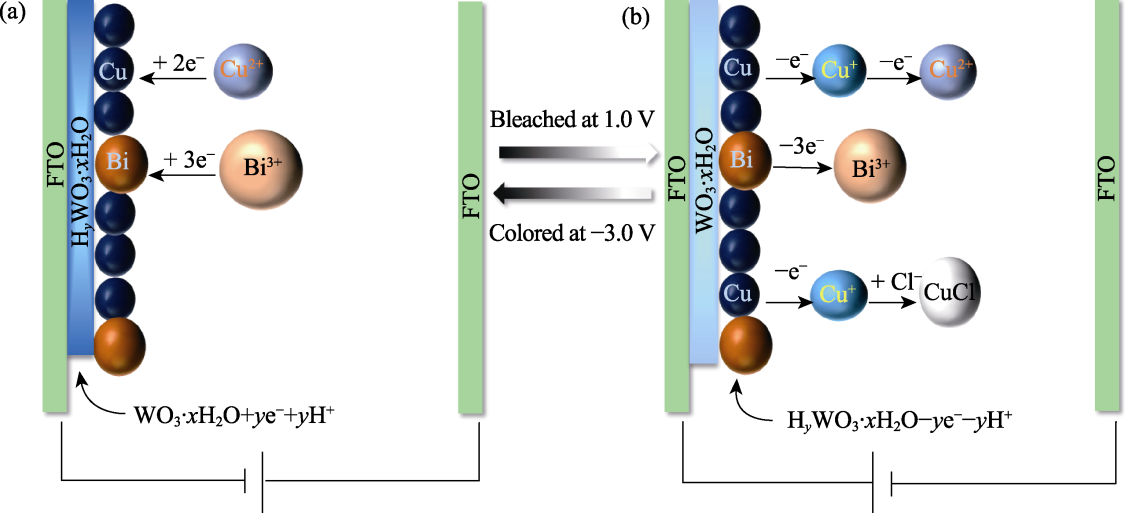
Fig. 3 Mechanisms of chemical and electrochemical reactions in the RMED during operation (a) Colored state (metal electrodeposition); (b) Bleached state (metal stripping)
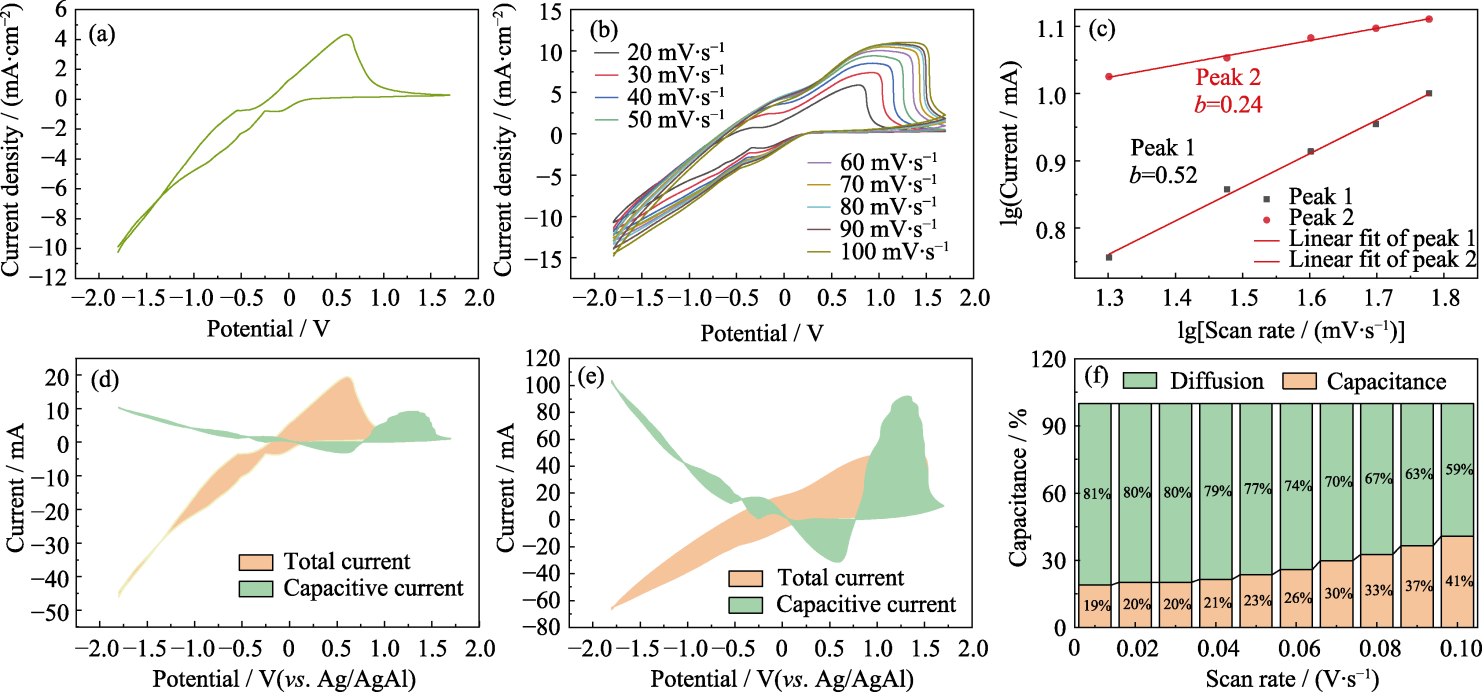
Fig. 6 Electrochemical behavior of the WO3·xH2O film (a) CV curve at a scan rate of 10 mV·s-1; (b) CV curves at different scan rates; (c) Linear relationship between lgi and lgv; (c, d) Contribution of surface capacitance to total charge storage (shaded area) in CV curves at scan rates of (d) 10 and (e)100 mV·s-1; (f) Proportion of charge storage attributed to diffusion-controlled and surface capacitance characteristics at various scan rates. Colorful figures are available on website
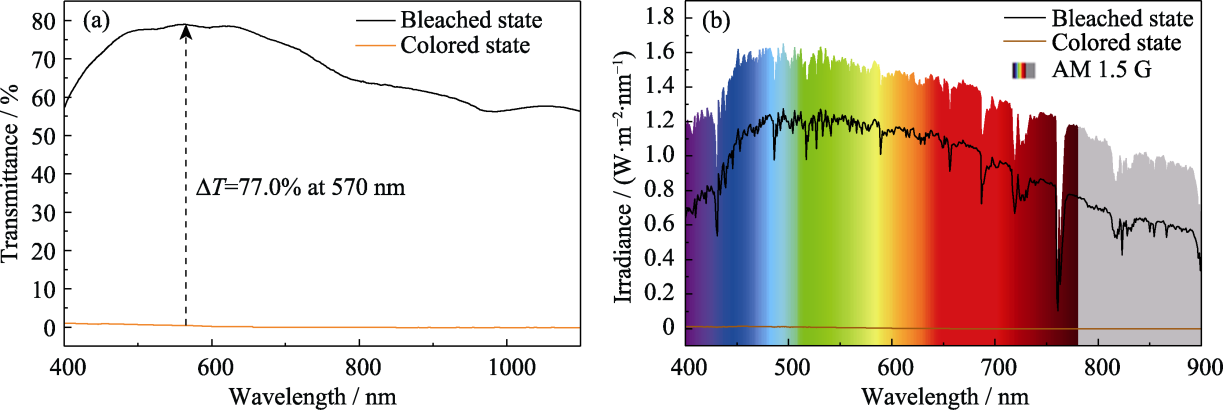
Fig. 7 Optical characteristics of the RMED (a) Transmission spectra at the colored and bleached states measured at -3.0 and 1.0 V, respectively; (b) Solar irradiance spectra of the colored and bleached states measured at -3.0 and 1.0 V, respectively. Colorful figures are available on website
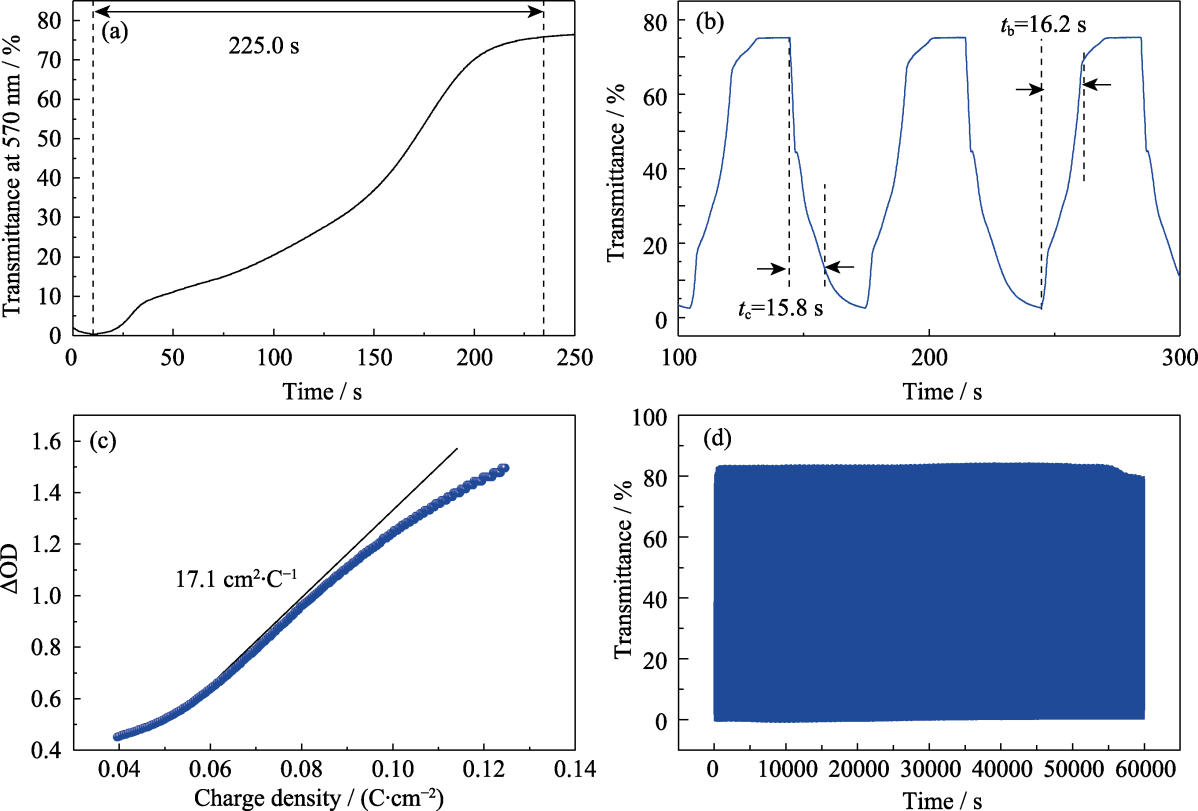
Fig. 8 Electrochemical and EC properties of the RMED (a) Duration needed for the RMED to go from coloration to bleaching at a wavelength of 570 nm when operating at open circuit voltage; (b) Real-time transmittance curve of the RMED recorded at 570 nm by applying a square wave potential of -3.0 V for 30 s and 1.0 V for 40 s; (c) Optical density variations with respect to charge density; (d) Cyclic performance of the RMED measured by applying -3.0 V for 30 s and 1.0 V for 40 s
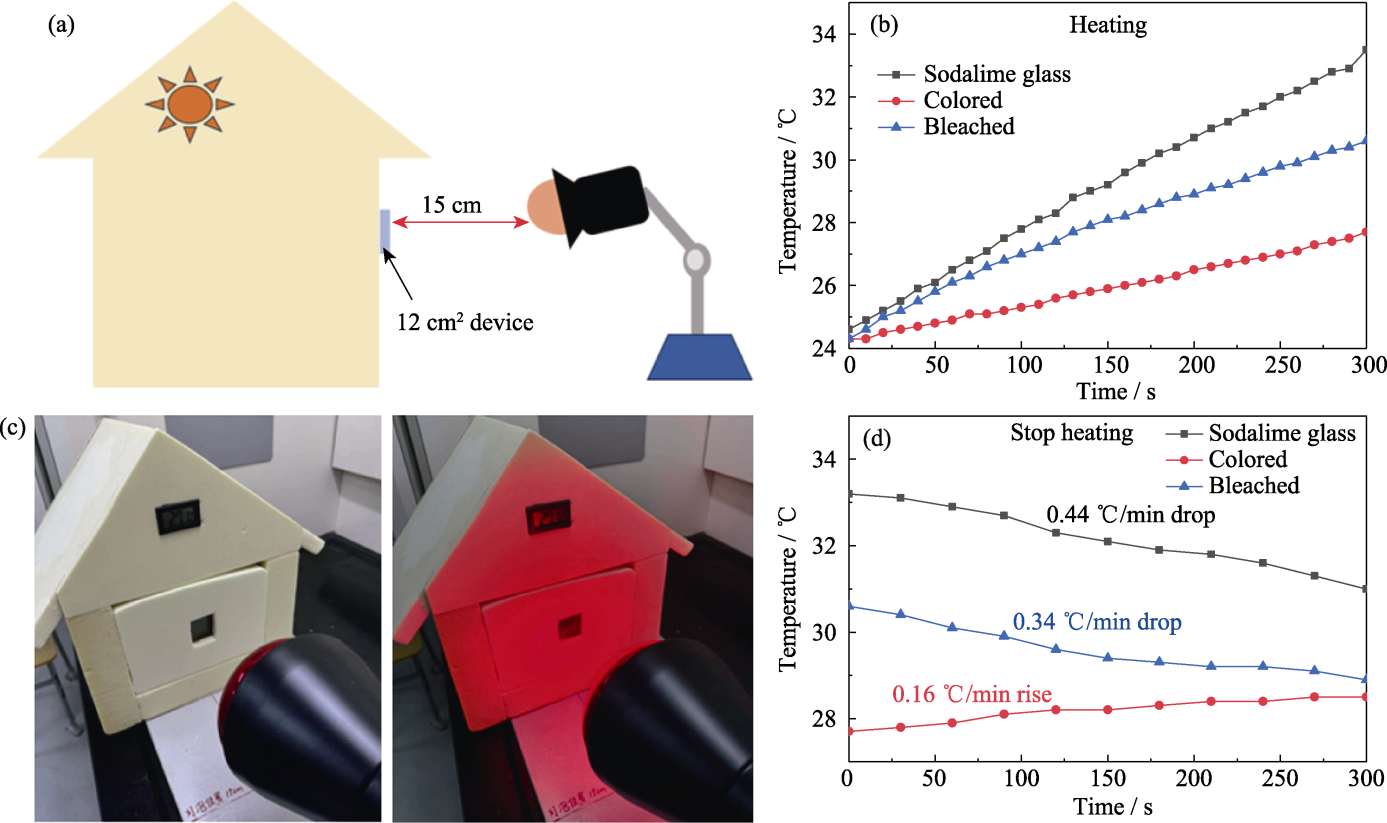
Fig. 9 Infrared blocking performance of the RMED smart window in a model house (a) Schematic diagram of the indoor temperature change experiment using the model house; (b) Indoor temperature change curves of each mode during heating process of the house; (c) Physical pictures of the house during heating and heating-stopping simulation; (d) Indoor temperature change curves of each mode during the heating-stopping process
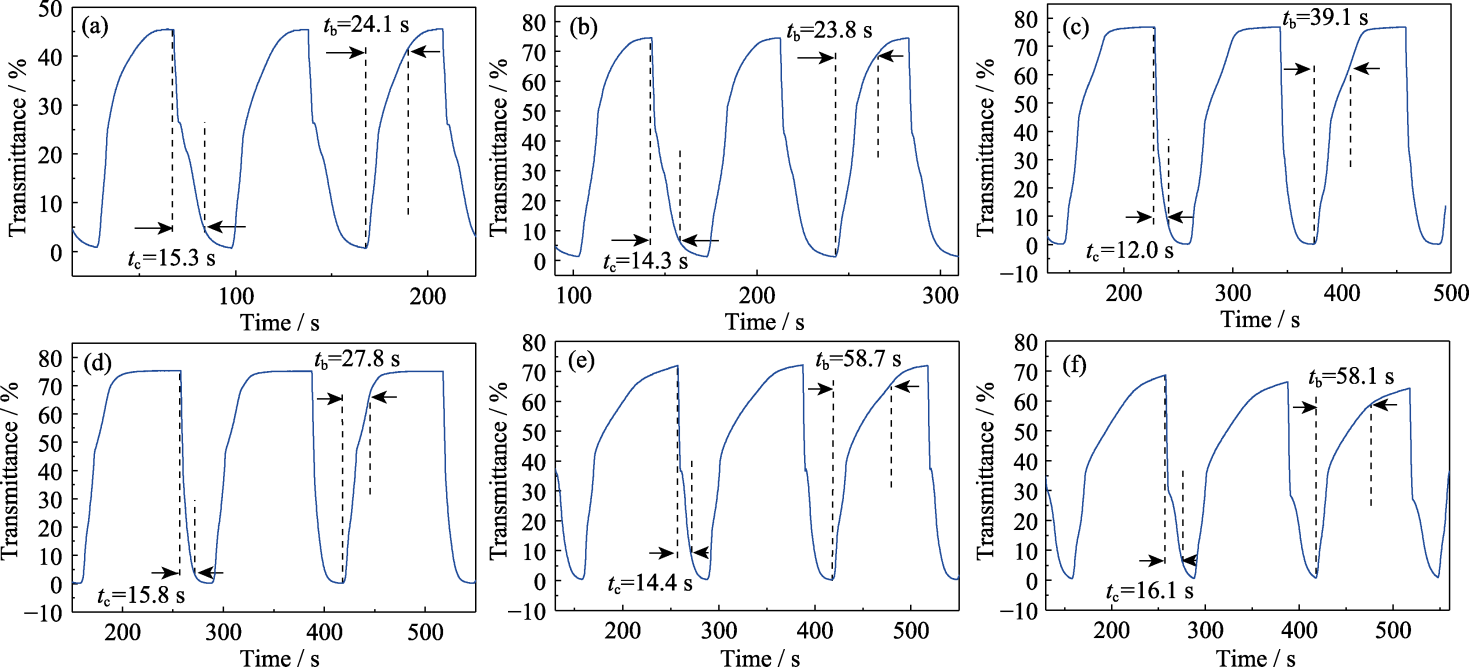
Fig. S1 Real-time transmittance curves at 570 nm for RMEDs with different metal atomic ratios under coloration (-3.0 V) and bleaching (1.0 V) conditions (a) Cu:Bi = 5 : 1; (b) Cu:Bi = 4 : 1; (c) Cu:Bi = 2 : 1; (d) Cu:Bi = 1 : 1; (e) Cu:Bi = 1 : 2; (f) Cu:Bi = 1 : 3
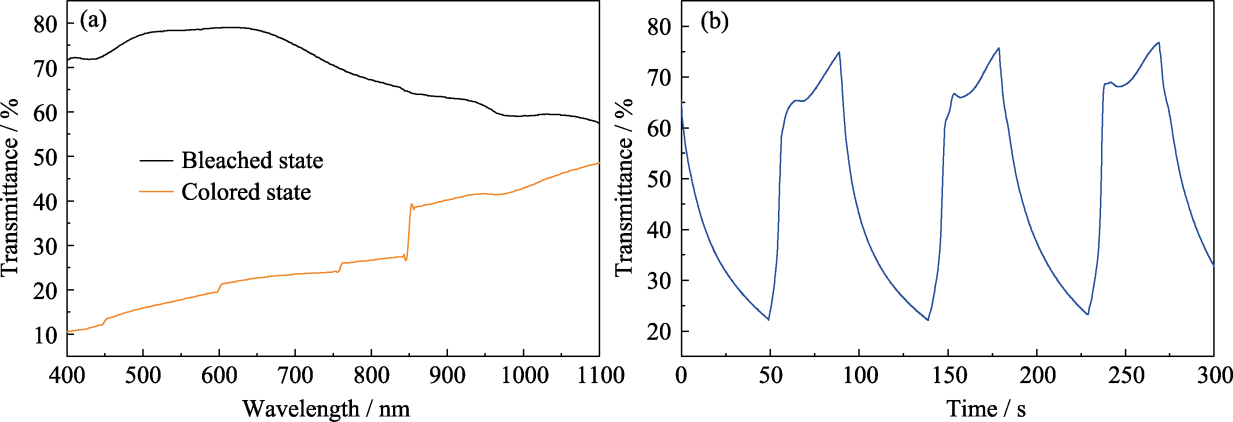
Fig. S2 Electrochromic properties of the RMED without WO3·xH2O film (a) Transmission spectra in the colored (-3.0 V for 30 s) and bleached (1.0 V for 40 s) states; (b) Real-time transmittance curve at 570 nm
| [1] | KHANDEKAR M L, MURTY T S, CHITTIBABU P. The global warming debate: a review of the state of science. Pure Appl. Geophys., 2005, 162(8/9): 1557. |
| [2] | GRANQVIST C G. Transparent conductors as solar energy materials: a panoramic review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2007, 91(15): 1529. |
| [3] |
SUMBOJA A, LIU J M, ZHENG W G, et al. Electrochemical energy storage devices for wearable technology: a rationale for materials selection and cell design. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47(15): 5919.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | KIM H, SON M, AHN S H, et al. Comparison of electrochromic characteristics of electrochromic device upon various sintering methods of Sol-Gel based WO3 electrode. Curr. Appl. Phys., 2020, 20(6): 782. |
| [5] | EH A L S, TAN A W M, CHENG X, et al. Recent advances in flexible electrochromic devices: prerequisites, challenges, and prospects. Energy Technol., 2018, 6(1): 33. |
| [6] | ZHANG R C, ZHANG Z B, HAN J C, et al. Advanced liquid crystal-based switchable optical devices for light protection applications: principles and strategies. Light Sci. Appl., 2023, 12(1): 11. |
| [7] | GLOGIC E, FUTSCH R, THENOT V, et al. Development of eco-efficient smart electronics for anticounterfeiting and shock detection based on printable inks. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(35): 11691. |
| [8] | WANG J L, LIU J W, SHENG S Z, et al. Manipulating nanowire assemblies toward multicolor transparent electrochromic device. Nano Lett., 2021, 21(21): 9203. |
| [9] | ALCARAZ G K A, JUAREZ-ROLON J S, BURPEE N A, et al. Thermally-stable dynamic windows based on reversible metal electrodeposition from aqueous electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, 6(8): 2132. |
| [10] | ARAKI S, NAKAMURA K, KOBAYASHI K, et al. Electrochemical optical-modulation device with reversible transformation between transparent, mirror, and black. Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(23): 122. |
| [11] | EH A L S, CHEN J, ZHOU X, et al. Robust trioptical-state electrochromic energy storage device enabled by reversible metal electrodeposition. ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(12): 4328. |
| [12] | ZIEGLER J P. Status of reversible electrodeposition electrochromic devices. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 1999, 56(3/4): 477. |
| [13] | LAIK B, CARRIÈRE D, TARASCON J M. Reversible electrochromic system based on aqueous solution containing silver. Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46(13/14): 2203. |
| [14] | BARILE C J, SLOTCAVAGE D J, HOU J Y, et al. Dynamic windows with neutral color, high contrast, and excellent durability using reversible metal electrodeposition. Joule, 2017, 1(1): 133. |
| [15] | BARILE C J. Electrolyte dynamics in reversible metal electrodeposition for dynamic windows. J. Appl. Electrochem., 2018, 48(4): 443. |
| [16] | HOWARD B M, ZIEGLER J P. Optical properties of reversible electrodeposition electrochromic materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 1995, 39(2/3/4): 309. |
| [17] | ISLAM S M, FINI C N, BARILE C J. Dynamic windows based on reversible metal electrodeposition with enhanced functionality. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166(8): D333. |
| [18] | JEONG K R, LEE I, PARK J Y, et al. Enhanced black state induced by spatial silver nanoparticles in an electrochromic device. NPG Asia Mater., 2017, 9: e362. |
| [19] | LUO G, SHEN L Y, ZHENG J M, et al. A europium ion doped WO3 film with the bi-functionality of enhanced electrochromic switching and tunable red emission. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2017, 5(14): 3488. |
| [20] |
DOV N E, SHANKAR S, COHEN D, et al. Electrochromic metallo-organic nanoscale films: fabrication, color range, and devices. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(33): 11471.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | ASSIS L M N, LEONES R, KANICKI J, et al. Prussian blue for electrochromic devices. J. Electroanal. Chem., 2016, 777: 33. |
| [22] | ZHI M Y, HUANG W X, SHI Q W, et al. Enhanced electrochromic performance of vanadium pentoxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite film prepared by the Sol-Gel method. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2016, 163(10): H891. |
| [23] | QIU M J, SUN P, ZHANG B, et al. Reliable information encryption and digital display applications based on multistate smart windows. Adv. Opt. Mater., 2018, 6(22): 1800338. |
| [24] | SUI C X, PU J K, CHEN T H, et al. Dynamic electrochromism for all-season radiative thermoregulation. Nat. Sustain., 2023, 6(4): 428. |
| [25] |
JIA Z F, SUI Y M, QIAN L, et al. Electrochromic windows with fast response and wide dynamic range for visible-light modulation without traditional electrodes. Nat. Commun., 2024, 15(1): 6110.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | ZHANG Y X, XU B, HUANG B K, et al. Color-neutral smart window enabled by gradient reversible alloy deposition. ACS Energy Lett., 2024, 9(8): 4162. |
| [27] | NGUYEN T V, DO H, GUO W W, et al. Tungsten oxide-modified ITO electrode for electrochromic window based on reversible metal electrodeposition. Electron. Mater. Lett., 2022, 18(1): 36. |
| [28] | SHENG K, XUE B, ZHENG J M, et al. A transparent to opaque electrochromic device using reversible Ag deposition on PProDOT- Me2 with robust stability. Adv. Opt. Mater., 2021, 9(11): 2002149. |
| [29] | ZHANG X Q, SUI Y M, YEASMIN S, et al. Fast-switching electrochromic device enabled by Fe2+-mediated MnO2/Mn2+ redox reactions. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2024, 6(11): 8163. |
| [30] | EVANS R C, AUSTIN R, MILLER R C, et al. Surface-facet- dependent electrochromic properties of WO3 nanorod thin films: implications for smart windows. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2021, 4(4): 3750. |
| [31] | LI Y Q, MCMASTER W A, WEI H, et al. Enhanced electrochromic properties of WO3 nanotree-like structures synthesized via a two-step solvothermal process showing promise for electrochromic window application. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018, 1(6): 2552. |
| [32] | ZHOU Z Q, CHEN Z, MA D Y, et al. Porous WO3·2H2O film with large optical modulation and high coloration efficiency for electrochromic smart window. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2023, 253: 112226. |
| [33] | ISLAM S M, HERNANDEZ T S, MCGEHEE M D, et al. Hybrid dynamic windows using reversible metal electrodeposition and ion insertion. Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(3): 223. |
| [34] | HERNANDEZ T S, BARILE C J, STRAND M T, et al. Bistable black electrochromic windows based on the reversible metal electrodeposition of Bi and Cu. ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3(1): 104. |
| [35] | EH A L S, LIN M F, CUI M Q, et al. A copper based reversible electrochemical mirror device with switchability between transparent, blue, and mirror states. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2017, 5(26): 6547. |
| [36] | GUPTA S, SINGH R, ANOOP M D, et al. Electrochemical sensor for detection of mercury (II) ions in water using nanostructured bismuth hexagons. Appl. Phys. A, 2018, 124(11): 737. |
| [37] | ZHANG C, LI S, WU R, et al. Robust MnO2-WO3 complementary electrochromic device enabled by reversible electrodeposition of MnO2. Nano Lett., 2024 24(51): 16360. |
| [38] | YUAN Y L, LU Y D, JIA B E, et al. Integrated system of solar cells with hierarchical NiCo2O4 battery-supercapacitor hybrid devices for self-driving optical-emitting diodes. Nano-Micro Lett., 2019, 11(1): 42. |
| [39] | SUN J W, WAN X Y, YANG T, et al. High-performance tungsten- niobium bimetallic oxide films with designable electrochromic properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2023, 256: 112318. |
| [40] | CHO S M, KIM S, KIM T Y, et al. New switchable mirror device with a counter electrode based on reversible electrodeposition. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2018, 179: 161. |
| [41] | TAO X, LIU D Q, LIU T W, et al. A bistable variable infrared emissivity device based on reversible silver electrodeposition. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(32): 2202661. |
| [42] | PENG Y C, FAN L L, JIN W L, et al. Coloured low-emissivity films for building envelopes for year-round energy savings. Nat. Sustain., 2021, 5(4): 339. |
| [1] | ZHEN Mingshuo, LIU Xiaoran, FAN Xiangqian, ZHANG Wenping, YAN Dongdong, LIU Lei, LI Chen. Electrochromic Intelligent Visual Humidity Indication System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 432-440. |
| [2] | FENG Xingzhe, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Porous NiMn-LDH Nanosheets Film: Solvothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1391-1396. |
| [3] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | SUN Jiawei, WAN Xinyi, YANG Ting, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Preparation and Electrochromic Properties of Ti2Nb10O29 Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1434-1440. |
| [5] | CHEN Zhang, ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng. Electrochromic WO3 Thin Films: Preparation by Nanocrystalloid Liquid Phase Coating and Performance Optimization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1355-1363. |
| [6] | HUANG Zhihang, TENG Guanhongwei, TIE Peng, FAN Desong. Electrochromic Property of Perovskite Ceramic Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 611-616. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiang, LI Wenjie, WANG Lebin, CHEN Xi, ZHAO Jiupeng, LI Yao. Reflective Property of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 451-460. |
| [8] | WANG Tianyue, WANG Mengying, HUANG Qingjiao, YANG Jiaming, WANG Shunhua, DIAO Xungang. Preparation of Lithium Titanate Thin Film for Electrochromic Smart Window by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 471-478. |
| [9] | JIA Hanxiang, SHAO Zewei, HUANG Aibin, JIN Pingshi, CAO Xun. Sandwich Structured Electrolyte of High Sputtering Efficiency for All-solid-state Electrochromic Devices by Optical Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 479-484. |
| [10] | ZHONG Xiaolan, LIU Xueqing, DIAO Xungang. Electrochromic Devices Based on Tungsten Oxide and Nickel Oxide: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 128-139. |
| [11] | ZHAO Qi, QIAO Ke, YAO Yongji, CHEN Zhang, CHEN Dongchu, GAO Yanfeng. High-conductivity Hydrophobic Fumed-SiO2 Composite Gel Electrolyte for High Performance Electrochromic Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 161-167. |
| [12] | ZHOU Kailing, WANG Hao, ZHANG Qianqian, LIU Jingbing, YAN Hui. Dynamic Process of Ions Transport and Cyclic Stability of WO3 Electrochromic Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 152-160. |
| [13] | FANG Huajing, ZHAO Zetian, WU Wenting, WANG Hong. Progress in Flexible Electrochromic Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| [14] | JIA Hanxiang, CAO Xun, JIN Pingshi. Advances in Inorganic All-solid-state Electrochromic Materials and Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 511-524. |
| [15] | CHEN Jun,MA Pei-Hua,ZHANG Cheng,Laurent RUHLMANN,LYU Yao-Kang. Preparation and Electrochemical Property of New Multifunctional Inorganic/Organic Composite Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||