无机材料学报 ›› 2012, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 1-10.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.00001 CSTR: 32189.14.SP.J.1077.2012.00001
• • 下一篇
张青红
收稿日期:2011-09-22
修回日期:2011-09-27
出版日期:2012-01-09
网络出版日期:2011-12-19
作者简介:张青红, 男, 博士, 东华大学教授, 博士生导师. 主要从事光催化、染料敏化太阳能电池、自组装、有机/无机杂化材料的研究, 在二氧化钛纳米结构的晶相控制、形貌调控、构效关系、锐钛矿水性溶胶、可见光催化等方面成果突出, 已在Chem. Commun., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., Langmuir, J. Mater. Chem., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 等国内外核心刊物发表学术论文80余篇, 论文他引超过1100余篇次, 单篇论文他引超过200余篇次, 获20余项中国发明专利授权, 合著《纳米氧化钛光催化材料及应用》一部. 先后主持科技部十一五支撑计划子课题1项、国家自然科学基金项目3项, 参与上海市纳米科技专项3项, 作为主要研究人员分别于2002年、2006年获得上海市自然科学奖二等奖各1项.
基金资助:ZHANG Qing-Hong
Received:2011-09-22
Revised:2011-09-27
Published:2012-01-09
Online:2011-12-19
Supported by:摘要:
二氧化钛纳米材料是当前纳米科技的研究热点, 其在太阳能光催化分解水制氢、二氧化碳的光催化还原、染料敏化太阳能电池等清洁能源技术方面均显示了重大的应用前景. 本文主要综述了近年来二氧化钛基纳米材料的研究趋势、存在的主要问题, 以及这些材料在上述清洁能源利用中的最新进展. 对备受关注的非金属掺杂、高能面暴露的二氧化钛、染料敏化太阳能电池阳极致密层等热点问题进行了评述和展望.
中图分类号:
张青红. 二氧化钛基纳米材料及其在清洁能源技术中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(1): 1-10.
ZHANG Qing-Hong. Progress on TiO2-based Nanomaterials and Its Utilization in the Clean Energy Technology[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(1): 1-10.
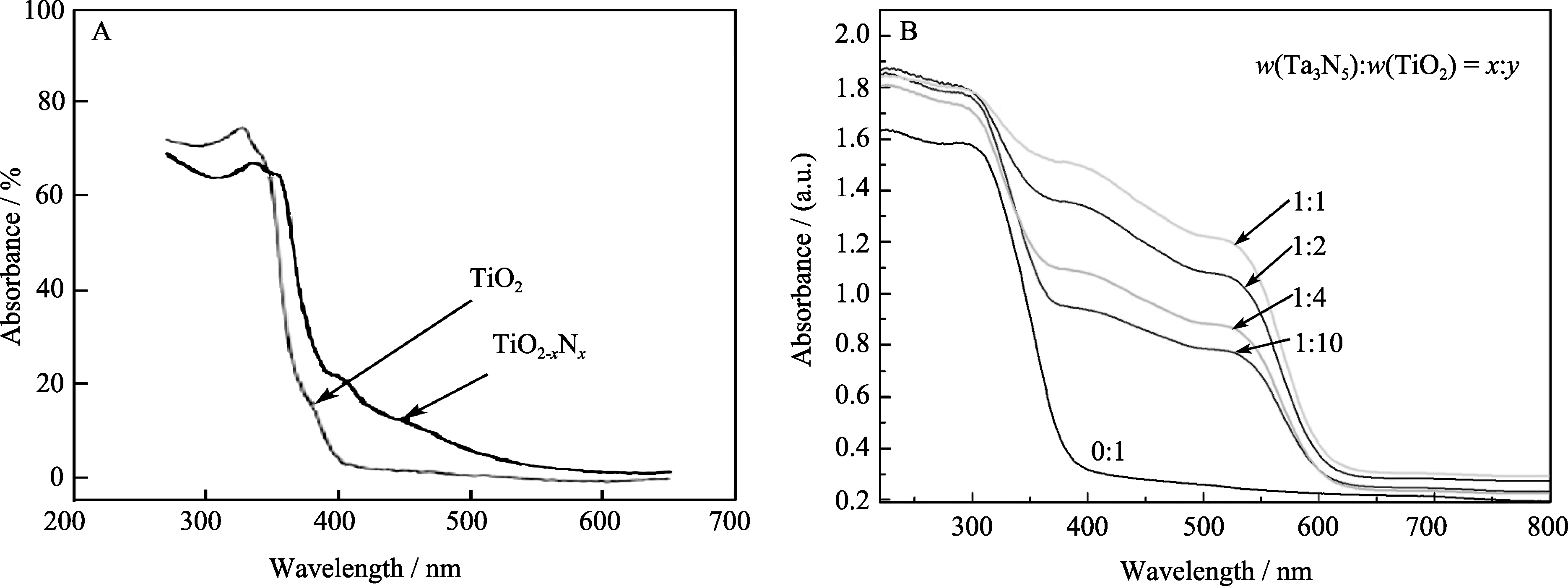
图1 氮掺杂TiO2[9](A)与TiO2/Ta3N5(B)纳米复合光催化材料的紫外-可见漫反射光谱
Fig. 1 UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of nitrogen doping TiO2[9] and TiO2/Ta3N5 nanocomposite photocatalyst
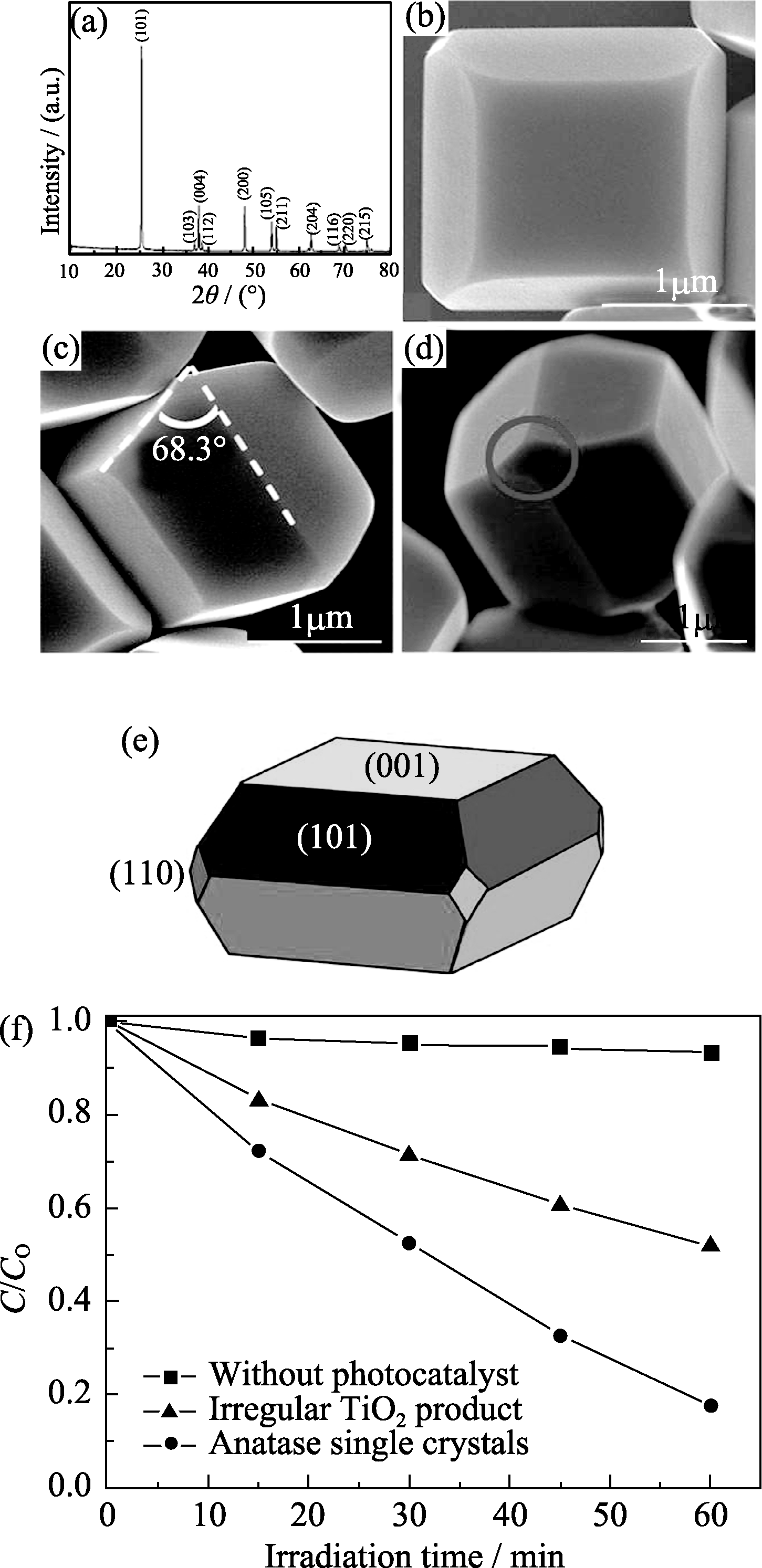
图3 (a) 单晶锐钛矿相二氧化钛的XRD图谱; (b) 单晶锐钛矿相二氧化钛的FE-SEM照片; (c) {001}面与{101}面的夹角, 白色虚线分别代表(001)面与(101)面; (d)单晶锐钛矿相二氧化钛暴露的{110}面(以圈表示); (e)单晶锐钛矿相二氧化钛的结构示意图; (f)单晶锐钛矿相二氧化钛与不规整二氧化钛光催化降解亚甲基蓝, 不同反应时间内亚甲基蓝溶液浓度的变化[30]
Fig. 3 (a) XRD pattern of the anatase single crystals; (b) FE-SEM image of the anatase single crystals; (c) Interfacial angle between {001} and {101} facets (68.3°±0.3° on average). The white dashed lines indicate the (001) and (101) crystal planes of anatase TiO2, respectively; (d) Small rhombus {110} facets (indicated by red circle) of the anatase single crystals; (e) Schematic diagram of the anatase single crystal; (f) The variation of MB concentration by photochemical reaction with the anatase TiO2 single crystals and the irregular TiO2 product[30]
| [1] | Kitano M, Matsuok M, Ueshima M, et al. Recent developments in titanium oxide-based photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. A, 2007, 325(1): 1-14. |
| 2 | <![CDATA[[2]Chen X B, Mao S S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials:]]><![CDATA[ synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev., 2007, 107(7): 2891-2959.<![CDATA[[2]Chen X B, Mao S S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials:]]><![CDATA[ synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev., 2007, 107(7): 2891-2959. ]]> |
| [3] | Hagfeldt A, Boschloo G, Sun L C, et al. Dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(11): 6595-6663. |
| [4] | Choi W Y, Termin A, Hoffmann M R. The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98(51): 13669-13679. |
| [5] | Fuerte A, Hernández-Alonso M D, Maira A J, et al. Visible light-activated nanosized doped-TiO2 photocatalysts. Chem. Commun., 2001, 2001(24): 2718-2719. |
| [6] | Ohno T, Akiyoshi M, Umebayashi T, et al. Preparation of S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. Appl. Catal. A, 2004, 265(1): 115-121. |
| [7] | Livraghi S, Paganini M C, Giamello E, et al. Origin of photoactivity of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide under visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(49): 15666-15671. |
| [8] | JIN Zhi-Liang, LV Gong-Xuan. Modification of TiO2 photocatalysts with metalloid anions and the applicaton in salt solution system. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 571-578. |
| [9] | Sato S. Photocatalytic activity of NOx-doped TiO2 in the visible light region. Chem. Phys. Lett., 1986, 123(1/2): 126-128. |
| [10] | Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T, et al. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science, 2001, 293(5528): 269-271. |
| [11] | Kazemeini M H, Berezin A A, Fukuhara N. Formation of thin TiNxOy films by using a hollow cathode reactive DC sputtering system. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 372(1-2): 70-77. |
| [12] | Mohamed S H, Kappertz O, Ngaruiya J M, et al. Influence of nitrogen content on properties of direct current sputtered TiOxNy films. Phys. Stat. Sol. A, 2004, 201(1): 90-102. |
| [13] | Irie H, Washizuka S, Yoshino N, et al. Visible-light induced hydrophilicity on nitrogen-substituted titanium dioxide films. Chem. Commun., 2003, 2003(11): 1298-1299. |
| [14] | Suda Y, Kawasaki H, Ueda T, et al. Preparation of high quality nitrogen doped TiO2 thin film as a photocatalyst using a pulsed laser deposition method. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 453-454: 162-166. |
| [15] | Irie H, Watanabe Y, Hashimoto K. Nitrogen-concentration dependence on photocatalytic activity of TiO2-xNx powders. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(23): 5483-5486. |
| [16] | Miyauchi M, Ikezawa A, Tobimatsu H, et al. Zeta potential and photocatalytic activity of nitrogen doped TiO2 thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2004, 6(4): 865-870. |
| [17] | Sakthivel S, Kisch H. Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide. Chem. Phys. Chem, 2003, 4(5): 487-490. |
| [18] | Ihara T, Miyoshi M, Iriyama Y, et al. Visible-light-active titanium oxide photocatalyst realized by an oxygen-deficient structure and by nitrogen doping. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2003, 42(4): 403-409. |
| [19] | Burda C, Lou Y B, Chen X B, et al. Enhanced nitrogen doping in TiO2 nanoparticles. Nano Lett., 2003, 3(8): 1049-1051. |
| [20] | Gole J L, Stout J D, Burda C, et al. Highly efficient formation of visible light tunable TiO2-xNx photocatalysts and their transformation at the nanoscale. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(4): 1230-1240. |
| [21] | Sano T, Negishi N, Koike K, et al. Preparation of a visible light- responsive photocatalyst from a complex of Ti4+ with a nitrogen- containing ligand. J. Mater. Chem., 2004, 14(3): 380-384. |
| [22] | Yin S, Yamaki H, Komatsu M, et al. Preparation of nitrogen-doped titania with high visible light induced photocatalytic activity by mechanochemical reaction of titania and hexamethylenetetramine. J. Mater. Chem., 2003, 13(12): 2996-3001. |
| [23] | Okada M, Yamada Y, Jin P, et al. Fabrication of multifunctional coating which combines low-e property and visible-light-responsive photocatalytic activity. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 442(1/2): 217-221. |
| [24] | Miao L, Tanemura S, Watanabe H, et al. The improvement of optical reactivity for TiO2 thin films by N2-H2 plasma surface-treatment. J. Crystal Growth, 2004, 260(1/2): 118-124. |
| [25] | Umebayashi T, Yamaki T, Itoh H, et al. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide by sulfur doping. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 81(3): 454-456. |
| [26] | Ohno T, Mitsui T, Matsumura M. Photocatalytic activity of S-doped TiO2 photocatalyst under visible light. Chem. Lett., 2003, 32(4): 364-365. |
| [27] | Nukumizu K, Nunoshige J, Takata T, et al. TiNxOyFz as a stable photocatalyst for water oxidation in visible light (<570 nm). Chem. Lett., 2003, 32(2): 196-197. |
| [28] | Yang H G, Sun C H, Qiao S Z, et al. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature, 2008, 453(7195): 638-641. |
| [29] | Han X G, Kuang Q, Jin M S, et al. Synthesis of titania nanosheets with a high percentage of exposed (001) facets and related photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Chemical Soc., 2009, 131(9): 3152-3153. |
| [30] | Liu M, Piao L Y, Zhao L, et al. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with exposed {001} and {110} facets: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(10): 1664-1666. |
| [31] | Yu J G, Fan J J, Lv K. Anatase TiO2 nanosheets with exposed (001) facets: improved photoelectric conversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale, 2010, 2: 2144-2149. |
| [32] | Pan J, Liu G, Lu G Q, et al. On the true photoreactivityorder of {001}, {010}, and {101} facets of anatase TiO2 crystals. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50(9): 2133-2137. |
| [33] | Pan J, Wu X, Wang L Z, et al. Synthesis of anatase TiO2 rods with dominant reactive {010} facets for the photoreduction of CO2 to CH4 and use in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(29): 8361-8363. |
| [34] | Amano F, Prieto-Mahaney O O, Terada Y, et al. Decahedral single- crystalline particles of anatase titanium(IV) oxide with high photocatalytic activity. Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(13): 2601-2603. |
| [35] | Dai Y Q, Cobley C M, Zeng J, et al. Synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets. Nano Lett., 2009, 9(6): 2455-2459. |
| [36] | Zhu J, Wang S H, Bian Z F, et al. Solvothermally controllable synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with dominant {001} facets and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2010, 12(7): 2219-2224. |
| [37] | Ma X Y, Chen Z G, Hartono S B, et al. Fabrication of uniform anatase TiO2 particles exposed by {001} facets. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(35): 6608-6610. |
| [38] | Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37-38. |
| [39] | Jing D W, Zhang Y J, Guo L J. Study on the synthesis of Ni doped mesoporous TiO2 and its photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution in aqueous methanol solution. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2005, 415(1/2/3): 74-78. |
| [40] | Wu Y Q, Lu G X, Li S B. The long-term photocatalytic stability of Co2+-modified P25-TiO2 powders for the H2 production from aqueous ethanol solution. J. Photochem. Photobio. A, 2006, 181(2/3): 263-267. |
| [41] | Kato H, Kudo A. Visible-light-response and photocatalytic activities of TiO2 and SrTiO3 photocatalystscodoped with antimony and chromium. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(19): 5029-5034. |
| [42] | Matsuoka M, Kitano M, Takeuchi M, et al. Photocatalysis for new energy production-recent advances in photocatalytic water splitting reactions for hydrogen production. Catal. Today, 2007, 122(1/2): 51-61. |
| [43] | Khan S U M, Al-Shahry M, Ingler W B. Efficient photochemical water splitting by a chemically modified n-TiO2. Science, 2002, 297(5590): 2243-2245. |
| [44] | In S, Orlov A, Berg R, et al. Effective visible light-activated B-doped and B, N-doped TiO2photocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(45): 13790-13791. |
| [45] | Liu G, Chen Z G, Dong C L, et al. Visible light photocatalyst: iodine-doped mesoporoustitania with a bicrystalline framework. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(42): 20823-20828. |
| [46] | Maeda K, Domen K. New non-oxide photocatalysts designed for overall water splitting under visible light. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(22): 7851-7861. |
| [47] | Maeda K, Terashima H, Kase K, et al. Nanoparticulate precursor route to fine particles of TaON and ZrO2-TaON solid solution and their photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution under visible light. Appl. Catal. A, 2009, 357(2): 206-212. |
| [48] | Hitoko G, Takata T, Kondo J N, et al. An oxynitride, TaON, as anefficient water oxidation photocatalyst under visible light irradiation (λ< 500 nm). Chem. Commun., 2002(16): 1698-1699. |
| [49] | Hitoki G, Ishikawa A, Takata T, et al. Ta3N5 as a novel visible light-driven photocatalyst (λ< 600 nm). Chem. Lett., 2002, 31(7): 736-737. |
| 50 | <![CDATA[[50]Hara M, Chiba E, Ishikawa A, et al. Ta3N5 and TaON thin films on Ta foil:]]><![CDATA[surface composition and stability. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(48): 13441-13445. ]]> |
| [51] | Hara M, Hitoki G, Takata T, et al. TaON and Ta3N5 as new visible light driven photocatalysts. Catal. Today, 2003, 78(1-4): 555-560. |
| [52] | Maeda K, Domen K. Solid solution of GaN and ZnO as a stable photocatalyst for overall water splitting under visible light. Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(3): 612-623. |
| [53] | Yashima M, Yamada H, Maeda K, et al. Experimental visualization of covalent bonds and structural disorder in a gallium zinc oxynitride photocatalyst (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx): origin of visible light absorption. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(14): 2379-2381. |
| [54] | Sun X J, Maeda K, Faucheur M, et al. Preparation of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) solid-solution from ZnGa2O4 and ZnO as a photo-catalyst for overall water splitting under visible light. Appl. Catal. A, 2007, 327(1): 114-121. |
| [55] | Maeda K, Takata T, Hara M, et al. GaN:ZnO solid solution as a photocatalyst for visible-light-driven overall water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(23): 8286-8287. |
| [56] | Maeda K, Teramura K, Lu D L, et al. Photocatalyst releasing hydrogen from water-enhancing catalytic performance holds promise for hydrogen production by water splitting in sunlight. Nature, 2006, 440(7082): 295. |
| [57] | Maeda K, Teramura K, Domen K. Effect of post-calcination on photocatalytic activity of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) solid solution for overall water splitting under visible light. J. Catal., 2008, 254(2): 198-204. |
| [58] | Maeda K, Sakamoto N, Ikeda T, et al. Preparation of core-shell- structured nanoparticles (with a noble-metal or metal oxide core and a chromiashell) and their application in water splitting by means of visible light. Chem. Eur. J., 2010, 16(26): 7750-7759. |
| [59] | Maeda K, Xiong A, Yoshinaga T, et al. Photocatalytic overall water splitting promoted by two different cocatalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution under visible light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 122(24): 4096-4099. |
| [60] | Ishikawa A, Takata T, Kondo J N, et al. Oxysulfide Sm2Ti2S2O5 as a stable photocatalyst for water oxidation and reduction under visible light irradiation (<650 nm). J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(45): 13547-13553. |
| [61] | Ishikawa A, Takata T, Matsumura T, et al. Oxysulfides Ln2Ti2S2O5 as stable photocatalysts for water oxidation and reduction under visible- light irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(8): 2637-2642. |
| [62] | Vogel R, Hoyer P, Weller H. Quantum-sized PbS, CdS, Ag2S, Sb2S3, and Bi2S3 particles as sensitizers for various nanoporous wide-bandgap semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98(12): 3183-3188. |
| [63] | Lin G F, Zheng J W, Xu R. Template-free synthesis of uniform CdS hollow nanospheres and their photocatalytic activities. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(19): 7363-7370. |
| [64] | Lei Z B, You W S, Liu M Y. Photocatalytic water reduction under visible light on a novel ZnIn2S4 catalyst synthesized by hydrothermal method. Chem. Commun., 2003(17): 2142-2143. |
| [65] | Kudo A, Omori K, Kato H. A novel aqueous process for preparation of crystal form-controlled and highly crystalline BiVO4 powder from layered vanadates at room temperature and its photocatalytic and photophysical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121(49): 11459-11467. |
| [66] | Tang J W, Zou Z G, Ye J H. Effects of substituting Sr2+ and Ba2+ for Ca2+ on the structural properties and photocatalytic behaviors of CaLn2O4. Chem. Mater., 2004, 16(9): 1644-1649. |
| [67] | Tian M K, Shangguan W F, Yuan J, et al. K4Ce2M10O30 (M=Ta, Nb) as visible light-driven photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution from water decomposition. Appl. Catal. A, 2006, 309(1): 76-84. |
| [68] | So W W, Kim K J, Moon S J. Photo-production of hydrogen over the CdS-TiO2 nano-composite particulate films treated with TiCl4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(3): 229-234. |
| [69] | Spanhel L, Weller H, Henglein A. Photochemistry of semiconductor colloids. 22. electron ejection from illuminated cadmium sulfide into attached titanium and zinc oxide particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109(22): 6632-6635. |
| [70] | Chai S Y, Kim Y J, Lee W I. Photocatalytic WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles working under visible light. J. Electroceramics, 2006, 17(2/3/4): 909-912. |
| [71] | Halmann M. Photoelectrochemicalreduction of aqueous carbon- dioxide on p-type gallium-phosphide in liquid junction solar-cells. Nature, 1978, 275(5676): 115-116. |
| [72] | Tan S S, Zou L, Hu E. Photosynthesis of hydrogen and methane as key components for clean energy system. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2007, 8(1/2): 89-92. |
| [73] | Lo C C, Hung C H, Yuan C S, et al. Photoreduction of carbon dioxide with H2 and H2O over TiO2 and ZrO2 in a circulated photocatalytic reactor. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2007, 91(19): 1765-1774. |
| [74] | Li G H, Ciston S, Zoran V, et al. Synthesizing mixed-phase TiO2 nanocomposites using a hydrothermal method for photo-oxidation and photoreduction applications. J. Catal., 2008, 253(1): 105-110. |
| [75] | Grätzel M. Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 338-344. |
| [76] | Frank A J, Kopidakis N, van de Lagemaat J. Electrons in nanostructured TiO2 solar cells: transport, recombination and photovoltaic properties,Coord. Chem. Rev., 2004, 248(13/14): 1165-1179. |
| [77] | Yu H, Zhang S Q, Zhao H J, et al. High-performance TiO2 photoanode with an efficient electron transport network for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(36): 16277-16282. |
| [78] | Adachi M, Murata Y, Takao J, et al. Highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with a titania thin-film electrode composed of a network structure of single-crystal-like TiO2 nanowires made by the "oriented attachment" mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(45): 14943-14949. |
| [79] | Li S, Li Y G, Wang H Z, et al. Peptization-hydrothermal method as a surfactant-free process toward nanorod-like anatase TiO2 nanocrystals. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2009, (27): 4078-4084. |
| [80] | 杨术明, 寇慧芝, 汪 玲, 等(YANG Shu-Ming, et al). N3敏化Ho3+ 离子修饰TiO2纳米晶电极的光电化学性质. 物理化学学报(Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica), 2009, 25(6): 1219-1224. |
| [81] | Zhu K, Schiff E A, Park N G, et al. Determining the locus for photocarrier recombination in dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 80(4): 685-687. |
| [82] | Cameron P, Peter L. Characterization of titanium dioxide blocking layers in dye-sensitized nanocrystalline solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(51): 14394-14400. |
| [83] | Barbe C J, Arendse F, Comte P, et al. Nanocrystalline titanium oxide electrodes for photovoltaic applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, 80(12): 3157-3171. |
| [84] | Burke A, Ito S, Snaith H J, et al. The function of a TiO2 compact layer in dye-sensitized solar cells incorporating "Planar" organic dyes. Nano Lett., 2008, 8(4): 977-981. |
| [85] | Xia J B, Masaki N, Jiang K J, et al. Deposition of a thin film of TiOx from a titanium metal target as novel blocking layers at conducting glass/TiO2 interfaces in ionic liquid mesoscopic TiO2 dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(50): 25222-25228. |
| [86] | Zhang L, Xie A J, Shen Y H, et al. Preparation of TiO2 films by layer-by-layer assembly and their application in solar cell. J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 505(2): 579-583. |
| [87] | Liu X M, X H Sun, Q D Tai, et al. Influences on photovoltage performance by interfacial modification of FTO/mesoporous TiO2 using ZnO and TiO2 as the compact film. J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509(37): 9264-9270. |
| [88] | ZHOU Wen-Qian, LU Yu-Ming, CHEN Chang-Zhao, et al. Effect of Li-doped TiO2 compact layers for dye sensitized solar cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(8): 819-822. |
| [89] | Liu Y M, Sun X H, Tai Q D, et al. Efficiency enhancement in dye-sensitized solar cells by interfacial modification of conducting glass/mesoporous TiO2 using a novel ZnO compact blocking film. J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(1): 475-481. |
| [90] | Xia J B, Masaki N, Jiang K J, et al. Sputtered Nb2O5 as an effective blocking layer at conducting glass and TiO2 interfaces in ionic liquid- based dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun., 2007(2): 138-140. |
| [91] | Xia J B, Masaki N, Jiang K J, et al. Sputtered Nb2O5 as a novel blocking layer at conducting glass/TiO2 interfaces in dye-sensitized ionic liquid solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(22): 8092-8097. |
| [92] | Qian D F, Li Y G, Zhang Q H, et al. Anatase TiO2 sols derived from peroxotitanium acid and to form transparent TiO2 compact film for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509(41): 10121-10126. |
| [93] | Sommeling P M, O’Regan B C, Haswell R R, et al. Influence of a TiCl4 post-treatment on nanocrystalline TiO2 films in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(29): 19191-19197. |
| [94] | O'Regan B C, Durrant J R, Sommeling P M, et al. Influence of the TiCl4 treatment on nanocrystalline TiO2 films in dye-sensitized solar cells. 2. Charge density, band edge shifts, and quantification of recombination losses at short circuit. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(37): 14001-14010. |
| [95] | 郝艳明, 石国英, 钱迪峰, 等(HAO Yan-Ming, et al). 基于锐钛矿相二氧化钛溶胶的高效染料敏化太阳能电池. 硅酸盐学报(Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society), 2011, 39(7): 1091-1097. |
| [98] | 作者学术成就介绍: |
| [99] | 张青红, 男, 博士, 东华大学教授, 博士生导师. 主要从事光催化、染料敏化太阳能电池、自组装、有机/无机杂化材料的研究, 在二氧化钛纳米结构的晶相控制、形貌调控、构效关系、锐钛矿水性溶胶、可见光催化等方面成果突出, 已在Chem. Commun., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., Langmuir, J. Mater. Chem., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 等国内外核心刊物发表学术论文80余篇, 论文他引超过1100余篇次, 单篇论文他引超过200余篇次, 获20余项中国发明专利授权, 合著《纳米氧化钛光催化材料及应用》一部. 先后主持科技部十一五支撑计划子课题1项、国家自然科学基金项目3项, 参与上海市纳米科技专项3项, 作为主要研究人员分别于2002年、2006年获得上海市自然科学奖二等奖各1项. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 陈莉波, 盛盈, 伍明, 宋季岭, 蹇建, 宋二红. Na和O元素共掺杂氮化碳高效光催化制氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 552-562. |
| [8] | 范小暄, 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心, 王绩伟. 基于富氧空位LiYScGeO4: Bi3+长余辉光催化剂的自激活余辉驱动有机污染物芬顿降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [9] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [10] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [11] | 贾相华, 张辉霞, 刘艳凤, 左桂鸿. 湿化学法制备Cu2O/Cu空心球异质结光催化剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [12] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [13] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [14] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [15] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||