无机材料学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 571-583.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2014.13506 CSTR: 32189.14.SP.J.1077.2014.13506
刘 岗1,2, 严 岩1
收稿日期:2013-10-01
修回日期:2013-11-29
出版日期:2014-06-20
网络出版日期:2014-05-27
作者简介:刘 岗(1980-), 男, 博士. E-mail: liugangswu@126.com
基金资助:LIU Gang1,2, YAN Yan1
Received:2013-10-01
Revised:2013-11-29
Published:2014-06-20
Online:2014-05-27
About author:LIU Gang. E-mail: liugangswu@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
冷冻干燥法作为一种制备多孔材料的技术在过去的十多年中发展迅速, 尤其是通过此法制得的多孔陶瓷展现出独特的微观结构和优良的力学性能, 引起了各国学者极大的研究兴趣, 成为当前多孔陶瓷的一个研究热点。 本文目的是回顾冷冻干燥技术的发展历史, 详细介绍了冷冻干燥技术的基本原理、特点, 工艺过程的影响因素, 以及潜在应用, 并指出了冷冻干燥法的发展趋势。
中图分类号:
刘 岗, 严 岩. 冷冻干燥法制备多孔陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(6): 571-583.
LIU Gang, YAN Yan. Research Progress of Porous Ceramics Produced by Freeze Casting Technique[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(6): 571-583.
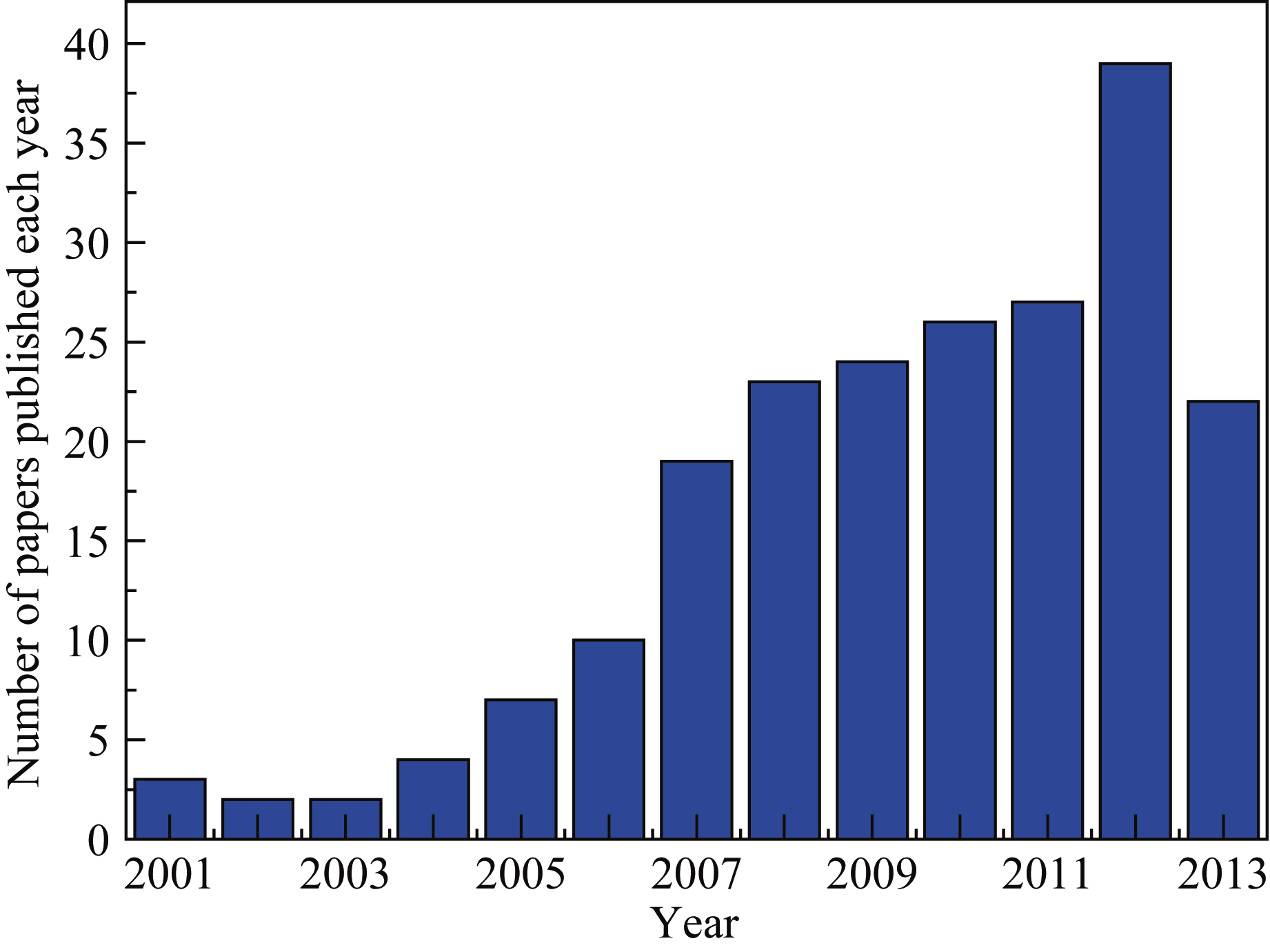
图1 冷冻干燥法制备多孔陶瓷近13年来论文发表数量(截止到2013年9月)
Fig. 1 Annually published papers on freeze casting of porous ceramics from Jan. 2001 to Sep. 2013 based on Web of ISI
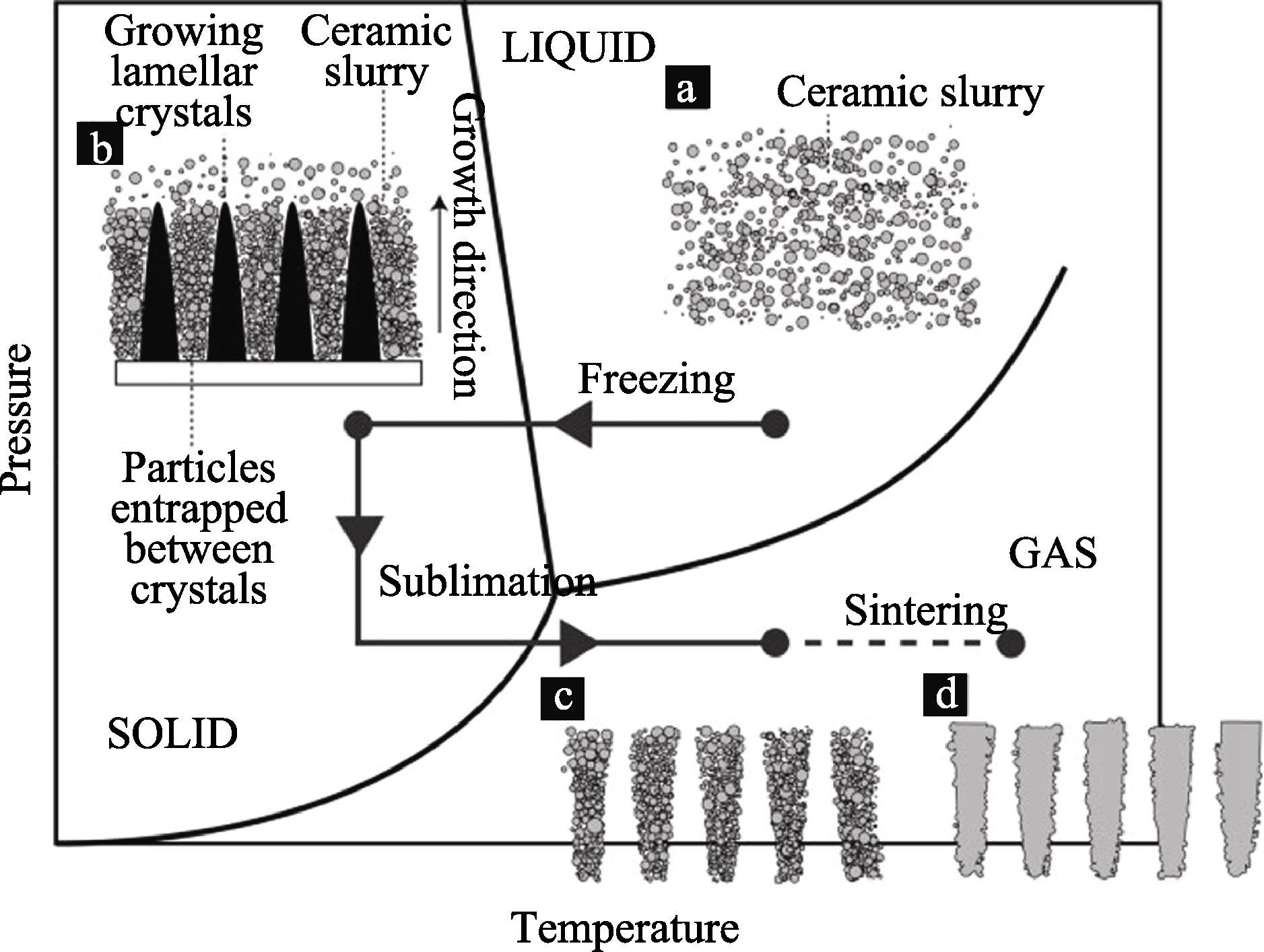
图2 冷冻干燥法四个基本步骤: 浆料的制备、冷冻、升华和烧结[19]
Fig. 2 The four processing steps of freeze-casting: slurry preparation, solidification, sublimation and sintering[19]
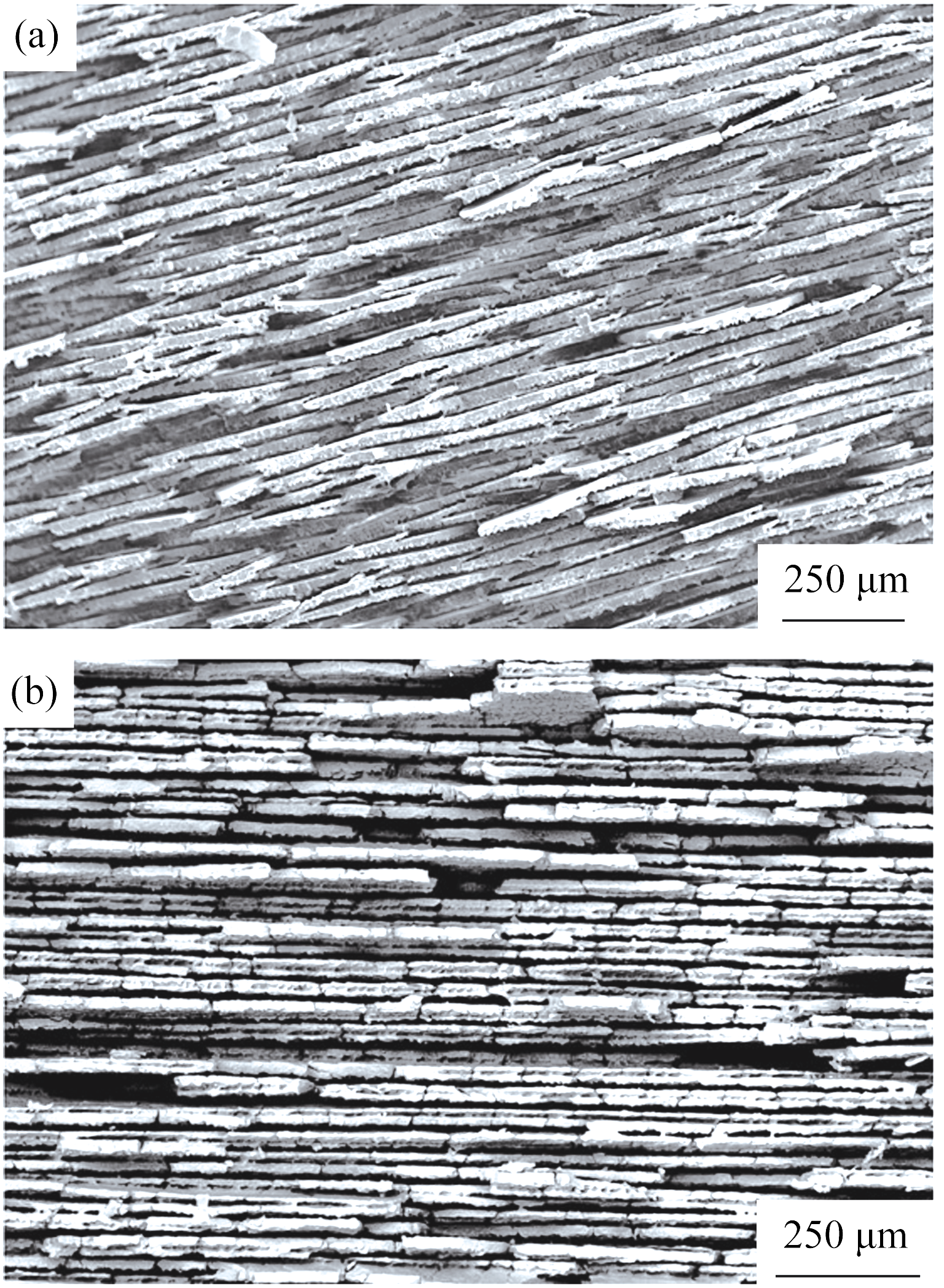
图8 典型的以水为溶剂获得的多孔氧化铝SEM照片[21]
Fig. 8 Typical cross-section SEM images of porous alumina obtained by water-based freeze casting[21] (a) Ice growth direction perpendicular to the page; (b) Ice growth direction from bottom to top
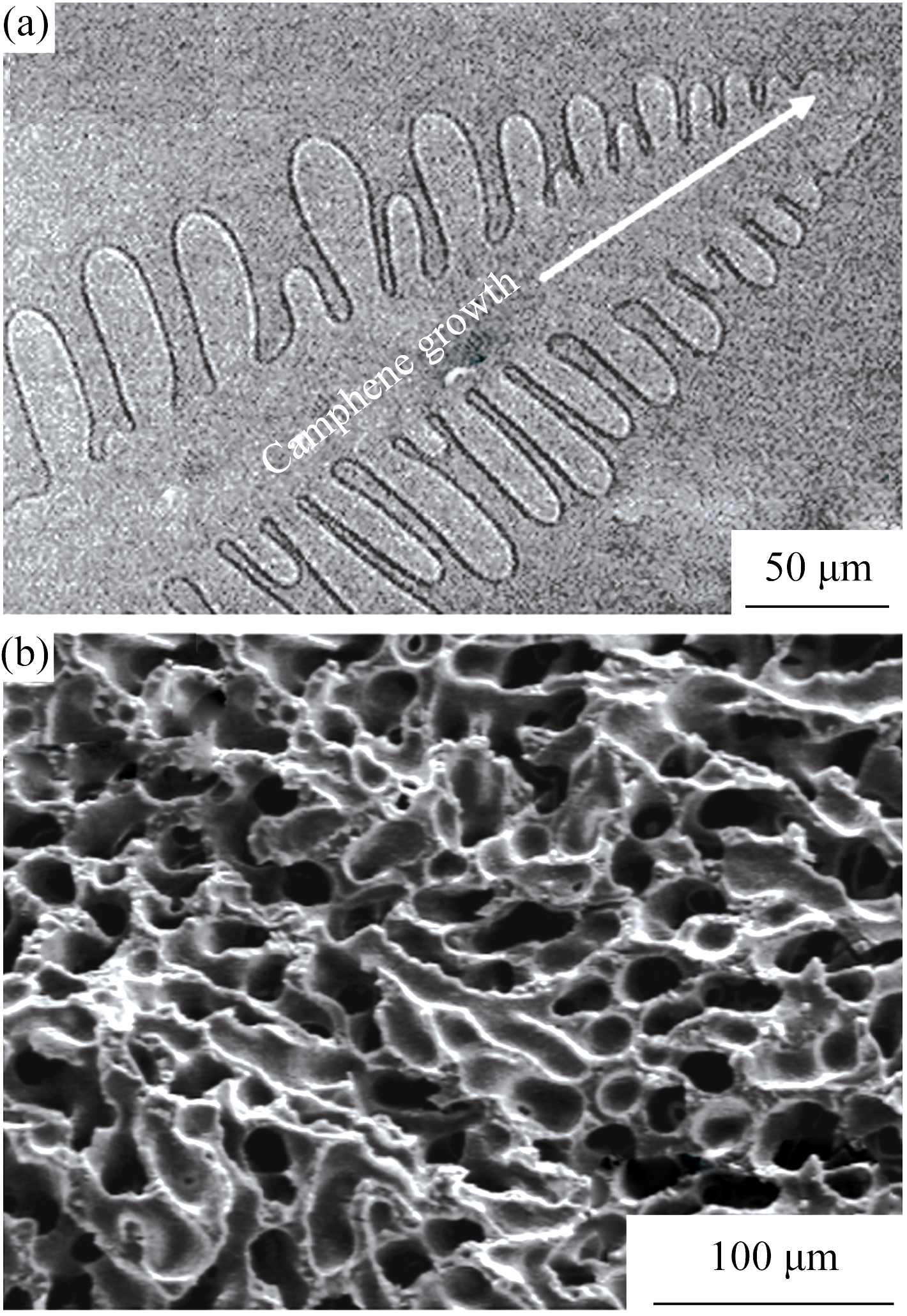
图9 固化中的莰烯形成的树枝状结构(a)及以此为溶剂获得的多孔氧化铝(b)
Fig. 9 Dentritic structure during solidification of camphene]43] (a) and typical SEM images of porous alumina obtained by camphene-based freeze casting (b)[20]

图10 多孔氧化铝-氧化锆复合物扫描电镜截面照片, 固相含量分别为40wt% (a)、50wt% (b)、60wt% (c)、70wt% (d)和80wt% (e)[23]
Fig. 10 Cross-sectional SEM images of the Al2O3-ZrO2 composite ceramics obtained from slurries with different initial solids loading[23] (a) 40wt%; (b) 50wt%; (c) 60wt%; (d) 70wt%; (e) 80wt%. Solidification direction is perpendicular to the page
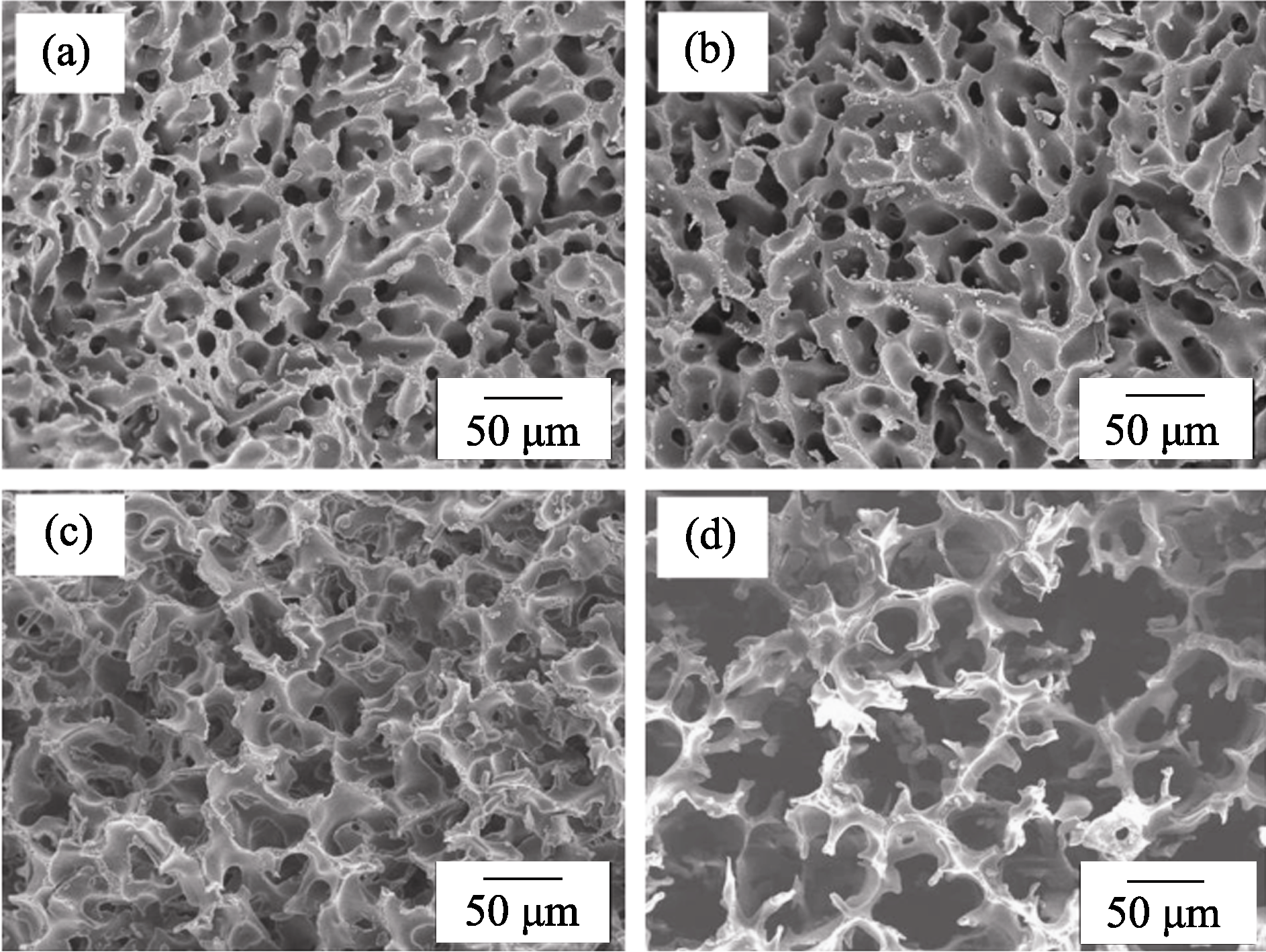
图11 多孔氧化铝陶瓷扫描电镜照片[44]
Fig. 11 SEM images of the porous alumina ceramics sintered at 1400℃ for 5 h with initial solid loadings of 20vol%(a), 15vol%(b), 10vol%(c), and 5vol% (d), showing porous structures at low magnification[44]
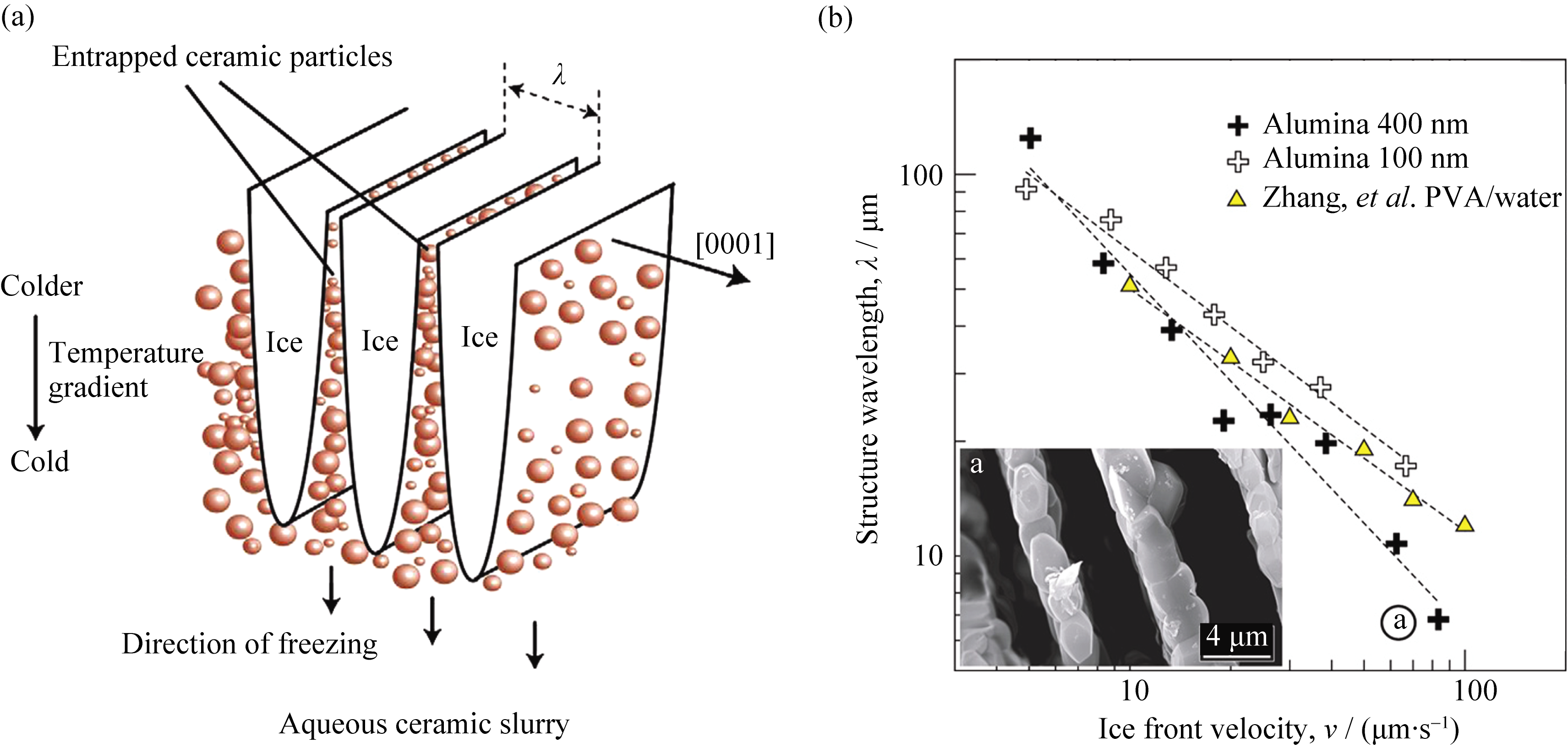
图13 薄片状结构(水系浆料冷冻)波长定义示意图(a)及薄片状结构波长随冷却速率变化图(b)[21]
Fig. 13 Pattern formation and particle segregation during freeze casting of ceramic slurries (a) and the wavelength of the <br/>structure is defined. (b) Variation of structure wavelength vs ice front velocity[21]
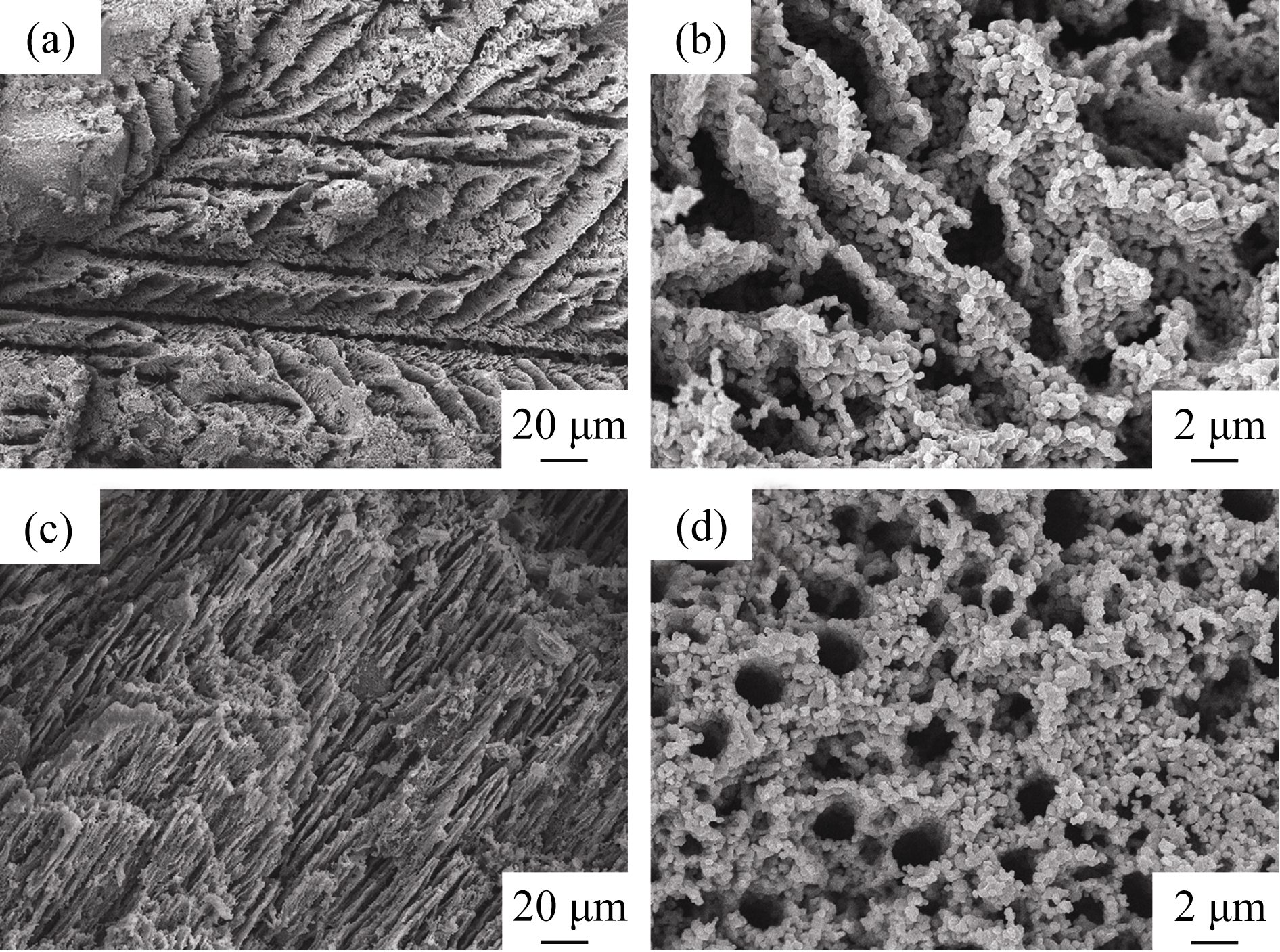
图14 多孔二氧化钛陶瓷截面扫描电镜照片[52]
Fig. 14 SEM images of porous TiO2 with cross-section parallel and perpendicular to the ice growth direction[52] (a) 3wt% PVA, parallel; (b) 3wt% PVA, perpendicular; (c) 6wt% PVA, parallel; (d) 6wt% PVA, perpendicular
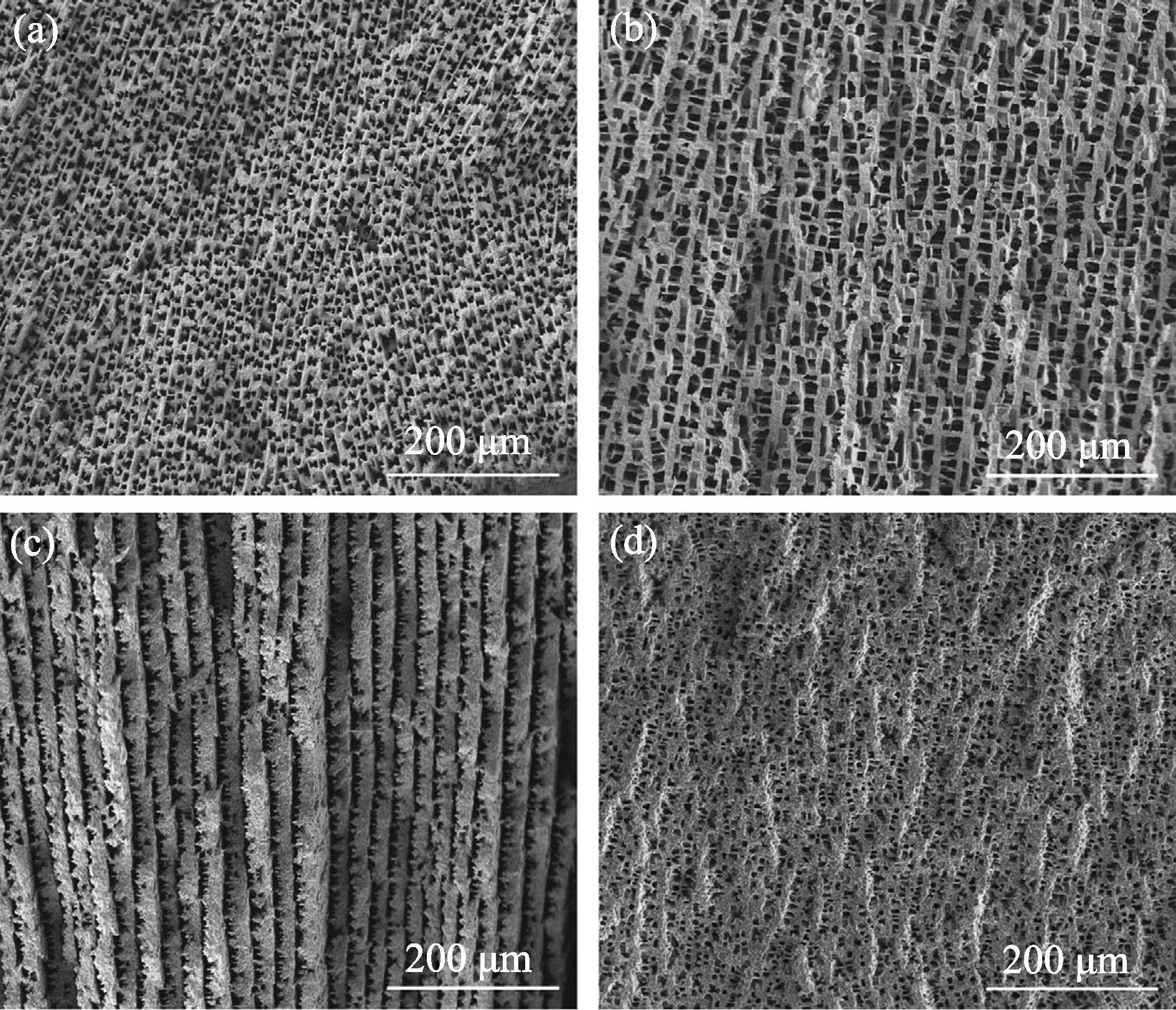
图15 多孔氧化铝陶瓷扫描电镜照片[55]
Fig. 15 SEM images of porous alumina ceramics, which are prepared by using (a) 20vol% slurry without glycerol, (b) 20vol% slurry with glycerol, (c) 30vol% slurry without glycerol and (d) 30vol% slurry with glycerol[55] The direction of fracture parallels to the ice front
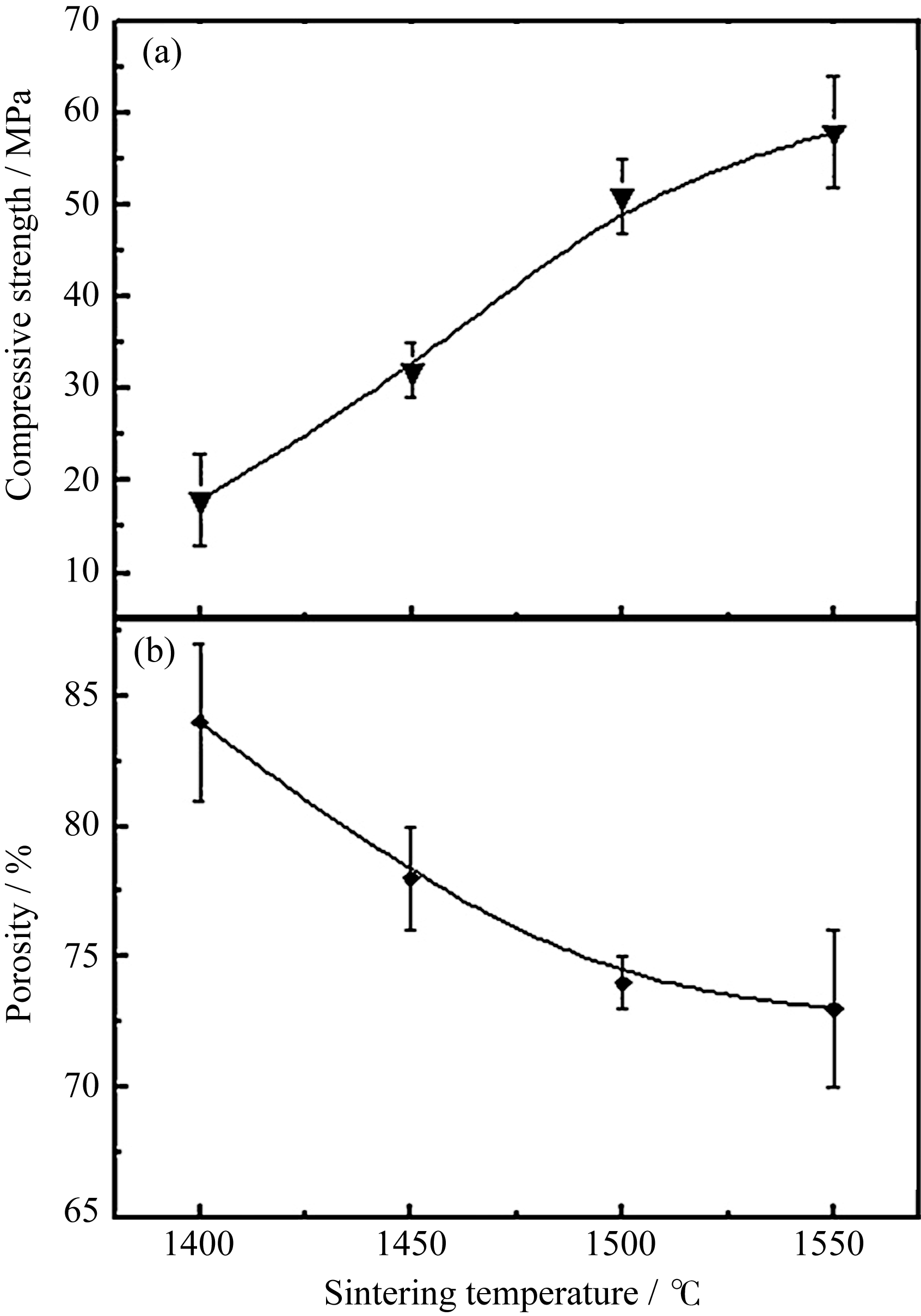
图16 烧结温度对抗压强度(a)和总气孔率(b)的影响[58]
Fig. 16 Influence of sintering temperature (2 h at dwell temperature) on compressive strength (a) and total porosity(b)[58]
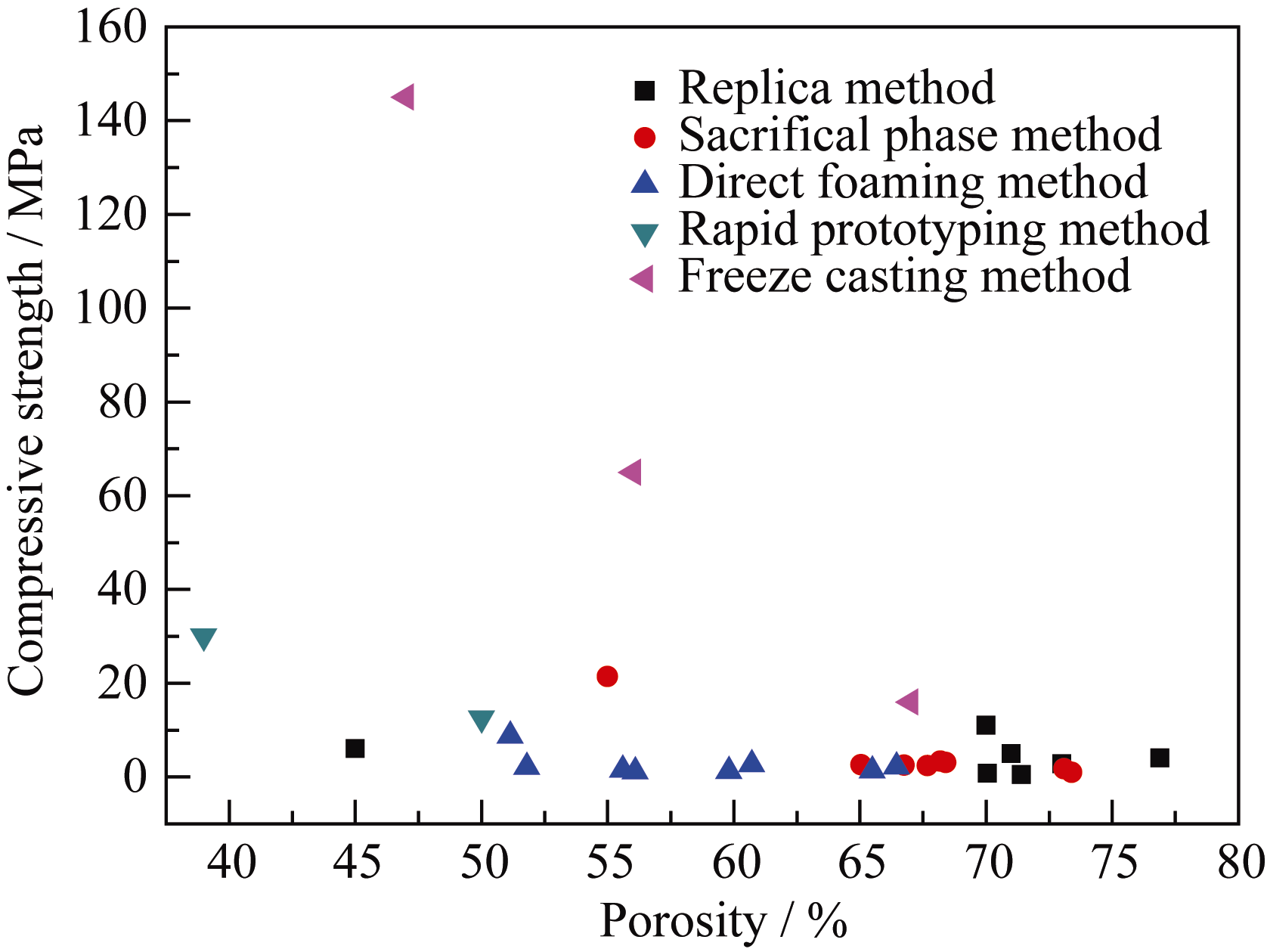
图17 不同制备技术获得的多孔羟基磷灰石抗压强度对比图
Fig. 17 Comparison of compressive strength of porous hydroxyapatite obtained by different techniques according to literature data
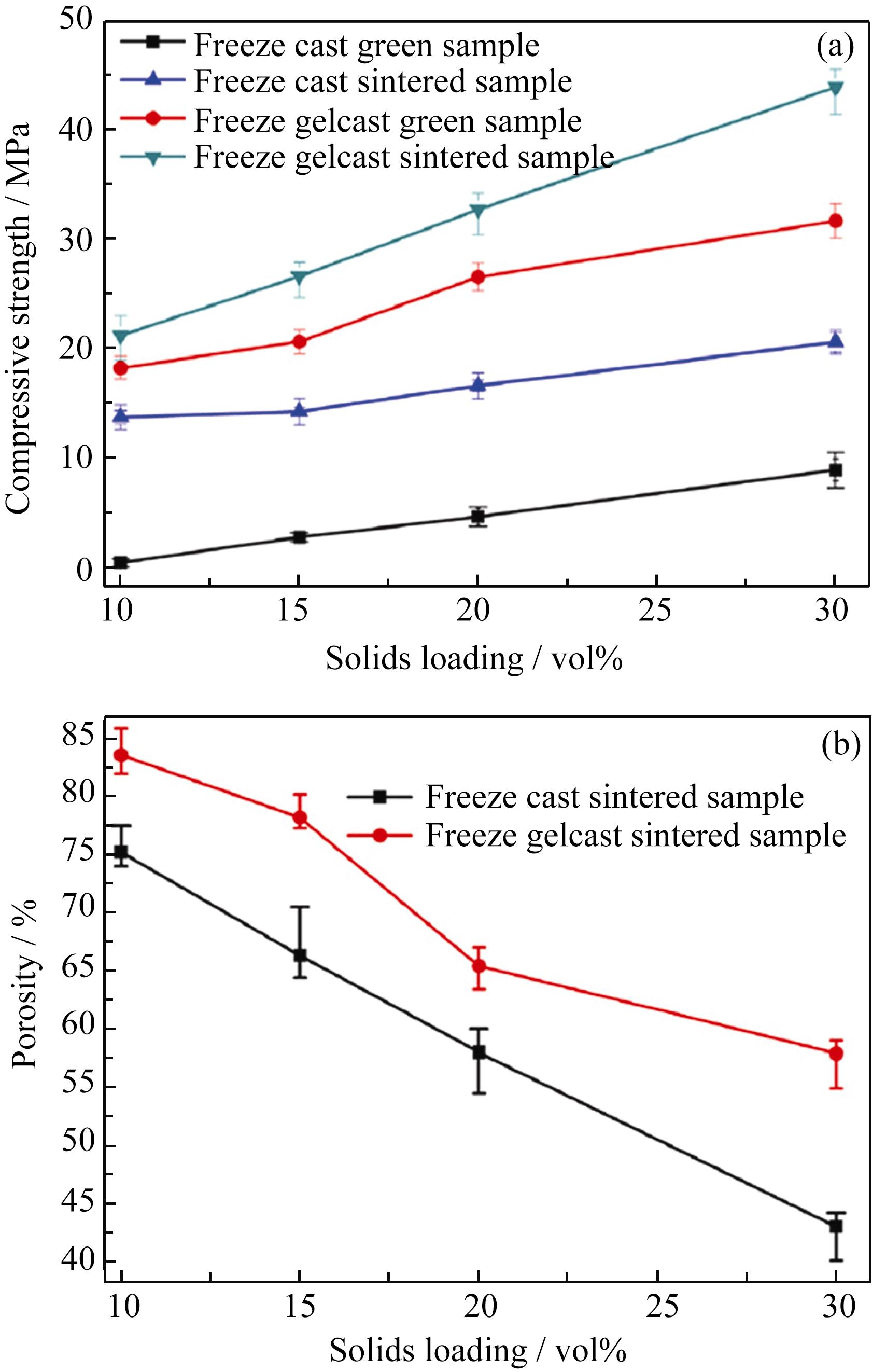
图23 不同方法获得的多孔氧化铝抗压强度对比(a)和不同方法获得的多孔氧化铝气孔率对比(b)图[24]
Fig. 23 Compressive strengths of freeze cast and freeze gelcast samples versus solids loading (a) and porosities of the sintered samples versus solids loading (b)[24]
| [1] | STUDART A R, GONZENBACH U T, TERVOORT E, et al. Processing routes to macroporous ceramics: a review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(6): 1771-1789. |
| [2] | COLOMBO P. Conventional and novel processing methods for cellular ceramics. Philos. T. R. Soc. A, 2006, 364(1838): 109-124. |
| [3] | SEPULVEDA P, BINNER J G P. Processing of cellular ceramics by foaming and in situ polymerisation of organic monomers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc, 1999, 19(12): 2059-2066. |
| [4] | NANGREJO M R, BAO X J, EDIRISINGHE M J. Preparation of silicon carbide-silicon nitride composite foams from pre-ceramic polymers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2000, 20(11): 1777-1785. |
| [5] | MATOVIC B, BABIC B, EGELJA A, et al. Preparation of porous silica ceramics using the wood template. Mater. Manuf. Process, 2009, 24(10/11): 1109-1113. |
| [6] | TULLIANI J M, MONTANARO L, BELL T J, et al. Semiclosed-cell mullite foams: preparation and macro- and micromechanical character-rization. .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 1999, 82(4): 961-968. |
| [7] | LI S H, WIJN DE, LAYROLLE P, et al. Synthesis of macroporous hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J. Biomed. Mater. Res, 2002, 61(1): 109-120. |
| [8] | LIU D M. Influence of porosity and pore size on the compressive strength of porous hydroxyapatite ceramic.Ceram. Int, 1997, 23(2):135-139. |
| [9] | PABST W, GREGOVOVÁ E, MALANGRÉ D, et al. Elastic properties and damping behavior of alumina-zirconia composites at room temperature. Ceram. Int., 2012, 38(7) : 5931-5939. |
| [10] | BINKS B P. Macroporous silica from solid-stabilized emulsion templates. Adv. Mater., 2002, 14(24): 1824-1827. |
| [11] | AHMAD R, HA J H, SONG I H. Particle-stabilized ultra-low density zirconia toughened alumina foams. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc, 2013, 33(13/14): 2559-2564. |
| [12] | GONZENBACH U T, STUDART A R, TERVOORT E, et al. Macroporous ceramics from particle-stabilized wet foams. J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2007, 90(1):16-22. |
| [13] | MORITZ T, RICHTER H J. Ceramic bodies with complex geometries and ceramic shells by freeze casting using ice as mold material.J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2006, 89(8): 2394-2398. |
| [14] | SOFIE S W, DOGAN F. Freeze casting of aqueous alumina slurries with glycerol. J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2001, 84(7): 1459-1464. |
| [15] | STATHAM M J, HAMMETT E, HARRIS B, et al. Net-shape manufacture of low-cost ceramic shapes by freeze-gelation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 1998, 13(1/2/3): 171-175. |
| [16] | FUKASAWA T, ANDO M, OHJI T, et al. Synthesis of porous ceramics with complex pore structure by freeze-dry processing. J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2001, 84(1): 230-232. |
| [17] | ZHANG H F, HUSSAIN I, BRUST M, et al. Aligned two- and three-dimensional structures by directional freezing of polymers and nanoparticles.Nat. Mater, 2005, 4(10): 787-793. |
| [18] | DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, NALLA R K. Freezing as a path to build complex composites. Science, 2006, 311(5760): 515-518. |
| [19] | DEVILLE S. Freeze-casting of porous ceramics: A review of current achievements and issues. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2008, 10(3): 155-169. |
| [20] | ARAKI K, HALLORAN J W. Porous ceramic bodies with interconnected pore channels by a novel freeze casting technique. J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2005, 88(5): 1108-1114. |
| [21] | DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, TOMSIA A P. Ice-templated porous alumina structures.Acta Mater, 2007, 55(6): 1965-1974. |
| [22] | ZHANG Y, ZUO K, ZENG Y P. Effects of gelatin addition on the microstructure of freeze-cast porous hydroxyapatite cerarmics.Ceram. Int, 2009, 35(6): 2151-2154. |
| [23] | LIU G, ZHANG D, MEGGS C, et al. Porous Al2O3-ZrO2 composites fabricated by an ice template method.Scr. Mater, 2010, 62(7): 466-468. |
| [24] | ZHANG D, ZHANG Y, XIE R, et al. Freeze gelcasting of aqueous alumina suspensions for porous ceramics. Ceram. Int, 2012, 38(7): 6063-6066. |
| [25] | ZHANG Y, ZHOU K C, BAO Y X, et al. Effects of rheological properties on ice-templated porous hydroxyapatite ceramics. Mater.Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl, 2013, 33(1): 340-346. |
| [26] | KORBER C, RAU G, COSMAN M D, et al. Interaction of particles and a moving ice-liquid interface .J. Cryst. Growth, 1985, 72(3): 649-662. |
| [27] | WEGST U G K, SCHECTER M, DONIUS A E, et al. Biomaterials by freeze casting . Philos. T. R. Soc. A, 2010, 368(1917): 2099-2121. |
| [28] | BOLLING G F, CISSE J. Theory for interaction of particles with a solidifying front.J. Cryst. Growth, 1971, 10(1): 56-66. |
| [29] | MACCHETTA A, TURNER I G, BOWEN C R. Fabrication of HA/TCP scaffolds with a graded and porous structure using a camphene-based freeze-casting method.Acta Biomater, 2009 5(4): 1319-1327. |
| [30] | HAN J, HU L, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of ceramics with complex porous structures by the impregnate-freeze-casting process .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2009, 92(9): 2165-2167. |
| [31] | JING L, ZUO K, ZHANG F, et al. The controllable microstructure of porous Al2O3 ceramics prepared via a novel freeze casting route .Ceram. Int, 2010, 36(8): 2499-2503. |
| [32] | RODRIGUEZ-PARRA J M, MORENO R, ISABEL NIETO M. Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and porosity of alumina produced by freeze casting .J. Serb. Chem.l Soc, 2012,77(12): 1775-1785. |
| [33] | YOON H J, KIM U C, KIM J H, et al. Macroporous alumina ceramics with aligned microporous walls by unidirectionally freezing foamed aqueous ceramic suspensions .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2010, 93(6): 1580-1582. |
| [34] | DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, TOMSIA A P. Freeze casting of hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering .Biomater, 2006, 27(32): 5480-5489. |
| [35] | FU Q, RAHAMAN M N, DOGAN F, et al. Freeze casting of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds. I. processing and general microstructure . J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2008, 86B(1): 125-135. |
| [36] | FU Q, RAHAMAN M N, DOGAN F, et al. Freeze casting of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds. II. sintering, microstructure, and mechanical behavior . J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2008, 86B(2): 514-522. |
| [37] | FU Q, RAHAMAN M N, DOGAN F, et al. Freeze-cast hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications .Biomed. Mater, 2008, 3(2): 025005. |
| [38] | LANDI E, VALENTINI F, TAMPIERI A. Porous hydroxyapatite/ gelatine scaffolds with ice-designed channel-like porosity for biomedical applications .Acta Biomater, 2008, 4(6): 1620-1626. |
| [39] | CHINO Y, DUNAND D C. Directionally freeze-cast titanium foam with aligned, elongated pores .Acta Mater, 2008, 56(1): 105-113. |
| [40] | LI J C, DUNAND D C. Mechanical properties of directionally freeze-cast titanium foams .Acta Mater, 2011, 59(1): 146-158. |
| [41] | WETTLAUFER J S, WORSTER M G, HUPPERT H E. Natural convection during solidification of an alloy from above with application to the evolution of sea ice. J Fluid Mech, 1997, 344(291-316): 291-316. |
| [42] | WETTLAUFER J S, WORSTER M G, HUPPERT H E. The phase evolution of young sea ice . Geophys. Res. Lett., 1997, 24(10): 1251-1254. |
| [43] | YOON B H, LEE E J, KIM H E. Highly aligned prous silicon carbide ceramics by freezing polycarbosilane/camphene solution .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2007, 90(6): 1753-1759. |
| [44] | KOH Y H, SONG J H, LEE E J, et al. Freezing dilute ceramic/ camphene slurry for ultra-high porosity ceramics with completely interconnected pore networks .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2006, 89(10): 3089-3093. |
| [45] | DU J, ZHANG X, HONG C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrB2-SiC porous ceramic by camphene-based freeze casting .Ceram. Int, 2013, 39(2): 953-957. |
| [46] | FARHANGDOUST S, ZAMANIAN A, YASAEI M, et al. The effect of processing parameters and solid concentration on the mechanical and microstructural properties of freeze-casted macroporous hydroxyapatite scaffolds .Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl, 2013, 33(1): 453-460. |
| [47] | HONG C, ZHANG X, HAN J, et al. Ultra-high-porosity zirconia ceramics fabricated by novel room-temperature freeze-casting .Scr. Mater , 2009, 60(7): 563-566. |
| [48] | HONG C, ZHANG X, HAN J, et al. Camphene-based freeze-cast ZrO2 foam with high compressive strength .Mater. Chem. and Phys, 2010, 119(3): 359-362. |
| [49] | HOU Z, YE F, LIU L, et al. Effects of solid content on the phase assemblages, mechanical and dielectric properties of porous α-SiAlON ceramics fabricated by freeze casting. Ceram. Int, 2013, 39(2): 1075-1079. |
| [50] | LEE S H, JUN S H, KIM H E, et al. Piezoelectric properites of PZT-based ceramic with highly aligned pores . J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91(6): 1912-1915. |
| [51] | LI D, LI M. Preparation of porous alumina ceramic with ultra-high porosity and long straight pores by freeze casting. J. Porous Mater., 2012,19(3): 345-349. |
| [52] | REN L, ZENG Y P, JIANG D. Preparation of porous TiO2 by a novel freeze casting .Ceram. Int, 2009, 35(3): 1267-1270. |
| [53] | YE F, ZHANG J, LIU L, et al. Effect of solid content on pore structure and mechanical properties of porous silicon nitride ceramics produced by freeze casting .Mater. Sci. Eng. A, Struct Mater, Prop. Microstruct.Process, 2011, 528(3): 1421-1424. |
| [54] | YOON B H, KOH Y H, PARK C S, et al. Generation of large pore channels for bone tissue engineering using camphene-based freeze casting .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2007, 90(6): 1744-1752. |
| [55] | ZHANG Y, HU L, HAN J, et al. Freeze casting of aqueous alumina slurries with glycerol for porous ceramics .Ceram. Int, 2010, 36(2): 617-621. |
| [56] | ZHANG R, FANG D, PEI Y, et al. Microstructure, mechanical and dielectric properties of highly porous silicon nitride ceramics produced by a new water-based freeze casting .Ceram. Int, 2012, 38(5): 4373-4377. |
| [57] | ZHANG Y, ZUO K, ZENG Y P. Effects of gelatin addition on the microstructure of freeze-cast porous hydroxyapatite cerarmics .Ceram. Inter, 2009, 35(6): 2151-2154. |
| [58] | HAN J, HONG C, ZHANG X, et al. Highly porous ZrO2 ceramics fabricated by a camphene-based freeze-casting route: microstructure and properties .J. Eur. Ceram. Soc, 2010, 30(1): 53-60. |
| [59] | CHU T M G, ORTON D G, HOLLISTER S J, et al. Mechanical and in vivo performance of hydroxyapatite implants with controlled archite-ctures .Biomater. , 2002, 23(5): 1283-1293. |
| [60] | DEL REAL R P, WOLKE J G C, VALLET-REGI M, et al. A new method to produce macropores in calcium phosphate cements. Biomater., 2002, 23(17): 3673-3680. |
| [61] | RAHAMAN M N, FU Q. Manipulation of porous bioceramic microstructures by freezing of suspensions containing binary mixtures of solvents .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2008, 91(12): 4137-4140. |
| [62] | LIU X, RAHAMAN M N, FU Q. Oriented bioactive glass (13-93) scaffolds with controllable pore size by unidirectional freezing of camphene-based suspensions: Microstructure and mechanical response. Acta Biomater, 2011,7(1): 406-416. |
| [63] | SOON Y M, SHIN K H, KOH Y H, et al. Compressive strength and processing of camphene-based freeze cast calcium phosphate scaffolds with aligned pores .Mater. Lett, 2009, 63(17): 1548-1550. |
| [64] | XIA Y, ZENG Y P, JIANG D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics prepared by freeze-casting .Mater. Des, 2012, 33: 98-103. |
| [65] | YE F, ZHANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of highly porous silicon nitride ceramics produced by freeze casting . Mater. Sci. Eng. A, Struct Mater, Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2010, 527(2425): 6501-6504. |
| [66] | LI J, ZUO K, LIU W, et al. Porous Al2O3 prepared via freeze casting and its biocompatibility.Ceramic Materials and Components for Energy and Environmental Applications 2010, 210(537-543): 537-543. |
| [67] | DEVILLE S. Freeze-casting of porous biomaterials: structure, properties and opportunities .Mater, 2010, 3(3): 1913-1927. |
| [68] | SOFIE S W. Fabrication of functionally graded and aligned porosity in thin ceramic substrates with the novel freeze- tape-casting process .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2007, 90(7): 2024-2031. |
| [69] | CHEN Y, BUNCH J, LI T, et al. Novel functionally graded acicular electrode for solid oxide cells fabricated by the freeze- tape-casting process. J. Power Sources, 2012, 213(93-99): 93-99. |
| [70] | REN L, ZENG Y P, JIANG D. Fabrication of gradient pore TiO2 sheets by a novel freeze-tape-casting process .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2007, 90(9): 3001-3004. |
| [71] | WEI P, SOFIE S, ZHANG Q, et al. Metal supported solid oxide fuel cell by freeze tape casting. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, 2011, 35(1): 379-383. |
| [72] | WASCHKIES T, OBERACKER R, HOFFMANN M J. Control of lamellae spacing during freeze casting of ceramics using doubleside cooling as a novel processing route .J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 2009, 92(1): S79-S84. |
| [73] | PREISS A, SU B, COLLINS S, et al. Tailored graded pore structure in zirconia toughened alumina ceramics using double-side cooling freeze casting . J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 32(8): 1575-1583. |
| [74] | LEE J H, CHOI H J, YOON S Y, et al. Porous mullite ceramics derived from coal fly ash using a freeze-gel casting/polymer sponge technique J. Porous Mater., 2013, 20(1): 219-226. |
| [75] | MONMATURAPOJ N, SOODSAWANG W, THEPSUWAN W. Porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds produced by the combination of the gel-casting and freeze drying techniques. J. Porous Mater., 2012, 19(4): 441-447. |
| [76] | CHEN P Y, MCKITTRICK J. XXX_record.do?product=UA&search_mode=GeneralSearch&qid=4&SID=P2Zcqa7oFMcmXTlScDM&page=1&doc=1&cacheurlFromRightClick=no"Compressive mechanical properties of demineralized and deproteinized cancellous bone . J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2011, 4(7): 961-973. |
| [77] | BARG S, INNOCENTINI M D M, MELONI R V, et al. Physical and high-temperature permeation features of double-layered cellular filtering membranes prepared via freeze casting of emulsified powder suspensions. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 383(1/2): 35-43. |
| [78] | XIE X, ZHOU Y L, BI H C, et al. Large-range control of the microstructures and properties of three-dimensional porous graphene. Sciencefic reports, 2013, 3(2117): 1-6. |
| [1] | 魏相霞, 张晓飞, 徐凯龙, 陈张伟. 增材制造柔性压电材料的现状与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [2] | 杨鑫, 韩春秋, 曹玥晗, 贺桢, 周莹. 金属氧化物电催化硝酸盐还原合成氨研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 979-991. |
| [3] | 刘鹏东, 王桢, 刘永锋, 温广武. 硅泥在锂离子电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 992-1004. |
| [4] | 黄洁, 汪刘应, 王滨, 刘顾, 王伟超, 葛超群. 基于微纳结构设计的电磁性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 853-870. |
| [5] | 陈乾, 苏海军, 姜浩, 申仲琳, 余明辉, 张卓. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造及组织性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [6] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [7] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [8] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [9] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| [10] | 方光武, 谢浩元, 张华军, 高希光, 宋迎东. CMC-EBC损伤耦合机理及一体化设计研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 647-661. |
| [11] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [12] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [13] | 李宗晓, 胡令祥, 王敬蕊, 诸葛飞. 氧化物神经元器件及其神经网络应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 345-358. |
| [14] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| [15] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||