
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 884-890.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160582
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Yun-Fei, ZHU Bo-Quan, LI Xiang-Cheng, CHEN Ping-An
Received:2016-10-21
Published:2017-08-15
Online:2017-07-19
About author:FU Yun-Fei(1991–), male, candidate of master degree. E-mail: vfuyunfeiv@tom.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
FU Yun-Fei, ZHU Bo-Quan, LI Xiang-Cheng, CHEN Ping-An. Synthesis and Rheological Property of Calcium Aluminate Cement Containing MgAl2O4 Spinel[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 884-890.
| Sample No. | Synthesis temperature | Constituent of raw materials/wt% | Designed phase composition of the cement/wt% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial alumina | Calcined magnesia | Calcium carbonate | MA | CA | CA2 | ||
| A | 1400℃ | 63.1 | 15.9 | 21.0 | 63.3 | 33.8 | 2.9 |
| B | 65.5 | 20.0 | 14.5 | 73.0 | 23.5 | 3.5 | |
| C | 1500℃ | 63.1 | 15.9 | 21.0 | 63.3 | 33.8 | 2.9 |
| D | 65.5 | 20.0 | 14.5 | 73.0 | 23.5 | 3.5 | |
Table 1 Chemical and mineral phase compositions of CMA cements
| Sample No. | Synthesis temperature | Constituent of raw materials/wt% | Designed phase composition of the cement/wt% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial alumina | Calcined magnesia | Calcium carbonate | MA | CA | CA2 | ||
| A | 1400℃ | 63.1 | 15.9 | 21.0 | 63.3 | 33.8 | 2.9 |
| B | 65.5 | 20.0 | 14.5 | 73.0 | 23.5 | 3.5 | |
| C | 1500℃ | 63.1 | 15.9 | 21.0 | 63.3 | 33.8 | 2.9 |
| D | 65.5 | 20.0 | 14.5 | 73.0 | 23.5 | 3.5 | |
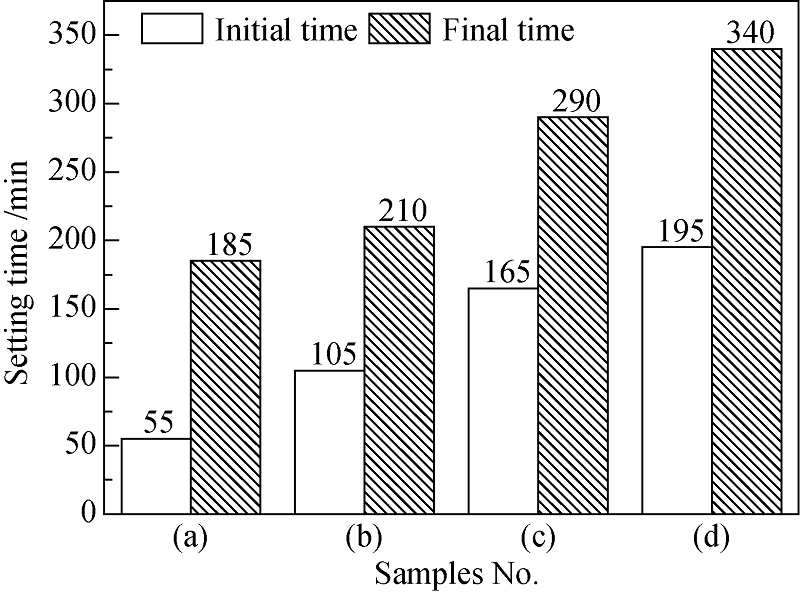
Fig. 4 Setting time of different CMA cements(a) Mortar for CMA cement A; (b) Mortar for CMA cement B; (c) Mortar for CMA cement C; (d) Mortar for CMA cement D
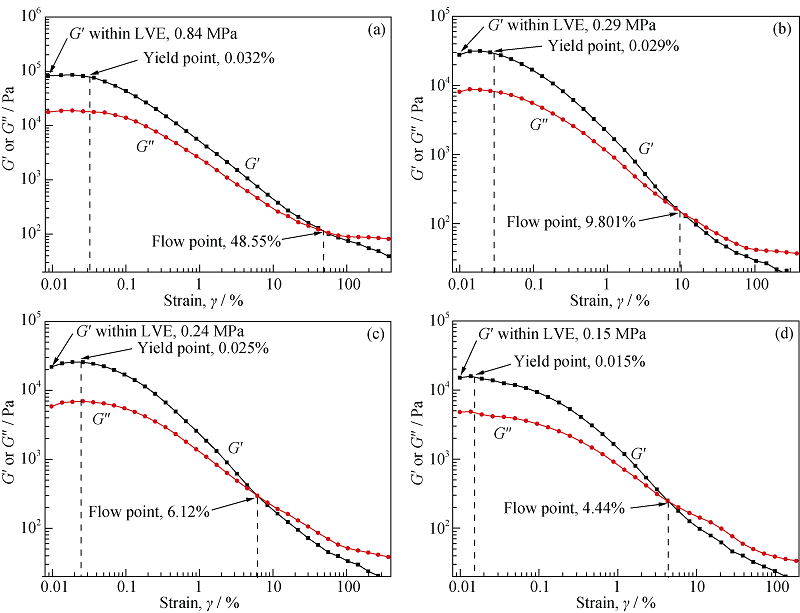
Fig. 7 Strain-sweep curves of different CMA cements(a) Slurry for CMA cement A; (b) Slurry for CMA cement B; (c) Slurry for CMA cement C; (d) Slurry for CMA cement D
| [1] | ABO-EL-ENEIN SALAH A, ABOU-SEKKINA MORSY M, KHALIL NAGY M, et al. Microstructure and refractory properties of spinel containing castables.Ceram. Int., 2010, 36(5): 1711-1717. |
| [2] | BRAULIO M A L, RIGAUD M, BUHR A, et al. Spinel-containing alumina-based refractory castables.Ceram. Int., 2011, 37(6): 1705-1724. |
| [3] | SAKO E Y, BRAULIO M A L, BRANT P O, et al. The impact of pre-formed and in situ spinel formation on the physical properties of cement-bonded high alumina refractory castables.Ceram. Int., 2010, 36(7): 2079-2085. |
| [4] | MUKHOPADHYAY S, DAS PODDAR P K. Effect of preformed and in situ spinels on microstructure and properties of a low cement refractory castable.Ceram. Int., 2004, 30(3): 369-380. |
| [5] | ARACELI ELISABET LAVAT, MARIA CRISTINA GRASSELLI, EUGENIA GIULIODORI LOVECCHIO.Effect of α andγ polymorphs of alumina on the preparation of MgAl2O4-spinel- containing refractory cements.Ceram. Int., 2010, 36(1): 15-21. |
| [6] | BRAULIO M A L, MORBIOLI G G, MILANEZ D H, et al. Calcium aluminate cement source evaluation for Al2O3-MgO refractory castables.Ceram. Int., 2011, 37(1): 215-221. |
| [7] | ZHANG ZHI-HUI, LI NAN.Effect of polymorphism of Al2O3 on the synthesis of magnesium aluminate spinel.Ceram. Int., 2005, 31(4): 583-589. |
| [8] | HAN BING-QIANG, WANG PENG, KE CHANG-MING, et al.Hydration behavior of spinel containing high alumina cement from high titania blast furnace slag.Cem. Concr. Res., 2016, 79: 257-264. |
| [9] | SOUZA T M, LUZ A P, PAGLIOSA CARLOS, et al.Mineralizing alumina-magnesia cement-bonded castables containing magnesium borates.Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(9): 11143-11152. |
| [10] | XIAO GUO-QING, GAO YUN-QIN, DUAN FENG.Preparation and corrosion resistance of aluminous cement containing magnesium aluminate spinel.J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 36(8): 1172-1177. |
| [11] | GEHRE P, ANEZIRIS C G, VERES D, et al.Improved spinel-containing refractory castables for slagging gasifiers.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2013, 33(6): 1077-1086. |
| [12] | BRAULIO M A L, BITTENCOURT L R M, PANDOLFELLI V C. Selection of binders for in situ spinel refractory castables.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29(13): 2727-2735. |
| [13] | NANDI P, GARG A, SINGH R K, et al.Effects of cement and magnesia fines on in situ spinel formation in alumina-magnesia castable.Adv. Appl. Ceram., 2005, 104(2): 83-88. |
| [14] | LUZ A P, BRAULIO M A L, TOMBA MARTINEZ A G, et al. Slag attack evaluation of in situ spinel-containing refractory castables via experimental tests and thermodynamic simulations.Ceram. Int., 2012, 38(2): 1497-1505. |
| [15] | TOMBA MARTINEZ A G, LUZ A P, BRAULIO M A L, et al. CA6 impact on the corrosion behavior of cement-bonded spinel- containing refractory castables: an analysis based on thermodynamic simulations.Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(3): 4714-4725. |
| [16] | LI JIN-HONG, CAI BI-YA, FENG WU-WEI, et al.Investigations on phase constitution, mechanical properties and hydration kinetics of aluminous cements containing magnesium aluminate spinel.Ceram. Int., 2013, 39(7): 8393-8400. |
| [17] | AUVRAY JEAN-MICHEL, GAULT CHRISTIAN, HUGER MARC.Microstructural changes and evolutions of elastic properties versus temperature of alumina and alumina-magnesia refractory castables.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 28(10): 1953-1960. |
| [18] | ZHU BO-QUAN, WANG YU-LONG, LI XIANG-CHENG.Effect of phase distribution on rheological behavior of calcium aluminate cement with built-in alumina-magnesia spinel.J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 42: 1383-1388. |
| [19] | STARK JOCHEN.Recent advances in the field of cement hydration and microstructure analysis.Cem. Concr. Res., 2011, 41(7): 666-678. |
| [20] | SILVA ABILIO P, SEGADÃES ANA M, PINTO DEESY G, et al. Effect of particle size distribution and calcium aluminate cement on the rheological behaviour of all-alumina refractory castables.Powder Technol., 2016, 226: 107-113. |
| [21] | OLIVEIRA I R, ORTEGA F S, PANDOLFELLI V C.Hydration of CAC cement in a castable refractory matrix containing processing additives.Ceram. Int., 2009, 35: 1545-1552. |
| [22] | WANG YU-LONG, ZHU BO-QUAN, LI XIANG-CHENG, et al.Effect of dispersants on the hydrate morphologies of spinel- containing calcium aluminate cement and on the properties of refractory castables. Ceram. Int., 2016, 42: 711-720. |
| [23] | LONG BIN, BUHR ANDREAS, XU GUI-YING.Thermodynamic evaluation and properties of refractory materials for steel ladle purging plugs in the system Al2O3-MgO-CaO.Ceram. Int., 2016, 42: 11930-11940. |
| [24] | DIAZ L A, Torrecillas R.Hot bending strength and creep behaviour at 1000-1400℃ of high alumina refractory castables with spinel, periclase and dolomite additions.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29: 53-58. |
| [25] | ZHU BO-QUAN, SONG YA-NAN, LI XIANG-CHENG, et al.Synthesis and hydration kinetics of calcium aluminate cement with micro MgAl2O4 spinels.Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 154: 158-163. |
| [26] | PENG JIAN-WEI, DENG DE-HUA, LIU ZAN-QUN, et al.Rheological models for fresh cement asphalt paste.Constr. Build. Mater., 2014, 71: 254-262. |
| [27] | MEZGER THOMAS G. The Rheology Handbook, 3rd, Vincentz Network: Hannover Press, 2011, 3: 38-51. |
| [28] | HAFIANE Y EL, SMITH A, BONNET J P, et al.Effect of a carboxylic acid on the rheological behavior of an aluminous cement paste and consequences on the properties of the hardened material.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 25(7): 1143-1147. |
| [1] | XIN Zhenyu, GUO Ruihua, WUREN Tuoya, WANG Yan, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Pt-Fe/GO Nanocatalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance on Ethanol Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [2] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [3] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [4] | XU Xiangming, Husam N ALSHAREEF. Perspective of MXetronics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 171-178. |
| [5] | YIN Jianyu, LIU Nishuang, GAO Yihua. Recent Progress of MXene in Pressure Sensing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 179-185. |
| [6] | YAO Lei, YANG Dongwang, YAN Yonggao, TANG Xinfeng. Laser-induced Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis of Skutterudite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 815-822. |
| [7] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [8] | JIN Xihai, DONG Manjiang, KAN Yanmei, LIANG Bo, DONG Shaoming. Fabrication of Transparent AlON by Gel Casting and Pressureless Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 193-198. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ye, YAO Dongxu, ZUO Kaihui, XIA Yongfeng, YIN Jinwei, ZENG Yuping. Combustion Synthesis of Si3N4-BN-SiC Composites by in-situ Introduction of BN and SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [11] | LIU Jinling, LIU Dianguang, REN Ke, WANG Yiguang. Research Progress on the Flash Sintering Mechanism of Oxide Ceramics and Its Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 473-480. |
| [12] | MENG Qing, LI Jiangtao. Hydrophobic BN Powders by Combustion Synthesis and Its Super-hydrophobic Coatings: Preparation and Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1037-1042. |
| [13] | YANG Dongwang, LUO Tingting, SU Xianli, WU Jinsong, TANG Xinfeng. Unveiling the Intrinsic Low Thermal Conductivity of BiAgSeS through Entropy Engineering in SHS Kinetic Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 991-998. |
| [14] | LI Ziyi, ZHANG Jiajia, ZOU Xiaoqin, ZUO Jiayu, LI Jun, LIU Yingshu, PUI David Youhong. Synthesis and Gas Separation of Chabazite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 579-591. |
| [15] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||