无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 390-398.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230473 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230473
所属专题: 【能源环境】污染物催化去除(202506)
吴光宇1,2( ), 舒松1,2, 张洪伟1,2, 李建军1,3(
), 舒松1,2, 张洪伟1,2, 李建军1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-13
修回日期:2023-12-04
出版日期:2024-04-20
网络出版日期:2023-12-25
通讯作者:
李建军, 教授. E-mail: jjli@scu.edu.cn作者简介:吴光宇(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1464075183@qq.com
基金资助:
WU Guangyu1,2( ), SHU Song1,2, ZHANG Hongwei1,2, LI Jianjun1,3(
), SHU Song1,2, ZHANG Hongwei1,2, LI Jianjun1,3( )
)
Received:2023-10-13
Revised:2023-12-04
Published:2024-04-20
Online:2023-12-25
Contact:
LI Jianjun, professor. E-mail: jjli@scu.edu.cnAbout author:WU Guangyu (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1464075183@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
活性炭以其丰富的孔道结构和高比表面积而在吸附苯乙烯废气上具有巨大的应用潜力, 然而含氧官能团对弱极性苯乙烯的吸附作用机理尚未明晰。本研究通过酸浸渍法制备改性活性炭AC-S和AC-N, 探究改性活性炭孔径结构、比表面积和含氧官能团的演变规律及其对苯乙烯吸附性能的影响。结果表明, 酸改性可以明显提高活性炭对苯乙烯的吸附量。通过吸附动力学、吸附等温拟合发现, 活性炭改性前后均受物理吸附与化学吸附的复合作用影响, 改性后活性炭更倾向于单层吸附。HNO3改性活性炭(AC-N)的孔隙结构在苯乙烯有效吸附孔径范围内没有显著改变, 表面含氧官能团含量增加提高了AC-N对苯乙烯的吸附性能。表面含氧官能团分析表明, 内酯基是提高改性活性炭对苯乙烯吸附量的关键因素。密度泛函理论(DFT)计算表明, AC-N上的内酯基官能团与苯乙烯的乙烯基产生强相互作用, 增强了苯乙烯在改性活性炭上的吸附。
中图分类号:
吴光宇, 舒松, 张洪伟, 李建军. 接枝内酯基活性炭增强苯乙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 390-398.
WU Guangyu, SHU Song, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jianjun. Enhanced Styrene Adsorption by Grafted Lactone-based Activated Carbon[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 390-398.
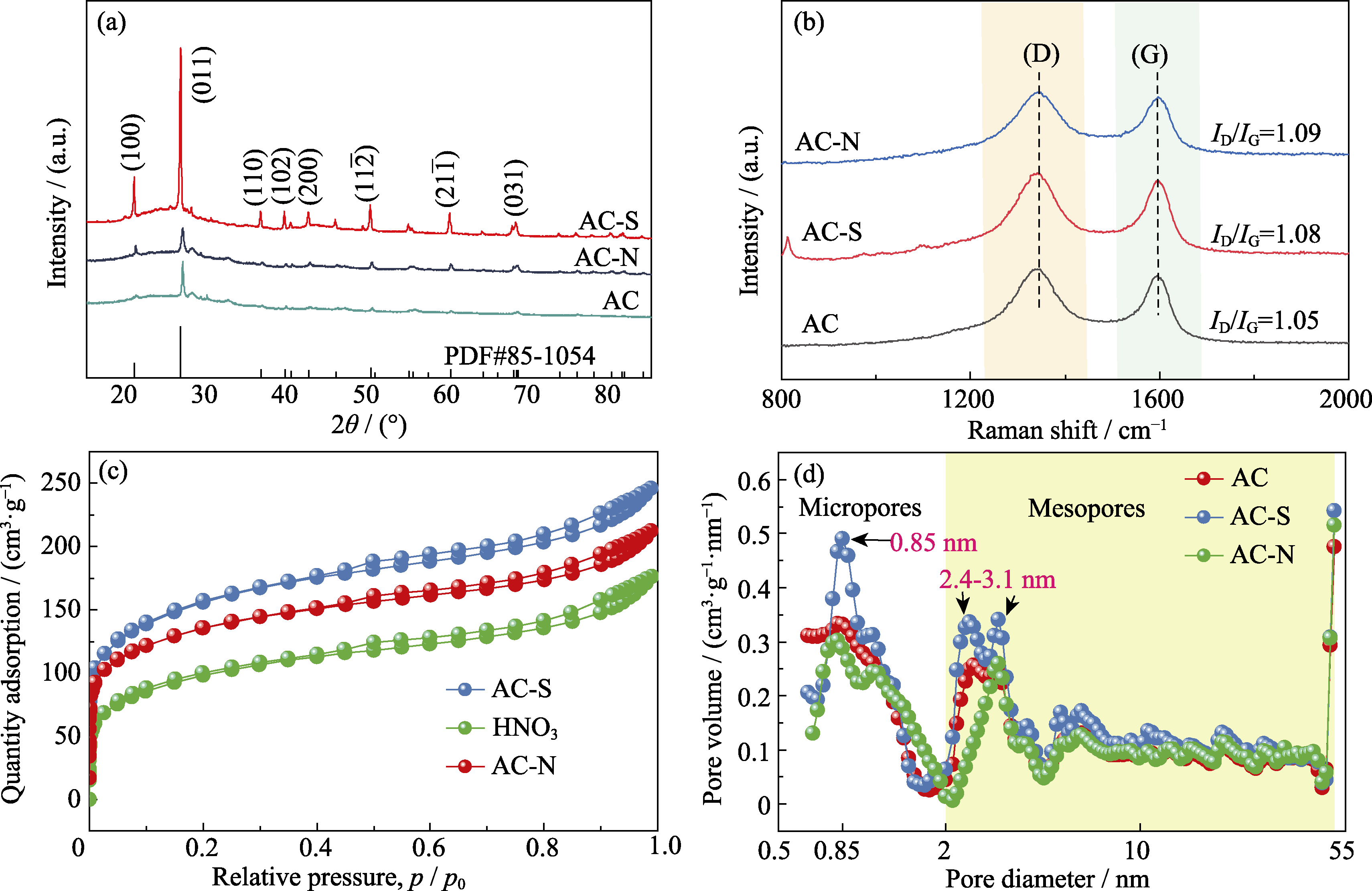
图1 AC、AC-S和AC-N的(a)XRD谱图, (b)Raman谱图, (c)N2吸脱附等温线和(d)孔径分布图
Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns, (b) Raman spectra, (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms, and (d) pore size distributions of AC, AC-S, and AC-N Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | SBET/ (m2•g-1) | Vmicro/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3•g-1) | Vtotal/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 485.51 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.33 |
| AC-S | 558.10 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.38 |
| AC-N | 348.88 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.27 |
表1 AC、AC-S和AC-N的孔径结构特征
Table 1 Textural characteristics of AC, AC-S, and AC-N
| Sample | SBET/ (m2•g-1) | Vmicro/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3•g-1) | Vtotal/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 485.51 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.33 |
| AC-S | 558.10 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.38 |
| AC-N | 348.88 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.27 |
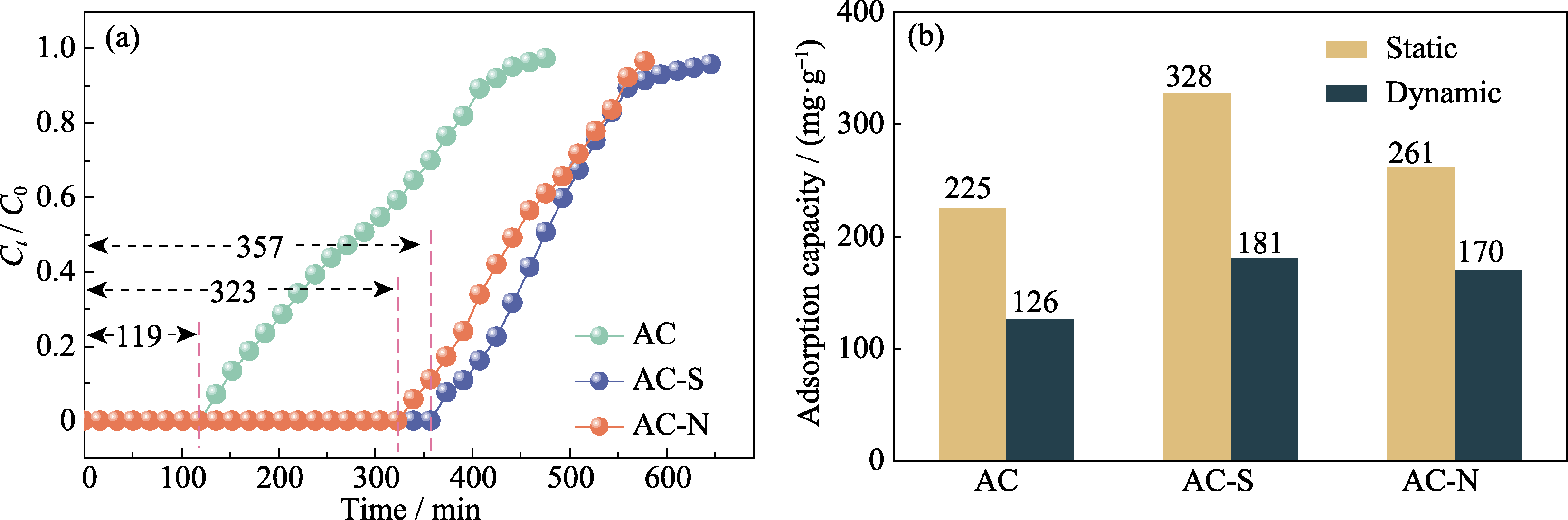
图3 AC、AC-S和AC-N对苯乙烯的(a)穿透曲线和(b)饱和吸附量
Fig. 3 (a) Breakthrough curves and (b) saturation adsorption capacity for the adsorption of styrene by AC, AC-S, and AC-N Colorful figures are available on website
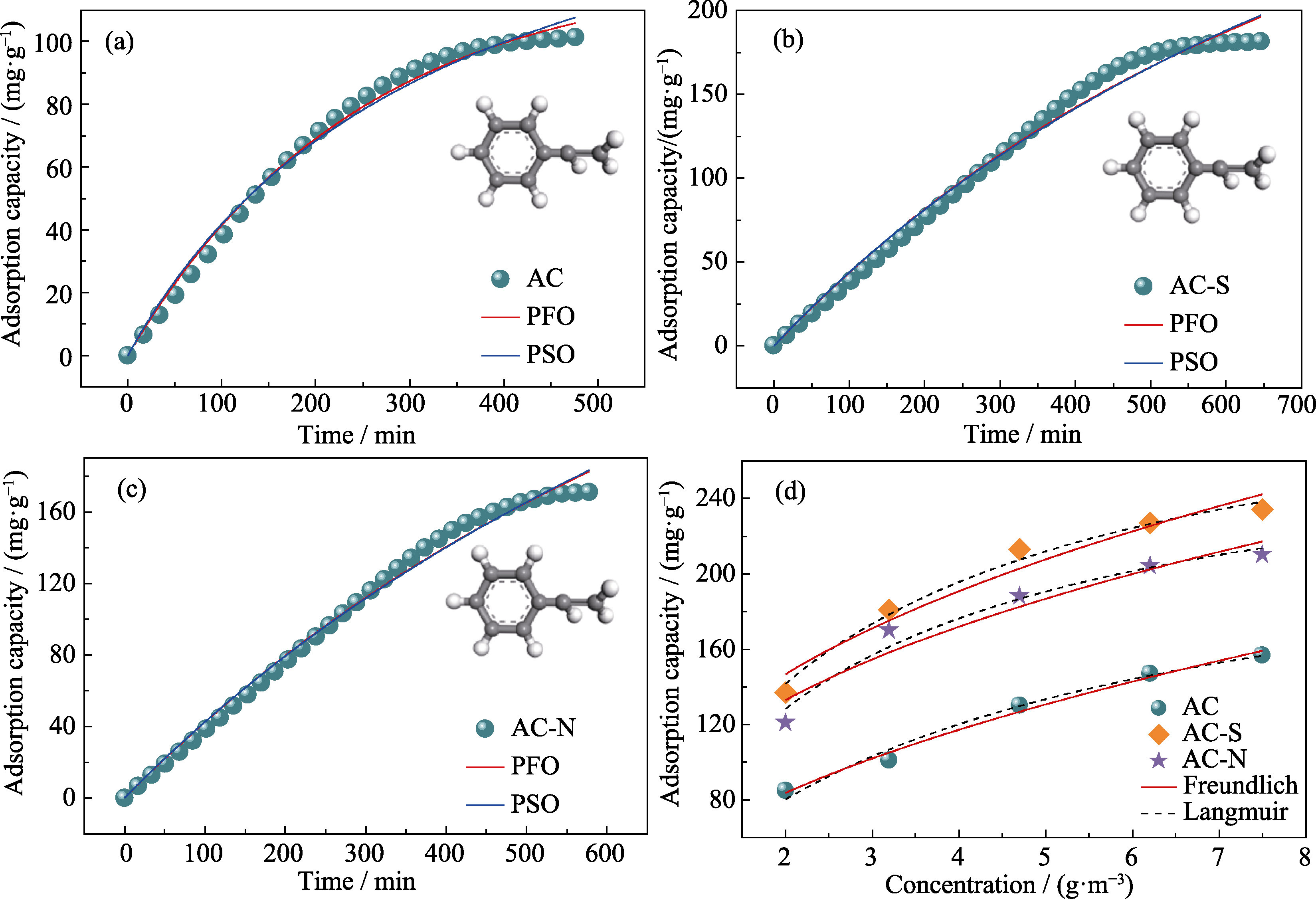
图4 (a)AC, (b)AC-S和(c)AC-N的吸附动力学及其(d)吸附等温线拟合
Fig. 4 Adsorption kinetics of (a) AC, (b) AC-S and (c) AC-N, and (d) correspoding adsorption isotherm fitting Colorful figures are available on website
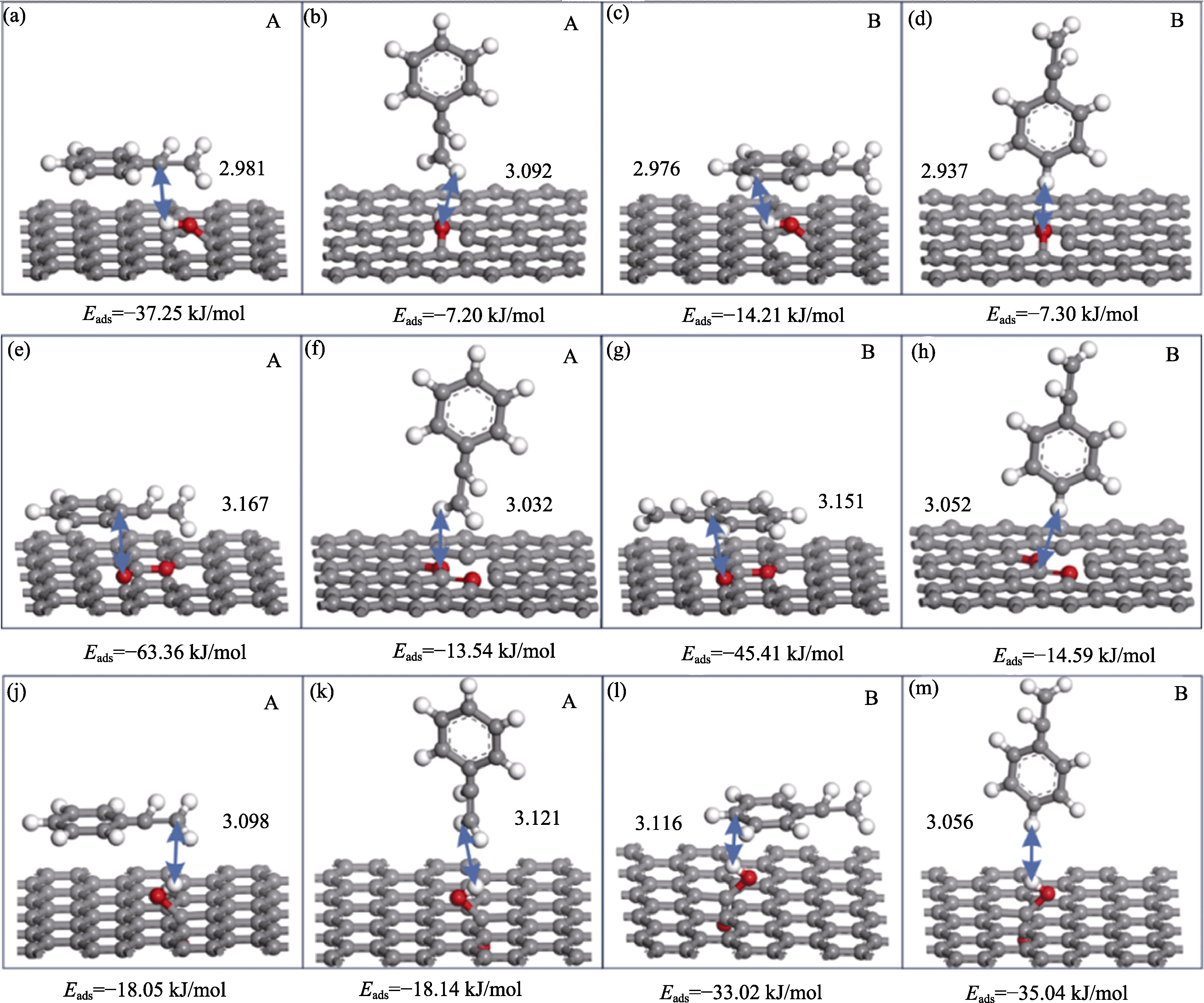
图5 苯乙烯(a~d)与羟基作用, (e~h)与内酯基作用以及(j~m)与羧基作用的构型
Fig. 5 Configurations of (a-d) styrene interacting with hydroxyl group, (e-h) styrene interacting with lactone group, and (j-m) styrene interacting with the carboxyl group
| Sample | PFO | PSO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg•g-1) | k1/min-1 | R2 | qe/(mg•g-1) | k2/(g•mg-1•min-1) | R2 | |
| AC | 123 | 0.0041 | 0.99 | 184 | 1.59×10-5 | 0.99 |
| AC-S | 319 | 0.0015 | 0.99 | 548 | 1.59×10-6 | 0.99 |
| AC-N | 338 | 0.0014 | 0.99 | 595 | 1.29×10-6 | 0.99 |
表S1 AC、AC-S、AC-N吸附苯乙烯的动力学参数
Table S1 Kinetic parameters of styrene adsorption by AC, AC-S, and AC-N
| Sample | PFO | PSO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg•g-1) | k1/min-1 | R2 | qe/(mg•g-1) | k2/(g•mg-1•min-1) | R2 | |
| AC | 123 | 0.0041 | 0.99 | 184 | 1.59×10-5 | 0.99 |
| AC-S | 319 | 0.0015 | 0.99 | 548 | 1.59×10-6 | 0.99 |
| AC-N | 338 | 0.0014 | 0.99 | 595 | 1.29×10-6 | 0.99 |
| Isotherm model | Parameter | AC | AC-S | AC-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qe/(mg•g-1) | 239 | 317 | 281 |
| KL/(m3•mg-1) | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.42 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| RMSE | 3.53 | 3.86 | 5.39 | |
| Freundlich | KF/((mg•g-1)·(m3•mg-1)1/n) | 59.82 | 122.75 | 102.76 |
| n | 2.06 | 2.63 | 2.69 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.93 | |
| RMSE | 2.73 | 7.74 | 8.52 |
表S2 苯乙烯吸附的Langmuir和Freundlich模型拟合参数
Table S2 Fitting parameters of the Langmuir and Freundlich models for styrene adsorption
| Isotherm model | Parameter | AC | AC-S | AC-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qe/(mg•g-1) | 239 | 317 | 281 |
| KL/(m3•mg-1) | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.42 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| RMSE | 3.53 | 3.86 | 5.39 | |
| Freundlich | KF/((mg•g-1)·(m3•mg-1)1/n) | 59.82 | 122.75 | 102.76 |
| n | 2.06 | 2.63 | 2.69 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.93 | |
| RMSE | 2.73 | 7.74 | 8.52 |
| Sample | Hydroxyl group/(mmol•g-1) | Lactone group/(mmol•g-1) | Carboxyl group/(mmol•g-1) | Total/(mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| AC-S | 0.21 | 0.82 | 0.15 | 1.18 |
| AC-N | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.37 | 1.14 |
表S3 AC、AC-S和AC-N的表面官能团含量
Table S3 Amounts of surface functional groups of AC, AC-S, and AC-N
| Sample | Hydroxyl group/(mmol•g-1) | Lactone group/(mmol•g-1) | Carboxyl group/(mmol•g-1) | Total/(mmol•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| AC-S | 0.21 | 0.82 | 0.15 | 1.18 |
| AC-N | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.37 | 1.14 |
| Sample | Relative content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C | C-O | C=O/COOH | O-C=O | |
| AC | 70.67 | 20.99 | 2.91 | 5.43 |
| AC-S | 65.14 | 16.56 | 4.99 | 13.32 |
| AC-N | 72.94 | 6.70 | 14.57 | 5.79 |
表S4 AC、AC-S、AC-N表面C1s的XPS分析结果
Table S4 XPS results of C1s on the surface of AC, AC-S, and AC-N
| Sample | Relative content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C | C-O | C=O/COOH | O-C=O | |
| AC | 70.67 | 20.99 | 2.91 | 5.43 |
| AC-S | 65.14 | 16.56 | 4.99 | 13.32 |
| AC-N | 72.94 | 6.70 | 14.57 | 5.79 |
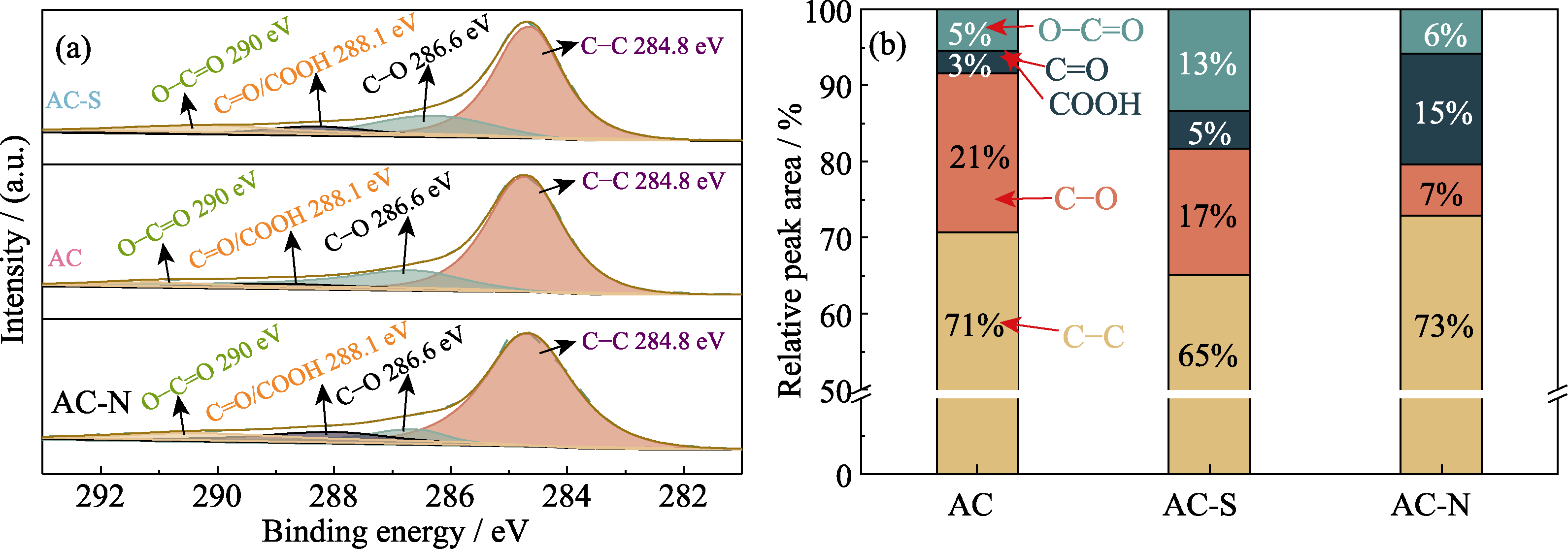
图S3 AC、AC-S和AC-N的(a)C1s XPS谱图和(b)含氧官能团的相对含量
Fig. S3 (a) C1s XPS spectra and (b) relative contents of oxygen-containing functional groups for AC, AC-S and AC-N
| [1] |
HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
BHAT A, VENKAT M, CHEN X, et al. Chemical surface modification of beaded activated carbon: a strategy to inhibit heel accumulation from VOC. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2021, 103: 205.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHU L, SHEN D, LUO K H. A critical review on VOCs adsorption by different porous materials: species, mechanisms and modification methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 122102.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHU J, LI Y, XU L, et al. Removal of toluene from waste gas by adsorption-desorption process using corncob-based activated carbons as adsorbents. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 165: 115.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
CANDIA-LOMELÍ M, COVARRUBIAS-GARCIA I, AIZPURU A, et al. Preparation and physicochemical characterization of deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids for the potential absorption and biodegradation of styrene vapors. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 441: 129835.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PAN H, HE Z, LIN Q, et al. The effect of copper valence on catalytic combustion of styrene over the copper based catalysts in the absence and presence of water vapor. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 468.
DOI |
| [7] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, LU J, et al. Investigation of defect-rich CeO2 catalysts for super low-temperature catalytic oxidation and durable styrene removal. Chemosphere, 2022, 303: 134863.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WANG Y, DU X, LONG Y, et al. Real-time detection of styrene using SAW sensors based on hexafluoroisopropanol group functionalized hydrogen-bond acidic polymers. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2015, 206: 252.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI D, SU R, MA X, et al. Porous carbon for oxygenated and aromatic VOCs adsorption by molecular simulation and experimental study: effect pore structure and functional groups. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 605: 154708.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG H, HUANG L, QING J, et al. Mesoporous organic- inorganic hybrid siliceous hollow spheres: synthesis and VOCs adsorption. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HOU B, ZHAO Y, SUN W, et al. Glycine based modification of activated carbons for VOCs adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2021, 7: 100126.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MATUSIK J, KOTEJA-KUNECKA A, MAZIARZ P, et al. Styrene removal by surfactant-modified smectite group minerals: efficiency and factors affecting adsorption/desorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 130848.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HOU S, HUANG Z H, ZHU T, et al. Adsorption removal of styrene on C-Cl grafted silica gel adsorbents. Chemosphere, 2023, 315: 137679.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI Z, JIN Y, CHEN T, et al. Trimethylchlorosilane modified activated carbon for the adsorption of VOCs at high humidity. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 272: 118659.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DIZBAY-ONAT M, FLOYD E, VAIDYA U K, et al. Applicability of industrial sisal fiber waste derived activated carbon for the adsorption of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Fibers and Polymers, 2018, 19(4): 805.
DOI |
| [16] | 刘俊岭. 用于吸附VOCs的碳基材料和MOFs研究. 北京: 北京石油化工学院硕士学位论文, 2021. |
| [17] |
YU H, LI T, YANG X, et al. Hydrophobic carbon-based coating on metal tube with efficient and stable adsorption-desorption of CO2 from wet flue gas. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 307: 122798.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YU X, LIU S, LIN G, et al. Insight into the significant roles of microstructures and functional groups on carbonaceous surfaces for acetone adsorption. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(38): 21541.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
BECKER P, GLENK F, KORMANN M, et al. Chlorination of titanium carbide for the processing of nanoporous carbon: a kinetic study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 159(1-3): 236.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU T, ZHANG R, ZHANG X, et al. One-step room-temperature preparation of expanded graphite. Carbon, 2017, 119: 544.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
THOMMES M, CYCHOSZ K A. Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials: progress and challenges. Adsorption, 2014, 20(2/3): 233.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
KAN Y, ZHANG R, XU X, et al. Comparative study of raw and HNO3-modified porous carbon from waste printed circuit boards for sulfadiazine adsorption: experiment and DFT study. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(7): 108272.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LI L, QUINLIVAN P A, KNAPPE D R U. Effects of activated carbon surface chemistry and pore structure on the adsorption of organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon, 2002, 40(12): 2085.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZEYNALI M E. Evaluation of the effect of catalyst pore-size distribution on the effectiveness factor in ethylbenzene dehydrogenation by orthogonal collocation. Defect and Diffusion Forum, 2011, 316-317: 155.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TANG L, LI L, CHEN R, et al. Adsorption of acetone and isopropanol on organic acid modified activated carbons. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(2): 2045.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
EL-HENDAWY A. Influence of HNO3 oxidation on the structure and adsorptive properties of corncob-based activated carbon. Carbon, 2003, 41(4): 713.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FU Y, SHEN Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Activated bio-chars derived from rice husk via one- and two-step KOH-catalyzed pyrolysis for phenol adsorption. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 646: 1567.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MA X, LV H, YANG L, et al. Removal characteristics of organic pollutants by the adsorbent injection coupled with bag filtering system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124193.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 杨颖, 李磊, 孙振亚, 等. 活性炭表面官能团的氧化改性及其吸附机理的研究. 科学技术与工程, 2012, 24(12): 1671. |
| [30] |
MA X, LI L, CHEN R, et al. Porous carbon materials based on biomass for acetone adsorption: effect of surface chemistry and porous structure. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 459: 657.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WANG X, YAO F, ZHU W, et al. Experimental and computational investigation on the organic acid modification of porous carbon for toluene adsorption under humid conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138070.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
KUTLUAY S. Excellent adsorptive performance of novel magnetic nano-adsorbent functionalized with 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid for the removal of volatile organic compounds (BTX) vapors. Fuel, 2021, 287: 119691.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 梁鑫. 有机酸改性活性炭及其VOCs吸附行为研究. 长沙: 中南大学能源科学与工程学院硕士学位论文, 2014. |
| [34] |
LAWAL A A, HASSAN M A, AHMAD FARID M A, et al. Adsorption mechanism and effectiveness of phenol and tannic acid removal by biochar produced from oil palm frond using steam pyrolysis. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 269: 116197.
DOI URL |
| [35] | KOMNITSAS K A, ZAHARAKI D. Morphology of modified biochar and its potential for phenol removal from aqueous solutions. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2016, 4: 26. |
| [36] |
YIN Q, SI L, WANG R, et al. DFT study on the effect of functional groups of carbonaceous surface on ammonium adsorption from water. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 132294.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
CHEN L, YUAN J, LI T, et al. A regenerable N-rich hierarchical porous carbon synthesized from waste biomass for H2S removal at room temperature. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 768: 144452.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
KRASNENKO V, KIKAS J, BRIK M G. Modification of the structural and electronic properties of graphene by the benzene molecule adsorption. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2012, 407(23): 4557.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
BHUVANESWARI R, NAGARAJAN V, CHANDIRAMOULI R. First-principles research on adsorption properties of o-xylene and styrene on 5-8 phosphorene sheets. Chemical Physics Letters, 2021, 765: 138244.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CUI H, ZHANG X, CHEN D, et al. Adsorption mechanism of SF6 decomposed species on pyridine-like PtN3 embedded CNT: a DFT study. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 447: 594.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
PÉREZ E M, MARTÍN N. π-π interactions in carbon nanostructures. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(18): 6425.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
CHOI H J. Assessment of sulfonation in lignocellulosic derived material for adsorption of methylene blue. Environmental Engineering Research, 2022, 27(3): 210034.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
MA X, YANG L, HOU Y, et al. Adsorption/desorption characteristics of low-concentration semi-volatile organic compounds in vapor phase on activated carbon. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 305: 114360.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 魏建文, 张丽娟, 耿琳琳, 李誉, 廖雷, 王敦球. 以ZSM-5/MCM-48为载体制备新型高容量CO2吸附剂的性能及机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | 洪培萍, 梁龙, 吴炼, 马颖康, 庞浩. ZIF-67结构调控及其对盐酸金霉素的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [4] | 谢天, 宋二红. 弹性应变对C、H、O在过渡金属氧化物表面吸附的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [5] | 晁少飞, 薛艳辉, 吴琼, 伍复发, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, 张伟. MXene异质结Ti-O-H-O电子快速通道促进高效率储钾[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [6] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [7] | 郭春霞, 陈伟东, 闫淑芳, 赵学平, 杨傲, 马文. 埃洛石纳米管负载锆氧化物吸附水中砷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [8] | 王世怡, 冯爱虎, 李晓燕, 于云. Fe3O4负载Ti3C2Tx对Pb(II)的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [9] | 于业帆, 徐玲, 倪忠斌, 施冬健, 陈明清. 普鲁士蓝/生物炭材料的制备及其氨氮吸附机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [10] | 凌洁, 周安宁, 王文珍, 贾忻宇, 马梦丹. Cu/Mg比对Cu/Mg-MOF-74的CO2吸附性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [11] | 汤亚, 孙盛睿, 樊佳, 杨庆峰, 董满江, 寇佳慧, 刘阳桥. 粉煤灰衍生水合硅酸钙PEI改性及吸附去除Cu(II)与催化降解有机污染物[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [12] | 戴洁燕, 冯爱虎, 米乐, 于洋, 崔苑苑, 于云. NaY沸石分子吸附涂层对典型空间污染物的吸附机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| [13] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 有机-无机氧化硅空心球的合成及VOCs吸附应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [14] | 刘城, 赵倩, 牟志伟, 雷洁红, 段涛. 新型铋基SiOCNF复合膜对放射性气态碘的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [15] | 周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||