无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 337-345.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160269 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20160269
• • 下一篇
张 瑞1,2,3, 王伯阳1, 王 海1,2,3
收稿日期:2016-04-19
修回日期:2016-06-08
出版日期:2017-04-20
网络出版日期:2017-03-24
基金资助:ZHANG Rui1,2,3, Wang Bo-Yang1, WANG Hai1,2,3
Received:2016-04-19
Revised:2016-06-08
Published:2017-04-20
Online:2017-03-24
Supported by:摘要:
荧光粉/玻璃复合材料(Phosphor-in-Glass, PiG)具有优异的发光性能、导热性和化学稳定性, 将有望替代传统白光LED产品中的有机树脂基荧光转换层, 同时解决散热、发光效率、品质、眩光、使用寿命等多项技术性难题, 具有广阔的市场应用前景。本文从发光性能、透明度、机械强度及批量化生产等方面分析了PiG材料研究过程中出现的关键科学问题, 并综述了解决上述问题所采取的针对性措施, 包括制备方法(压片烧结法、熔体急冷法、涂膜烧结法)、材料组分设计和荧光粉层结构优化等, 从而全面阐述了高性能PiG材料的最新研究现状, 最后展望了其未来的研究趋势。
中图分类号:
张 瑞, 王伯阳, 王 海. 白光LED用Phosphor-in-Glass荧光材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 337-345.
ZHANG Rui, Wang Bo-Yang, WANG Hai. Advances in Phosphor-in-Glass for White LED[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 337-345.
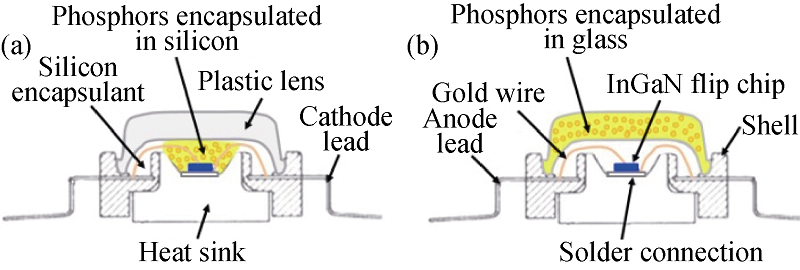
图1 SMT型大功率白光LED的结构示意图
Fig. 1 Comparative structural schematic diagrams of SMT typed high powered white LEDs(a) Traditional organic resin based[4]; (b) Glass ceramic based[5-8]
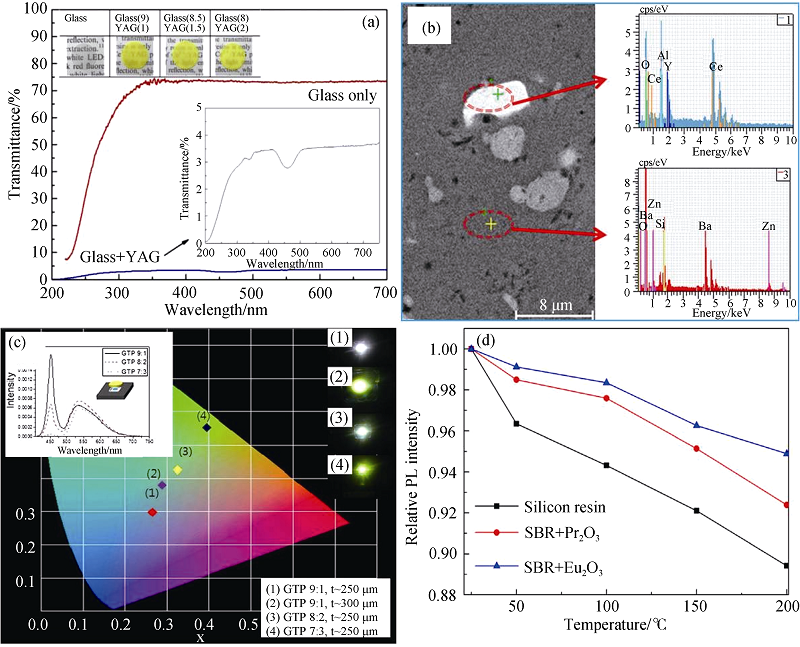
图2 PiG样品的透射光谱(a)和SEM照片(b), 不同YAG掺杂浓度和样品厚度的PiG基LED器件的发射光谱(c), PiG和硅胶基LED器件的发光热猝灭曲线(d)[16-18]
Fig. 2 Transmittance spectra (a) and SEM image (b) of PiG samples, emission spectra of PiG based LED with different YAG contents or thicknesses (c), and thermal-quenching results of WLEDs with PiGs or commercial silicone resin (d)[16-18]
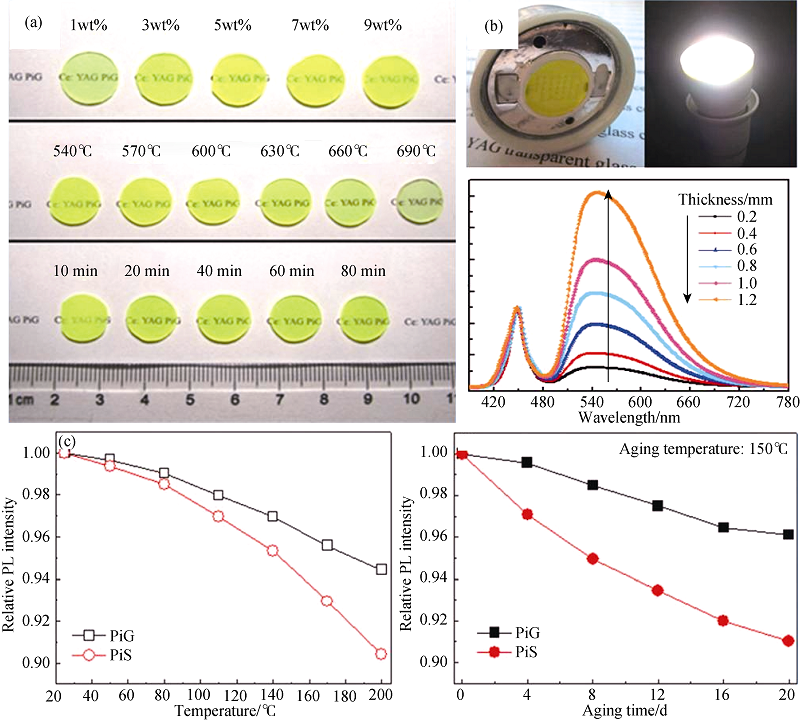
图3 (a)不同制备条件下的PiG, (b) PiG基LED器件及不同厚度的发射光谱, (c) PiG与PiS的耐热性与耐候性测试[31]
Fig. 3 Photographs of PiG prepared via different conditions (a), the images and emission spectra of different thicked PiG based LED (b), and the temperature dependent and heat resistance test for PiG and PiS (c)[31]
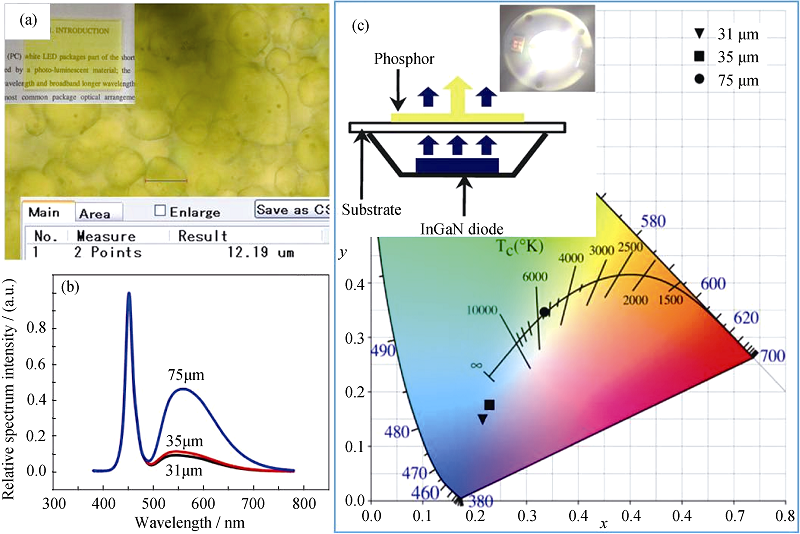
图4 PiG荧光板的显微图像(a), 不同荧光粉层厚度PiG基LED器件的归一化发射光谱(b)和色坐标(c)[39]
Fig. 4 Optical microstructure of PiG (a), normalized emission spectra (b) and CIE color coordinate (c) of PiG based LED with different phosphor thicknesses[39]
| Precursor glass composition | Phosphors | References |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2-R2O3-R’O-R”2O (R = B, Al, La), (R’ = Zn, Ca, Ba), (R” = Li, K) | Ce3+:Lu3Al5O12 (green) Eu2+: SrGa2S4 (green) Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Eu2+: CaAlSiN3 (red) | [14, 16-23, 26, 44, 45-47] |
| B2O3-R2O3-ZnO-K2O (R = Bi, Al, Sb) | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Eu2+: (Ba,Sr,Ca)2SiO4 (yellow) Eu2+: CaAlSiN3 (red) | [25, 34-35, 40-41] |
| TeO2-R2O3-ZnO-R”2O (R = B, Bi, Al, Sb) (R” = Na, K) | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Ce3+, Mn2+, Si4+: YAG (orange) | [27-28, 31-33, 36] |
| SiO2-B2O3-PbO-ZnO | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) | [24, 37-39, 42, 46] |
| P2O5-R’O (R’= Zn, Ca, Ba) | Eu2+: Ca-α-SiAlON (yellow) | [29] |
| Nano SiO2 or B2O3 | Eu2+: Ca-α-SiAlON (yellow) | [30] |
表1 玻璃基体、荧光粉的种类及发光颜色
Table 1 Glass matrix, phosphors and their luminescent color
| Precursor glass composition | Phosphors | References |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2-R2O3-R’O-R”2O (R = B, Al, La), (R’ = Zn, Ca, Ba), (R” = Li, K) | Ce3+:Lu3Al5O12 (green) Eu2+: SrGa2S4 (green) Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Eu2+: CaAlSiN3 (red) | [14, 16-23, 26, 44, 45-47] |
| B2O3-R2O3-ZnO-K2O (R = Bi, Al, Sb) | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Eu2+: (Ba,Sr,Ca)2SiO4 (yellow) Eu2+: CaAlSiN3 (red) | [25, 34-35, 40-41] |
| TeO2-R2O3-ZnO-R”2O (R = B, Bi, Al, Sb) (R” = Na, K) | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) Ce3+, Mn2+, Si4+: YAG (orange) | [27-28, 31-33, 36] |
| SiO2-B2O3-PbO-ZnO | Ce3+: YAG (yellow) | [24, 37-39, 42, 46] |
| P2O5-R’O (R’= Zn, Ca, Ba) | Eu2+: Ca-α-SiAlON (yellow) | [29] |
| Nano SiO2 or B2O3 | Eu2+: Ca-α-SiAlON (yellow) | [30] |
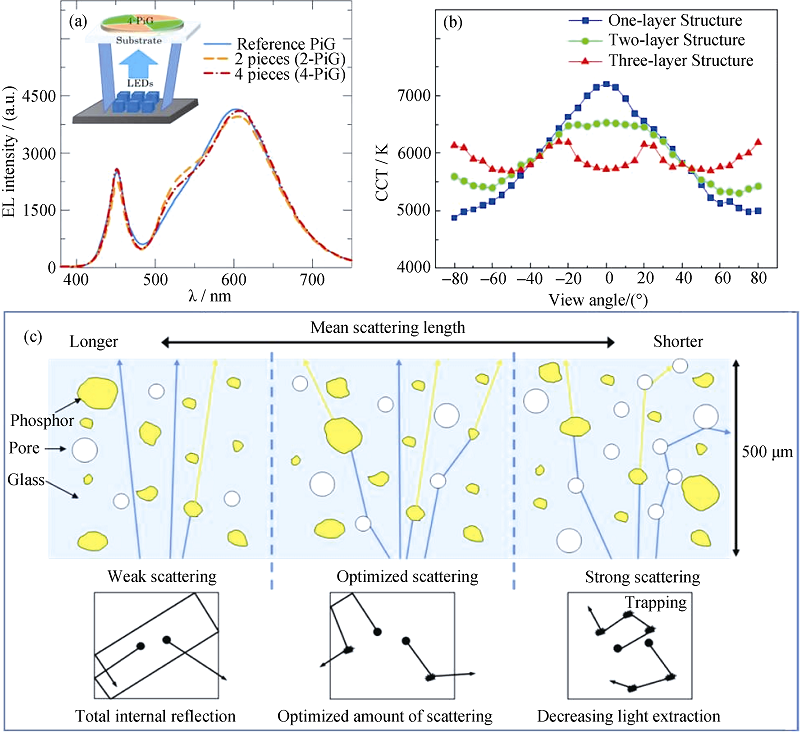
图5 (a)多组块PiG远程LED器件的电致发光光谱[14], (b)不同荧光粉层结构的LED器件的空间色温分布[46]和(c)基于平均散射长度/散射类型的荧光粉与蓝光之间的相互作用[47]
Fig. 5 (a) EL spectra of reference and multi-PiGs mounted on a remote-type configuration[14], (b) measurements of angular color distributions of LEDs with different layer cone-shaped PiG[46], and (c) interaction between phosphor and blue light based on the mean scattering length and scattering type[47]
| [1] | TAGUCHI T.Present status of white LED lighting technologies in Japan. Journal of Light & Visual Environment, 2003, 27(3): 131-139. |
| [2] | YE S, XIAO F, PAN Y X, et al.Phosphors in phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes: recent advances in materials, technique and properties. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2010, 71: 1-34. |
| [3] | XIE R J, HIROSAKI N.Silicon-based oxynitride and nitride phosphors for white LEDs-a review. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2007, 8: 588-600. |
| [4] | NAKAMURA S, FASOL G.The Blue Laser Diode: GaN Based Light Emitters and Lasers. Springer, Berlin, 1997. |
| [5] | FERGUSON I T, FUJITA S, CARRANO J C, et al.YAG glass- ceramic phosphor for white LED (I): background and development. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5941: 594111. |
| [6] | FERGUSON I T, TANABE S, CARRANO J C, et al.YAG glass-ceramic phosphor for white LED (II): Luminescence characteristics. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5941: 594112. |
| [7] | FUJITA S, TANABE S.Thermal quenching of Ce3+: Y3Al5O12 glass- ceramic phosphor. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 48: 120210. |
| [8] | FUJITA S, UMAYAHARA Y, TANABE S.Influence of light scattering on luminous efficacy in Ce: YAG glass-ceramic phosphor. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2010, 118(2): 128-131. |
| [9] | WOODROW S.Remote Phosphor Brings Higher Efficacy to Area Lighting. LEDs Magazine, April 2013. |
| [10] | CHANG L B, PAN K W, YEN C Y, et al.Comparison of silicone and spin-on glass packaging materials for light-emitting diode encapsulation. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 570: 496-499. |
| [11] | XIAO Y H, LV Y J, XU Y X, et al.The difference of luminous performance between traditional phosphor packaging LED and remote phosphor LED. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2014, 35(1): 66-72. |
| [12] | CHEN D Q, XIANG W D, LIANG X J, et al.Advances in transparent glass-ceramic phosphors for white light-emitting diodes-a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(3): 859-869. |
| [13] | SAKUMA K, OMICHI K, KIMURA N, et al.Warm-white light-emitting diode with yellowish orange SiAlON ceramic phosphor. Optics Letters, 2004, 29: 2001-2003. |
| [14] | LEE J S, ARUNKUMAR P, KIM S, et al.Smart design to resolve spectral overlapping of phosphor-in-glass for high-powered remote type white light-emitting devices. Optics Letters, 2014, 39: 762-765. |
| [15] | SNOWDON S C.Light Scattering by Small Particles: by H. C. van de Hulst. New York, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1957, 264: 248-249. |
| [16] | LEE Y K, LEE J S, HEO J, et al.Phosphor in glasses with Pb-free silicate glass powders as robust color-converting materials for white LED applications. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(15): 3276-3278. |
| [17] | KIM C, PARK H A, JANG H W, et al.All-in-one-type organic light-emitting diodes for color tuning using phosphor in glasses with Pb-free silicate powders. Current Applied Physics, 2014, 14(12): 1677-1681. |
| [18] | PARK H A, LEE Y K, IM W B, et al.Phosphor in glass with Eu3+ and Pr3+-doped silicate glasses for LED color conversion. Optical Materials, 2015, 41: 67-70. |
| [19] | LEE Y K, KIM Y H, HEO J, et al.Control of chromaticity by phosphor in glasses with low temperature sintered silicate glasses for LED applications. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(14): 4084-4087. |
| [20] | CHEN L Y, CHANG J K, WU Y R, et al.Optical model for novel glass-based phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes. Journal of Display Technology, 2013, 9(6): 441-446. |
| [21] | CHEN L Y, CHENG W C, TSAI C C, et al.High-performance glass phosphor for white-light-emitting diodes via reduction of Si-Ce3+: YAG inter-diffusion. Optical Materials Express, 2014, 4(1): 121-128. |
| [22] | TSAI C C.Color rendering index thermal stability improvement of glass-based phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes for solid-state lighting. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2014, 2014: 1-6. |
| [23] | TSAI C C.Thermal aging performance analyses of high color rendering index of glass-based phosphor-converted white-light-emitting diode. Ieee Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2015, 15(4): 617-620. |
| [24] | YI S, CHUNG W J, HEO J.Stable and color-tailorable white light from blue leds using color-converting phosphor-glass composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(2): 342-345. |
| [25] | LIU G, TIAN Z, CHEN Z, et al.CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphors bonding with bismuth borate glass for high power light excitation. Optical Materials, 2015, 40: 63-67. |
| [26] | LEE J S, UNITHRATTIL S, KIM S, et al.Robust moisture and thermally stable phosphor glass plate for highly unstable sulfide phosphors in high-power white light-emitting diodes. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(17): 3298-3300. |
| [27] | SEGAWA H, OGATA S, HIROSAKI N, et al.Fabrication of glasses of dispersed yellow oxynitride phosphor for white light emitting diodes. Optical Materials, 2010, 33(2): 170-175. |
| [28] | SEGAWA H, HIROSAKI N.Europium-doped SiAlON and borosilicate glass composites for white light-emitting diode, Applied Optics, 2015, 54: 8727-8730. |
| [29] | SEGAWA H, HIROSAKI N, OHKI S, et al.Exploration of metaphosphate glasses dispersed with Eu-doped SiAlON for white LED applications. Optical Materials, 2015, 42: 399-405. |
| [30] | MAO Z Y, ZHU Y C, GAN L, et al.Novel white-light-emitting SiAlON-crystal/glass composite phosphor prepared by facile strategy for white light-emitting-diode. Materials Letters, 2012, 80: 63-65. |
| [31] | ZHANG R, LIN H, YU Y L, et al.A new-generation color converter for high-power white LED: transparent Ce3+: YAG phosphor-in- glass. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2014, 8(1): 158-164. |
| [32] | CHEN H, LIN H, XU J, et al.Chromaticity-tunable phosphor-in- glass for long-lifetime high-power warm w-LEDs. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3(31): 8080-8089. |
| [33] | LIN Z B, LIN H, XU J, et al.Highly thermal-stable warm w-LED based on Ce: YAG PiG stacked with a red phosphor layer. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 649: 661-665. |
| [34] | CHEN D Q, CHEN Y.Transparent Ce3+: Y3Al5O12 glass ceramic for organic-resin-free white-light-emitting diodes. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(9): 15325-15329. |
| [35] | ZHOU Y, CHEN D Q, TIAN W, et al.Impact of Eu3+ dopants on optical spectroscopy of Ce3+: Y3Al5O12-embedded transparent glass-ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(8): 2445-2450. |
| [36] | CHEN D Q, ZHOU Y, XU W, et al.Enhanced luminescence of Mn4+: Y3Al5O12 red phosphor via impurity doping. J. Mater. Chem., 2016, 4: 1704-1712. |
| [37] | HUANG J, HU X L, SHEN J J, et al.Facile synthesis of a thermally stable Ce3+: Y3Al5O12 phosphor-in-glass for white LEDs. CrystEngComm, 2015, 17(37): 7079-7085. |
| [38] | GONG M G, LIANG X J, WANG Y Y, et al.Novel synthesis and optical characterization of phosphor-converted WLED employing Ce: YAG-doped glass. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 664: 125-132. |
| [39] | YANG L, CHEN M, LV Z, et al.Preparation of a YAG: Ce phosphor glass by screen-printing technology and its application in LED packaging. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(13): 2240-2243. |
| [40] | KIM J S, KWON O H, JANG J W, et al.Long-term stable, low-temperature remote silicate phosphor thick films printed on a glass substrate. ACS Combinatorial Science, 2015, 17(4): 234-238. |
| [41] | JANG J W, KIM J S, KWON O H, et al.UV-curable silicate phosphor planar films printed on glass substrate for white light emitting diodes. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(16): 3723-3726. |
| [42] | WANG F Y, LIN Y, SHI H, et al.Introduction on the fabrication technique of phosphor in glass by tape-casting and investigation on the chromaticity property. Optics Express, 2014, 22(17): 1355-1362. |
| [43] | SHVALEVA M A, SHULGA E, KINK I, et al.Na2SiO3 liquid glass-based phosphor material for white LEDs. Physica Status Solidi (a), 2015, 212(12): 2964-2967. |
| [44] | SEO J, KIM S, KIM Y, et al.Effect of glass refractive index on light extraction efficiency of light-emitting diodes. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(9): 2789-2793. |
| [45] | XU J, HASSAN D A, ZENG R J, et al.Lu3Al5O12: Ce @SiO2 phosphor-in-glass: Its facile synthesis, reduced thermal/chemical degradation and application in high-power white LEDs. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36: 2017-2025. |
| [46] | WANG S, CHEN X, CHEN M, et al.Improvement in angular color uniformity of white light-emitting diodes using screen- printed multilayer phosphor-in-glass. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(36): 8492-8498. |
| [47] | KIM S, YIE H, CHOI S, et al.Pore characteristics for improving luminous efficacy of phosphor-in-glass. Optics Express, 2015, 23(24): 1499-1511. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 潘泽晟, 游雅萍, 郑雅, 陈海杰, 王连军, 江莞. 面向紫光激发白光LED用荧光材料的耐候性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 314-322. |
| [12] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [13] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [14] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [15] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||