
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1119-1128.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240538
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAO Luhan1,2( ), MENG Jia1(
), MENG Jia1( ), XUE Yudong3,4, SHENG Xiaochen1, CUI Yuanyuan5, LE Jun1, SONG Lixin1,2(
), XUE Yudong3,4, SHENG Xiaochen1, CUI Yuanyuan5, LE Jun1, SONG Lixin1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-26
Revised:2025-03-15
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-04-02
Contact:
MENG Jia, professor. E-mail: jiameng@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:CAO Luhan (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: caoluhan22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
CLC Number:
CAO Luhan, MENG Jia, XUE Yudong, SHENG Xiaochen, CUI Yuanyuan, LE Jun, SONG Lixin. Effect of SiC Transition Layer on Bonding Properties of MoSi2-SABB Coating on SiC/SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1119-1128.
| Sample | Temperature, T/℃ | Density, ρ/(kg·m−3) | Elastic modulus/GPa | Poisson’s ratio | Thermal expansion coefficient, α/ (×10−6, K-1) | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Specific heat capacity/ (J·kg-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoSi2-SABB coating | 25 | 2192 | 33.370 | 0.208 | 3.30 | 1.130 | 716 |
| 100 | - | 33.805 | 0.208 | 3.30 | 1.206 | 789 | |
| 200 | - | 34.125 | 0.208 | 3.51 | 1.277 | 883 | |
| 300 | - | 34.499 | 0.208 | 3.66 | 1.368 | 975 | |
| 400 | - | 34.824 | 0.208 | 3.70 | 1.475 | 1068 | |
| 500 | - | 34.861 | 0.208 | 3.64 | 1.702 | 1159 | |
| 600 | - | 35.246 | 0.208 | 3.59 | 1.849 | 1252 | |
| CMCs | 25 | 2600 | 150 | 0.130 | 2.929 | 4.83 | 759 |
| 200 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.128 | / | 706 | |
| 400 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 3.880 | / | 299 | |
| 600 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 3.831 | / | 410 | |
| 800 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.124 | 4.68 | 805 | |
| 1000 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.157 | 4.57 | 963 | |
| SiC layer[ | 3200 | 340 | 0.142 | 4.0 | 39 | 700 |
Table 1 Thermophysical properties of the relevant materials
| Sample | Temperature, T/℃ | Density, ρ/(kg·m−3) | Elastic modulus/GPa | Poisson’s ratio | Thermal expansion coefficient, α/ (×10−6, K-1) | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Specific heat capacity/ (J·kg-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoSi2-SABB coating | 25 | 2192 | 33.370 | 0.208 | 3.30 | 1.130 | 716 |
| 100 | - | 33.805 | 0.208 | 3.30 | 1.206 | 789 | |
| 200 | - | 34.125 | 0.208 | 3.51 | 1.277 | 883 | |
| 300 | - | 34.499 | 0.208 | 3.66 | 1.368 | 975 | |
| 400 | - | 34.824 | 0.208 | 3.70 | 1.475 | 1068 | |
| 500 | - | 34.861 | 0.208 | 3.64 | 1.702 | 1159 | |
| 600 | - | 35.246 | 0.208 | 3.59 | 1.849 | 1252 | |
| CMCs | 25 | 2600 | 150 | 0.130 | 2.929 | 4.83 | 759 |
| 200 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.128 | / | 706 | |
| 400 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 3.880 | / | 299 | |
| 600 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 3.831 | / | 410 | |
| 800 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.124 | 4.68 | 805 | |
| 1000 | - | 150 | 0.130 | 4.157 | 4.57 | 963 | |
| SiC layer[ | 3200 | 340 | 0.142 | 4.0 | 39 | 700 |
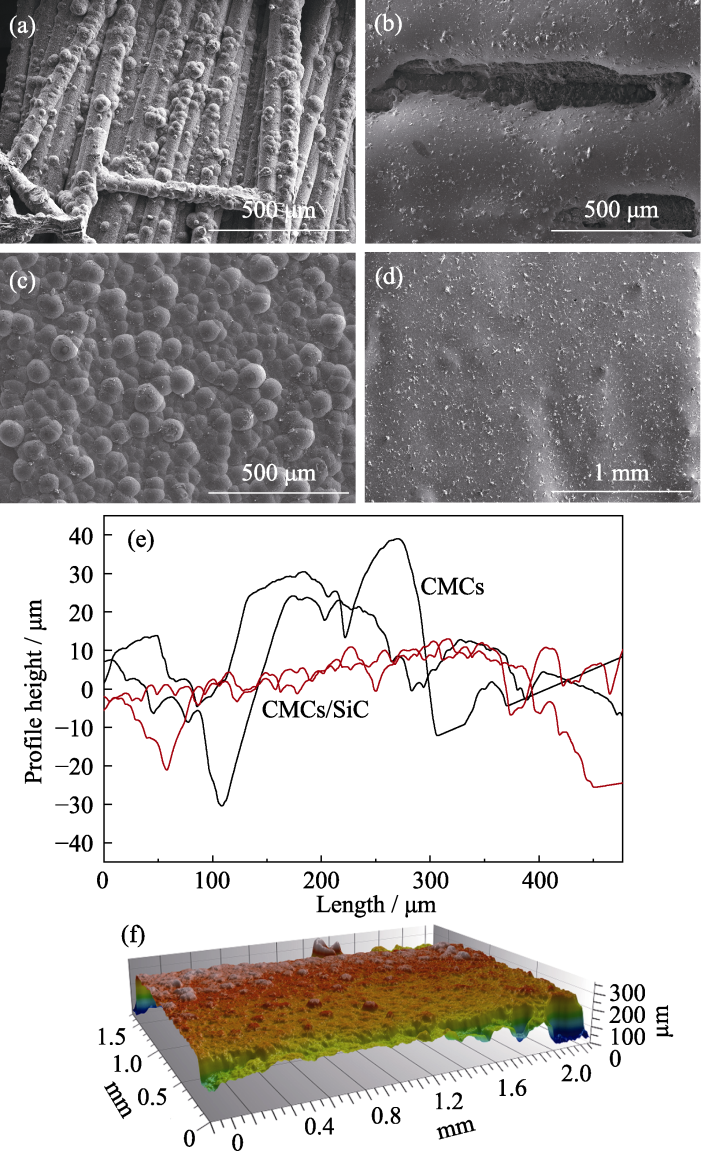
Fig. 2 Surface morphologies and structures of CMCs substrates before and after preparation of the SiC transition layer, along with morphology of the MoSi2-SABB coating prepared on its surface (a-d) SEM images of (a) CMCs, (b) CMCs/MoSi2-SABB coating, (c) CMCs/SiC, and (d) CMCs/SiC/MoSi2-SABB coating; (e) Surface profile curves of CMCs and CMCs/SiC; (f) Surface 3D profile curves of CMCs/SiC
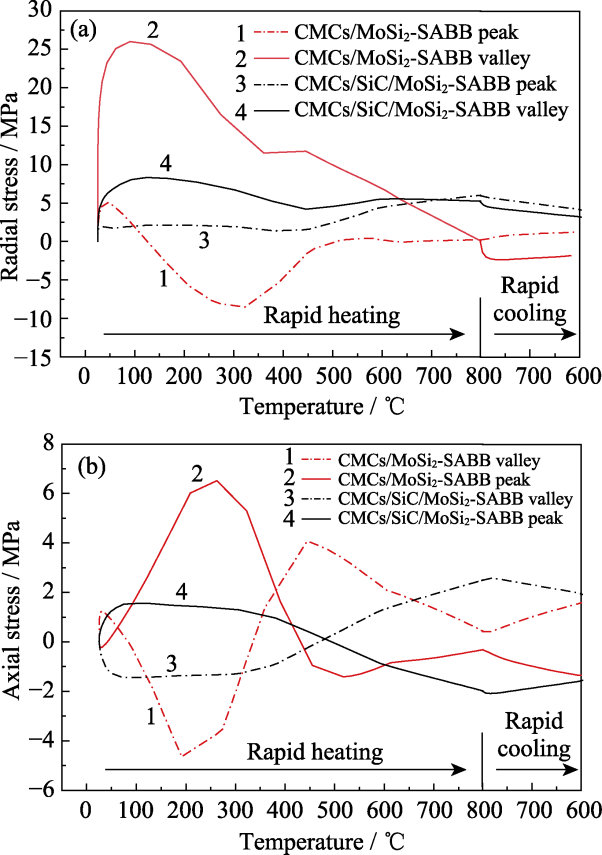
Fig. 3 Curves of temperature and residual stress at peaks and valleys of MoSi2-SABB coating interfaces in CMCs/MoSi2- SABB and CMCs/SiC/MoSi2-SABB models (a) Radial stress; (b) Axial stress
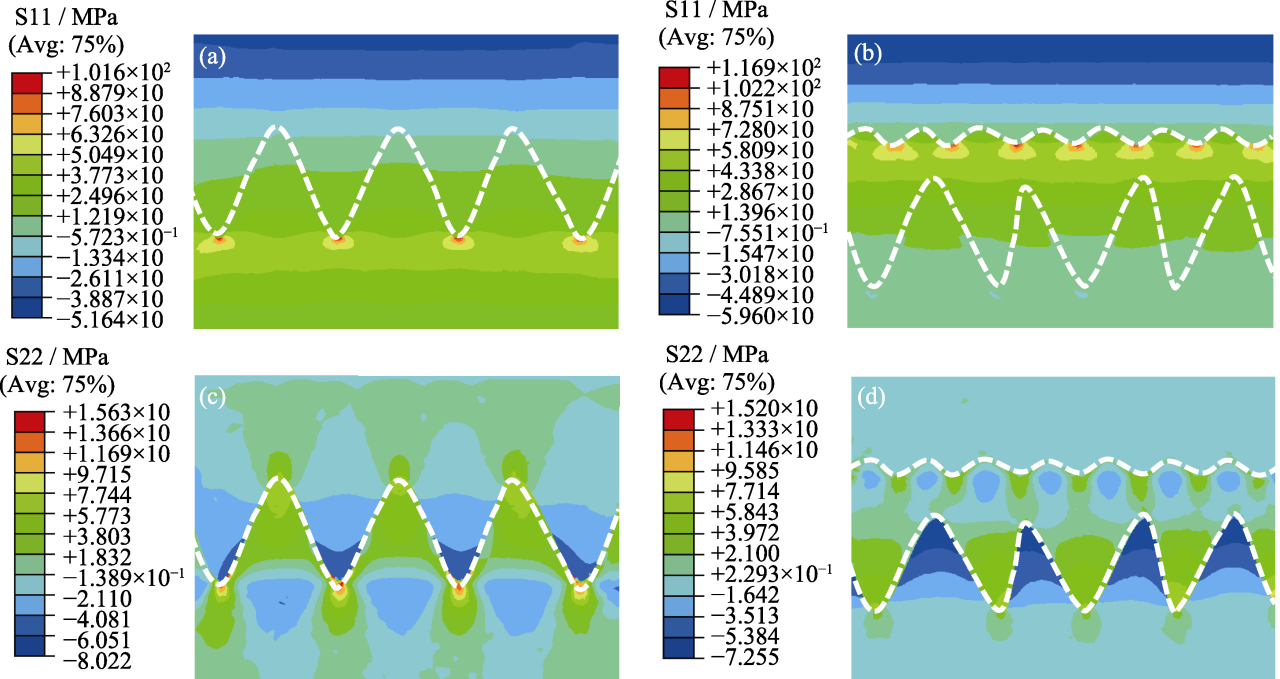
Fig. 4 Radial stress (a, b) and axial stress (c, d) of coating interface of CMCs/MoSi2-SABB (a, c) and CMCs/SiC/MoSi2-SABB (b, d) S11: radial stress; S22: axial stress. Colorful figures are available on website
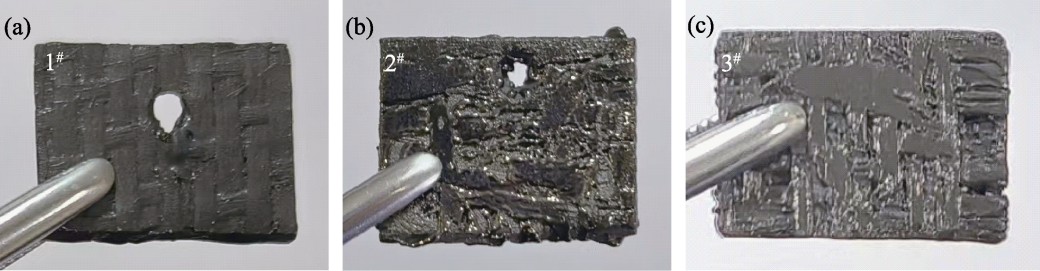
Fig. 6 Macroscopic morphologies of MoSi2-SABB coatings on the surface of three SiC transition layers prepared by different CVD processes (a) 1# sample; (b) 2# sample; (c) 3# sample
| Wsep/(J·m-2) | 6H-SiC/ MoSi2 | 6H-SiC/ SiO2 | 3C-SiC/ MoSi2 | 3C-SiC/ SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si termination | 3.64 | 6.67 | 2.91 | 4.79 |
| C termination | 4.80 | 1.60 | 7.41 | 0.49 |
Table 2 Adhesion strength of 6H-SiC, 3C-SiC and MoSi2, SiO2 interfaces
| Wsep/(J·m-2) | 6H-SiC/ MoSi2 | 6H-SiC/ SiO2 | 3C-SiC/ MoSi2 | 3C-SiC/ SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si termination | 3.64 | 6.67 | 2.91 | 4.79 |
| C termination | 4.80 | 1.60 | 7.41 | 0.49 |
| [1] | WANG X, GAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. Advances in modifications and high-temperature applications of silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites in aerospace: a focused review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(9): 4671. |
| [2] | KÖNIG T, GALETZ M, ALBERT B. Application of the pack cementation process on SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(16): 101. |
| [3] | KARADIMAS G, SALONITIS K. Ceramic matrix composites for aero engine applications—a review. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(5): 3017. |
| [4] | MAZLAN N, SAPUAN S, ILYAS R A. Advanced composites in aerospace engineering applications. New York: Springer, 2022: 367. |
| [5] |
ZOK F W, MAXWELL P T, KAWANISHI K, et al. Degradation of a SiC-SiC composite in water vapor environments. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(3): 1927.
DOI |
| [6] | HU C, TANG S, PANG S, et al. Long-term oxidation behaviors of C/SiC composites with a SiC/UHTC/SiC three-layer coating in a wide temperature range. Corrosion Science, 2019, 147: 1. |
| [7] | RUGGLES-WRENN M B, WILLIAMS T M. Fatigue of a SiC/SiC ceramic composite with an ytterbium-disilicate environmental barrier coating at elevated temperature. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(5): 2074. |
| [8] | XU Y, CHENG L, ZHANG L, et al. Oxidation behavior and mechanical properties of C/SiC composites with Si-MoSi2 oxidation protection coating. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34: 6009. |
| [9] | CAO X, LUAN X, WANG Y, et al. Oxidation and corrosion behavior of 2D laminated SiC/SiC with Si/mullite/BSAS EBC in dry oxygen/water vapor at 1200 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2023, 219: 111237. |
| [10] | ABDUL-AZIZ A, BHATT R T. Modeling of thermal residual stress in environmental barrier coated fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Journal of Composite Materials, 2012, 46(10): 1211. |
| [11] | ZHAO K, DONG S, LÜ K, et al. Feasibility research of Yb3Al5O12 garnet as environmental barrier coating materials. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(10): 15413. |
| [12] | LEE K N. Yb2Si2O7 environmental barrier coatings with reduced bond coat oxidation rates via chemical modifications for long life. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(3): 1507. |
| [13] | LEE K N, ZHU D, LIMA R S. Perspectives on environmental barrier coatings (EBCs) manufactured via air plasma spray (APS) on ceramic matrix composites (CMCs): a tutorial paper. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2021, 30: 40. |
| [14] | TEJERO-MARTIN D, BENNETT C, HUSSAIN T. A review on environmental barrier coatings: history, current state of the art and future developments. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(3): 1747. |
| [15] | WANG Z, ZENG F, LI Y, et al. Self-healing effect and oxidation resistance of ZrSiO4-glass coating for C/C composites at 1173 K- 1573 K. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 792: 496. |
| [16] | FENG T, LI H J, WANG S L, et al. Boron modified multi-layer MoSi2-CrSi2-SiC-Si oxidation protective coating for carbon/carbon composites. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(9): 15167. |
| [17] | YANG X, ZOU Y, HUANG Q, et al. Influence of preparation technology on the structure and phase composition of MoSi2-Mo5Si3/SiC multi-coating for carbon/carbon composites. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2010, 26(2): 106. |
| [18] | FANG G, REN J, SHI J, et al. Thermal stress analysis of environmental barrier coatings considering interfacial roughness. Coatings, 2020, 10(10): 947. |
| [19] | FANG G, ZHENG M, CHEN M, et al. Stochastic simulation of thermal residual stress in environmental barrier coated 2.5D woven ceramic matrix composites. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2024, 33(8): 4114. |
| [20] | WANG B, LI G, LI J, et al. Interfacial modification and oxidation resistance behavior of a CVD-SiC coating for C/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(22): 36816. |
| [21] | KIM J G, PARK S J, PARK J Y, et al. The effect of temperature on the growth and properties of chemical vapor deposited ZrC films on SiC-coated graphite substrates. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1): 211. |
| [22] | HU D, FU Q, LIU T, et al. Structural design and ablation performance of ZrB2/MoSi2 laminated coating for SiC coated carbon/carbon composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(2): 212. |
| [23] | HU D, FU Q, LIU B, et al. Multi-layered structural designs of MoSi2/mullite anti-oxidation coating for SiC-coated C/C composites. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 409: 126901. |
| [24] | LOMBARD C, VAN SITTERT C, MUGO J, et al. Computational investigation of α-SiO2 surfaces as a support for Pd. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(8): 6121. |
| [25] | JIANG D, CARTER E A. Prediction of strong adhesion at the MoSi2/Fe interface. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(17): 4489. |
| [26] | GUO D, XU B, JIA X, et al. Bonding strength and thermal conductivity of novel nanostructured Lu2Si2O7/Lu2SiO5 environmental barrier coating. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2024, 480: 130600. |
| [27] | YANG H, YANG Y, CAO X, et al. Thermal shock resistance and bonding strength of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/mullite/Si coating on SiCf/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(17): 27292. |
| [28] | HUANG J, LIU R, HU Q, et al. High temperature abradable sealing coating for SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(2): 1779. |
| [29] | KIM J G, YOO W S, PARK J Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of contact angle of water on SiC: polytype and polarity dependence. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2020, 9(12): 123006. |
| [30] | OWENS D K, WENDT R. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1969, 13(8): 1741. |
| [1] | LING Yihan, GUO Sheng, CAO Zhiqiang, TIAN Yunfeng, LIU Fangsheng, JIN Fangjun, GAO Yuan. Research Progress on Preparation Technologies and Performance of Straight-pore Electrode Structures for Solid Oxide Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323. |
| [2] | WU Mingxuan, LI Junjie, CHEN Shuo, YAN Yonggao, SU Xianli, ZHANG Qingjie, TANG Xinfeng. Homogeneity of Zone-melted n-type Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30 Thermoelectric Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260. |
| [3] | ZHANG Haifeng, JIANG Meng, SUN Tingting, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Preparation of p-type GeMnTe2 Based Thermoelectric Materials with Stable Cubic Phase [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1245-1251. |
| [4] | LI Chengming, ZHOU Chuang, LIU Peng, ZHENG Liping, LAI Yongji, CHEN Liangxian, LIU Jinlong, WEI Junjun. Stress in CVD Diamond Films: Generation, Suppression, Application, and Measurement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1188-1200. |
| [5] | YUAN Long, JIA Ru, YUAN Meng, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Yu, MENG Xiangdong. Mechanism and Application of X-ray Induced Photochromic Materials: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1097-1110. |
| [6] | AI Yizhaotong, REN Jiulong, QIANG Linya, ZHANG Xiaozhen, YANG Kai, GAO Yanfeng. Friction and Wear Properties of Al2O3-GdAlO3 (GAP) Amorphous Ceramic Coatings under High Load Capacity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1111-1118. |
| [7] | WAN Xinyi, WANG Wenqi, LI Jiacheng, ZHAO Junliang, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Colorless/Black Switching Electrochromic Device Based on WO3·xH2O and Reversible Metal Electrodeposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1163-1174. |
| [8] | ZHAO Lihua, WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao. Bismuth Sulfide Nanoclusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Preparation and Photothermal Antibacterial Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [9] | WU Huaxin, ZHANG Qihao, YAN Haixue, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Optimization of Thermoelectric Transport Properties in Nanocomposite MgAgSb-based Alloys [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [10] | WANG Liangjun, OUYANG Yuzhao, ZHAO Junliang, YANG Chang. Cu-Mn-I Solid Solution Thin Films: Preparation and Control of p-type Transparent Conductive Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1022-1028. |
| [11] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [12] | LI Tingsong, WANG Wenli, LIU Qiang, WANG Yanbin, ZHOU Zhenzhen, HU Chen, LI Jiang. Influence of Cr3+ Doping Concentration on the Persistent Performance of YAGG:Ce3+,Cr3+ Luminescent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1037-1044. |
| [13] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [14] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [15] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||