无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1193-1199.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230065 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230065
所属专题: 【结构材料】高导热陶瓷(202506)
吴松泽1( ), 周洋1(
), 周洋1( ), 李润丰2, 刘晓倩1, 李翠伟1, 黄振莺1
), 李润丰2, 刘晓倩1, 李翠伟1, 黄振莺1
收稿日期:2023-02-08
修回日期:2023-03-15
出版日期:2023-10-20
网络出版日期:2023-04-11
通讯作者:
周 洋, 教授. E-mail: yzhou@bjtu.edu.cn作者简介:吴松泽(1997-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: 20116052@bjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Songze1( ), ZHOU Yang1(
), ZHOU Yang1( ), LI Runfeng2, LIU Xiaoqian1, LI Cuiwei1, HUANG Zhenying1
), LI Runfeng2, LIU Xiaoqian1, LI Cuiwei1, HUANG Zhenying1
Received:2023-02-08
Revised:2023-03-15
Published:2023-10-20
Online:2023-04-11
Contact:
ZHOU Yang, professor. E-mail: yzhou@bjtu.edu.cnAbout author:WU Songze (1997-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 20116052@bjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
为拓展铁尾矿的资源化利用途径, 本研究分别以细颗粒高硅铁尾矿、铁尾矿+石墨粉以及铁尾矿+石墨粉+碳化硅粉为原料, 采用泡沫注凝成形-常压烧结、泡沫注凝成形-反应烧结和模压成形-反应烧结工艺制备了铁尾矿多孔陶瓷和三种以碳化硅为主晶相的多孔陶瓷。通过DSC-TG和XRD分析, 研究了铁尾矿自身的烧结过程以及铁尾矿与石墨之间的碳热还原反应烧结过程, 对比分析了四种多孔陶瓷材料的孔隙率、压缩强度、热导率等性能。结果表明, 以铁尾矿为原料可制备具有较高孔隙率(87.2%)、压缩强度(1.37 MPa)和低热导率(0.036 W/(m·K))的铁尾矿多孔陶瓷, 它是一种高效保温隔热材料; 利用铁尾矿与石墨之间的碳热还原反应可获得碳化硅多孔陶瓷, 其热导率显著提高, 但强度偏低; 而在原料中加入部分碳化硅, 可以明显改善多孔陶瓷的压缩强度, 获得具有高孔隙率(91.6%)、较高压缩强度(1.19 MPa)和热导率(0.31 W/(m·K))的碳化硅多孔陶瓷, 它可作为轻质导热材料或复合相变材料的载体使用; 与泡沫注凝成形工艺相比, 采用模压成形工艺制备的碳化硅多孔陶瓷虽然孔隙率有所降低(79.3%), 但热导率得到显著提升(1.15 W/(m·K)), 同时原料和生产成本大幅降低, 有利于实现产品的工业化生产。
中图分类号:
吴松泽, 周洋, 李润丰, 刘晓倩, 李翠伟, 黄振莺. 铁尾矿及其反应烧结多孔陶瓷的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1193-1199.
WU Songze, ZHOU Yang, LI Runfeng, LIU Xiaoqian, LI Cuiwei, HUANG Zhenying. Reaction Sintered Porous Ceramics Using Iron Tailings: Preparation and Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1193-1199.
| Composition | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %(in mass) | 61.03 | 13.49 | 7.75 | 7.53 | 6.7 | 1.71 | 1.79 |
表1 铁尾矿主要成分
Table 1 Composition of iron tailings raw materials
| Composition | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %(in mass) | 61.03 | 13.49 | 7.75 | 7.53 | 6.7 | 1.71 | 1.79 |
| Sample | Iron tailings/%(in mass) | Graphite/%(in mass) | SiC/%(in mass) | Forming method | Sintering temperature | Holding time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100 | - | - | Foam gelcasting | 1090 ℃ | 3 h |
| B | 75 | 25 | - | Foam gelcasting | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
| C | 48.7 | 16.3 | 35 | Foam gelcasting | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
| D | 71.3 | 23.8 | 5 | Mold forming | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
表2 铁尾矿多孔陶瓷的原料配方、成形及烧结工艺
Table 2 Composition, forming and sintering technology of porous ceramics prepared using iron tailings by different methods
| Sample | Iron tailings/%(in mass) | Graphite/%(in mass) | SiC/%(in mass) | Forming method | Sintering temperature | Holding time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100 | - | - | Foam gelcasting | 1090 ℃ | 3 h |
| B | 75 | 25 | - | Foam gelcasting | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
| C | 48.7 | 16.3 | 35 | Foam gelcasting | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
| D | 71.3 | 23.8 | 5 | Mold forming | 1600 ℃ | 3 h |
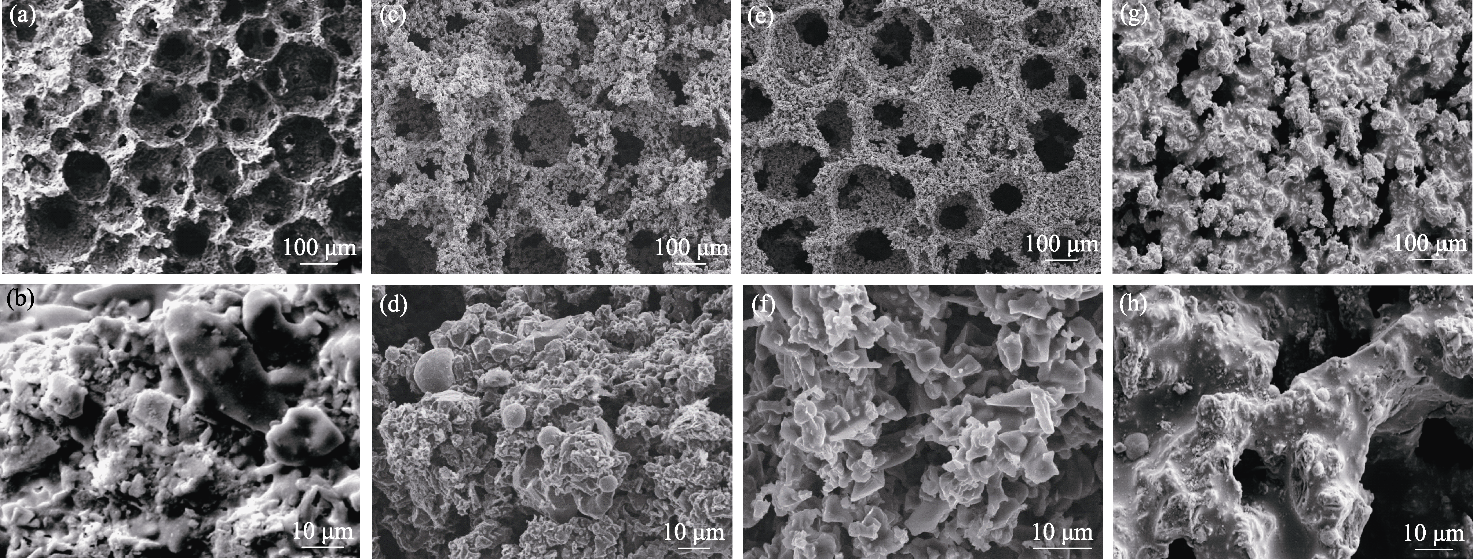
图4 多孔陶瓷样品A、B、C、D的(a, c, e, g)断口形貌和(b, d, f, h)骨架微观结构
Fig. 4 (a, c, e, g) Fracture morphologies and (b, d, f, h) skeleton microstructures of porous ceramic Sample A, Sample B, Sample C, and Sample D
| [1] |
SARKER S K, HAQUE N, BHUIYAN M, et al. Recovery of strategically important critical minerals from mine tailings. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(3): 107622.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BEYLOT A, BODéNAN F, GUEZENNEC A G, et al. LCA as a support to more sustainable tailings management: critical review, lessons learnt and potential way forward. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 183: 106347. |
| [3] | PIFFER V S, SOARES K, GALDINO A G S. Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of PP/iron ore tailing composites. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 221: 109001. |
| [4] |
TANG C, LI K, NI W, et al. Recovering iron from iron ore tailings and preparing concrete composite admixtures. Minerals, 2019, 9(4): 232.
DOI URL |
| [5] | YANG C, CUI C, QIN J. Recycling of low-silicon iron tailings in the production of lightweight aggregates. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1, Part B): 1213. |
| [6] | ZHAO J, NI K, SU Y, et al. An evaluation of iron ore tailings characteristics and iron ore tailings concrete properties. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 286: 122968. |
| [7] | LEMOUGNA P N, YLINIEMI J, NGUYEN H, et al. Utilisation of glass wool waste and mine tailings in high performance building ceramics. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 31: 101383. |
| [8] | CHENG Y, HUANG F, LI W, et al. Test research on the effects of mechanochemically activated iron tailings on the compressive strength of concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 118: 164. |
| [9] | LUO Y, WANG F, LIAO Q, et al. Effect of TiO2 on crystallization kinetics, microstructure and properties of building glass-ceramics based on granite tailings. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2021, 572: 121092. |
| [10] | PENG Y, LIU Z, LIU X, et al. Preparation of composite micro-slag based on the application of tailings slag in cement and concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 322: 126515. |
| [11] | ADIANSYAH J S, ROSANO M, VINK S, et al. A framework for a sustainable approach to mine tailings management: disposal strategies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 108: 1050. |
| [12] |
FRANKS D M, BOGER D V, CôTE C M, et al. Sustainable development principles for the disposal of mining and mineral processing wastes. Resources Policy, 2011, 36(2): 114.
DOI URL |
| [13] | HUNG ANH L D, PÁSZTORY Z. An overview of factors influencing thermal conductivity of building insulation materials. Journal of Building Engineering, 2021, 44: 102604. |
| [14] | ADITYA L, MAHLIA T M I, RISMANCHI B, et al. A review on insulation materials for energy conservation in buildings. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 73: 1352. |
| [15] | NKWETTA D N, HAGHIGHAT F. Thermal energy storage with phase change material—a state-of-the art review. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2014, 10: 87. |
| [16] | VILLASMIL W, FISCHER L J, WORLITSCHEK J. A review and evaluation of thermal insulation materials and methods for thermal energy storage systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 103: 71. |
| [17] | WI S, PARK J H, KIM Y U, et al. Thermal, hygric, and environmental performance evaluation of thermal insulation materials for their sustainable utilization in buildings. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 272: 116033. |
| [18] | GAO H, LIU H, LIAO L, et al. A novel inorganic thermal insulation material utilizing perlite tailings. Energy and Buildings, 2019, 190: 25. |
| [19] | ZHAO J, LI S. Life cycle cost assessment and multi-criteria decision analysis of environment-friendly building insulation materials—a review. Energy and Buildings, 2022, 254: 111582. |
| [20] | ABU-JDAYIL B, MOURAD A H, HITTINI W, et al. Traditional, state-of-the-art and renewable thermal building insulation materials: an overview. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 214: 709. |
| [21] | ARUMUGAM P, RAMALINGAM V, VELLAICHAMY P. Effective PCM, insulation, natural and/or night ventilation techniques to enhance the thermal performance of buildings located in various climates—a review. Energy and Buildings, 2022, 258: 111840. |
| [22] | GAO D C, SUN Y, FONG A M L, et al. Mineral-based form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage: a state-of-the art review. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 46: 100. |
| [23] |
WU J, CHEN H, LUO X, et al. Design, fabrication, microstructure, and properties of highly porous alumina whisker foam ceramic. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(2): 2776.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WU Q, HUANG Z. Preparation and performance of lightweight porous ceramics using metallurgical steel slag. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(18): 25169.
DOI URL |
| [25] | VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, ZEYDANLI D, COLOMBO P. Porous polymer derived ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2016, 106: 1. |
| [26] | SONG Q, BAO J, XUE S, et al. Study on the recycling of ceramic polishing slag in autoclaved aerated foam concrete by response surface methodology. Journal of Building Engineering, 2022, 56: 104827. |
| [27] |
TORKITTIKUL P, CHAIPANICH A. Utilization of ceramic waste as fine aggregate within Portland cement and fly ash concretes. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2010, 32(6): 440.
DOI URL |
| [28] | WANG Y, HUANG X, CHU J, et al. Analysis of polishing waste ceramic foam packing in evaporative cooling. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 212: 118477. |
| [29] |
ZHANG B, HUANG H, LU X. Fabrication and properties of C/SiC porous ceramics by grinding-mould pressing-sintering process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(5): 1775.
DOI URL |
| [30] | TIAN C, HUANG X, GUO W, et al. Preparation of SiC porous ceramics by a novel gelcasting method assisted with surface modification. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10, Part B): 16047. |
| [31] |
LIANG X, LI Y, YAN W, et al. Preparation of SiC reticulated porous ceramics with high strength and increased efficient filtration via fly ash addition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(4): 2290.
DOI URL |
| [32] | HAMMEL E C, IGHODARO O L R, OKOLI O I. Processing and properties of advanced porous ceramics: an application based review. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(10, Part A): 15351. |
| [33] |
ZHANG W. Tribology of SiC ceramics under lubrication: features, developments, and perspectives. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2022, 26(4): 101000.
DOI URL |
| [34] | KARUNADASA K S P, MANORATNE C H, PITAWALA H M T G A, et al. Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (calcite polymorph) as examined by in-situ high-temperature X-ray powder diffraction. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2019, 134: 21. |
| [35] | 李润丰, 周洋, 李世波, 等. 北京地区细颗粒铁尾矿烧结过程与机理研究. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(04): 672. |
| [36] | CHEN H, LI B, ZHAO M, et al. Lanthanum modification of crystalline phases and residual glass in augite glass ceramics produced with industrial solid wastes. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2019, 524: 119638. |
| [37] | 陈伟丽, 李保卫, 张雪峰, 等. 烧结工艺对Fe/辉石基高熵陶瓷显微结构的影响. 人工晶体学报, 2019, 48(9): 1685. |
| [38] |
LIU X, ZHOU Y, LIU X, et al. SiC-based porous ceramic carriers for heat-conductive phase change materials through carbothermal reduction method. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2021, 18(1): 91.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 张广强. 不同初始状态的SiO2在高温高压下的结构转变研究. 长春: 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2009. |
| [40] | 刘和兴. 原位制备多孔生物质碳化硅/碳复合材料的研究. 武汉: 武汉科技大学硕士学位论文, 2020. |
| [1] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [2] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [3] | 王浩, 刘学超, 郑重, 潘秀红, 徐锦涛, 朱新锋, 陈锟, 邓伟杰, 汤美波, 郭辉, 高攀. 非本征背照触发平面型4H-SiC光导开关性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1070-1076. |
| [4] | 王康龙, 殷杰, 陈晓, 王力, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对选区激光烧结打印结合常压固相烧结制备碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 754-760. |
| [5] | 郑雅雯, 张翠萍, 张瑞杰, 夏乾, 茹红强. 硼酸碳热还原-渗硅反应烧结制备碳化硼陶瓷复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 707-714. |
| [6] | 孙川, 何鹏飞, 胡振峰, 王荣, 邢悦, 张志彬, 李竞龙, 万春磊, 梁秀兵. 含有石墨烯阵列的SiC基陶瓷材料的制备与力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [7] | 徐昊, 钱伟, 花银群, 叶云霞, 戴峰泽, 蔡杰. 皮秒激光加工的微织构对碳化硅润湿性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 923-930. |
| [8] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [9] | 顾薛苏, 殷杰, 王康龙, 崔崇, 梅辉, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对黏结剂喷射打印碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1373-1378. |
| [10] | 汪德文, 王俊平, 袁厚呈, 刘章, 周进, 邓佳杰, 王鑫, 吴贲华, 章健, 王士维. 真空反应烧结制备米级尺寸钇铝石榴石(YAG)透明陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1483-1484. |
| [11] | 欧阳琴, 王艳菲, 徐剑, 李寅生, 裴学良, 莫高明, 李勉, 李朋, 周小兵, 葛芳芳, 张崇宏, 何流, 杨磊, 黄政仁, 柴之芳, 詹文龙, 黄庆. 核用碳化硅纤维增强碳化硅复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [12] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 三维碳化硅纳米线增强碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的电磁屏蔽性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 579-584. |
| [13] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增强多孔碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [14] | 祝泉, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 周海军, 董绍明. 采用定向SiC纳米线烧结制备高强多孔SiC陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 547-551. |
| [15] | 张力, 杨现锋, 徐协文, 郭金玉, 周哲, 刘鹏, 谢志鹏. 熔融沉积法3D打印制备氧化锆陶瓷及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 436-442. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||