无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 893-903.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200632 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20200632
所属专题: 【虚拟专辑】污染物吸附水处理(2020~2021)
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-11-05
修回日期:2020-12-08
出版日期:2021-08-20
网络出版日期:2020-12-10
通讯作者:
黄富强, 研究员. E-mail: huangfq@mail.sic.ac.cn
作者简介:周 帆(1994-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1175106021@qq.com
ZHOU Fan1,2( ), BI Hui1, HUANG Fuqiang1,2,3(
), BI Hui1, HUANG Fuqiang1,2,3( )
)
Received:2020-11-05
Revised:2020-12-08
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2020-12-10
Contact:
HUANG Fuqiang, professor. E-mail: huangfq@mail.sic.ac.cn
About author:ZHOU Fan (1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1175106021@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
活性炭因具有高比表面积和丰富的孔结构而被广泛应用于吸附水处理中的污染物。稻壳具有独特的组成和微观结构, 是制备活性炭的优质碳源。以稻壳为原料, 利用过饱和KOH溶液的预活化和活化双重作用, 在不同温度下制备出超高比表面积活性炭。随着活化温度的升高, 活性炭的比表面积和总孔容逐渐增大。900 ℃下制得的活性炭具有超高比表面积, 达到3600 m2/g, 总孔容为3.164 cm3/g, 明显优于商用活性炭(YP-80, 比表面积为1310 m2/g, 总孔容为0.816 cm3/g)。具有最高比表面积的稻壳活性炭对亚甲基蓝的最大吸附量达到983 mg/g, 几乎是YP-80 (525 mg/g)的两倍。通过吸附动力学拟合, 吸附亚甲基蓝的过程与拟二级动力学模型一致, 表明该过程为化学吸附。
中图分类号:
周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903.
ZHOU Fan, BI Hui, HUANG Fuqiang. Ultra-large Specific Surface Area Activated Carbon Synthesized from Rice Husk with High Adsorption Capacity for Methylene Blue[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 893-903.
| Carbon | YP-80 | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID: IG | 0.997 | 0.992 | 1.017 | 1.025 | 1.020 |
| SSABET/(m2•g-1) | 1310 | 2380 | 3173 | 3366 | 3600 |
| Pore volumetotal/(cm3•g-1) | 0.816 | 1.352 | 1.733 | 1.829 | 3.164 |
| Micropore volume/(cm3•g-1) | 0.516 | 0.393 | 0.429 | 0.606 | 0.537 |
| Adsorption limit/(mg•g-1) | 525 | 851 | 935 | 919 | 983 |
Table 1 The ratio of ID to IG, SSABET, pore volumestotal, micropore volumes and adsorption limits of RHACs and YP-80
| Carbon | YP-80 | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID: IG | 0.997 | 0.992 | 1.017 | 1.025 | 1.020 |
| SSABET/(m2•g-1) | 1310 | 2380 | 3173 | 3366 | 3600 |
| Pore volumetotal/(cm3•g-1) | 0.816 | 1.352 | 1.733 | 1.829 | 3.164 |
| Micropore volume/(cm3•g-1) | 0.516 | 0.393 | 0.429 | 0.606 | 0.537 |
| Adsorption limit/(mg•g-1) | 525 | 851 | 935 | 919 | 983 |
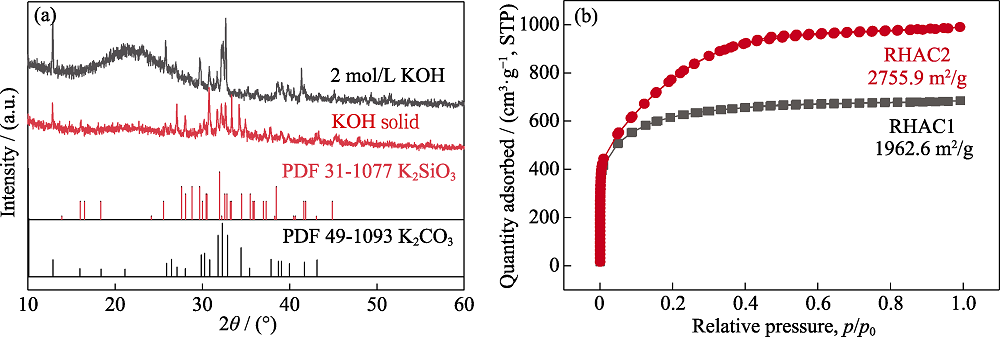
Fig. S2 (a) XRD patterns of dried RHBC mixture impregnated with two different concentrations of KOH solution; (b) Nitrogen adsorption desorption curves of two RHAC with different concentrations of KOH solution
| Biomass | Activator | Pore volume/(cm3•g-1) | SSABET/(m2•g-1) | qm/(mg•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco stalks[ | ZnCl2+Microwave | 0.45 | 684.68 | 123.45 |
| Dipterocarpus alatus[ | ZnCl2/500 ℃ | 0.473 | 843 | 269.3 |
| Sugar beet pulp[ | H3PO4/450 ℃ | 0.445 | 1029.3 | 250.0 |
| Palm kernel shell[ | ZnCl2/550 ℃ | 0.571 | 1058 | 225.3 |
| Rice by-products[ | H3PO4/450 ℃ | 0.612/0.607 | 814/1000 | 246.9/213.7 |
| Viscose fibers[ | Steam/900 ℃ | 0.54/0.76 | 1284/1614 | 256.1/325.8 |
| Cotton[ | H3PO4+Microwave | 0.98 | 1370 | 476.2 |
| Cashew nut shell[ | ZnCl2/400 ℃ | 0.973 | 1478 | 476 |
| Arundo donax[ | ZnCl2/400 ℃ | 1.113 | 1784 | 416.7 |
| Sawdust[ | KOH/1000 ℃ | 1.27 | 2254 | 303.03 |
| Bamboo shoots[ | KHCO3/700 ℃/800 ℃ | 0.73/1.25 | 1476/2271 | 458 |
| Bagasse/Cluster stalks[ | KOH/1300 ℃ | 0.82/1.4 | 1861/2662 | 714.3/925.9 |
| This work | KOH/800 ℃/900 ℃ | 1.829/3.164 | 3366/3600 | 919/983 |
Table S1 Comparison of activator, SSABET, total pore volume and qm (the maximum adsorption of MB) between RHACs and other AC prepared from biomass
| Biomass | Activator | Pore volume/(cm3•g-1) | SSABET/(m2•g-1) | qm/(mg•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco stalks[ | ZnCl2+Microwave | 0.45 | 684.68 | 123.45 |
| Dipterocarpus alatus[ | ZnCl2/500 ℃ | 0.473 | 843 | 269.3 |
| Sugar beet pulp[ | H3PO4/450 ℃ | 0.445 | 1029.3 | 250.0 |
| Palm kernel shell[ | ZnCl2/550 ℃ | 0.571 | 1058 | 225.3 |
| Rice by-products[ | H3PO4/450 ℃ | 0.612/0.607 | 814/1000 | 246.9/213.7 |
| Viscose fibers[ | Steam/900 ℃ | 0.54/0.76 | 1284/1614 | 256.1/325.8 |
| Cotton[ | H3PO4+Microwave | 0.98 | 1370 | 476.2 |
| Cashew nut shell[ | ZnCl2/400 ℃ | 0.973 | 1478 | 476 |
| Arundo donax[ | ZnCl2/400 ℃ | 1.113 | 1784 | 416.7 |
| Sawdust[ | KOH/1000 ℃ | 1.27 | 2254 | 303.03 |
| Bamboo shoots[ | KHCO3/700 ℃/800 ℃ | 0.73/1.25 | 1476/2271 | 458 |
| Bagasse/Cluster stalks[ | KOH/1300 ℃ | 0.82/1.4 | 1861/2662 | 714.3/925.9 |
| This work | KOH/800 ℃/900 ℃ | 1.829/3.164 | 3366/3600 | 919/983 |
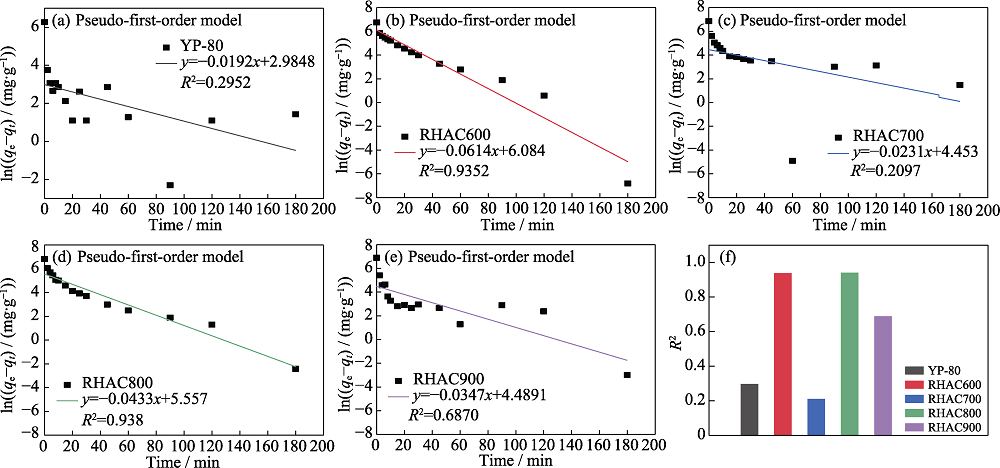
Fig. S3 Linear fits of the pseudo-first-order models for five carbons: (a) YP-80, (b) RHAC600,(c) RHAC700, (d) RHAC800, (e) RHAC900 and (f) correlation coefficients
| Sample | qe(exp)/(mg•g-1) | q1(cal)/(mg•g-1) | Percentual difference, (qe-q1)/% | k1/min-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP-80 | 525 | 19.8 | 96.23 | 0.0192 | |
| RHAC600 | 851 | 438.8 | 48.44 | 0.0614 | |
| RHAC700 | 935 | 85.9 | 90.81 | 0.0231 | |
| RHAC800 | 919 | 259 | 71.82 | 0.0433 | |
| RHAC900 | 983 | 89 | 90.95 | 0.0347 | |
Table S2 Kinetic parameters obtained by the pseudo-first-order model for RHACs and YP-80 for the adsorption of MB
| Sample | qe(exp)/(mg•g-1) | q1(cal)/(mg•g-1) | Percentual difference, (qe-q1)/% | k1/min-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP-80 | 525 | 19.8 | 96.23 | 0.0192 | |
| RHAC600 | 851 | 438.8 | 48.44 | 0.0614 | |
| RHAC700 | 935 | 85.9 | 90.81 | 0.0231 | |
| RHAC800 | 919 | 259 | 71.82 | 0.0433 | |
| RHAC900 | 983 | 89 | 90.95 | 0.0347 | |
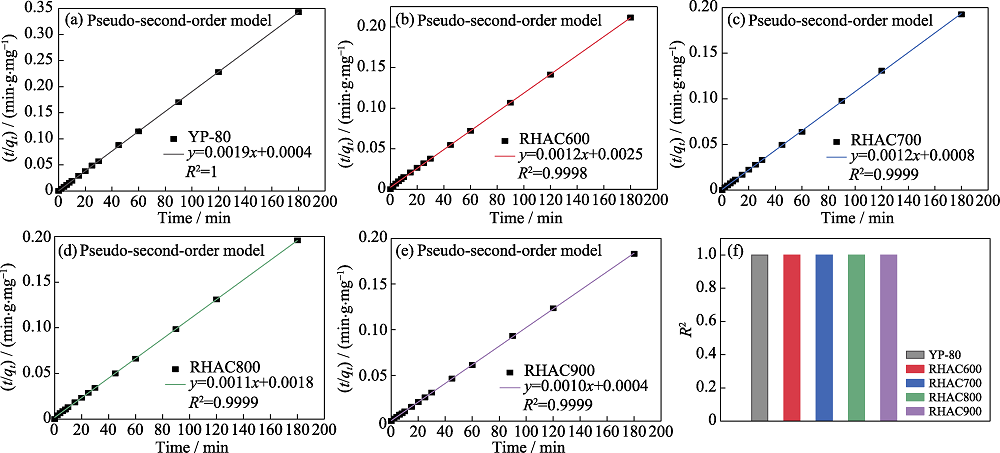
Fig. 4 Linear fits of the pseudo-second-order models for the adsorption of MB on (a) YP-80, (b) RHAC600, (c) RHAC700, (d) RHAC800, (e) RHAC900, and (f) corresponding correlation coefficients
| Sample | qe (exp)/ (mg•g-1) | q2(cal)/ (mg•g-1) | Percentual difference (qe-q2)/% | k2/(g•mg-1•min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP-80 | 525 | 526.3 | -0.25 | 0.0090 |
| RHAC600 | 851 | 833.3 | 2.08 | 0.0006 |
| RHAC700 | 935 | 833.3 | 10.88 | 0.0018 |
| RHAC800 | 919 | 909.1 | 1.08 | 0.0007 |
| RHAC900 | 983 | 1000 | -1.73 | 0.0025 |
Table 2 Kinetic parameters obtained of RHACs and YP-80 by the pseudo-second-order model for the adsorption of MB
| Sample | qe (exp)/ (mg•g-1) | q2(cal)/ (mg•g-1) | Percentual difference (qe-q2)/% | k2/(g•mg-1•min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YP-80 | 525 | 526.3 | -0.25 | 0.0090 |
| RHAC600 | 851 | 833.3 | 2.08 | 0.0006 |
| RHAC700 | 935 | 833.3 | 10.88 | 0.0018 |
| RHAC800 | 919 | 909.1 | 1.08 | 0.0007 |
| RHAC900 | 983 | 1000 | -1.73 | 0.0025 |
| RHBC | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 19.48 | 95.18 | 97.21 | 94.16 | 95.63 |
| O | 35.59 | 4.82 | 2.79 | 3.15 | 2.28 |
| Si | 40.73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ca | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table S3 Element analysis of RHBC, RHAC600, RHAC700, RHAC800 and RHAC900 by EDS/wt%
| RHBC | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 19.48 | 95.18 | 97.21 | 94.16 | 95.63 |
| O | 35.59 | 4.82 | 2.79 | 3.15 | 2.28 |
| Si | 40.73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ca | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| RH | RHBC | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before/mg | 2502.0 | 1002.4 | 148.1 | 76.3 | 88.7 | 53.9 |
| After/mg | 375.0 | 330.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ash content/% | 14.99 | 32.92 | — | — | — | — |
Table S4 Mass and ash content of RH, RHBC, RHAC600, RHAC700, RHAC800 and RHAC900 before and after calcination
| RH | RHBC | RHAC600 | RHAC700 | RHAC800 | RHAC900 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before/mg | 2502.0 | 1002.4 | 148.1 | 76.3 | 88.7 | 53.9 |
| After/mg | 375.0 | 330.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ash content/% | 14.99 | 32.92 | — | — | — | — |
| [1] |
MENYA E, OLUPOT P W, STORZ H, et al. Production and performance of activated carbon from rice husks for removal of natural organic matter from water: a review. Chemical Engineering Research and Design , 2018, 129:271-296.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YAGUB M T, SEN T K, AFROZE S, et al. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science , 2014, 209:172-84.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHOU Y, LU J, ZHOU Y, et al. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environmental Pollution , 2019, 252:352-365.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SILVA L A D, BORGES S M S, PAULINO P N, et al. Methylene blue oxidation over iron oxide supported on activated carbon derived from peanut hulls. Catalysis Today , 2017, 289:237-248.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GUO Z, XIAO Z, REN G, et al. Natural tea-leaf-derived, ternary- doped 3D porous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Research , 2016, 9(5):1244-1255.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DUAN X, SRINIVASAKANNAN C, WANG X, et al. Synthesis of activated carbon fibers from cotton by microwave induced H3PO4 activation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers , 2017, 70:374-381.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TAN I A W, AHMAD A L, HAMEED B H. Adsorption of basic dye on high-surface-area activated carbon prepared from coconut husk: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials , 2008, 154(1-3):337-346.
DOI URL |
| [8] | CHOMA J, OSUCHOWSKI L, MARSZEWSKI M, et al. Developing microporosity in Kevlar®-derived carbon fibers by CO2 activation for CO2 adsorption. Journal of CO2 Utilization , 2016, 16:17-22. |
| [9] | LIU Q X, ZHOU Y R, WANG M, et al. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto viscose-based activated carbon fiber felts: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Adsorption Science & Technology , 2019, 37(3-4):312-332. |
| [10] |
PATAWAT C, SILAKATE K, CHUAN-UDOM S, et al. Preparation of activated carbon from Dipterocarpus alatus fruit and its application for methylene blue adsorption. RSC Advances , 2020, 10(36):21082-21091.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHU G, XING X, WANG J, ET AL. Effect of acid and hydrothermal treatments on the dye adsorption properties of biomass- derived activated carbon. Journal of Materials Science , 2017, 52(13):7664-7676.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI D, YAN J, LIU Z, et al. Adsorption kinetic studies for removal of methylene blue using activated carbon prepared from sugar beet pulp. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology , 2016, 13(7):1815-1822.
DOI URL |
| [13] | MUDYAWABIKWA B, MUNGONDORI H H, TICHAGWA L, et al. Methylene blue removal using a low-cost activated carbon adsorbent from tobacco stems: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Science & Technology , 2017, 75(10):2390-2402. |
| [14] |
MI B, WANG J, XIANG H, et al. Nitrogen self-doped activated carbons derived from bamboo shoots as adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption. Molecules , 2019, 24(16):3012.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG Z, SMITH A T, WANG W, et al. Versatile nanostructures from rice husk biomass for energy applications. Angewandte Chemie International Edition , 2018, 57(42):13722-13734.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CHEN Z, XU Y, SHIVKUMAR S. Microstructure and tensile properties of various varieties of rice husk. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture , 2018, 98(3):1061-1070.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHEN Z, WANG X, XUE B, et al. Rice husk-based hierarchical porous carbon for high performance supercapacitors: The structure- performance relationship. Carbon , 2020, 161:432-444.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ISLAM M A, AHMED M J, KHANDAY W A, et al. Mesoporous activated carbon prepared from NaOH activation of rattan (Lacosperma secundiflorum) hydrochar for methylene blue removal. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety , 2017, 138:279-285.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ISLAM M A, SABAR S, BENHOURIA A, et al. Nanoporous activated carbon prepared from karanj (Pongamia pinnata) fruit hulls for methylene blue adsorption. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers , 2017, 74:96-104.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BASTA A H, LOTFY V F, HASANIN M S, et al. Efficient treatment of rice byproducts for preparing high-performance activated carbons. Journal of Cleaner Production , 2019, 207:284-295.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HE X, LING P, YU M, et al. Rice husk-derived porous carbons with high capacitance by ZnCl2 activation for supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta , 2013, 105:635-641.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LOZANO-CASTELLÓ D, CALO J M, CAZORLA-AMORÓS D, et al. Carbon activation with KOH as explored by temperature programmed techniques, and the effects of hydrogen. Carbon , 2007, 45(13):2529-2536.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GAO Y, LI L, JIN Y, et al. Porous carbon made from rice husk as electrode material for electrochemical double layer capacitor. Applied Energy , 2015, 153:41-47.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LI C, HE D, HUANG Z H, et al. Hierarchical micro-/mesoporous carbon derived from rice husk by hydrothermal pre-treatment for high performance supercapacitor. Journal of The Electrochemical Society , 2018, 165(14):A3334-A3341.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SPAGNOLI A A, GIANNAKOUDAKIS D A, BASHKOVA S. Adsorption of methylene blue on cashew nut shell based carbons activated with zinc chloride: the role of surface and structural parameters. Journal of Molecular Liquids , 2017, 229:465-471.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
VADIVELAN V, KUMAR K V. Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science , 2005, 286(1):90-100.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ÜNER O. Hydrogen storage capacity and methylene blue adsorption performance of activated carbon produced from Arundo donax. Materials Chemistry and Physics , 2019, 237:121852.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ORLANDI G, CAVASOTTO J, MACHADO F R, et al. An adsorbent with a high adsorption capacity obtained from the cellulose sludge of industrial residues. Chemosphere , 2017, 169:171-180.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
MAHMOUDI K, HOSNI K, HAMDI N, et al. Kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of methylene blue and methyl orange by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from date pits-A comparative study. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering , 2014, 32(2):274-283.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 魏建文, 张丽娟, 耿琳琳, 李誉, 廖雷, 王敦球. 以ZSM-5/MCM-48为载体制备新型高容量CO2吸附剂的性能及机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | 洪培萍, 梁龙, 吴炼, 马颖康, 庞浩. ZIF-67结构调控及其对盐酸金霉素的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [4] | 吴光宇, 舒松, 张洪伟, 李建军. 接枝内酯基活性炭增强苯乙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [5] | 谢天, 宋二红. 弹性应变对C、H、O在过渡金属氧化物表面吸附的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [6] | 晁少飞, 薛艳辉, 吴琼, 伍复发, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, 张伟. MXene异质结Ti-O-H-O电子快速通道促进高效率储钾[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [7] | 蔡梦宇, 李杨虹淼, 杨彩云, 周雨婷, 吴昊. 基于活性污泥焚灰的类Fenton催化剂的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142. |
| [8] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [9] | 郭春霞, 陈伟东, 闫淑芳, 赵学平, 杨傲, 马文. 埃洛石纳米管负载锆氧化物吸附水中砷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [10] | 王世怡, 冯爱虎, 李晓燕, 于云. Fe3O4负载Ti3C2Tx对Pb(II)的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [11] | 于业帆, 徐玲, 倪忠斌, 施冬健, 陈明清. 普鲁士蓝/生物炭材料的制备及其氨氮吸附机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [12] | 凌洁, 周安宁, 王文珍, 贾忻宇, 马梦丹. Cu/Mg比对Cu/Mg-MOF-74的CO2吸附性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [13] | 汤亚, 孙盛睿, 樊佳, 杨庆峰, 董满江, 寇佳慧, 刘阳桥. 粉煤灰衍生水合硅酸钙PEI改性及吸附去除Cu(II)与催化降解有机污染物[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [14] | 王梦桃, 索军, 方东, 易健宏, 刘意春, Olim RUZIMURADOV. ITO/TiO2纳米管阵列复合材料的可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1292-1300. |
| [15] | 戴洁燕, 冯爱虎, 米乐, 于洋, 崔苑苑, 于云. NaY沸石分子吸附涂层对典型空间污染物的吸附机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||