无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 923-930.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230073 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230073
徐昊1( ), 钱伟2,3, 花银群1,2,3(
), 钱伟2,3, 花银群1,2,3( ), 叶云霞3,4, 戴峰泽3, 蔡杰2,3
), 叶云霞3,4, 戴峰泽3, 蔡杰2,3
收稿日期:2023-02-14
修回日期:2023-04-05
出版日期:2023-08-20
网络出版日期:2023-05-04
通讯作者:
花银群, 教授. E-mail: huayq@ujs.edu.cn作者简介:徐 昊(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1574686698@qq.com
基金资助:
XU Hao1( ), QIAN Wei2,3, HUA Yinqun1,2,3(
), QIAN Wei2,3, HUA Yinqun1,2,3( ), YE Yunxia3,4, DAI Fengze3, CAI Jie2,3
), YE Yunxia3,4, DAI Fengze3, CAI Jie2,3
Received:2023-02-14
Revised:2023-04-05
Published:2023-08-20
Online:2023-05-04
Contact:
HUA Yinqun, professor. E-mail: huayq@ujs.edu.cnAbout author:XU Hao (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1574686698@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
为改善碳化硅的表面润湿性能, 本研究利用脉冲激光加工表面处理和化学改性分别改善了碳化硅的表面形貌和表面能。实验选用皮秒激光加工方式构造表面微织构, 利用激光共聚焦显微镜分析了微织构的微观形貌, 并进一步分析了烧蚀形态与激光自身特性和加工参数之间的联系。研究发现, 激光加工效果以烧蚀为主, 重熔为辅, 而由于碳化硅烧蚀阈值和激光能量在光斑中的高斯分布特性, 形成的微织构的烧蚀凹槽呈倒三角形。此外, 选用的氟硅烷修饰剂使碳化硅表面从亲水表面转变为疏水表面; 通过改变加工参数获得不同微织构并进行氟硅烷修饰后, 碳化硅表面接触角最大提高到157°, 达到了超疏水效果。为了进一步探讨微织构对疏水性的影响原理, 提出了一个基于实际形貌参数的固液接触角模型。该模型阐释了接触角随微织构特征参数变化的机制, 固、气、液两两之间的接触面积影响了表面润湿性, 这为寻找具有最佳疏水性能的微织构提供了新的理论指导。
中图分类号:
徐昊, 钱伟, 花银群, 叶云霞, 戴峰泽, 蔡杰. 皮秒激光加工的微织构对碳化硅润湿性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 923-930.
XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 923-930.
| Serial number | Power/ W | Speed/ (mm·s-1) | Interval/ μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-1~A-10 | 9 | 125 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 | |||
| B-1~B-10 | 6 | 100 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 | |||
| C-1~C-10 | 3 | 50 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 |
表1 皮秒激光加工参数
Table 1 Processing parameters of laser processing
| Serial number | Power/ W | Speed/ (mm·s-1) | Interval/ μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-1~A-10 | 9 | 125 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 | |||
| B-1~B-10 | 6 | 100 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 | |||
| C-1~C-10 | 3 | 50 | 64/80/100/125/150/ |
| 200/250/300/400/500 |
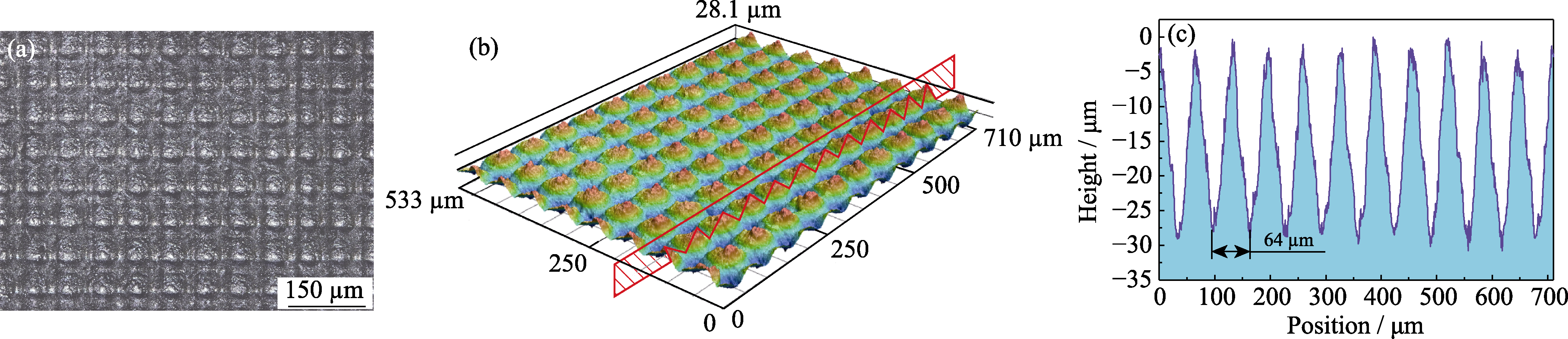
图6 样品A-1表面形貌的图像、3d图和对应横截面
Fig. 6 Surface morphologies of A-1 (a) Photograph of laser machined reticular micro-texture; (b) Laser confocal 3D model; (c) Cross-sectional shape of (b)
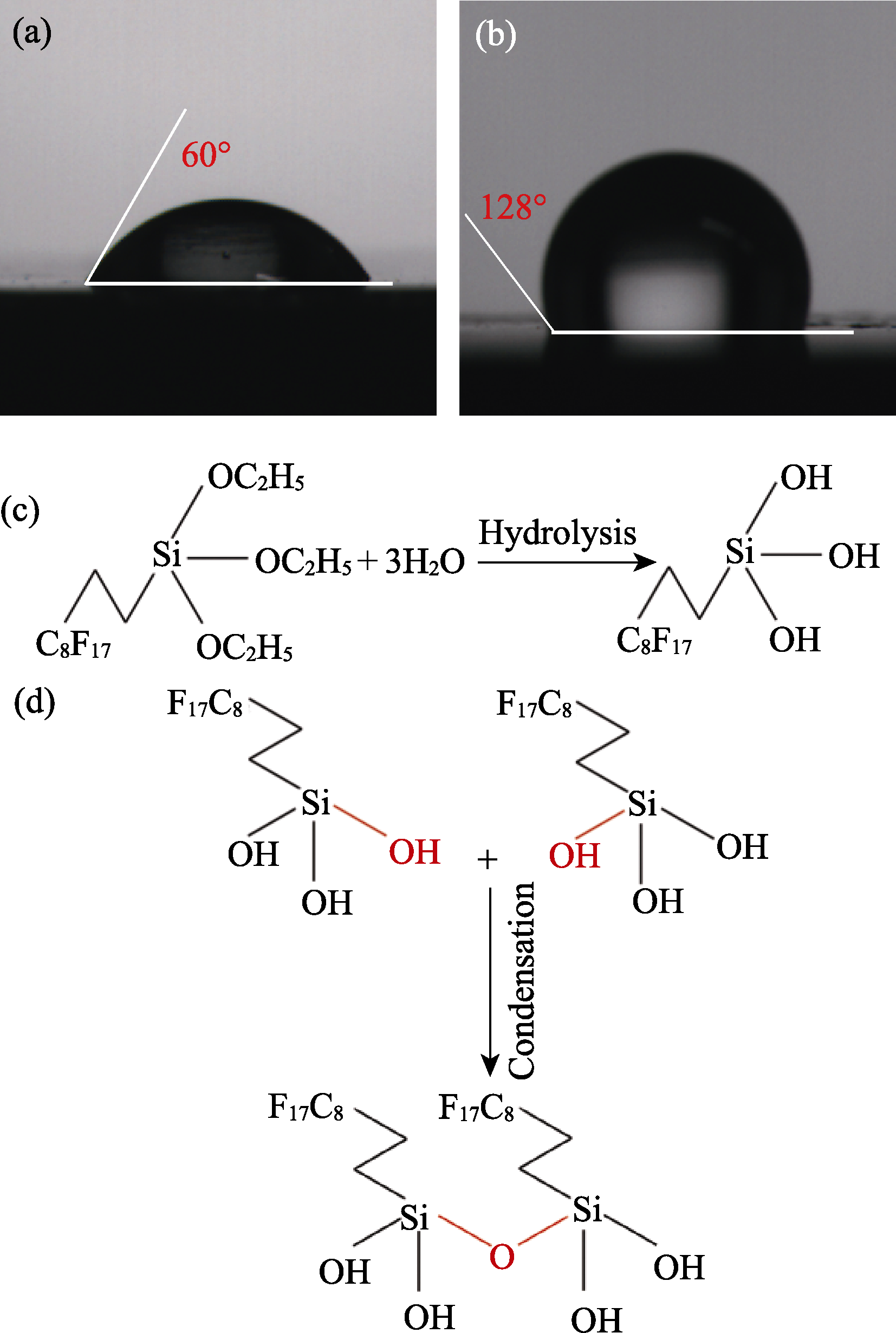
图7 修饰对接触角的影响及修饰过程中的水解缩合
Fig. 7 Effect of modification on contact angle and its modification principle (a) Contact angle of R-0; (b) Contact angle of R-1; (c) Hydrolysis of FAS; (d) Dehydration condensation

图8 三组样品的接触角变化和图像
Fig. 8 Statistics and photographs of contact angle for samples (a) Contact angles of three groups with processing intervals; (b) Contact angle photographs of three groups
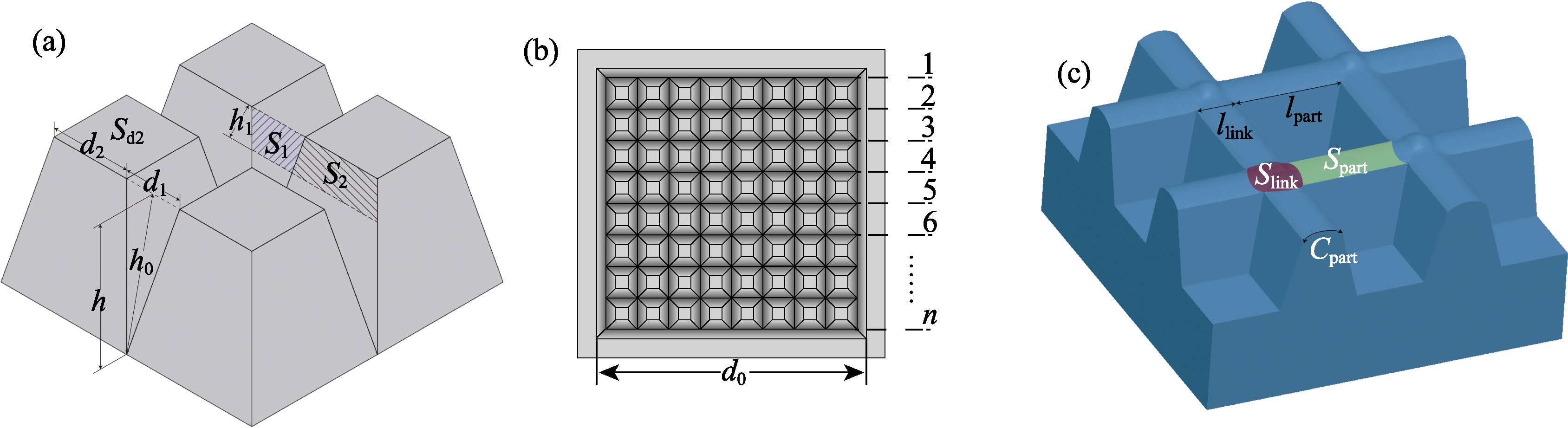
图10 微观纹理的形态特征参数
Fig. 10 Morphological parameters of micro-texture (a) Micro grooves; (b) Micro-texture area; (c) Solid-liquid contact area of infiltrated water
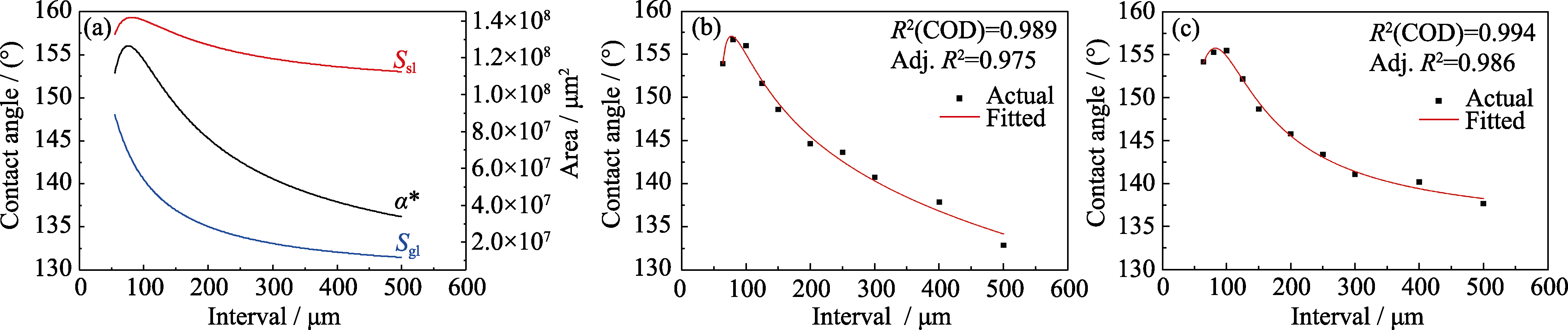
图11 理论接触角变化和两组样品的拟合预测曲线
Fig. 11 Theoretical contact angle variation and fitted curves (a) Theoretical variation of contact angle; (b) Fitted curve of variation of contact angle of group B; (c) Fitted curve of variation of contact angle of group C
| [1] |
KHADER I, KOPLIN C, SCHRÖDER C, et al. Characterization of a silicon nitride ceramic material for ceramic springs. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(10): 3541.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
KHADER I, RENZ A, KAILER A, et al. Thermal and corrosion properties of silicon nitride for copper die casting components. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(3): 593.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BREYSSE J, CASTEL D, LAVIRON B, et al. All-SiC telescope technology: recent progress and achievements. International Conference on Space Optics — ICSO 2004, 2019: 201. |
| [4] |
SPITSBERG I, STEIBEL J. Thermal and environmental barrier coatings for SiC/SiC CMCs in aircraft engine applications. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2005, 1(4): 291.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KOUCHAKI S, ROSHANI H, PROZZI J A, et al. Evaluation of aggregates surface micro-texture using spectral analysis. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 156: 944.
DOI URL |
| [6] | TIEJUN Z, NAN W. Analysis of the research status of surface texture technology. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Technology, 2020, 49(11): 116. |
| [7] |
NEINHUIS C, BARTHLOTT W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Annals of Botany, 1997, 79(6): 667.
DOI URL |
| [8] | DAVIS A, YEONG Y H, STEELE A, et al. Superhydrophobic nanocomposite surface topography and ice adhesion. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(12): 9272. |
| [9] |
QU N, CHEN X, LI H, et al. Electrochemical micromachining of micro-dimple arrays on cylindrical inner surfaces using a dry-film photoresist. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2014, 27(4): 1030.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SUN Y, JIN L, GONG Y, et al. Experimental evaluation of surface generation and force time-varying characteristics of curvilinear grooved micro end mills fabricated by EDM. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 73: 799.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NAKANO M, KORENAGA A, KORENAGA A, et al. Applying micro-texture to cast iron surfaces to reduce the friction coefficient under lubricated conditions. Tribology Letters, 2007, 28(2): 131.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
OBIKAWA T, KAMIO A, TAKAOKA H, et al. Micro-texture at the coated tool face for high performance cutting. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2011, 51(12): 966.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SCARAGGI M, MEZZAPESA F P, CARBONE G, et al. Friction properties of lubricated laser-microtextured-surfaces: an experimental study from boundary-to hydrodynamic-lubrication. Tribology Letters, 2012, 49(1): 117.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHAO B, LI P, ZHAO C, et al. Fractal characterization of surface microtexture of Ti6Al4V subjected to ultrasonic vibration assisted milling. Ultrasonics, 2020, 102: 106052. |
| [15] |
MA C, BAI S, PENG X, et al. Improving hydrophobicity of laser textured SiC surface with micro-square convexes. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 266: 51.
DOI URL |
| [16] | ZHAO M, HE Q, LEI B, et al. Preparation of ceramic superhydrophobic surface based on laser engraving technology. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 43(1): 107. |
| [17] |
WANG S, JIANG L. Definition of superhydrophobic states. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(21): 3423.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BICO J, THIELE U, QUÉRÉ D. Wetting of textured surfaces. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2002, 206(1): 41.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KANG C, LU H, YUAN S, et al. Superhydrophilicity/superhydrophobicity of nickel micro-arrays fabricated by electroless deposition on an etched porous aluminum template. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 203: 1.
DOI URL |
| [20] | ZHAI Z, WEI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Investigations on the oxidation phenomenon of SiC/SiC fabricated by high repetition frequency femtosecond laser. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 502:144131. |
| [21] |
FU C, YANG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Investigation on the laser ablation of SiC ceramics using micro-Raman mapping technique. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2016, 5(3): 253.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
DENG D, XIE Y, CHEN L, et al. Experimental investigation on laser micromilling of SiC microchannels. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 101(1): 9.
DOI |
| [23] | TEMMLER A, KÜPPER M, WALOCHNIK M A, et al. Surface structuring by laser remelting of metals. Journal of Laser Applications, 2017, 29(1): 012015. |
| [24] |
ZHAI Z, WANG W, ZHAO J, et al. Influence of surface morphology on processing of C/SiC composites via femtosecond laser. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 102: 117.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHANG M, ZHU H, XI B, et al. Surface hydrophobic modification of biochar by silane coupling agent KH-570. Processes, 2022, 10(301): 301.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WU X L, XIONG S J, ZHU J, et al. Identification of surface structures on 3C-SiC nanocrystals with hydrogen and hydroxyl bonding by photoluminescence. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(12): 4053.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SONG J, ROJAS O J. Approaching super-hydrophobicity from cellulosic materials: a review. Nordic Pulp and Paper Research Journal, 2013, 28(2): 216.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LAW K Y. Definitions for hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity, and superhydrophobicity: getting the basics right. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2014, 5(4): 686.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SEDEV R. Surface tension, interfacial tension and contact angles of ionic liquids. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2011, 16(4): 310.
DOI URL |
| [30] | CRICK C R, PARKIN I P. Preparation and characterisation of super-hydrophobic surfaces. Chemistry, 2010, 16(12): 3568. |
| [31] |
HAN T Y, SHR J F, WU C F, et al. A modified Wenzel model for hydrophobic behavior of nanostructured surfaces. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(11): 4666.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
WOLANSKY G, MARMUR A. Apparent contact angles on rough surfaces: the Wenzel equation revisited. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1999, 156(1): 381.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YEN T H, SOONG C Y. Hybrid Cassie-Wenzel model for droplets on surfaces with nanoscale roughness. Physical Review E, 2016, 93(2): 22805.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
XU X, WANG X. Derivation of the Wenzel and Cassie equations from a phase field model for two phase flow on rough surface. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2010, 70(8): 2929.
DOI URL |
| [35] | NAKAYAMA Y. Introduction to Fluid Mechanics(2nd Edition). Britain: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2018: 25. |
| [1] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [2] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [3] | 王浩, 刘学超, 郑重, 潘秀红, 徐锦涛, 朱新锋, 陈锟, 邓伟杰, 汤美波, 郭辉, 高攀. 非本征背照触发平面型4H-SiC光导开关性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1070-1076. |
| [4] | 王康龙, 殷杰, 陈晓, 王力, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对选区激光烧结打印结合常压固相烧结制备碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 754-760. |
| [5] | 孙川, 何鹏飞, 胡振峰, 王荣, 邢悦, 张志彬, 李竞龙, 万春磊, 梁秀兵. 含有石墨烯阵列的SiC基陶瓷材料的制备与力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [6] | 赵雅文, 屈发进, 汪岩屹, 王智文, 陈初升. 基于硅酸铝纤维的柔性氧敏感元件的制备和性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1084-1090. |
| [7] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [8] | 顾薛苏, 殷杰, 王康龙, 崔崇, 梅辉, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对黏结剂喷射打印碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1373-1378. |
| [9] | 吴松泽, 周洋, 李润丰, 刘晓倩, 李翠伟, 黄振莺. 铁尾矿及其反应烧结多孔陶瓷的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1193-1199. |
| [10] | 欧阳琴, 王艳菲, 徐剑, 李寅生, 裴学良, 莫高明, 李勉, 李朋, 周小兵, 葛芳芳, 张崇宏, 何流, 杨磊, 黄政仁, 柴之芳, 詹文龙, 黄庆. 核用碳化硅纤维增强碳化硅复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [11] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 三维碳化硅纳米线增强碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的电磁屏蔽性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 579-584. |
| [12] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增强多孔碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [13] | 赵起, 乔科, 姚勇吉, 陈长, 陈东初, 高彦峰. 基于高电导率的疏水气相SiO2复合凝胶电解质的高性能电致变色器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 161-167. |
| [14] | 李陇彬, 薛玉冬, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增韧碳化硅纤维/碳化硅基体损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| [15] | 陈钧,马培华,张诚,劳伦·鲁尔曼,吕耀康. 新型多功能无机/有机复合薄膜的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||