
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 293-300.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190381
Special Issue: 2020年环境材料论文精选(二)重金属元素去除
Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Lijia1,GUO Xiaojie2,LI Xue1,CHEN Chaogui1,JIN Yang1( ),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAR Hayat3,4,ZHAO Qingzhou5,SHENG Guodong6(
),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAR Hayat3,4,ZHAO Qingzhou5,SHENG Guodong6( )
)
Received:2019-07-24
Revised:2019-09-11
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2019-09-20
About author:DONG Lijia(1984-), female, PhD. E-mail: Donglijia@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
DONG Lijia, GUO Xiaojie, LI Xue, CHEN Chaogui, JIN Yang, AHMED Alsaedi, TASAWAR Hayat, ZHAO Qingzhou, SHENG Guodong. Microscopic Insights into pH-dependent Adsorption of Cd(II) on Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 293-300.
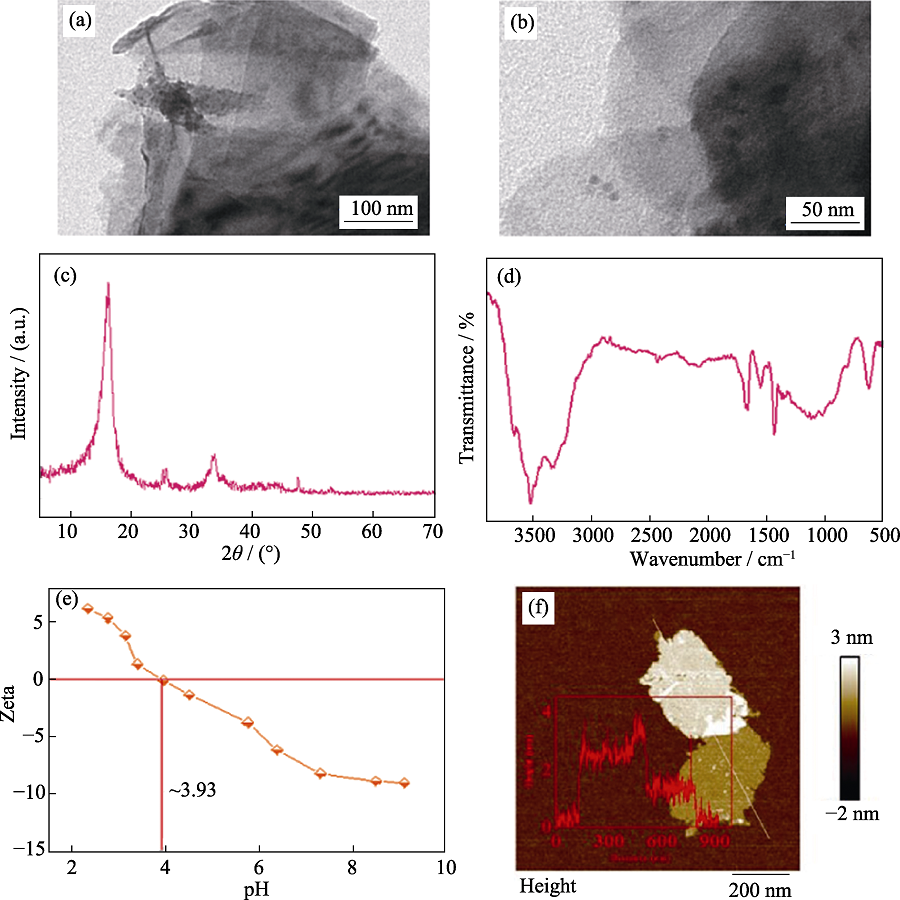
Fig. S1 SEM image (a), TEM image (b), XRD pattern (c), FT-IR spectrum (d), Zeta potentials (e), and height cross-section profile (inset) and corresponding AFM image (f) of MoS2 samples
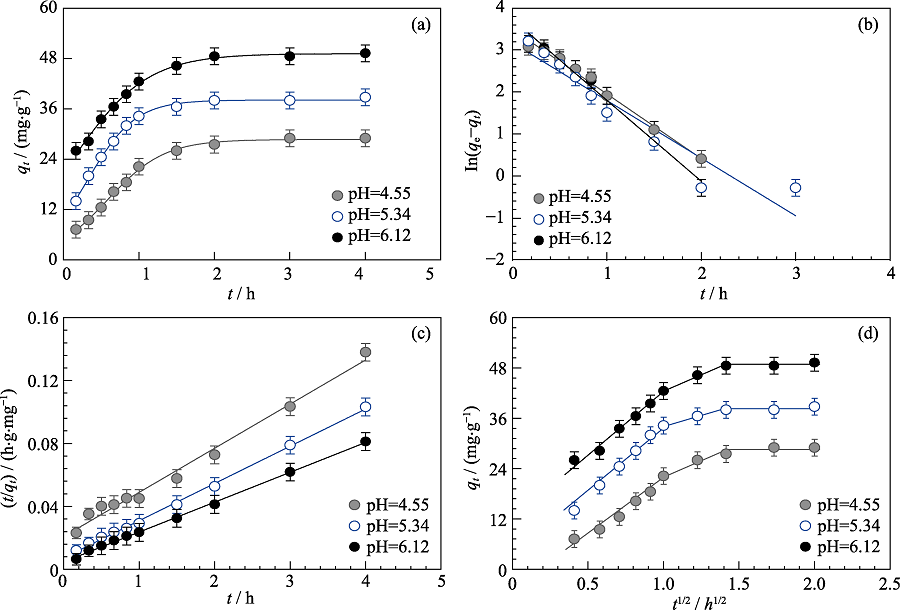
Fig. 3 Cd(II) adsorption on MoS2 nanosheets as a function of contact time (a) and the fitting of pseudo-first-order kinetic model (b), pseudo-second-order kinetic model (c) and intra-particle diffusion model (d) at different pH Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I=0.01 mol/L NaNO3, T=293 K
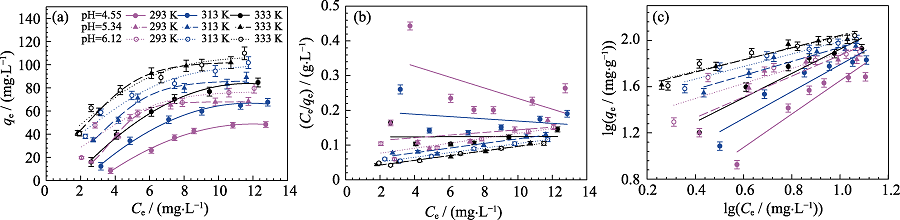
Fig. S2 Adsorption isotherms (a) and fitting results of Langmuir (b) and Freundlich (c) sorption isotherms of Cd(II) sorption on MoS2 at different temperatures and different pH Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I = 0.01 mol/L NaNO3
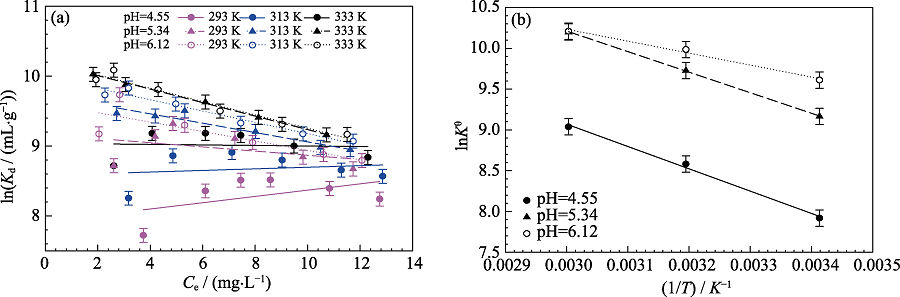
Fig. S3 Linear plots of lnKd versus Ce for Cd(II) at different temperatures and different pH(a), and linear regression plots of lnKθ versus 1/T for Cd(II) sorption on MoS2 at different pH(b) Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I=0.01 mol/L NaNO3
| pH | T/K | KF/(mg1-n·Ln∙g-1) | n | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich equation | 4.55 | 293 | 1.624 | 1.440 | 0.887 |
| 313 | 4.256 | 1.160 | 0.881 | ||
| 333 | 7.461 | 1.052 | 0.904 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 9.363 | 0.899 | 0.801 | |
| 313 | 21.627 | 0.603 | 0.907 | ||
| 333 | 32.734 | 0.526 | 0.939 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 17.298 | 0.650 | 0.812 | |
| 313 | 28.054 | 0.542 | 0.935 | ||
| 333 | 34.119 | 0.499 | 0.919 | ||
| pH | T/K | qmax /(mg∙g-1) | KL /(L∙mg-1) | R2 | |
| Langmuir equation | 4.55 | 293 | 0.040 | 64.516 | 0.299 |
| 313 | 0.016 | 305.157 | 0.069 | ||
| 333 | 0.001 | 754.717 | 0.017 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 0.036 | 262.536 | 0.162 | |
| 313 | 0.132 | 149.276 | 0.918 | ||
| 333 | 0.236 | 147.580 | 0.978 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 0.114 | 140.449 | 0.759 | |
| 313 | 0.172 | 152.022 | 0.974 | ||
| 333 | 0.224 | 151.492 | 0.978 |
| pH | T/K | KF/(mg1-n·Ln∙g-1) | n | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich equation | 4.55 | 293 | 1.624 | 1.440 | 0.887 |
| 313 | 4.256 | 1.160 | 0.881 | ||
| 333 | 7.461 | 1.052 | 0.904 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 9.363 | 0.899 | 0.801 | |
| 313 | 21.627 | 0.603 | 0.907 | ||
| 333 | 32.734 | 0.526 | 0.939 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 17.298 | 0.650 | 0.812 | |
| 313 | 28.054 | 0.542 | 0.935 | ||
| 333 | 34.119 | 0.499 | 0.919 | ||
| pH | T/K | qmax /(mg∙g-1) | KL /(L∙mg-1) | R2 | |
| Langmuir equation | 4.55 | 293 | 0.040 | 64.516 | 0.299 |
| 313 | 0.016 | 305.157 | 0.069 | ||
| 333 | 0.001 | 754.717 | 0.017 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 0.036 | 262.536 | 0.162 | |
| 313 | 0.132 | 149.276 | 0.918 | ||
| 333 | 0.236 | 147.580 | 0.978 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 0.114 | 140.449 | 0.759 | |
| 313 | 0.172 | 152.022 | 0.974 | ||
| 333 | 0.224 | 151.492 | 0.978 |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 33.023 | 0.059 | 0.9896 | |
| Pseudo-first- order model | 5.34 | 23.903 | 0.053 | 0.9069 |
| 6.12 | 41.777 | 0.074 | 0.9835 | |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 35.638 | 0.038 | 0.9869 | |
| Pseudo-second- order model | 5.34 | 42.230 | 0.078 | 0.9978 |
| 6.12 | 52.659 | 0.077 | 0.9986 | |
| pH | C/(mg·L-1) | ki/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 19.985 | 2.628 | 0.942 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | 5.34 | 32.500 | 1.877 | 0.987 |
| 6.12 | 39.759 | 3.004 | 0.980 |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 33.023 | 0.059 | 0.9896 | |
| Pseudo-first- order model | 5.34 | 23.903 | 0.053 | 0.9069 |
| 6.12 | 41.777 | 0.074 | 0.9835 | |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 35.638 | 0.038 | 0.9869 | |
| Pseudo-second- order model | 5.34 | 42.230 | 0.078 | 0.9978 |
| 6.12 | 52.659 | 0.077 | 0.9986 | |
| pH | C/(mg·L-1) | ki/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 19.985 | 2.628 | 0.942 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | 5.34 | 32.500 | 1.877 | 0.987 |
| 6.12 | 39.759 | 3.004 | 0.980 |
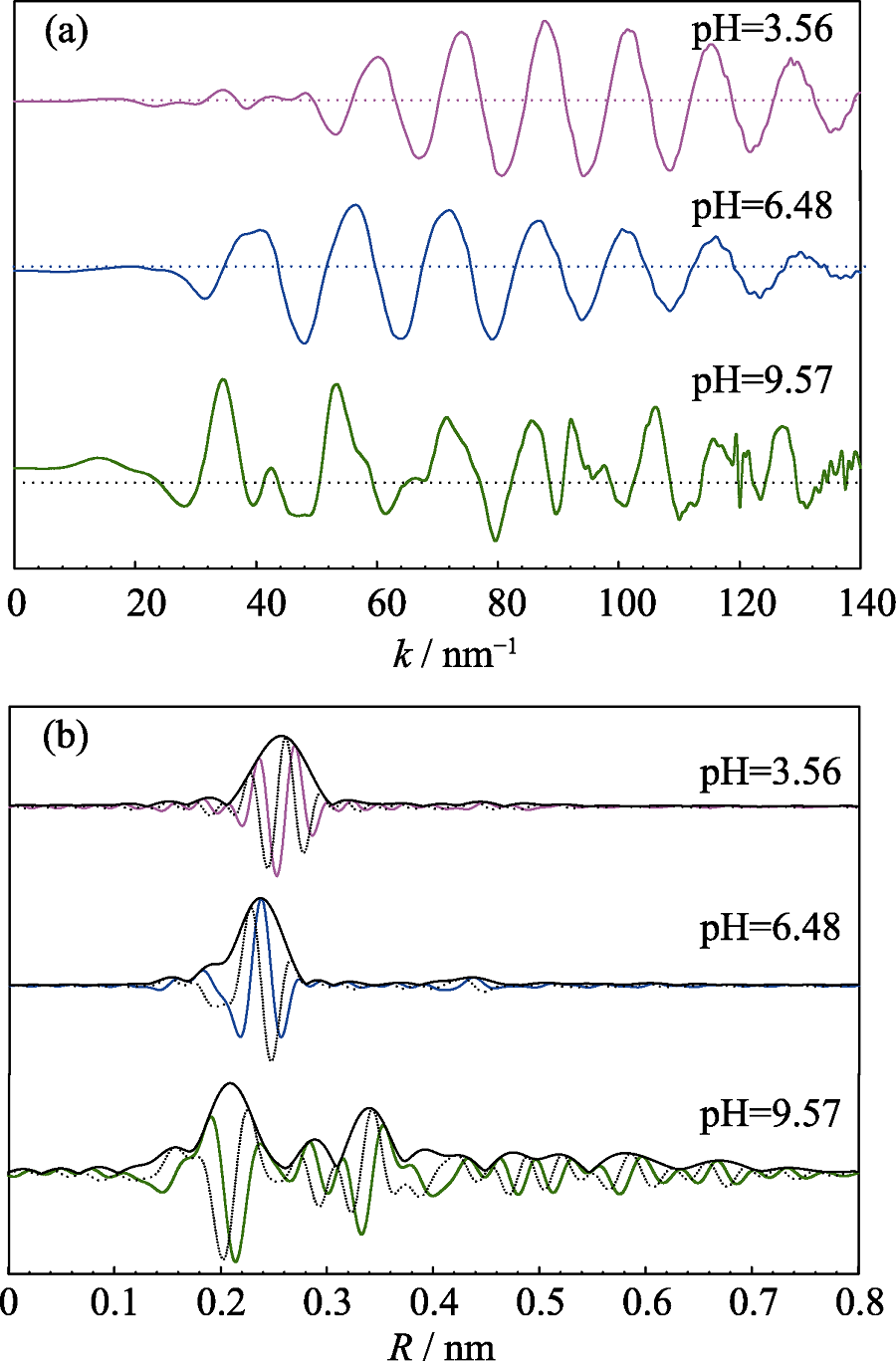
Fig. 4 Normalized, background-subtracted and k3-weighted EXAFS spectra (a) and corresponding RSF magnitudes and imaginary parts (b) of Cd reference samples
| pH | T | ΔGθ/(kJ/mg) | ΔSθ/(J∙mg-1· K-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ∙mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 293 | -19.291 | 143.66592 | 22.803 |
| 313 | -22.333 | 22.635 | ||
| 333 | -25.022 | 22.818 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | -22.331 | 147.73978 | 20.957 |
| 313 | -25.312 | 20.930 | ||
| 333 | -28.239 | 20.958 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | -23.412 | 121.71696 | 12.251 |
| 313 | -25.986 | 12.111 | ||
| 333 | -28.267 | 12.265 |
| pH | T | ΔGθ/(kJ/mg) | ΔSθ/(J∙mg-1· K-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ∙mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 293 | -19.291 | 143.66592 | 22.803 |
| 313 | -22.333 | 22.635 | ||
| 333 | -25.022 | 22.818 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | -22.331 | 147.73978 | 20.957 |
| 313 | -25.312 | 20.930 | ||
| 333 | -28.239 | 20.958 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | -23.412 | 121.71696 | 12.251 |
| 313 | -25.986 | 12.111 | ||
| 333 | -28.267 | 12.265 |
| Sample conditions | shells | R/nm | CN | σ2 /nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(NO3)2(aq) | Cd-O | 0.233(4) | 6.2(3) | 0.0010(1) |
| Cd(OH)2 | Cd-O | 0.238(2) | 6.1(4) | 0.0014(5) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.359(3) | 5.9(4) | 0.0032(5) | |
| CdS | Cd-S | 0.259(1) | 4.1(3) | 0.0024(2) |
| pH 3.56, sorption | Cd-S | 0.255(2) | 3.9(5) | 0.0027(3) |
| pH 6.48, sorption | Cd-S | 0.257(1) | 3.8(4) | 0.0023(5) |
| pH 9.57, sorption | Cd-O | 0..34(5) | 5.9(6) | 0.0016(3) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.357(3) | 5.6(4) | 0.0037(2) |
| Sample conditions | shells | R/nm | CN | σ2 /nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(NO3)2(aq) | Cd-O | 0.233(4) | 6.2(3) | 0.0010(1) |
| Cd(OH)2 | Cd-O | 0.238(2) | 6.1(4) | 0.0014(5) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.359(3) | 5.9(4) | 0.0032(5) | |
| CdS | Cd-S | 0.259(1) | 4.1(3) | 0.0024(2) |
| pH 3.56, sorption | Cd-S | 0.255(2) | 3.9(5) | 0.0027(3) |
| pH 6.48, sorption | Cd-S | 0.257(1) | 3.8(4) | 0.0023(5) |
| pH 9.57, sorption | Cd-O | 0..34(5) | 5.9(6) | 0.0016(3) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.357(3) | 5.6(4) | 0.0037(2) |
| [1] | ZENG G, LIU Y, TANG L , et al. Enhancement of Cd(II) adsorption by polyacrylic acid modified magnetic mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J., 2015,259:153-160. |
| [2] | YANG G, TANG L, LEI X , et al. Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on ketoglutaric acid-modified magnetic chitosan. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014,292:710-716. |
| [3] | LUO L, MA Y B, ZHANG S Z , et al. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manage, 2009,90(8):2524-2530. |
| [4] | KHAN T A, CHAUDHRY S A, ALI I . Equilibrium uptake, isotherm and kinetic studies of Cd(II) adsorption onto iron oxide activated red mud from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq., 2015,202:165-175. |
| [5] | AWUAL M R, KHRAISHEH M, ALHARTHI N H , et al. Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,343:118-127. |
| [6] | LIAO Q, ZOU D, PAN W , et al. Highly-efficient scavenging of P(V), Cr(VI), Re(VII) anions onto g-C3N4 nanosheets from aqueous solutions as impacted via water chemistry. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,258:275-284. |
| [7] | DONG L, YANG J, MOU Y , et al. Effect of various environmental factors on the adsorption of U(VI) onto biochar derived from rice straw. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2017,314(1):377-386. |
| [8] | SHENG G D, YANG Q, PENG F , et al. Determination of colloidal pyrolusite, Eu(III) and humic substance interaction: a combined batch and EXAFS approach. Chem. Eng. J., 2014,245:10-16. |
| [9] | YU S J, WANG X X, PANG H W , et al. Boron nitride-based materials for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,333:343-360. |
| [10] | YAO W, WANG X, LIANG Y , et al. Synthesis of novel flower-like layered double oxides/carbon dots nanocomposites for U(VI) and 241Am(III) efficient removal: batch and EXAFS studies. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,332:775-786. |
| [11] | WANG J, WANG X X, ZHAO G X , et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyacrylamide intercalated molybdenum disulfide as adsorbents for enhanced removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,334:569-578. |
| [12] | LIAO Q, ZOU D S, PAN W , et al. Highly efficient capture of Eu(III), La(III), Nd(III), Th(IV) from aqueous solutions using g-C3N4 nanosheets. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,252:351-361. |
| [13] | WANG X X, YU S J, WANG X K . Removal of radionuclides by metal-organic framework-based materials. J. Inorg. Mater., 2019,34(1):17-26. |
| [14] | WANG N, PANG H, YU S , et al. Investigation of adsorption mechanism of layered double hydroxides and their composites on radioactive uranium: a review. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019,77(2):143-152. |
| [15] | LIU X, MA R, WANG X , et al. Graphene oxide-based materials for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution: a review. Environ. Pollut., 2019,252:62-73. |
| [16] | WANG X X, CHEN L, WANG L , et al. Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem., 2019,62(8):933-967. |
| [17] | FENG B, YAO C, CHEN S , et al. Highly efficient and selective recovery of Au(III) from a complex system by molybdenum disulfide nanoflakes. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,350:692-702. |
| [18] | CHEN H J, HUANG J, LEI X L , et al. Adsorption and diffusion of lithium on MoS2 monolayer: the role of strain and concentration. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013,8:2196-2203. |
| [19] | JIA F, WANG Q, WU J , et al. Two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide as a superb adsorbent for removing Hg+ from water. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017,5:7410-7419. |
| [20] | JIA F, ZHANG X, SONG S . AFM study on the adsorption of Hg 2+ on natural molybdenum disulfide in aqueous solutions . Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19:3837-3844. |
| [21] | WANG Z, MI B . Environmental applications of 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheet. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017,51:8229-8244. |
| [22] | AI K, RUAN C, SHEN M , et al. MoS2 nanosheets with widened interlayer spacing for high-efficiency removal of mercury in aquatic systems. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016,26:5542-5549. |
| [23] | TONG S, DENG H, WANG L , et al. Multi-functional nanohybrid of ultrathin molybdenum disulfide nanosheets decorated with cerium oxide nanoparticles for preferential uptake of lead (II) ions. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,335:22-31. |
| [24] | LI X, LI Q, LINGHU W , et al. Sorption properties of U(VI) and Th(IV) on two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets: effects of pH, ionic strength, contact time, humic acids and temperature. Environ. Technol. Innov., 2018,11:328-338. |
| [25] | WANG Q, YANG L, JIA F , et al. Removal of Cd(II) from water by using nano-scale molybdenum disulphide sheets as adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,263:526-533. |
| [26] | ZHI L, ZUO W, CHEN F , et al. 3D MoS2 composition aerogel as chemosensors and adsorbents for colorimetric detection and high- capacity adsorption of Hg2+. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2016,4:3398-3408. |
| [27] | AI K, RUAN C, SHEN M , et al. MoS2 nanosheets with widened interlayer spacing for high-efficiency removal of mercury in aquatic systems. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016,26:5542-5549. |
| [28] | AGHAGOLI M J, BEYKI M H, SHEMIRANI F . Application of dahlia-like molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for solid phase extraction of Co(II) in vegetable and water samples. Food Chem., 2017,223:8-15. |
| [29] | GAO X, SHENG G D, HUANG Y Y . Mechanism and microstructure of Eu(III) interaction with γ-MnOOH by a combination of batch and high resolution EXAFS investigation. Sci. China Chem., 2013,56:1658-1666. |
| [30] | DONG L, LIAO Q, LINGHU W , et al. Application of EXAFS with a bent crystal analyzer to study the pH-dependent microstructure of Eu(III) onto birnessite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2018,6:842-848. |
| [31] | VASCONCELOS I F, HAACK E A, MAURICE P A , et al. EXAFS analysis of cadmium(II) adsorption to kaolinite. Chem. Geol., 2008,249:237-249. |
| [32] | LIU C, FRENKEL A I, VAIRAVAMURTHY A , et al. Sorption of cadmium on humic acid: mechanistic and kinetic studies with atomic force microscopy and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Can. J. Soil Sci., 2001,81:337-348. |
| [33] | SHENG G D, YANG S T, LI Y M , et al. Retention mechanisms and microstructure of Eu(III) on manganese dioxides studied by batch and high resolution EXAFS technique. Radiochim. Acta, 2014,102:155-167. |
| [34] | COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O’NEILL A , et al. Two dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2011,331(6017):568-571. |
| [35] | SPLENDIANI A, SUN L, ZHANG Y , et al. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett., 2010,10:1271-1275. |
| [36] | KUMAR A S K, JIANG S J, WARCHOL J K . Synthesis and characterization of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide magnetic MoS2@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for adsorption of Cr(VI)/Cr(III). ACS Omega, 2017,2:6187-6200. |
| [37] | TAKAMATSU R, ASAKURA K, CHUN W J , et al. EXAFS studies about the sorption of cadmium ions on montmorillonite. Chem. Lett., 2006,35:224-225. |
| [38] | HUANG X, CHEN T, ZOU X , et al. The adsorption of Cd(II) on manganese oxide investigated by batch and modeling techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2017,14(10):1145. |
| [39] | GUECHI E, BEGGAS D . Removal of cadmium (II) from water using fibre fruit lufa as biosorbent. Desalin. Water Treat., 2017,94:181-188. |
| [40] | ABASIYAN S M A, MAHDANINIA G R . Polyvinyl alcohol- based nanocomposite hydrogels containing magnetic laponite RD to remove cadmium. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res., 2018,25:14977-14988. |
| [41] | CORBETT J F . Pseudo first-order kinetics. J. Chem. Educ., 1972,49:663. |
| [42] | HO Y S, MCKAY G . A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process. Saf. Environ., 1998,76:332-340. |
| [43] | GRAAF G H, SCHOLTENS H, STAMHUIS E J , et al. Intra-particle diffusion limitations in low-pressure methanol synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci., 1990,45:773-783. |
| [44] | HO Y S, MCKAY G . The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Rer., 2000,34:735-742. |
| [45] | TEMKIN M J, PYZHEV V . Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physchim, 1940,12:217-222. |
| [46] | XUE C, QI P S, LIU Y Z . Adsorption of aquatic Cd 2+ using a combination of bacteria and modified carbon fiber . Adsorpt. Sci. Technol., 2017,36:857-871. |
| [47] | GU P, ZHANG S, ZHANG C , et al. Two-dimensional MAX- derived titanate nanostructures for efficient removal of Pb(II). Dalton Trans., 2019,48(6):2100-2107. |
| [48] | CHEN W, LU Z, XIAO B , et al. Enhanced removal of lead ions from aqueous solution by iron oxide nanomaterials with cobalt and nickel doping. J. Clean. Prod., 2019,211:1250-1258. |
| [49] | ZHANG D, NIU H Y, ZHANG X L , et al. Strong adsorption of chlorotetracycline on magnetite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011,192:1088-1093. |
| [50] | ZHANG H, YU X, CHEN L , et al. Study of 63Ni adsorption on NKF-6 zeolite. J. Environ. Radioact., 2010,101:1061-1069. |
| [51] | BEKCI Z, SEKI Y, YURDAKOC M K . A study of equilibrium and FTIR, SEM/EDS analysis of trimethoprim adsorption onto K10. J. Mol. Struct., 2007,827:67-74. |
| [52] | GRÄFE M, SINGH B, BALASUBRAMANIAN M . Surface speciation of Cd(II) and Pb(II) on kaolinite by EXAFS spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2007,315:21-32. |
| [53] | SHENG G, DONG H, SHEN R , et al. Microscopic insights into the temperature dependent adsorption of Eu(III) onto titanate nanotubes studied by FTIR, XPS, XAFS and batch technique. Chem. Eng. J., 2013,217:486-494. |
| [1] | TANG Xinli, DING Ziyou, CHEN Junrui, ZHAO Gang, HAN Yingchao. In vivo Distribution and Metabolism of Calcium Phosphate Nanomaterials Based on Fluorescent Labeling with Rare Earth Europium Ions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [2] | TAN Bowen, GENG Shuanglong, ZHANG Kai, ZHENG Bailin. Composition-gradient Design of Silicon Electrodes to Mitigate Mechanochemical Coupling Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 772-780. |
| [3] | YU Leyangyang, ZHAO Fangxia, ZHANG Shuxin, XU Yixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHENG Xuebin. Preparation of High-entropy Boride Powders for Plasma Spraying by Inductive Plasma Spheroidization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | CHEN Xiangjie, LI Ling, LEI Tianfu, WANG Jiajia, WANG Yaojin. Enhanced Piezoelectric Properties of (1-x)(0.8PZT-0.2PZN)-xBZT Ceramics via Phase Boundary and Domain Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 729-734. |
| [5] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [6] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [7] | CHEN Libo, SHENG Ying, WU Ming, SONG Jiling, JIAN Jian, SONG Erhong. Na and O Co-doped Carbon Nitride for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 552-562. |
| [8] | YANG Mingkai, HUANG Zeai, ZHOU Yunxiao, LIU Tong, ZHANG Kuikui, TAN Hao, LIU Mengying, ZHAN Junjie, CHEN Guoxing, ZHOU Ying. Co-production of Few-layer Graphene and Hydrogen from Methane Pyrolysis Based on Cu and Metal Oxide-KCl Molten Medium [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [9] | GUO Ziyu, ZHU Yunzhou, WANG Li, CHEN Jian, LI Hong, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Zn2+ Catalyst on Microporous Structure of Porous Carbon Prepared from Phenolic Resin/Ethylene Glycol [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 466-472. |
| [10] | CHEN Xi, YUAN Yuan, TAN Yeqiang, LIU Changsheng. Strategic Study on the Development of Inorganic Non-metallic Biomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 449-456. |
| [11] | WAN Junchi, DU Lulu, ZHANG Yongshang, LI Lin, LIU Jiande, ZHANG Linsen. Structural Evolution and Electrochemical Performance of Na4FexP4O12+x/C Cathode Materials for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [12] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [13] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [14] | YUAN Liping, WU Yuanbo, YU Jiajing, ZHANG Shiyan, SUN Yi, HU Yunchu, FAN Youhua. CNFs Aerogel Composite with Phosphomolybdic Acid Intercalated Hydrotalcite: Preparation and Thermal Insulation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 415-424. |
| [15] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||