无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 899-903.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190013 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190013
程田盛1,2,3,潘炯4,徐鹰鹰1,2,3,鲍群群1,2,3,胡萍1( ),施剑林1(
),施剑林1( )
)
收稿日期:2019-01-06
出版日期:2019-08-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:CHENG Tian-Sheng (1994-), male, candidate of Master degree. E-mail: chengtsh@shanghaitech.edu.cn
CHENG Tian-Sheng1,2,3,PAN Jiong4,XU Ying-Ying1,2,3,BAO Qun-Qun1,2,3,HU Ping1( ),SHI Jian-Lin1(
),SHI Jian-Lin1( )
)
Received:2019-01-06
Published:2019-08-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
锌锰掺杂的Fe3O4纳米颗粒具有优异的磁性能, 在生物医药领域有广泛的应用前景。磁性纳米颗粒的尺寸与其磁学性质以及生物磁性应用密切相关。因此, 为了适应不同生物应用对尺寸的需求, 研究其尺寸调控具有重要的意义。在本研究中, 我们采用高温热分解法, 通过加入还原剂1,2-十六烷二醇, 改变金属前躯体和回流时间成功制备了尺寸在5~20 nm的锌锰掺杂Fe3O4纳米颗粒。研究发现:强还原剂1,2-十六烷二醇的加入有利于合成小尺寸的纳米颗粒, 而以金属氯化物作为金属前躯体和延长回流时间可以进一步合成更大尺寸的纳米颗粒; 纳米颗粒的饱和磁化强度随着尺寸的增大而增大。
中图分类号:
程田盛, 潘炯, 徐鹰鹰, 鲍群群, 胡萍, 施剑林. 锌锰掺杂Fe3O4纳米颗粒的尺寸可控合成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 899-903.
CHENG Tian-Sheng, PAN Jiong, XU Ying-Ying, BAO Qun-Qun, HU Ping, SHI Jian-Lin. Synthesis of Zn, Mn doped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with Tunable Size[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 899-903.
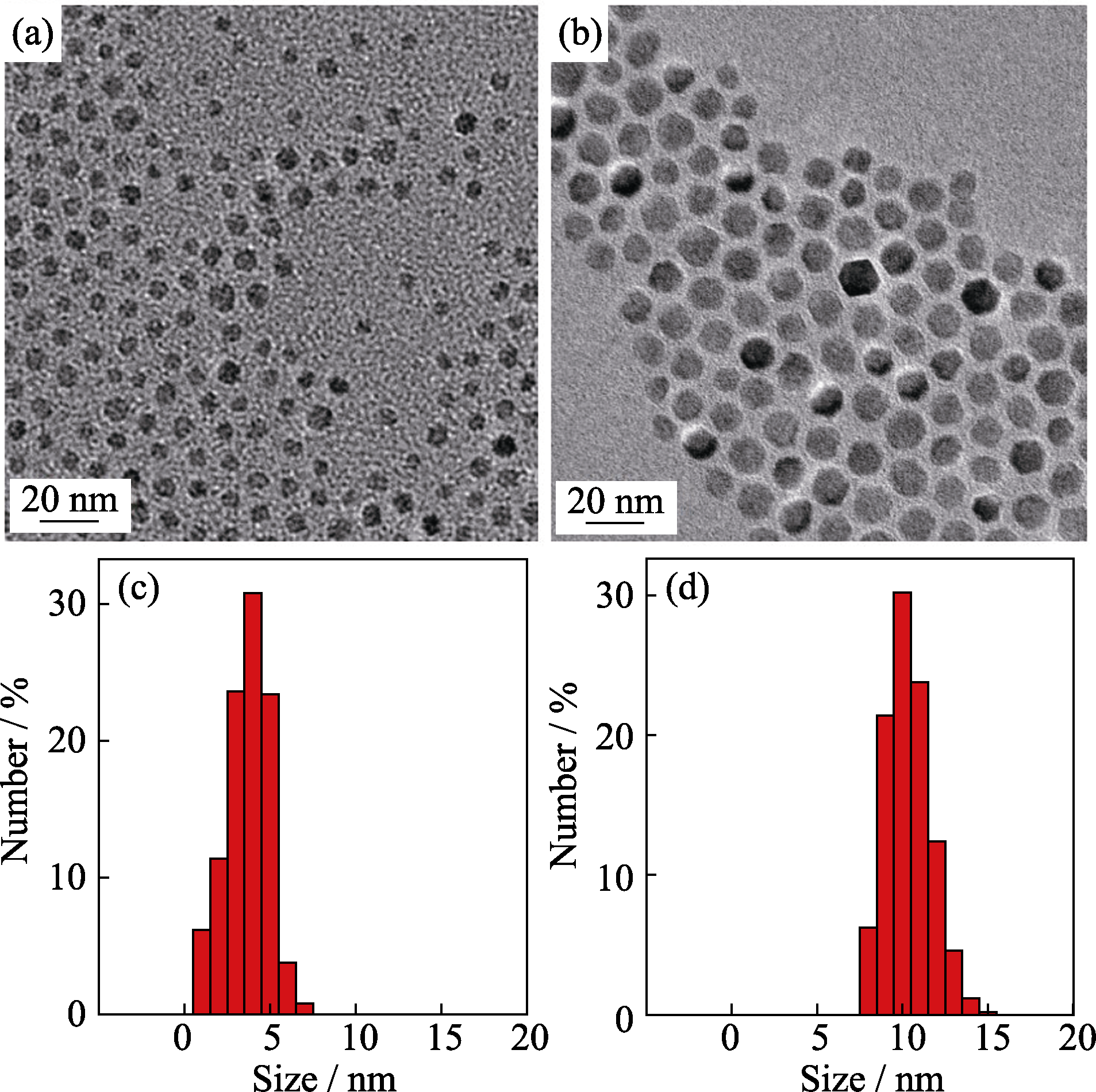
Fig. 1 TEM images of ZnMn-Fe3O4 nanoparticles and histograms of their size distributions obtained by Fe(acac)3, Mn(acac)2 and Zn(acac)2 with (a, c) and without (b, d) adding 1,2-hexadecanediol
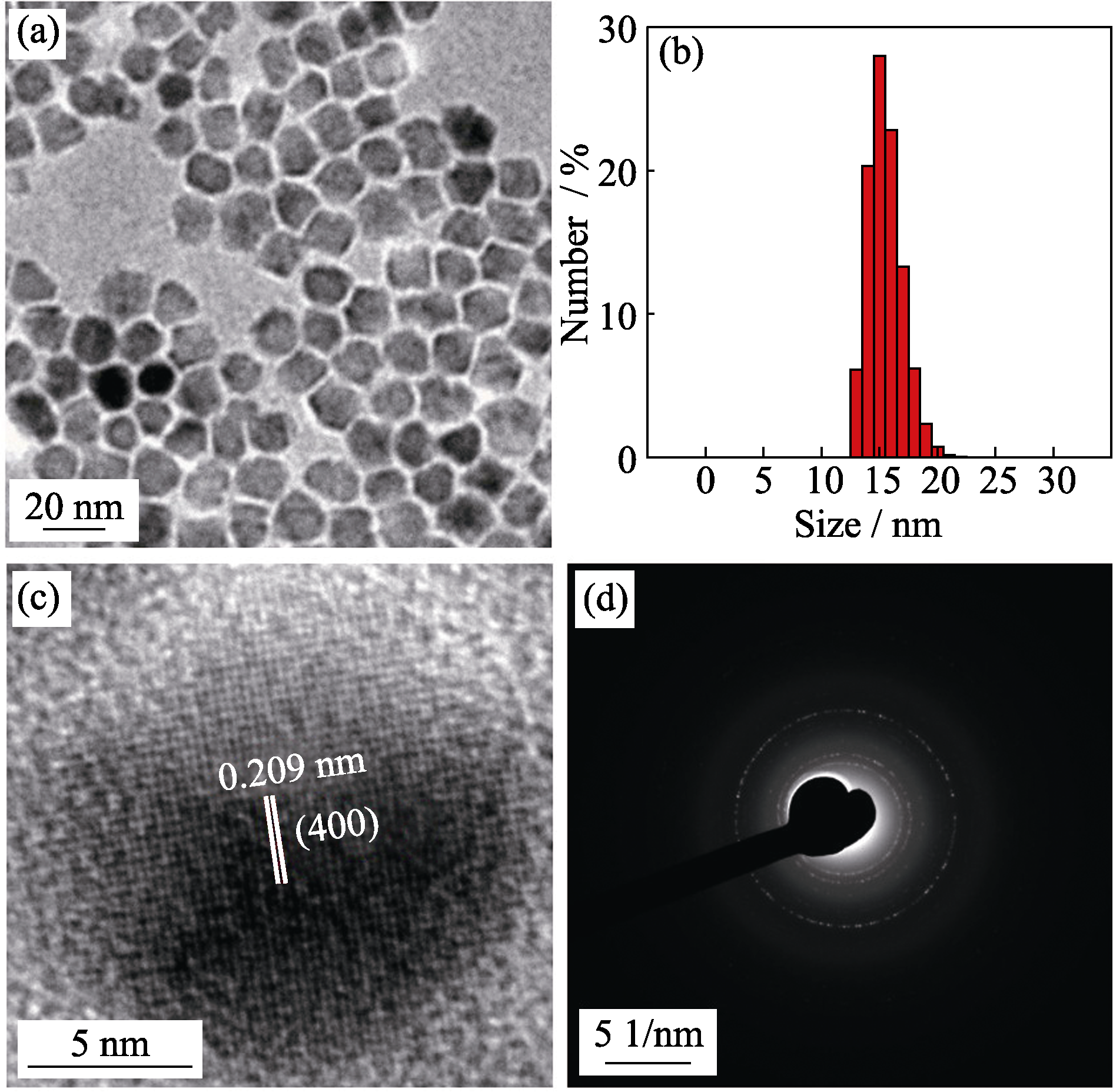
Fig. 2 TEM image (a), histograms of their size distributions (b), high-resolution TEM image (c) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (d) of 15 nm-sized ZnMn-Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared from Fe(acac)3, MnCl2 and ZnCl2
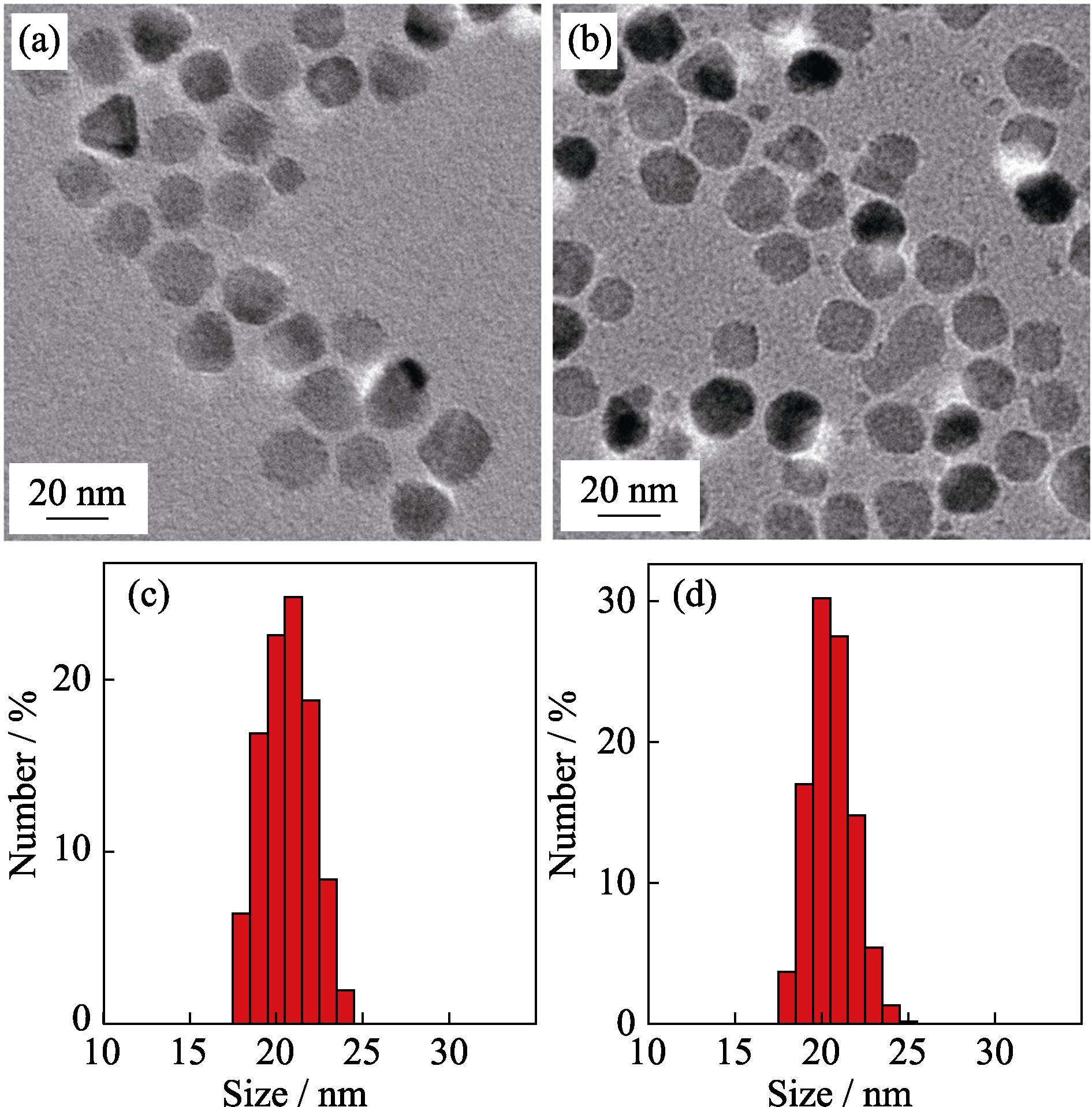
Fig. 3 TEM images of 20 nm-sized ZnMn-Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized from Fe(acac)3, MnCl2 and ZnCl2 with different reflux time durations of 1.5 h (a) and 2 h (b), and the corresponding histograms of size distributions of 1.5 h (c) and 2 h (d)
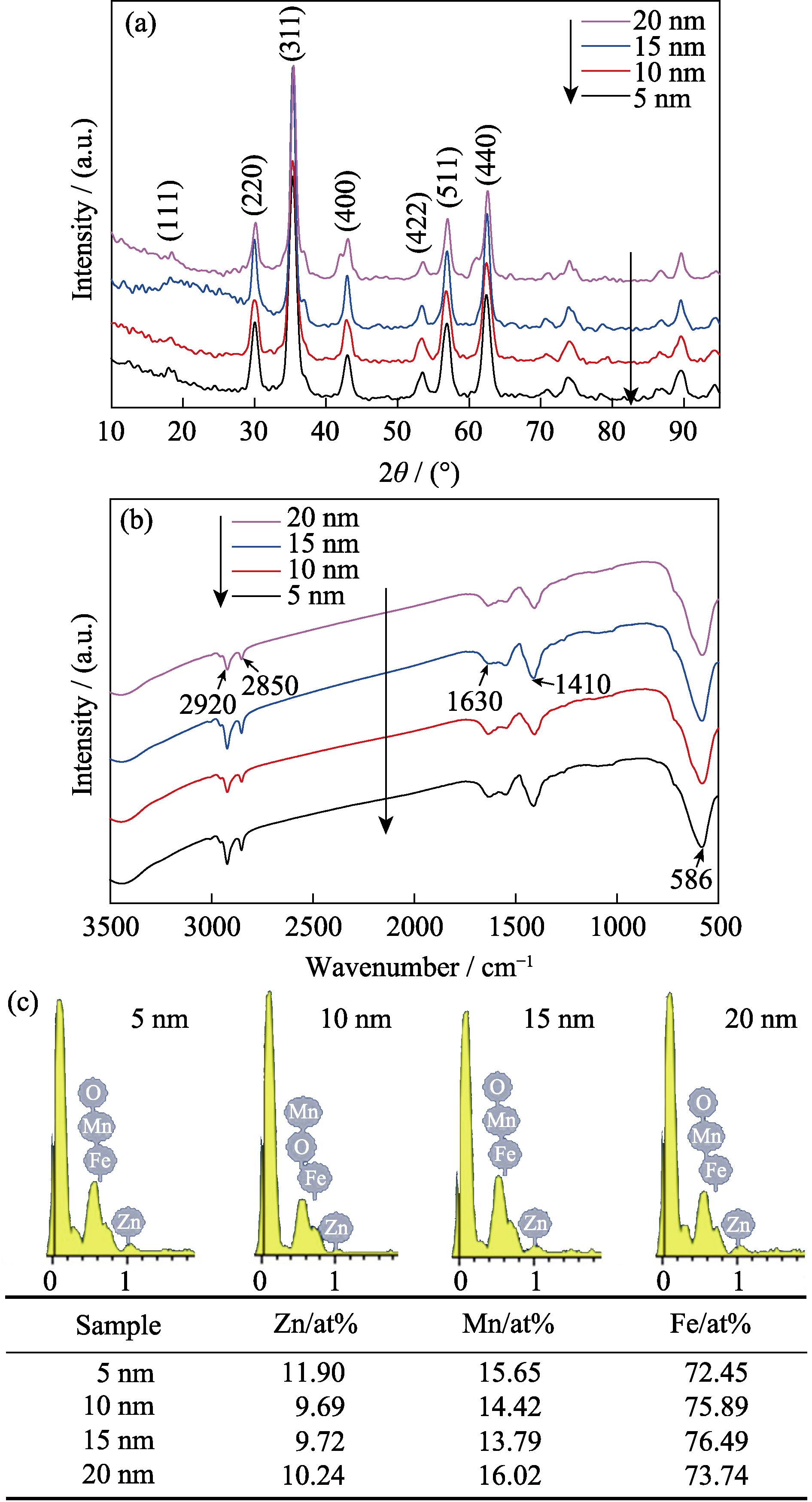
Fig. 4 XRD patterns (a), FT-IR spectra (b) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) data (c) of 5 nm, 10 nm, 15 nm, and 20 nm-sized ZnMn-Fe3O4 nanoparticles
| [1] | NOH S H, NA W, JANG J T , et al. Nanoscale magnetism control via surface and exchange anisotropy for optimized ferrimagnetic hysteresis. Nano Letters, 2012,12(7):3716-3721. |
| [2] | DI CORATO R, BEALLE G, KOLOSNJAJ-TABI J , et al. Combining magnetic hyperthermia and photodynamic therapy for tumor ablation with photoresponsive magnetic liposomes. ACS Nano, 2015,9(3):2904-2916. |
| [3] |
NA H B, SONG I C, HYEON T . Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Advanced Materials, 2009,21(21):2133-2148.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GAO J H, GU H W, XU B . Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2009,42(8):1097-1107.
DOI URL |
| [5] | WAN Y, CHENG G, LIU X , et al. Rapid magnetic isolation of extracellular vesicles via lipid-based nanoprobes. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017,1:0058. |
| [6] |
LU A H, SALABAS E L, SCHUTH F . Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007,46(8):1222-1244.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HOCHEPIED J F, PILENI M P . Magnetic properties of mixed cobalt- zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000,87(5):2472-2478.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ARULMURUGAN R, JEYADEVAN B, VAIDYANATHAN G , et al. Effect of zinc substitution on Co-Zn and Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-pecipitation. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2005,288:470-477. |
| [9] | JANG J T, NAH H, LEE J H , et al. Critical enhancements of MRI contrast and hyperthermic effects by dopant-controlled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009,48(7):1234-1238. |
| [10] | DENG H, LI X, PENG Q , et al. Monodisperse magnetic single- crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005,44(18):2782-2785. |
| [11] | WOO K, LEE H J, AHN J P , et al. Sol-Gel mediated synthesis of Fe2O3 nanorods. Advanced Materials, 2003,15(20):1761-1764. |
| [12] | WU J H, KO S P, LIU H L , et al. Sub 5 nm magnetite nanoparticles: synthesis, microstructure, and magnetic properties. Materials Letters, 2007,61(14/15):3124-3129. |
| [13] |
XIE J, LEE S, CHEN X . Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents . Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2010,62(11):1064-1079.
DOI URL |
| [14] | LEE J H, HUH Y M, JUN Y W , et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nature Medicine, 2007,13(1):95-99. |
| [15] | SINGH M, RAMANATHAN R, MAYES E L H , et al. One-pot synthesis of maghemite nanocrystals across aqueous and organic solvents for magnetic hyperthermia. Applied Materials Today, 2018,12:250-259. |
| [16] | FORTIN J P, WILHELM C, SERVAIS J , et al. Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007,129(9):2628-2635. |
| [17] | GU H, XU K, XU C , et al. Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for protein separation and pathogen detection. Chem. Commun., 2006(9):941-949. |
| [18] | XU H, AGUILAR Z P, YANG L , et al. Antibody conjugated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer cell separation in fresh whole blood. Biomaterials, 2011,32(36):9758-9765. |
| [19] | LEE J H, JANG J T, CHOI J S , et al. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nature Nanotechnology, 2011,6(7):418-422. |
| [20] | LARTIGUE L, INNOCENTI C, KALAIVANI T , et al. Water- dispersible sugar-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. An evaluation of their relaxometric and magnetic hyperthermia properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011,133(27):10459-10472. |
| [21] | WU L, MENDOZA-GARCIA A, LI Q , et al. Organic phase syntheses of magnetic nanoparticles and their applications. Chemical Reviews, 2016,116(18):10473-10512. |
| [22] | SUN S H, ZENG H, ROBINSON D B , et al. Monodisperse MFe2O4(M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004,126(1):273-279. |
| [23] | QU Y, LI J, REN J , et al. Enhanced magnetic fluid hyperthermia by micellar magnetic nanoclusters composed of Mn(x)Zn(1-x)Fe, 2014,6(19):16867-16879. |
| [24] | RONG C B, LI D, NANDWANA V , et al. Size-dependent chemical and magnetic ordering in L10-FePt nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 2006,18(22):2984-2988. |
| [25] | JUN Y W, HUH Y M, CHOI J S , et al. Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005,127(16):5732-5733. |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 汤新丽, 丁自友, 陈俊锐, 赵刚, 韩颖超. 基于稀土铕离子荧光标记的磷酸钙纳米材料体内分布与代谢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [5] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [6] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [10] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [11] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [12] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [13] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [14] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [15] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||