
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 493-501.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180218
Previous Articles Next Articles
Han-Qing YU1,2,Zhi-Jun DONG1,2( ),Guan-Ming YUAN1,2,Ye CONG1,2,Xuan-Ke LI3(
),Guan-Ming YUAN1,2,Ye CONG1,2,Xuan-Ke LI3( ),Yong-Ming LUO4
),Yong-Ming LUO4
Received:2018-05-04
Revised:2018-12-17
Published:2019-05-20
Online:2019-05-14
Supported by:CLC Number:
Han-Qing YU, Zhi-Jun DONG, Guan-Ming YUAN, Ye CONG, Xuan-Ke LI, Yong-Ming LUO. Boron-carbon doped Silicon Carbide Fibers: Preparation and Property[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 493-501.
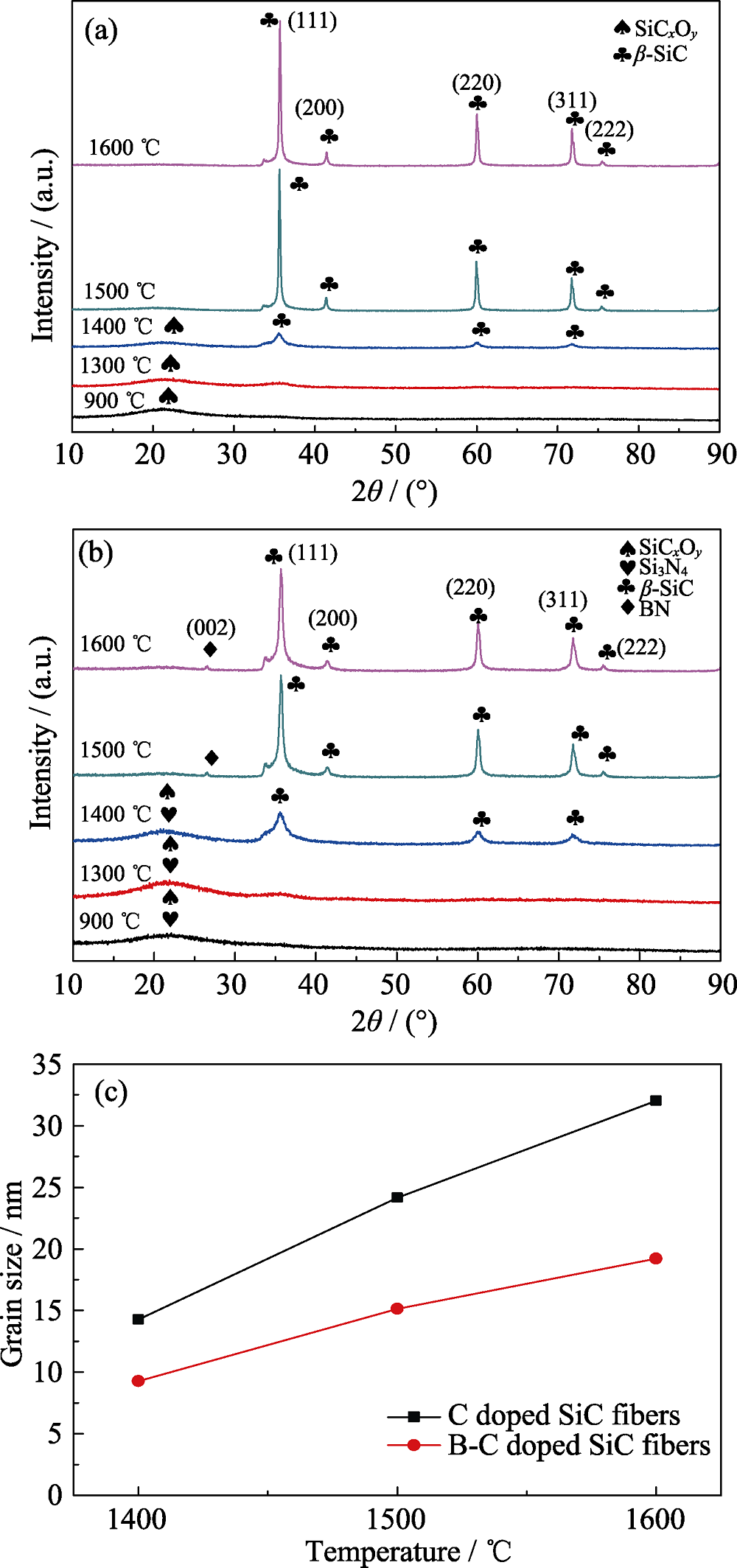
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of C doped SiC fibers (a) and B-C doped SiC fibers (b), dependence of grain size on the heat-treatment temperature for the doped SiC fibers (c)
| Composition/wt% | 900 ℃ | 1300 ℃ | 1400 ℃ | 1500 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 42.68 | 51.82 | 54.98 | 64.54 |
| C | 36.46 | 31.76 | 30.87 | 25.75 |
| O | 20.68 | 16.42 | 14.15 | 9.71 |
Table 1 Chemical composition of C doped SiC fibers after heat-treatment at different temperatures
| Composition/wt% | 900 ℃ | 1300 ℃ | 1400 ℃ | 1500 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 42.68 | 51.82 | 54.98 | 64.54 |
| C | 36.46 | 31.76 | 30.87 | 25.75 |
| O | 20.68 | 16.42 | 14.15 | 9.71 |
| Composition/wt% | 900 ℃ | 1300 ℃ | 1400 ℃ | 1500 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 47.94 | 58.73 | 61.90 | 71.43 |
| C | 34.75 | 30.32 | 28.36 | 23.48 |
| O | 16.95 | 12.58 | 9.34 | 4.80 |
| B | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 |
| N | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
Table 2 Chemical composition of B-C doped SiC fibers after heat-treatment at different temperatures
| Composition/wt% | 900 ℃ | 1300 ℃ | 1400 ℃ | 1500 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 47.94 | 58.73 | 61.90 | 71.43 |
| C | 34.75 | 30.32 | 28.36 | 23.48 |
| O | 16.95 | 12.58 | 9.34 | 4.80 |
| B | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 |
| N | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
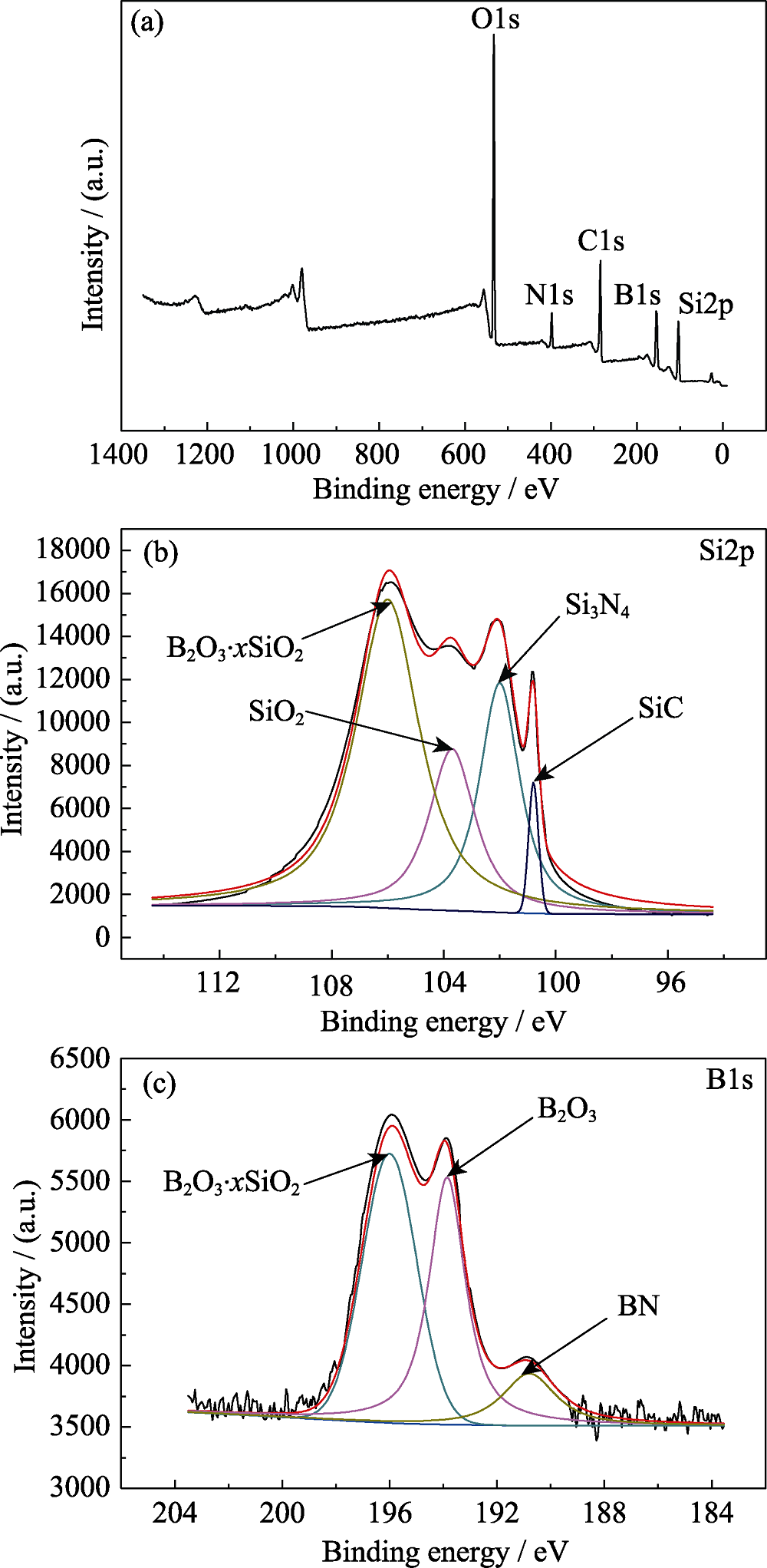
Fig. 9 XPS wide scan spectra (a) and high resolution XPS spectra for B1s (b) and Si2p (c) region of the B-C doped SiC fibers after oxidation at 1200 ℃ for 1 h
| [1] | 杨连, 黎阳, 洪流 , 等. 功能化碳化硅纤维研究进展. 人工晶体学报, 2016,45(5):1397-1403. |
| [2] |
班国东, 刘朝辉, 叶圣天 , 等. 新型涂覆型雷达吸波材料的研究进展. 表面技术, 2016,45(6):140-146.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
宋永才, 王娟, 冯春祥 . 由PDMS与PVC共热解聚碳硅烷制备SiC-C纤维. 材料研究学报, 2004,18(3):295-300.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ZUO X, DONG Z, LI W , et al. Oxidation behavior of carbon-silicon and carbon-boron-silicon alloys derived from solvent-soluble silicon and boron-silicon-doped coal-tar pitches. Materials and Technology, 2014,48(1):59-66. |
| [5] |
BERNARD S, MAJOULET O, SANDRA F , et al. Direct synthesis of periodic mesoporous silicoboron carbonitride frameworks via the nanocasting from ordered mesoporous silica with boron-modified polycarbosilazane. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2013,15(3):134-140.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HANG S X, HAO S C, ZHU Y . Preparation and properties of pinacolborane modified polycarbosilane as SiC fiber precursor. Journal of Inorganic & Organometallic Polymers & Materials, 2015,25(6):1-5.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XU X H, MAO Y, CHEN F , et al. Effects of oxidation cross-linking and sintering additives (TiN, B) on the formation and heat-resistant performance of polymer-derived SiC (Ti, B) films. Ceramics International, 2016,42(7):8636-8644.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LEE J, BUTT D P, BANEY R H , et al. Synthesis and pyrolysis of novel polysilazane to SiBCN ceramic. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2005,351(37):2995-3005.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GUO A, ROSO M, MODESTI M , et al. Characterization of porosity, structure, and mechanical properties of electrospun SiOC fiber mats. Journal of Materials Science, 2015,50(12):4221-4231.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TANG Y, WANG J, LI X D , et al. Preceramic polymer for SiBNC fiber via one-step condensation of silane, BCl3, and silazane. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2010,110(2):921-928.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FU Q, LI H, S HI X , et al. Microstructure and growth mechanism of SiCw hiskers on carbon/carbon composites prepared by CVD. Materials Letters, 2005,59(19/20):2593-2597.
DOI URL |
| [12] | HEMIDA A T, TENAILLEAU H, BARDEAU L , et al. A quasi-stoic hiometric SiC-based experimental fibre obtained from a boron- doped polycarbosilane precursor. Journal of Materials Science, 1997,32(21):5791-5796. |
| [13] |
CAO F, LI X D, KIM D P . Efficient curing of polymet hylsilane by borazine and reaction mechanism study. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2003,688(1):125-131.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
YUAN QIN, SONG YONG-CAI . Effect of SiCxOy decompositim on densification of SiCO(Al) fibers during sintering process. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016,31(12):1320-1326.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHOLLON G, CZERNIAK M, PAILLER R , et al. A model SiC- based fibre with a low oxygen content prepared from a polycarbosilane precursor. Journal of Materials Science, 1997,32(4):893-911.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CINIBULK M K, PART HASARAT HY T A . Characterization of oxidized polymer-derived SiBCN fibers. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001,84(10):2197-2202.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MULLER A, ZERN A, GERSTEL P , et al. Boron-modified poly (propenylsilazane)-derived Si-B-C-N ceramics: preparation and high temperature properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002,22(9/10):1631-1643.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIPOWITZ J . Structure and properties of ceramic fibers prepared from organosilicon polymers. Journal of Inorganic & Organometallic Polymers, 1991,1(3):277-297.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KOBAYAS HI K, MAEDA K, SANO H , et al. Formation and oxidation resistance of the coating formed on carbon material composed of B4C-SiC powders. Carbon, 1995,33(4):397-403.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WU H, ZHANG W . Fabrication and properties of ZrB2-SiC-BN machinable ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010,30(4):1035-1042.
DOI URL |
| [1] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [2] | ZHOU Yangyang, ZHANG Yanyan, YU Ziyi, FU Zhengqian, XU Fangfang, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Properties in CaBi4Ti4O15-based Ceramics through Bi3+ Self-doping Strategy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [3] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [4] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [5] | PAN Yuzhou, HE Fajian, XU Lulu, DAI Shixun. Broadband 3 μm Mid-infrared Emission in Dy3+/Yb3+ Co-doped Tellurite Glass under 980 nm LD Excitation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 521-528. |
| [6] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [7] | GOU Yanzi, KANG Weifeng, WANG Pengren. Influence of Sintering Conditions on Preparation of Nearly Stoichiometric SiC Fibers with Highly Crystalline Microstructure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [8] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [9] | LI Wei, XU Zhiming, GOU Yanzi, YIN Senhu, YU Yiping, WANG Song. Preparation and Performance of Sintered SiC Fiber-bonded Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [10] | SHEN Hao, CHEN Qianqian, ZHOU Boxiang, TANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Yuanyuan. Preparation and Energy Storage Properties of A-site La/Sr Co-doped PbZrO3 Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1022-1028. |
| [11] | CHENG Jun, ZHANG Jiawei, QIU Pengfei, CHEN Lidong, SHI Xun. Preparation and Thermoelectric Transport Properties of P-doped β-FeSi2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 895-902. |
| [12] | ZHAO Zhihan, GUO Peng, WEI Jing, CUI Li, LIU Shanze, ZHANG Wenlong, CHEN Rende, WANG Aiying. Ti Doped Diamond Like Carbon Films: Piezoresistive Properties and Carrier Transport Behavior [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 879-886. |
| [13] | LI Jiaqi, LI Xiaosong, LI Xuanhe, ZHU Xiaobing, ZHU Aimin. Transition Metal-doped Manganese Oxide: Synthesis by Warm Plasma and Electrocatalytic Performance for Oxygen Evolution Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 835-844. |
| [14] | TAM YU Puy Mang, XU Yu, GAO Quanhao, ZHOU Haiqiong, ZHANG Zhen, YIN Hao, LI Zhen, LÜ Qitao, CHEN Zhenqiang, MA Fengkai, SU Liangbi. Spectroscopic Properties and Optical Clusters in Erbium-doped CaF2, SrF2 and PbF2 Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 330-336. |
| [15] | GOU Yanzi, KANG Weifeng, ZHANG Qingyu. Preparation of Nearly Stoichiometric SiC(Ti) Fibers with Highly Crystalline Microstructure from Polytitanocarbosilane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1377-1383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||