无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 137-149.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250124 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250124
• 综述 • 下一篇
任先培1( ), 李超1, 胡启威1, 向晖1(
), 李超1, 胡启威1, 向晖1( ), 彭跃红2(
), 彭跃红2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-25
修回日期:2025-06-12
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-07-16
通讯作者:
向 晖, 副教授. E-mail: hxiang0717@163.com;作者简介:任先培(1982-), 男, 副教授. E-mail: renxianpei@163.com
基金资助:
REN Xianpei1( ), LI Chao1, HU Qiwei1, XIANG Hui1(
), LI Chao1, HU Qiwei1, XIANG Hui1( ), PENG Yuehong2(
), PENG Yuehong2( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Revised:2025-06-12
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-07-16
Contact:
XIANG Hui, associate professor. E-mail: hxiang0717@163.com;About author:REN Xianpei (1982-), male, associate professor. E-mail: renxianpei@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
氢能作为一种理想的能源载体, 对推动能源结构转型具有重要意义。电解水制氢技术是实现制氢规模化的重要手段, 而催化剂的析氢活性、稳定性和成本则是该技术发展的核心要素。过渡金属化合物(TMCs)凭借其成本低、资源丰富以及电子结构可调等优点, 已成为替代贵金属催化剂的热门候选材料。构建半导体与金属之间的莫特-肖特基(Mott-Schottky, M-S)结是一种有效提升催化活性的策略。本文系统综述了金属/TMCs M-S结催化剂的研究进展, 包括其分类(如金属/氧化物、硫化物、硒化物、磷化物、氮化物)、构建策略(如水热法、原位还原、磷化处理等)及析氢增强机制。研究表明, M-S结通过界面电荷重排和形成内建电场, 优化电子结构和氢吸附自由能, 促进电荷分离和传输, 从而显著提升析氢活性。此外, 本文还探讨了M-S结催化剂需深入探索和厘清的关键问题, 并对未来研究方向和发展趋势进行了展望。本文旨在为设计高效、廉价析氢电催化剂提供理论指导, 推动氢能技术的可持续发展。
中图分类号:
任先培, 李超, 胡启威, 向晖, 彭跃红. 金属/过渡金属化合物莫特-肖特基析氢催化剂研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 137-149.
REN Xianpei, LI Chao, HU Qiwei, XIANG Hui, PENG Yuehong. Research Progress on Mott-Schottky Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts Based on Metal/Transition Metal Compounds[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 137-149.
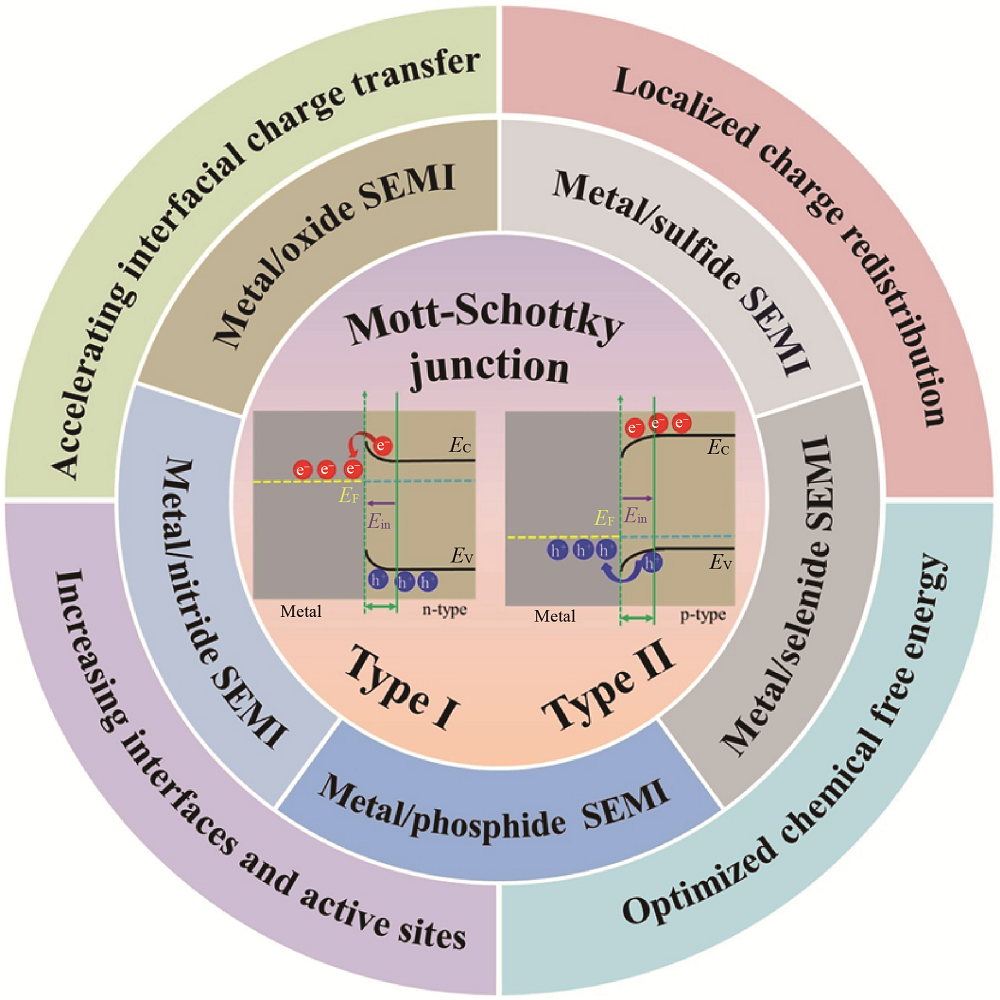
图1 金属/TMCs半导体M-S结催化剂的结构、类型以及增强析氢机制
Fig. 1 Structures, types and enhanced hydrogen evolution mechanisms of metal/TMCs semiconductor M-S junction catalysts SEMI: semiconductor
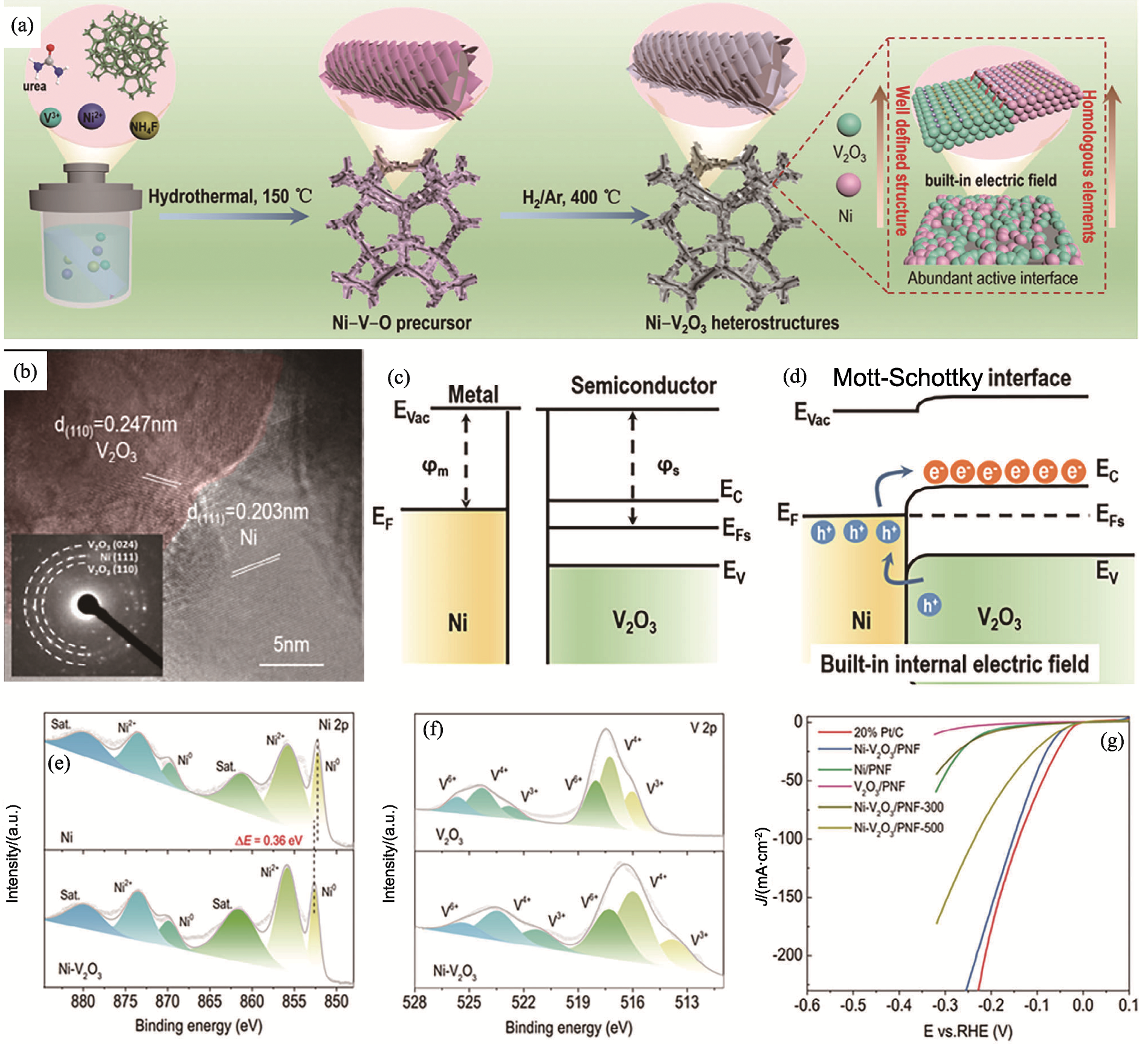
图2 Ni-V2O3/PNF的制备、表征与析氢性能[37]
Fig. 2 Preparation, characterization and hydrogen evolution performance of Ni-V2O3/PNF[37] (a) Schematic diagram of synthesis process for Ni-V2O3/PNF; (b) HRTEM image of Ni-V2O3/PNF; (c) Energy band diagram of Ni and V2O3;(d) Schematic diagram of band structures; (e, f) High-resolution XPS spectra of Ni2p (e) and V2p (f);(g) Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves of 20% Pt/C, Ni-V2O3/PNF, Ni/PNF, V2O3/PNF, and Ni-V2O3/PNF-300/500, where 300 and 500 represent the thermal reduction temperatures in unit ℃, while 400 ℃ for Ni-V2O3/PNF
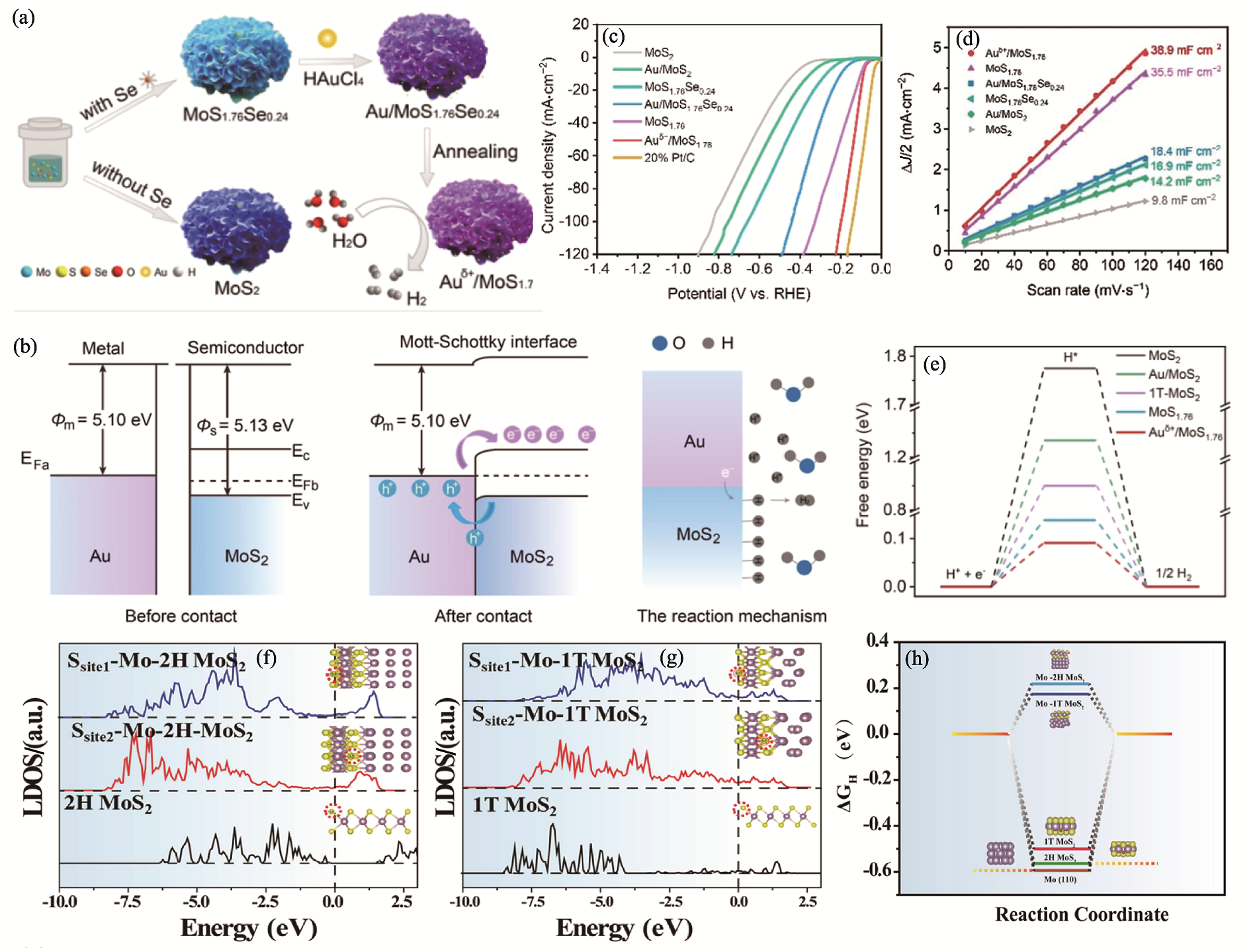
图3 Auδ+/1T-MoS1.76与Mo-MoS2 M-S结催化剂的制备、理论计算与析氢性能[44-45]
Fig. 3 Preparation, theoretical calculations and hydrogen evolution performance of Auδ+/1T-MoS1.76 and Mo-MoS2 M-S junction catalysts[44-45] (a) Schematic diagram of synthesis process for Auδ+/1T-MoS1.76[44]; (b) Schematic illustration of the energy band structure for Auδ+/1T-MoS1.76 heterostructure and the proposed charge-transfer mechanism[44]; (c) LSV curves and (d) linear fits of half capacitive current vs. scan rate for the extraction of Cdl for different samples[44]; (e) Free-energy diagram for HER[44]; (f) LDOS for different S sites of 2H MoS2 and Mo-2H MoS2[45]; (g) LDOS for different S sites of 1T MoS2 and Mo-1T MoS2[45]; (h) Optimal ΔGH* for HER[45]
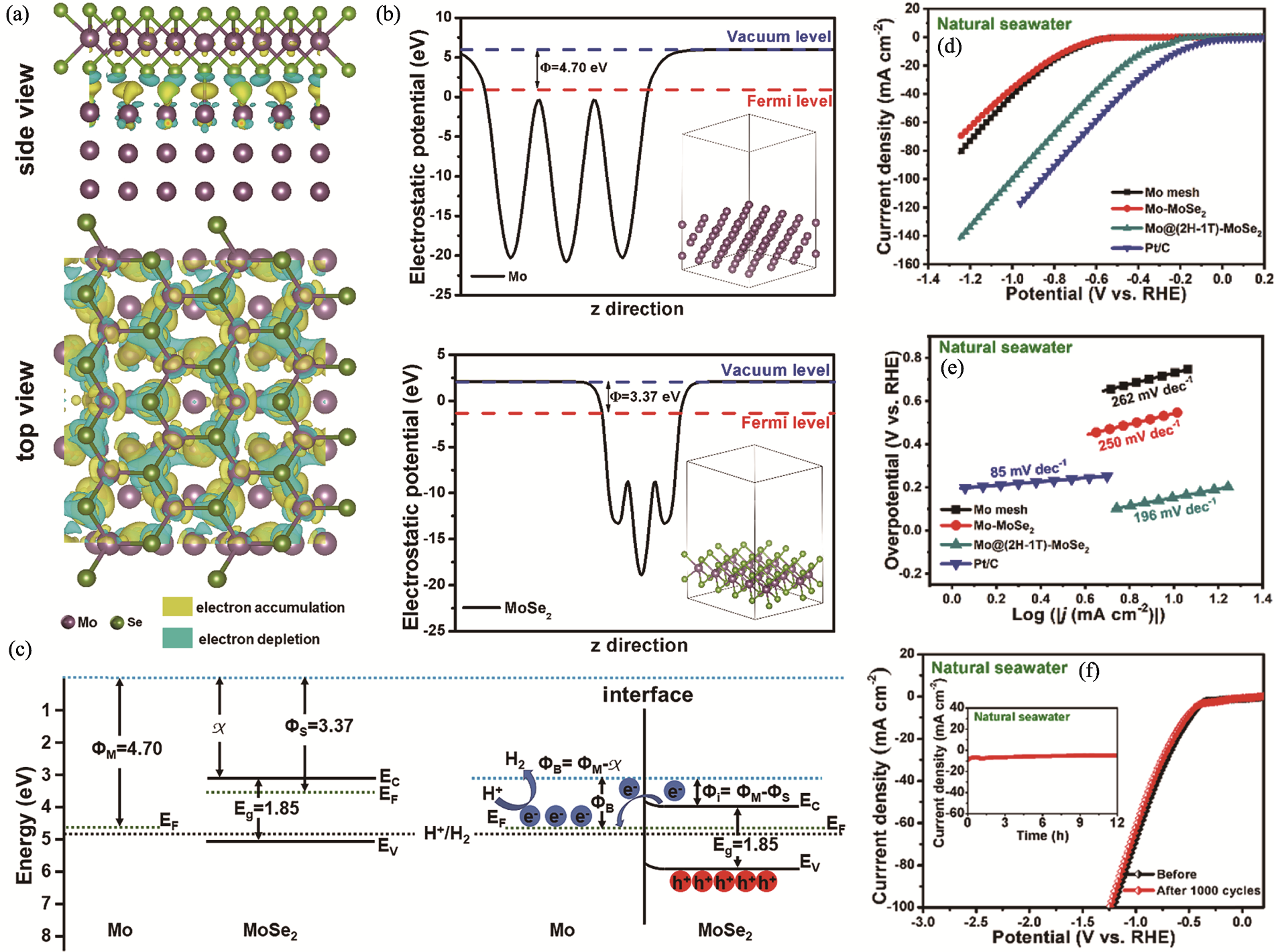
图4 Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 M-S结催化剂的理论计算、能带结构与析氢性能[48]
Fig. 4 Theoretical calculations, band structure and hydrogen evolution performance of Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 M-S junction catalyst[48] (a) Charge density distribution at interface of the Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 heterostructure; (b) Electrostatic potential calculations of Mo metal (top) and MoSe2 (bottom); (c) Energy levels of the two components in Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 before and after contact; (d) LSV curves and (e) corresponding Tafel slopes for the electrodes Mo mesh, Mo-MoSe2, Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 and Pt/C in natural seawater; (f) LSV curves for Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 before and after 1000 CV cycles
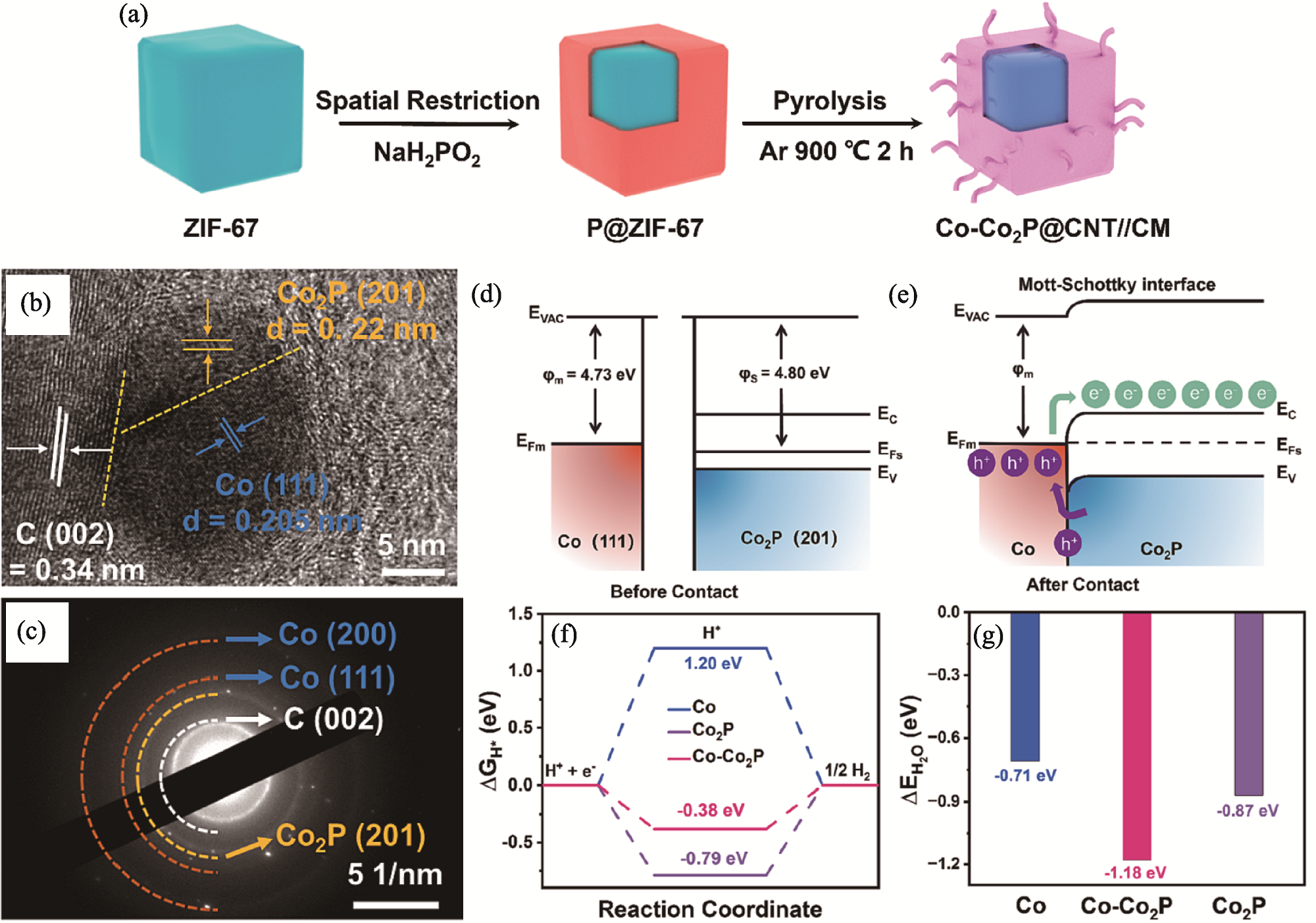
图5 M-S型Co-Co2P@CNT//CM异质结的制备、结构、能带与自由能[53]
Fig. 5 Preparation, structure, band alignment and free energy of M-S type Co-Co2P@CNT//CM heterojunction[53] (a) Schematic diagram of synthesis process for M-S type Co-Co2P@CNT//CM heterojunction; (b) HRTEM and (c) SAED images of Co-Co2P@CNT//CM; (d, e) Energy diagrams for Co and Co2P before and after Schottky contact; (f) Calculated ΔGH* and (g) ΔEH2O of Co, Co2P and Co-Co2P
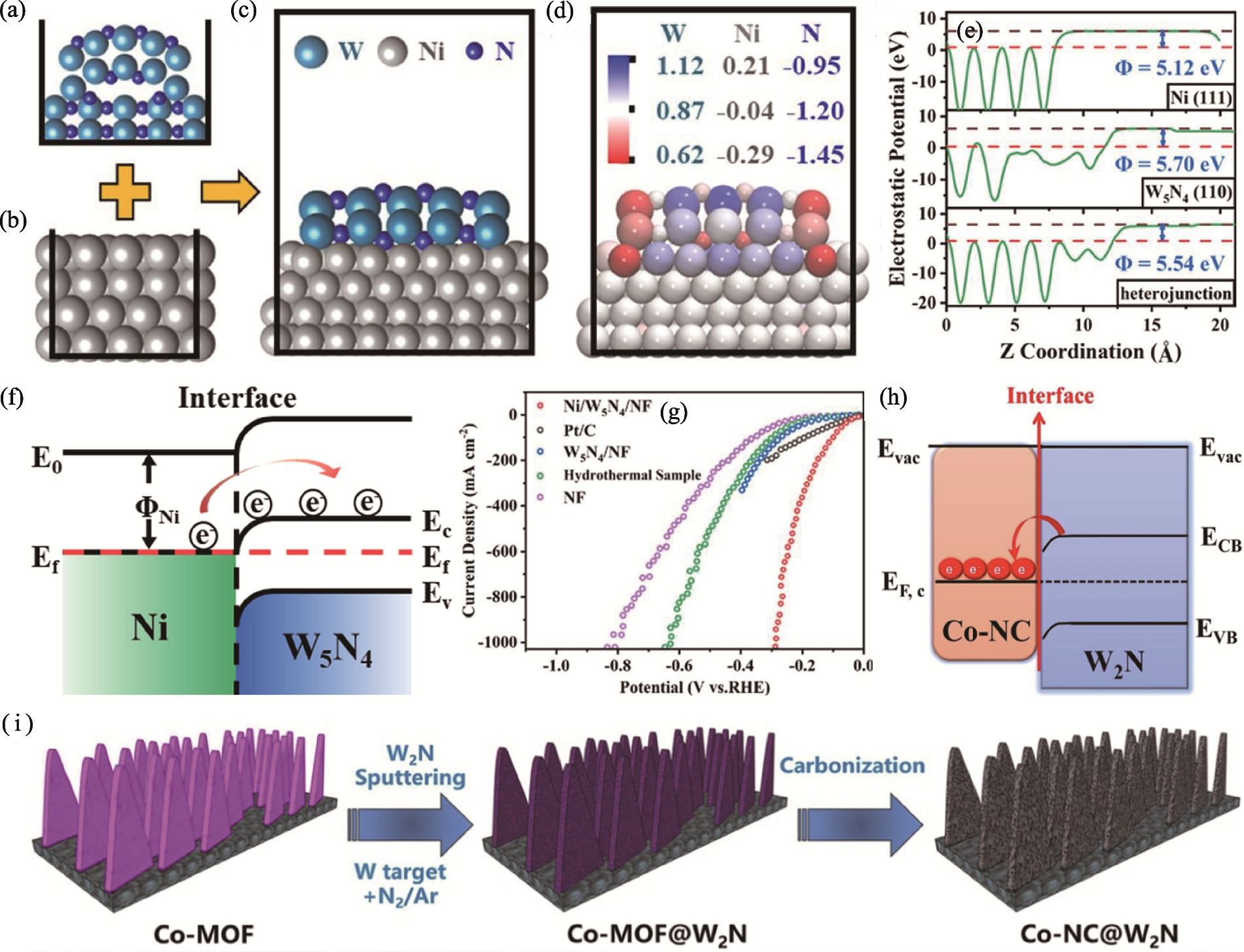
图6 Ni/W5N4与Co-NC@W2N M-S结催化剂的结构模型、能带结构与制备示意图[59-60]
Fig. 6 Structural models, band structures and preparation schematic diagrams of Ni/W5N4 and Co-NC@W2N M-S junction catalysts[59-60] (a-c) Calculated geometries of (a) W5N4 (100), (b) Ni (111) and (c) M-S heterojunction[59]; (d) Structure diagram of atomic Bader charge coloring for the M-S heterojunction[59]; (e) Electrostatic potential for the corresponding geometries[59]; (f) Energy band diagram of metallic Ni and W5N4 with M-S interface after Schottky contact[59]; (g) HER polarization curves of the series of catalysts[59]; (h) Schematic illustration of Co-NC@W2N M-S junction after contacting[60]; (i) Schematic diagram of synthesis process for Co-NC@W2N[60]
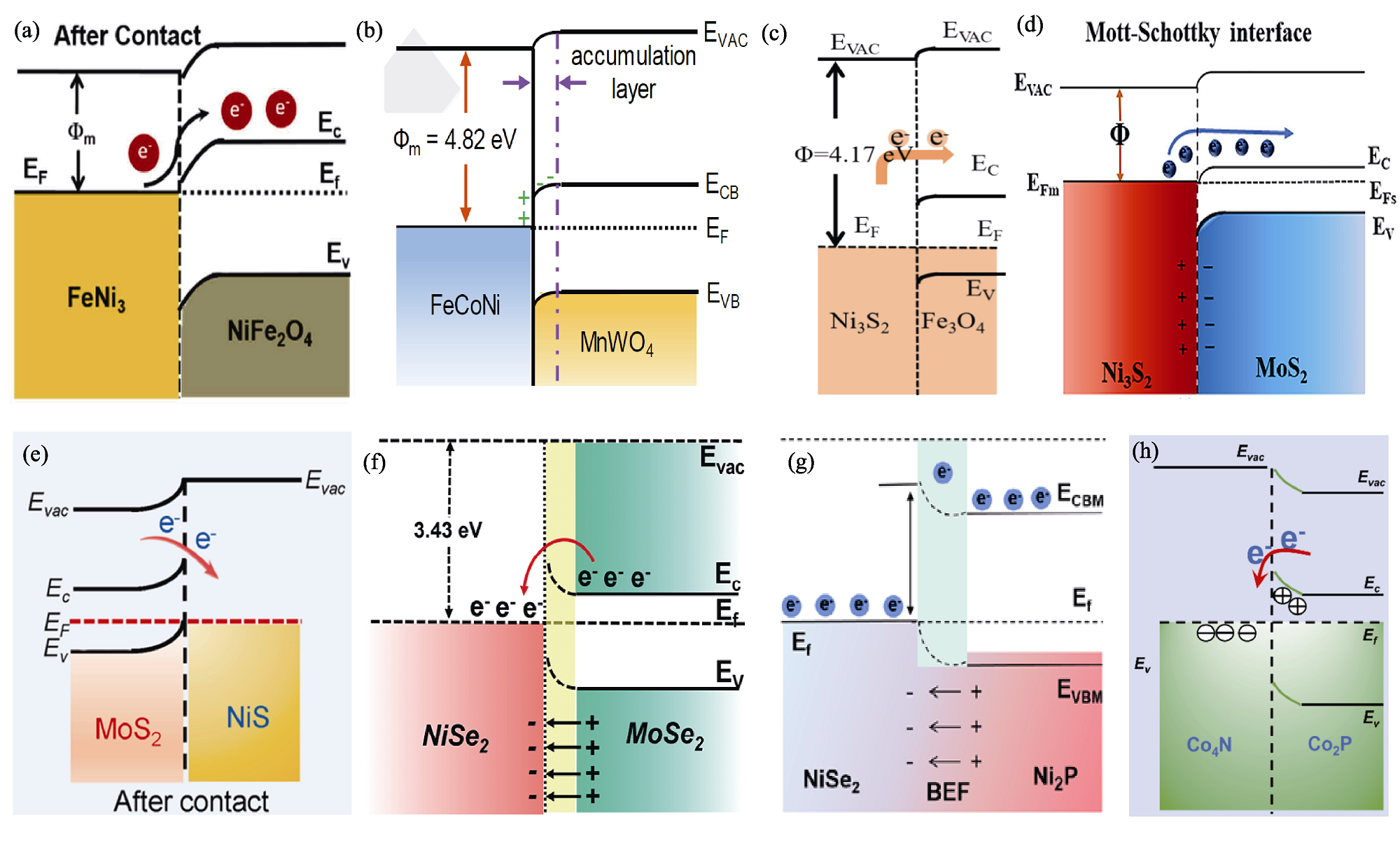
图7 金属性质的化合物与TMCs半导体形成的M-S结[62-69]
Fig. 7 M-S junction formed between metallic compounds and TMCs semiconductors[62-69] (a) FeNi3/NiFe2O4[62]; (b) FeCoNi/MnWO4[63]; (c) Ni3S2/Fe3O4[64]; (d) Ni3S2/MoS2[65]; (e) NiS/MoS2[66]; (f) NiSe2/MoSe2[67]; (g) NiSe2/Ni2P[68]; (h) Co4N/Co2P[69]
| No. | Mott-Schottky catalyst | Metal | Semiconductor | Electron transfer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | V2O3/Ni | Ni | V2O3 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 2 | Ni@NiO | Ni | NiO | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 3 | Co/a-WOx | Co | a-WOx | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 4 | Ni/NiFeO | Ni | NiFeO | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 5 | Au/MoS2 | Au | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 6 | Mo-MoS2 | Mo | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 7 | Co-Co2P | Co | Co2P | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 8 | NiCoP-Co | Co | NiCoP | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 9 | Ni/W5N4 | Ni | W5N4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 10 | Ni/Ni3N | Ni | Ni3N | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 11 | FeNi3/NiFe2O4 | FeNi3 | NiFe2O4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 12 | FeCoNi/MnWO4 | FeCoNi | MnWO4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 13 | Ni3S2/Fe3O4 | Ni3S2 | Fe3O4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 14 | Ni3S2/MoS2 | Ni3S2 | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 15 | Ru-WO2.72 | Ru | WO2.72 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 16 | Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 | Mo | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 17 | Co/Co0.85Se | Co | Co0.85Se | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 18 | Co/MoSe2 | Co | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 19 | Ru/Ru, Fe-CoP | Ru | Ru, Fe-CoP | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 20 | Co/CoP | Co | CoP | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 21 | Co-NC@W2N | Co | W2N | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 22 | NiS/MoS2 | NiS | MoS2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 23 | NiSe2/MoSe2 | NiSe2 | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 24 | NiSe2/Ni2P | NiSe2 | Ni2P | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 25 | Co4N/Co2P | Co4N | Co2P | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
表1 M-S结催化剂中电子传输方向汇总
Table 1 Summary of the direction of electron transfer in M-S junction catalysts
| No. | Mott-Schottky catalyst | Metal | Semiconductor | Electron transfer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | V2O3/Ni | Ni | V2O3 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 2 | Ni@NiO | Ni | NiO | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 3 | Co/a-WOx | Co | a-WOx | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 4 | Ni/NiFeO | Ni | NiFeO | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 5 | Au/MoS2 | Au | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 6 | Mo-MoS2 | Mo | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 7 | Co-Co2P | Co | Co2P | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 8 | NiCoP-Co | Co | NiCoP | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 9 | Ni/W5N4 | Ni | W5N4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 10 | Ni/Ni3N | Ni | Ni3N | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 11 | FeNi3/NiFe2O4 | FeNi3 | NiFe2O4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 12 | FeCoNi/MnWO4 | FeCoNi | MnWO4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 13 | Ni3S2/Fe3O4 | Ni3S2 | Fe3O4 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 14 | Ni3S2/MoS2 | Ni3S2 | MoS2 | Metal to semiconductor | [ |
| 15 | Ru-WO2.72 | Ru | WO2.72 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 16 | Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 | Mo | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 17 | Co/Co0.85Se | Co | Co0.85Se | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 18 | Co/MoSe2 | Co | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 19 | Ru/Ru, Fe-CoP | Ru | Ru, Fe-CoP | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 20 | Co/CoP | Co | CoP | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 21 | Co-NC@W2N | Co | W2N | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 22 | NiS/MoS2 | NiS | MoS2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 23 | NiSe2/MoSe2 | NiSe2 | MoSe2 | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 24 | NiSe2/Ni2P | NiSe2 | Ni2P | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| 25 | Co4N/Co2P | Co4N | Co2P | Semiconductor to metal | [ |
| [57] | 秦睿, 王鹏彦, 林灿, 等. 过渡金属氮化物的活性起源、合成方法及电催化应用. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(7): 41. |
| [58] |
TANG S, ZHANG Z, XIANG J, et al. Recent advances in transition metal nitrides for hydrogen electrocatalysis in alkaline media: from catalyst design to application. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 1073175.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
ZHOU Y M, CHU B X, SUN Z J, et al. Surface reconstruction and charge distribution enabling Ni/W5N4 Mott-Schottky heterojunction bifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient urea-assisted water electrolysis. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 323: 122168.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
HONG Z Z, XU Z L, WU Z T, et al. Construction of core-shell Co-NC@W2N Schottky heterojunctions for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution reaction. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 608: 155159.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
RUI D, LI J, DU X, et al. VFe@Ni/Ni3N Mott-Schottky heterojunction induced electronic modulation for efficient alkaline water splitting. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2023, 947: 117763.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
SAKILA K, PAL S, ROY P, et al. Surface oxygen vacancy engineering of Cr-doped FeNi3/NiFe2O4Mott-Schottky heterojunction as efficient electrocatalyst for high current density water oxidation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 977: 173393.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
JIANG M M, XU J, CHEN Y J, et al. High-efficiency photo- assisted large current-density water splitting with Mott-Schottky heterojunctions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 64(3): e202415492.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
HUANG Z, CHEN L, ZHANG H, et al. Manipulating interfacial charge redistribution in Mott-Schottky electrocatalyst for high-performance water-seawater splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 501: 157628.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
REN Y, WANG C, DUAN W, et al. MoS2/Ni3S2Schottky heterojunction regulating local charge distribution for efficient urea oxidation and hydrogen evolution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 628: 446.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
GU C, ZHOU G Y, YANG J, et al. NiS/MoS2 Mott-Schottky heterojunction-induced local charge redistribution for high- efficiency urea-assisted energy-saving hydrogen production. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 443: 136321.
DOI URL |
| [1] |
XU Y, WANG C, HUANG Y, et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for neutral and large-current-density water electrolysis. Nano Energy, 2021, 80: 105545.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XU Z, WU Z S. Scalable production of high-performance electrocatalysts for electrochemical water splitting at large current densities. eScience, 2025, 5(4): 100334.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
李宇明, 徐砚文, 刘红宇, 等. 镍基磷化物的合成及其在电解水制氢中的应用. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4385.
DOI |
| [4] |
陈心悦, 陈彬剑, 毛煜东, 等. 碱性电解水析氢催化剂的研究进展及展望. 化工进展, 2025, 44(11): 6334.
DOI |
| [5] |
HU C, LV C, ZENG N, et al. Recent advances in Ni-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Technology, 2023, 11(1): 2201048.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HE H, MAI J H, HU K S, et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Metals, 2025, 44: 2208.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 王红霞, 徐婉怡, 张早校. 可再生电力电解制绿色氢能的发展现状与建议. 化工进展, 2022, 41(S1): 118. |
| [8] | 张正, 宋凌珺. 电解水制氢技术: 进展、挑战与未来展望. 工程科学学报, 2025, 47(2): 282. |
| [9] |
DOU S, WANG X, WANG S Y, et al. Rational design of transition metal-based materials for highly efficient electrocatalysis. Small Methods, 2019, 3(1): 1800211.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 张博轩, 崔金星, 李智芳, 等. 非贵金属析氢电催化剂的结构调控研究进展. 化学通报, 2023, 86(7): 784. |
| [11] |
DO H H, TRAN N T, VAN TRAN V. Recent advancements and perspectives in MoO2-based heterostructures for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 105: 234.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XIONG W, YIN H, WU T, et al. Challenges and opportunities of transition metal oxides as electrocatalysts. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2023, 29(5): e202202872.
DOI URL |
| [13] | ZHU Y L, LIN Q, ZHONG Y J, et al. Metal oxide-based materials as an emerging family of hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13: 3361. |
| [14] |
SHIRAZ H G, CRISPIN X, BERGGREN M. Transition metal sulfides for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(47): 24060.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
GUO Y, PARK T, YI J W, et al. Nanoarchitectonics for transition- metal-sulfide-based electrocatalysts for water splitting. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(17): 1807134.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 万凯, 向志朋, 刘文博, 等. 过渡金属硫化物电解水析氢/析氧反应电催化剂研究进展. 科学通报, 2022, 67(19): 2126. |
| [17] |
WANG Z Y, LIU S L, DUAN W, et al. Transition metal selenides as catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 60: 1414.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LI Y, WANG C, ABDUKAYUM A, et al. Advances in green hydrogen generation based on MoSe2 hybrid catalysts. Electrochimica Acta, 2024, 503: 144891.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
白苗苗, 刘江英, 韩婕, 等. 硒化镍基电催化水裂解催化剂的研究进展. 功能材料, 2023, 54(11): 11050.
DOI |
| [20] |
DU M, LI D, LIU S F, et al. Transition metal phosphides: a wonder catalyst for electrocatalytic hydrogen production. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(9): 108156.
DOI |
| [21] |
DENG R, GUO M, WANG C, et al. Recent advances in cobalt phosphide-based materials for electrocatalytic water splitting: from catalytic mechanism and synthesis method to optimization design. Nano Materials Science, 2024, 6(2): 139.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG W Y, GUO R H, YUE Q X, et al. High-entropy phosphide bifunctional catalyst: preparation and performance of efficient water splitting. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1265.
DOI URL |
| [23] | PENG X, PI C, ZHANG X, et al. Recent progress of transition metal nitrides for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2019, 3(2): 366. |
| [67] |
YUN S, GAO Z, YANG T, et al. Constructing NiSe2/MoSe2 Mott- Schottky heterojunctions onto N-doped brain coral-carbon spheres by phase separation strategies for advanced energy conversion applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 34(17): 2314226.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
SUN Y, CAO W, GE X, et al. Built-in electric field induced interfacial charge distributions of Ni2P/NiSe2 heterojunction for urea-assisted hydrogen evolution reaction. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 10: 6674.
DOI URL |
| [69] | QIN M, CHEN L, ZHANG H, et al. Achieving highly efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution by Mott-Schottky heterojunction of Co2P/Co4N. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 14023. |
| [24] |
蒋博龙, 崔艳艳, 史顺杰, 等. 双金属氮化物NiMoN析氢催化剂制备及其电解海水析氢性能的研究. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1394.
DOI |
| [25] |
JIANG J, QIU Y, DONG H, et al. Enhancing hydrogen evolution by heterointerface engineering of Ni/MoN catalysts. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 686: 681.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
XU C, HONG Y, LI Z, et al. Transition metal-based heterojunctions for alkaline electrocatalytic water splitting. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2025, 523: 216287.
DOI URL |
| [27] | LONG X, MENG J, GU J, et al. Interfacial engineering of NiFeP/ NiFe-LDH heterojunction for efficient overall water splitting. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 2204046. |
| [28] |
ZHAO G, JIANG Y, DOU S X, et al. Interface engineering of heterostructured electrocatalysts towards efficient alkaline hydrogen electrocatalysis. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(1): 85.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
REN X P, LI Q, LING F, et al. Construction of MoO2/MoS2 heterojunction on carbon nanotubes as high-efficiency electrocatalysts for H2 production. CrystEngComm, 2023, 25: 5238.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
XU D, ZHANG S N, LI X H, et al. Design of the synergistic rectifying interfaces in Mott-Schottky catalysts. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(1): 1.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHANG H M, LI R, MUHAMMAD H, et al. Recent progress in Mott-Schottky junction electrocatalysts for the pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 8(12): 2811.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
TONG Y X, LIU W, LI C M, et al. A metal/semiconductor contact induced Mott-Schottky junction for enhancing the electrocatalytic activity of water-splitting catalysts. Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2023, 7(1): 12.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
QIAO D, YUN S, SUN M, et al. 1D/3D trepang-like N-modified carbon confined bimetal carbides and metal cobalt: boosting electron transfer via dual Mott-Schottky heterojunctions triggered built-in electric fields for efficient hydrogen evolution and tri-iodide reduction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 334: 122830.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 刘恩科, 朱秉升, 罗晋生. 半导体物理学. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017. |
| [35] |
张伶, 陈红梅, 魏子栋. 过渡金属氧化物催化析氧反应研究进展. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 3876.
DOI |
| [36] |
SAHOO S, WICKRAMATHILAKA K Y, NJERI E, et al. A review on transition metal oxides in catalysis. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2024, 12: 1374878.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
CHEN L, WANG H, TIAN W W, et al. Enabling internal electric field in heterogeneous nanosheets to significantly accelerate alkaline hydrogen electrocatalysis. Small, 2024, 20(18): 2307252.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LI R, PU Z, ZHOU R, et al. In situ controllable construction of Ni@NiO Schottky heterojunctions for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(46): 18849.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
CHEN J, ZHENG J, HE W, et al. Self-standing hollow porous Co/a-WOx nanowire with maximum Mott-Schottky effect for boosting alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Research, 2023, 16(4): 4603.
DOI |
| [40] |
LIU M, YANG H, ZHOU Z, et al. Homologous heterostructures of Ni/NiFeO Mott-Schottky for alkaline water electrolysis. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12: 22210.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
PENG L, SU L, YU X, et al. Electron redistribution of ruthenium- tungsten oxides Mott-Schottky heterojunction for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 308: 121229.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
何倩倩, 王哲, 孟令佳, 等. 基于过渡金属二硫族化物析氢催化的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 523.
DOI |
| [43] |
SUN J, MENG X. Modulating the electronic properties of MoS2 nanosheets for electrochemical hydrogen production: a review. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(11): 11413.
DOI URL |
| [44] | JIANG L, XIA Y X, LI J J, et al. Engineering Mott-Schottky heterojunction Auδ+/1T-MoS1.76 electrocatalyst for boosting hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(6): 3255. |
| [45] |
SUN Z, LIN L, YUAN M W, et al. Mott-Schottky heterostructure induce the interfacial electron redistribution of MoS2 for boosting pH-universal hydrogen evolution with Pt-like activity. Nano Energy, 2022, 101: 107563.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
WAZIR M B, DAUD M, SAFEER S, et al. Review on 2D molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) and its hybrids for green hydrogen (H2) generation applications. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(20): 16856.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
YANG C M, LI X, LIANG Y C. Recent advances in molybdenum diselenide-based electrocatalysts: preparation and application in the hydrogen evolution reaction. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 10(19): 5517.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YANG C, ZHOU L, WANG C, et al. Large-scale synthetic Mo@(2H-1T)-MoSe2 monolithic electrode for efficient hydrogen evolution in all pH scale ranges and seawater. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 304: 120993.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
SONG T, ZHANG Z, ZHAO B, et al. Boosting catalytic performance of hierarchical Co/Co0.85Se microspheres via Mott- Schottky effect toward triiodide reduction and alkaline hydrogen evolution. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 918: 165608.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
REN X P, HU Q W, LING F, et al. Mott-Schottky heterojunction formation between Co and MoSe2 on carbon nanotubes towards superior hydrogen evolution. New Carbon Materials, 2023, 38(6): 1059.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
SHI Y M, ZHANG B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(6): 1529.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
杨博, 吕功煊, 马建泰, 等. 过渡金属磷化物在催化反应中的稳定性. 化学进展, 2024, 36(7): 998.
DOI |
| [53] |
LIU Z Y, FENG C, YANG S T, et al. 1D/3D dual carbon-supported Mott-Schottky-type Co-Co2P heterojunctions for pH-universal hydrogen evolution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 657: 559.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
WANG Z, WANG S. Constructing built-in electric field to accelerate the asymmetric local charge distribution for efficient alkaline overall water/seawater splitting. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 352: 124002.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
XUE Z H, SU H, YU Q Y, et al. Janus Co/CoP nanoparticles as efficient Mott-Schottky electrocatalysts for overall water splitting in wide pH range. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(12): 1602355.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
YAN L, CHEN Y H, XIE J C, et al. Optimizing heterointerface of NiCoP-Co/MXene with regulated charge distribution via built-in electric field for efficient overall water-splitting. Rare Metals, 2025, 44(2): 1067.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘占一, 李勉, 欧阳晓平, 柴之芳, 黄庆. 干法后处理熔盐中Sr/Cs去除方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 150-158. |
| [2] | 孙炼, 张磊磊, 薛泽旭, 吴坤, 陈晔, 李志远, 王鲁凯, 王尊刚. 面向辐射探测应用的零维金属卤化物闪烁体研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 159-176. |
| [3] | 范雨竹, 王媛, 王林燕, 向美玲, 鄢雨婷, 黎本慧, 李敏, 文志东, 王海超, 陈永福, 邱会东, 赵波, 周成裕. 氧化石墨烯基吸附材料去除水体中Pb(II): 制备、性能及机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 12-26. |
| [4] | 邬博宇, 张深根, 张生杨, 刘波, 张柏林. CeO2对MnOx催化剂低温脱硝性能的影响及其机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 87-95. |
| [5] | 徐锦涛, 高攀, 何唯一, 蒋圣楠, 潘秀红, 汤美波, 陈锟, 刘学超. 3C-SiC晶体制备研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [6] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [7] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [8] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [9] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [10] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [11] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [12] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [13] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [14] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [15] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||