无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 1285-1291.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170072 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170072
邓子谦1,2, 刘敏2,3, 毛杰2, 张小锋2, 陈文龙2, 陈志坤2
收稿日期:2017-02-20
修回日期:2017-04-27
出版日期:2017-12-20
网络出版日期:2017-11-21
作者简介:邓子谦(1988-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: dengziqian0404@163.com
基金资助:DENG Zi-Qian1,2, LIU Min2,3, MAO Jie2, ZHANG Xiao-Feng2, CHEN Wen-Long2, CHEN Zhi-Kun2
Received:2017-02-20
Revised:2017-04-27
Published:2017-12-20
Online:2017-11-21
摘要:
以等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积(PS-PVD)喷涂团聚的 ZrO2-7wt%Y2O3(7YSZ)粉末在五个喷距下制备了热障涂层。通过场发射-扫描电镜(FE-SEM)和X射线衍射(XRD)分析了五个涂层样品的微观结构和相成分差异。另外, 通过发射光谱(OES)诊断研究了射流中7YSZ粉末气相浓度随喷距的变化。最后, 阐述了3种不同的气相沉积涂层生长机制, 说明了射流中粉末的状态和气相浓度对涂层结构的影响。研究表明:(1)350 mm和1800 mm喷距下形成的均是致密结构涂层, 而650~1250 mm喷距下形成的是典型的PS-PVD柱状结构涂层。(2)350 mm喷距下制备的涂层由四方相(t’)和单斜相(m)氧化锆构成; 当喷距大于650 mm时, 涂层以四方相(t’)氧化锆为主。(3)350 mm喷距下涂层是由高浓度气相过饱和自发形核形成的新核和液/固粒子共同作用形成的; 喷距650~1250 mm下, 涂层生长以气相沉积于基体进行非自发形核为主, 气相在射流中的自发形核为辅; 喷距1800 mm下涂层由气相过冷凝固的粒子堆积而成。
中图分类号:
邓子谦, 刘敏, 毛杰, 张小锋, 陈文龙, 陈志坤. 等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积的气相沉积机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(12): 1285-1291.
DENG Zi-Qian, LIU Min, MAO Jie, ZHANG Xiao-Feng, CHEN Wen-Long, CHEN Zhi-Kun. Deposition Mechanism Based on Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1285-1291.
| Gun | Power/ kW | Ar/ slpm | He/ slpm | Chamber pressure/Pa | Feed rate/ (g•min-1) | Stand-off distance/ mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3CP | 127 | 35 | 60 | 150 | 20 | 350, 650, 950, 1250, 1800 |
表1 PS-PVD 喷涂 7YSZ 热障涂层参数
Table 1 Parameters of 7YSZ coating by PS-PVD
| Gun | Power/ kW | Ar/ slpm | He/ slpm | Chamber pressure/Pa | Feed rate/ (g•min-1) | Stand-off distance/ mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3CP | 127 | 35 | 60 | 150 | 20 | 350, 650, 950, 1250, 1800 |
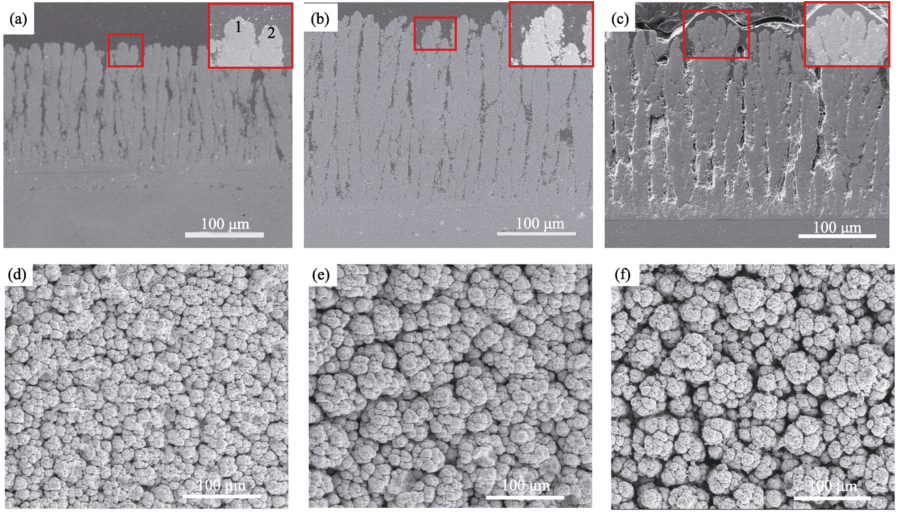
图2 不同喷涂距离下的PS-PVD YSZ柱状结构涂层的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM morphologies of 7YSZ columnar coating formed at different stand-off distances^(a) (d) 650 mm; (b) (e) 950 mm; (c) (f) 1250 mm
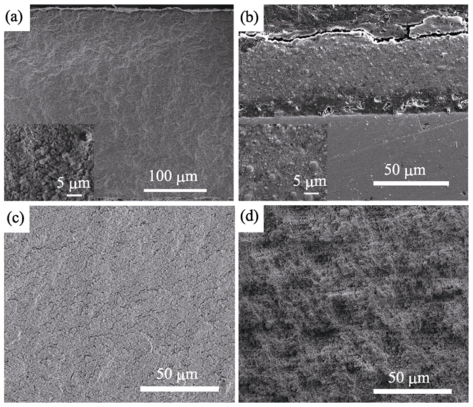
图3 不同喷涂距离下的PS-PVD YSZ致密结构涂层的SEM照片
Fig. 3 SEM morphologies of 7YSZ dense coating formed at different stand-off distances^(a) (c) 350 mm; (b) (d) 1800 mm
| [1] | REFKE A, GINDRAT M, VON NIESSEN K, et al.LPPS Thin Film: a Hybrid Coating Technology between Thermal Spray and PVD for Functional Thin Coatings and Large Area Applications. ITSC,Beijing, 2007: 14-16. |
| [2] | DORIER J L, GINDRAT M, HOLLENSTEIN C, et al.Plasma Jet Properties in a New Spraying Process at Low Pressure for Large Area Thin Film Deposition. ITSC,Singapore, 2001: 759-764. |
| [3] | HALL A C, MCCLOSKEY J F, URREA D A, et al.Low Pressure Plasma Spray—Thin Film® at Sandia National Laboratories. ITSC, 2009: 725-728. |
| [4] | SMITH M F, HALL A C, FLEETWOOD J D, et al.Very low pressure plasma spray—a review of an emerging technology in the thermal spray community. Coatings, 2011, 1(2): 117-132. |
| [5] | MAUER G, VAßEN R, STOVER D. Thin and dense ceramic coatings by plasma spraying at very low pressure. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2010, 19(1/2): 495-501. |
| [6] | SHINOZAWA A, EGUCHI K, KAMBARA M, et al.Feather-like structured YSZ coatings at fast rates by plasma spray physical vapor deposition. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2010, 19(1/2): 190-197. |
| [7] | VON NIESSEN K, GINDRAT M, REFKE A.Vapor phase deposition using plasma spray-PVD™. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2010, 19(1/2): 502-509. |
| [8] | KAMBARA M, SHINOZAWA A, AOSHIKA K, et al.Development of porous YSZ coatings with modified thermal and optical properties by plasma spray physical vapor deposition. Journal of Solid Mechanics and Materials Engineering, 2010, 4(2): 94-106. |
| [9] | MAUER G.Plasma characteristics and plasma-feedstock interaction under PS-PVD process conditions. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2014, 34(5): 1171-1186. |
| [10] | SCHMITT M P, HARDER B J, WOLFE D E.Process-struc¬ture- property relations for the erosion durability of plasma spray- physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD) thermal barrier coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 297: 11-18. |
| [11] | REFKE A, HAWLEY D, DOESBURG J, et al.LPPS Thin Film Technology for the Application of TBC Systems. ITSC,Basel, 2005: 438-443 |
| [12] | HOSPACH A, MAUER G, VAßEN R, et al. Columnar-structured thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) by thin film low-pressure plasma spraying (LPPS-TF). Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2011, 20(1/2): 116-120. |
| [13] | GORAL M, KOTOWSKI S, NOWOTNIK A, et al.PS-PVD deposition of thermal barrier coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 237: 51-55. |
| [14] | REZANKA S, MAUER G, VAßEN R. Improved thermal cycling durability of thermal barrier coatings manufactured by PS-PVD. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2014, 23(1/2): 182-189. |
| [15] | SONG J, ZHANG X, DENG C, et al.Research of in situ modified PS-PVD thermal barrier coating against CMAS (CaO-MgO-Al2 O3-SiO2) corrosion. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(2): 3163-3169. |
| [16] | GAO L, GUO H, WEI L, et al.Microstructure, thermal conductivity and thermal cycling behavior of thermal barrier coatings prepared by plasma spray physical vapor deposition. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2015, 276: 424-430. |
| [17] | MAUER G, HOSPACH A, VAßEN R. Process development and coating characteristics of plasma spray-PVD. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 220: 219-224. |
| [18] | MAUER G, HOSPACH A, ZOTOV N, et al.Process conditions and microstructures of ceramic coatings by gas phase deposition based on plasma spraying. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2013, 22(2/3): 83-89. |
| [19] | VON NIESSEN K, GINDRAT M.Plasma spray-PVD: a new thermal spray process to deposit out of the vapor phase. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2011, 20(4): 736-743. |
| [20] | MAUER G, VAßEN R. Plasma spray-PVD: plasma characteristics and impact on coating properties. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2012, 406: 012005-012017. |
| [21] | LI C, GUO H, GAO L, et al.Microstructures of yttria-stabilized zirconia coatings by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2015, 24(3): 534-541. |
| [22] | GAO L, WEI L, GUO H, et al.Deposition mechanisms of yttria-stabilized zirconia coatings during plasma spray physical vapor deposition. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(4): 5530-5536. |
| [23] | GAO L, GUO H, WEI L, et al.Microstructure and mechanical properties of yttria stabilized zirconia coatings prepared by plasma spray physical vapor deposition. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(7): 8305-8311. |
| [24] | ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, DENG C M, et al.Gas-deposition mechanisms of 7YSZ coating based on plasma spray-physical vapor deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(3): 697-703. |
| [25] | ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, SONG J B, et al.Deposition and CMAS corrosion mechanism of 7YSZ thermal barrier coatings prepared by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| [26] | GINDRAT M.Characterization of Supersonic Low Pressure Plasma Jets. Doctoral Thesis, 2004. |
| [27] | ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, ZHANG J F, et al.Structure evolution of 7YSZ thermal barrier coating during thermal shock testing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1261-1266. |
| [28] | GARVIE R C, HANNINK R H, PASCOE R T.Ceramic steel? Nature, 1975, 258(5537): 703-704. |
| [29] | HAN P, YOSHIDA T.Numerical investigation of thermophoretic effects on cluster transport during thermal plasma deposition process. Journal of applied physics, 2002, 91(4): 1814-1818. |
| [30] | ORHING M.Materials Science of Thin Films: Deposition and Structure, 2nd ed. London: Academic Press, 2001: 357-406. |
| [31] | VENABLES J A, SPILLER G D T, HANBUCKEN M. Nucleation and growth of thin films. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1984, 47(4): 399. |
| [32] | THORNTON J A.Influence of substrate temperature and deposition rate on structure of thick sputtered Cu coatings. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1975, 12(4): 830-835. |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 汤新丽, 丁自友, 陈俊锐, 赵刚, 韩颖超. 基于稀土铕离子荧光标记的磷酸钙纳米材料体内分布与代谢研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 754-764. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [5] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [6] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [7] | 王鲁杰, 张玉新, 李彤阳, 于源, 任鹏伟, 王建章, 汤华国, 姚秀敏, 黄毅华, 刘学建, 乔竹辉. 深海服役环境下碳化硅陶瓷材料的腐蚀及磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [8] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [9] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [10] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [11] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [12] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [13] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [14] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [15] | 安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||