无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 245-252.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250086 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250086
严弥迦1,2( ), 张佳乐1,2, 张秋红1(
), 张佳乐1,2, 张秋红1( ), 陈航榕1,2
), 陈航榕1,2
收稿日期:2025-02-26
修回日期:2025-03-21
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-10
通讯作者:
张秋红, 副研究员. E-mail: zhangqh@ucas.ac.cn作者简介:严弥迦(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: yanmijia22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
YAN Mijia1,2( ), ZHANG Jiale1,2, ZHANG Qiuhong1(
), ZHANG Jiale1,2, ZHANG Qiuhong1( ), CHEN Hangrong1,2
), CHEN Hangrong1,2
Received:2025-02-26
Revised:2025-03-21
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-10
Contact:
ZHANG Qiuhong, associate professor. E-mail: zhangqh@ucas.ac.cnAbout author:YAN Mijia (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: yanmijia22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
对乙酰氨基酚(Acetaminophen, APAP)过量服用是临床上急性肝损伤(Acute Liver Injury, ALI)的常见诱因, 主要病理特征为大量活性氧(Reactive Oxygen Species, ROS)累积和炎性细胞浸润。本研究通过仿生矿化工艺制备了一种超小尺寸(约1.3 nm)氧化铈团簇酶(CeO2 Clusterzymes, CeCs), 该材料具有高的氧空位含量(52.6%)和高的Ce3+/Ce4+比例(1.06), 对多种ROS(包括自由基)具有优异的吸附和清除能力, 可用于肝细胞保护。动物体内实验进一步证实CeCs可以实现APAP诱导的ALI的高效干预治疗, 显著延长治疗窗口和逆转无菌炎症, 表现出潜在的临床应用价值。
中图分类号:
严弥迦, 张佳乐, 张秋红, 陈航榕. 氧化铈团簇酶仿生合成及其对急性肝损伤治疗的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 245-252.
YAN Mijia, ZHANG Jiale, ZHANG Qiuhong, CHEN Hangrong. CeO2 Clusterzymes: Biomimetic Synthesis and Treatment for Acute Liver Injury[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 245-252.
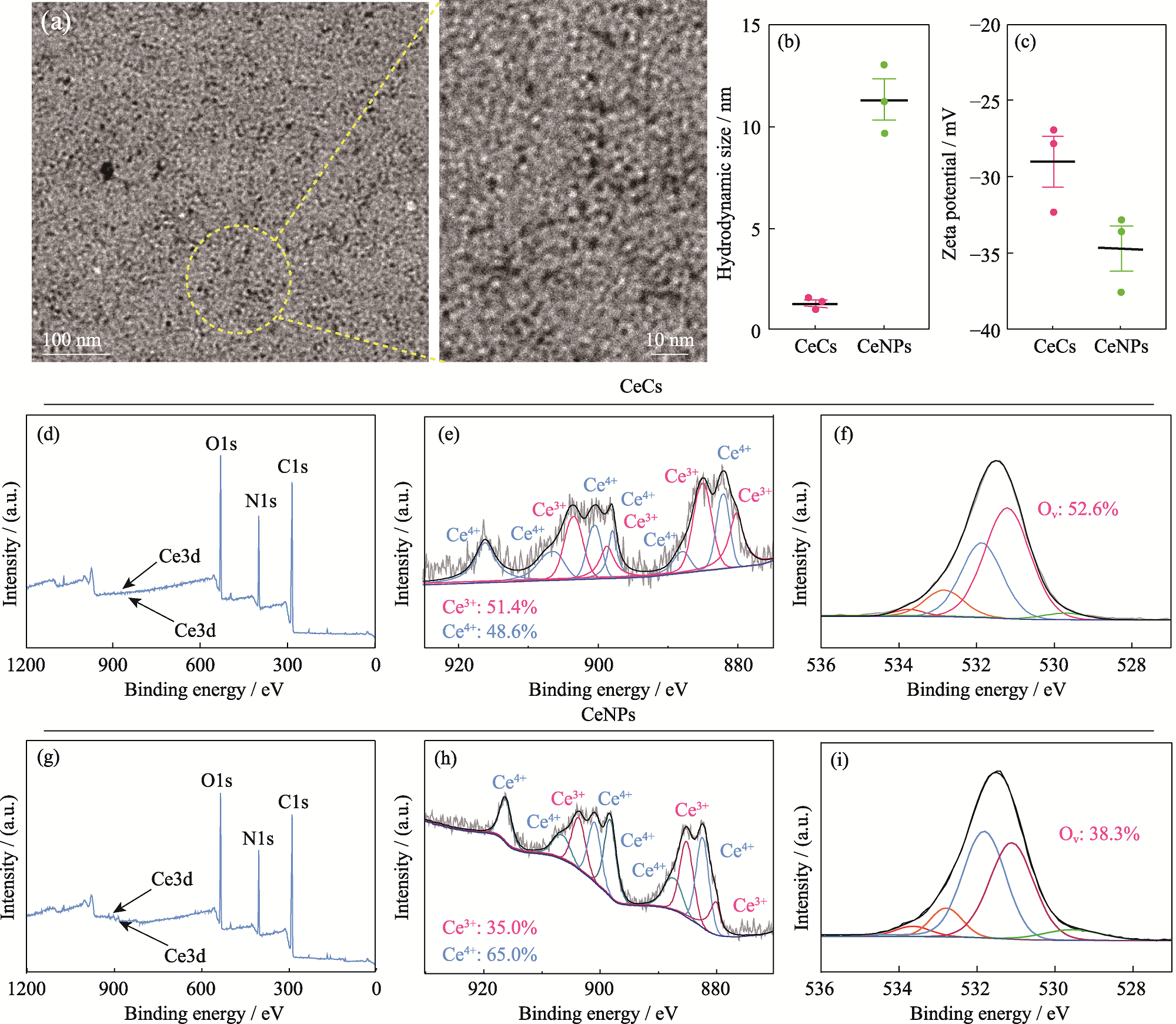
图1 CeCs和CeNPs的理化性能表征
Fig. 1 Physical and chemical properties of CeCs and CeNPs (a) TEM images of CeCs; (b) Hydrodynamic size of CeCs and CeNPs; (c) Zeta potential of CeCs and CeNPs; (d) XPS total spectrum of CeCs; (e, f) High resolution XPS spectra on Ce3d (e) and O1s (f) of CeCs; (g) XPS total spectrum of CeNPs; (h, i) High resolution XPS spectra on Ce3d (h) and O1s (i) of CeNPs
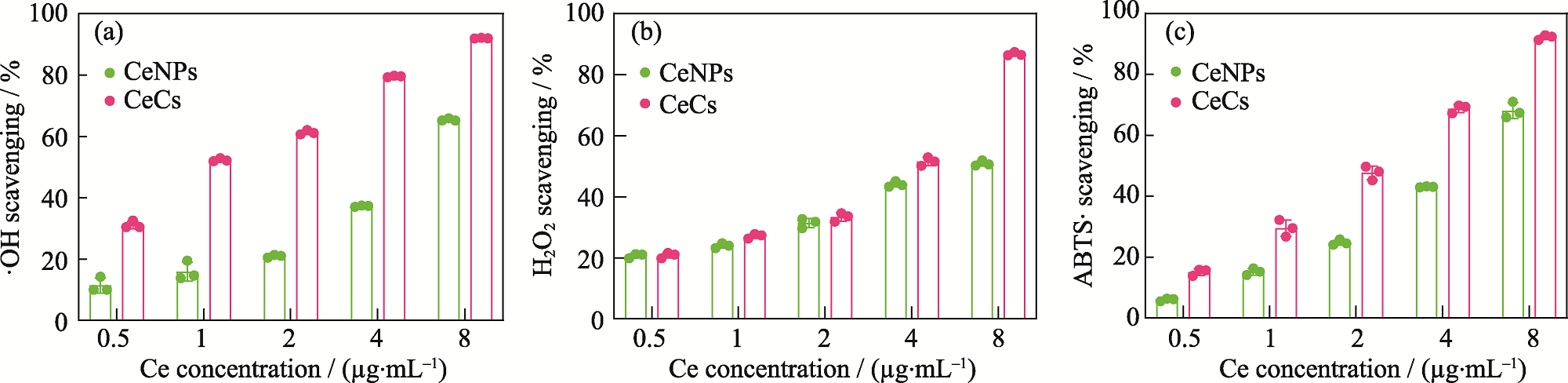
图2 CeCs和CeNPs对多种ROS的清除能力
Fig. 2 Scavenging capability of CeCs and CeNPs to various ROS (a)·OH; (b) H2O2; (c) ABTS·. Corlorful figures are available on website
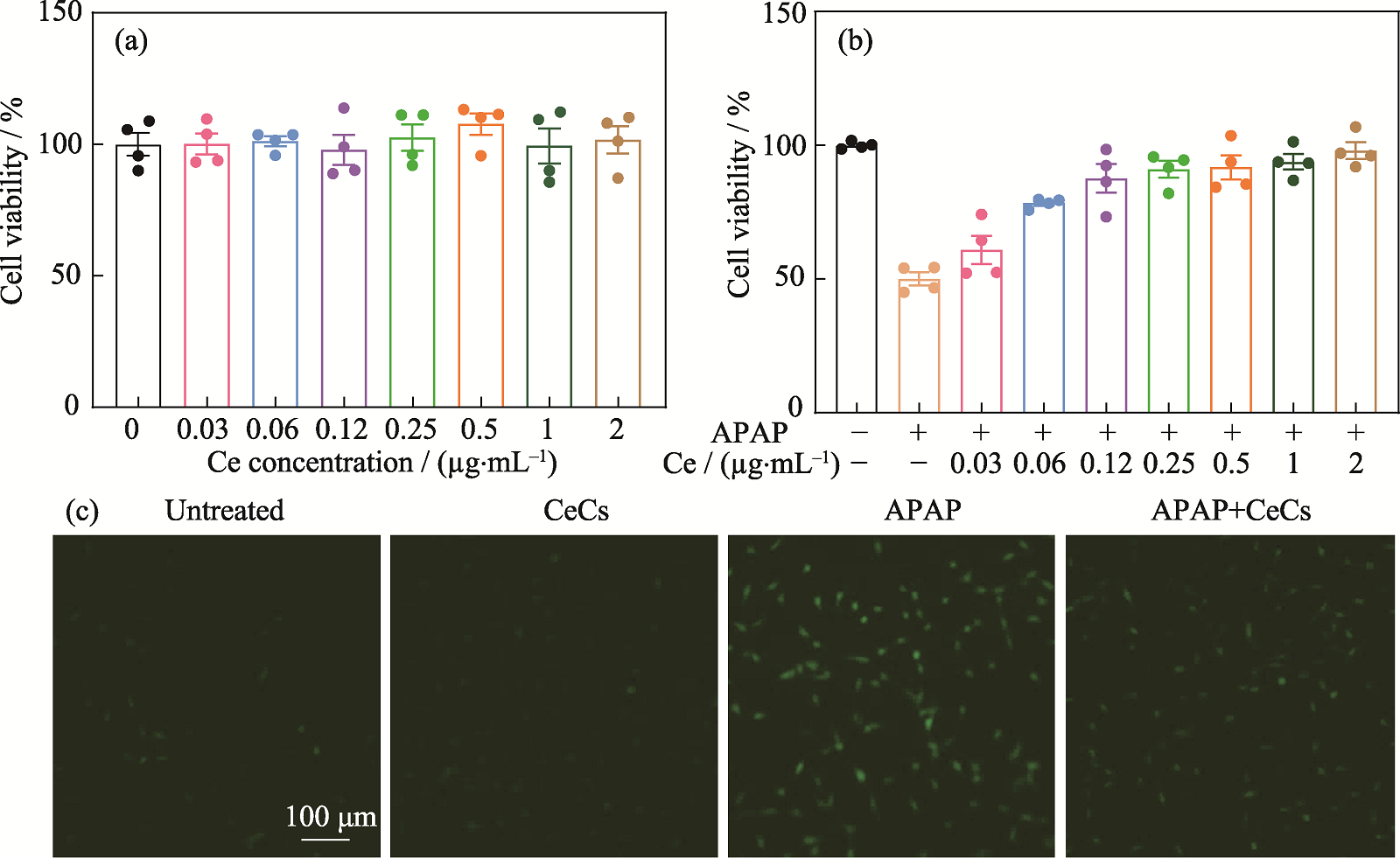
图3 细胞内抗氧化活性与肝细胞保护
Fig. 3 Intracellular antioxidant activity and hepatocytes protection (a) Cytotoxicity profiles of different concentrations of CeCs on BNL CL.2 cells; (b) Protective effect of different concentrations of CeCs on APAP-treated cells; (c) Fluorescence images of generation of ROS by APAP-treated cells incubated with different samples APAP: Acetaminophen
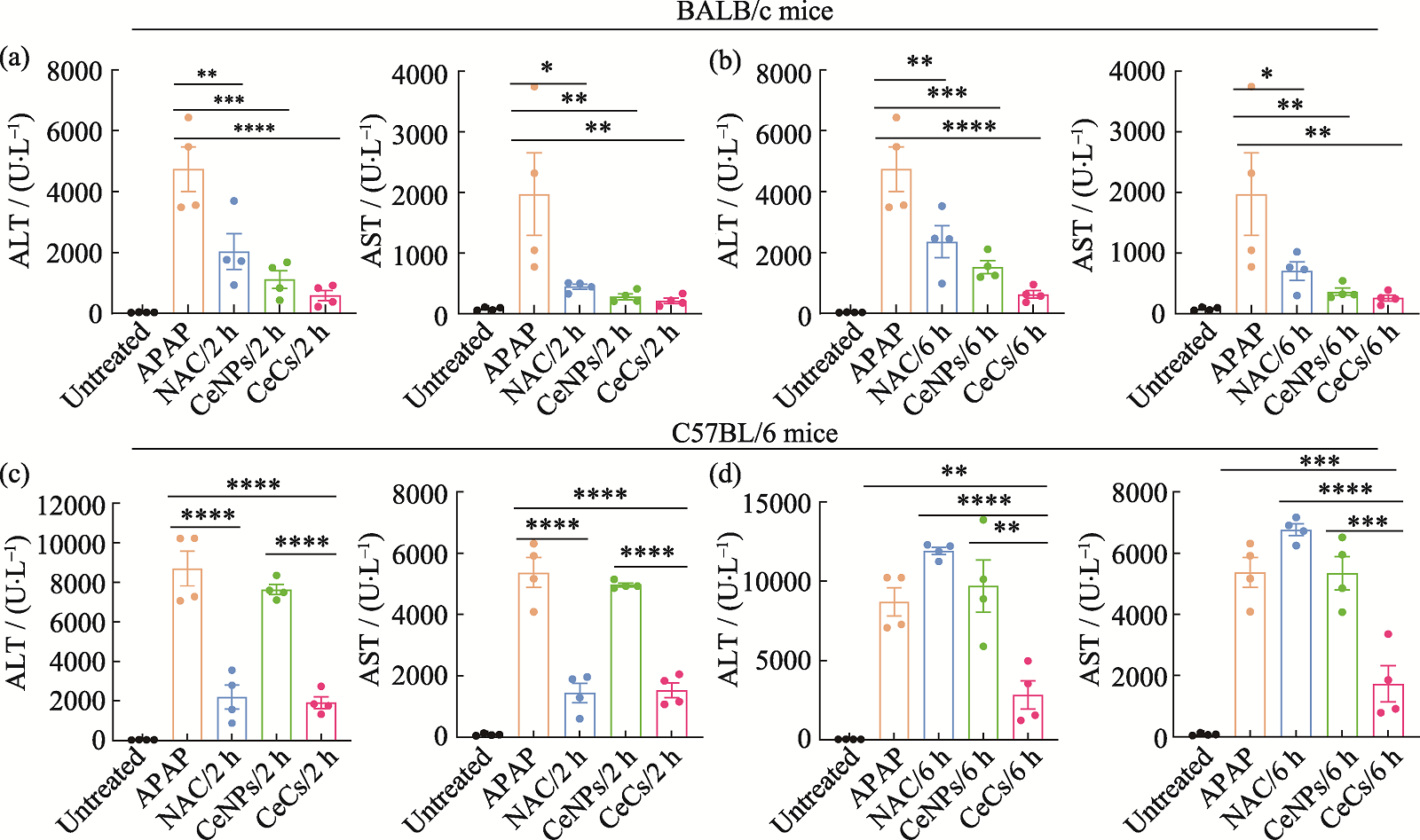
图5 APAP诱导急性肝损伤小鼠的治疗效果评价
Fig. 5 Evaluation of therapeutic effect of APAP-induced acute liver injury mice (a, b) Serum levels of ALT and AST in APAP-induced acute liver injury BALB/c mice in 2 (a) and 6 h (b) treatment groups; (c, d) Serum levels of ALT and AST in APAP-induced acute liver injury C57BL/6 mice in 2 (c) and 6 h (d) treatment groups APAP: Acetaminophen; ALT: Glutamate aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase
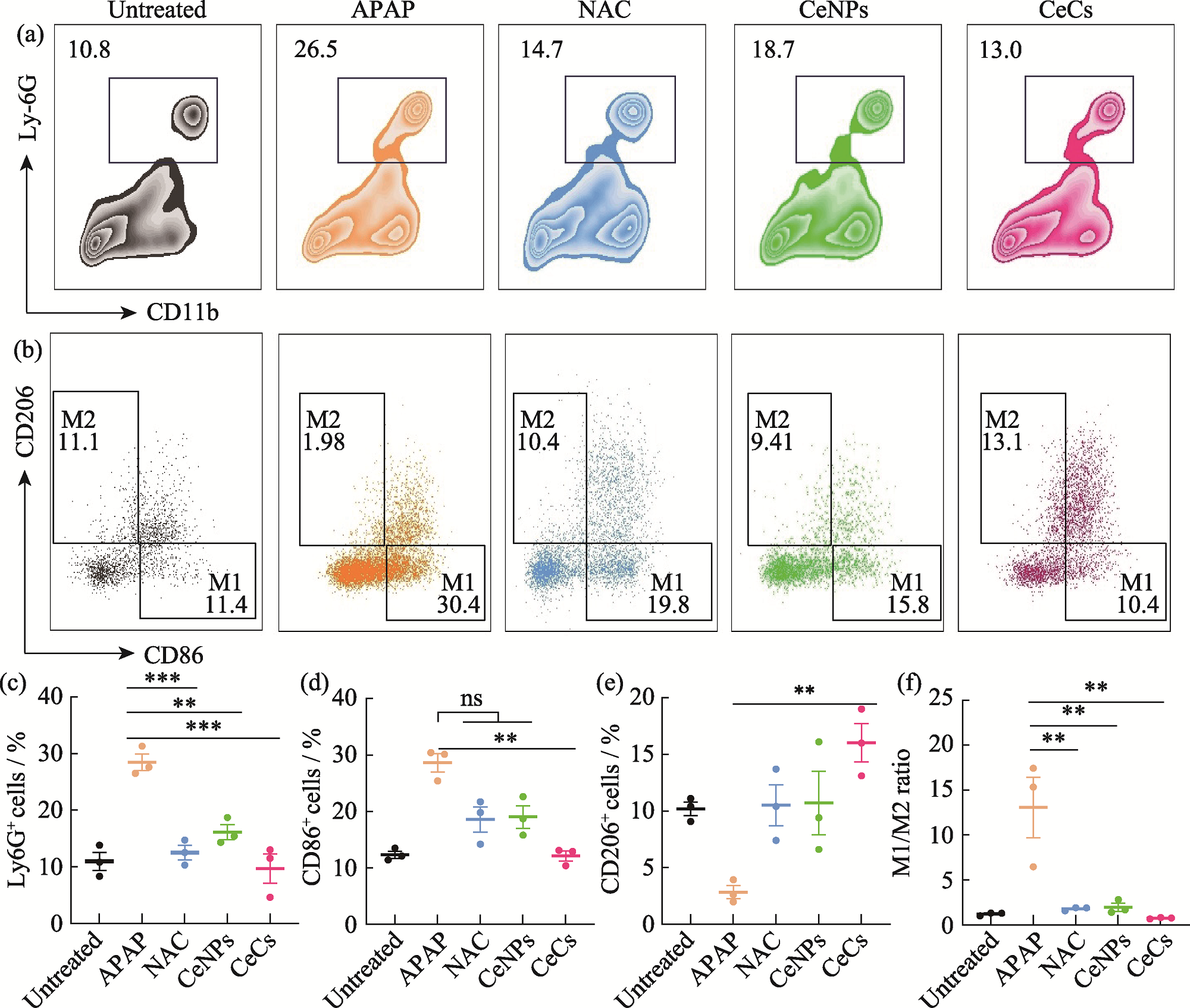
图6 APAP诱导急性肝损伤小鼠的抗炎效果评价
Fig. 6 Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of APAP-induced ALI mice (a, b) Flow cytometry to determine expression of Ly-6G (neutrophil markers), CD86 (M1 phenotypic macrophage markers) and CD206 (M2 phenotypic macrophage markers) on liver tissues after different treatment; (c) Quantification of neutrophils; (d) M1 macrophages; (e) M2 macrophages; (f) M1/M2 ratio APAP: Acetaminophen; ALI: Acute liver injury
| [1] |
STRAVITZ R T, LEE W M. Acute liver failure. The Lancet, 2019, 394(10201): 869.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FERNÁNDEZ J, BASSEGODA O, TOAPANTA D, et al. Acute liver failure: a practical update. JHEP Reports, 2024, 6(9): 101131.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BERNAL W, WENDON J. Acute liver failure. New England Journal of Medicine, 2013, 369(26): 2525.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DU K, RAMACHANDRAN A, JAESCHKE H. Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biology, 2016, 10: 148.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
WANG F, YUAN H, SHEN J, et al. Nanozymes with broad-spectrum scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) alleviate inflammation in acute liver injury. ACS Materials Letters, 2024, 6(4): 1304.
DOI URL |
| [6] | AHMED O, ROBINSON M W, O’FARRELLY C. Inflammatory processes in the liver: divergent roles in homeostasis and pathology. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 2021, 18(6): 1375. |
| [7] | LIU J, HAN X, ZHANG T, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: from mechanism to therapy. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 2023, 16(1): 100124. |
| [8] |
TENÓRIO M C D S, GRACILIANO N G, MOURA F A, et al. N-acetylcysteine (NAC): impacts on human health. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(6): 967.
DOI URL |
| [9] | LI F, QIU Y, XIA F, et al. Dual detoxification and inflammatory regulation by ceria nanozymes for drug-induced liver injury therapy. Nano Today, 2020, 35: 100925. |
| [10] | YANG R, MIKI K, HE X, et al. Prolonged treatment with N-acetylcystine delays liver recovery from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Critical Care, 2009, 13(2): R55. |
| [11] |
MUHAMMAD F, HUANG F, CHENG Y, et al. Nanoceria as an electron reservoir: spontaneous deposition of metal nanoparticles on oxides and their anti-inflammatory activities. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(12): 20567.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
KOO S, SOHN H S, KIM T H, et al. Ceria-vesicle nanohybrid therapeutic for modulation of innate and adaptive immunity in a collagen-induced arthritis model. Nature Nanotechnology, 2023, 18(12): 1502.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
IM G B, KIM Y G, YOO T Y, et al. Ceria nanoparticles as copper chaperones that activate SOD1 for synergistic antioxidant therapy to treat ischemic vascular diseases. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(16): 2208989.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG L, ZHU B, DENG Y, et al. Biocatalytic and antioxidant nanostructures for ROS scavenging and biotherapeutics. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(31): 2101804.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
KIM Y G, LEE Y, LEE N, et al. Ceria-based therapeutic antioxidants for biomedical applications. Advanced Materials, 2023, 36(10): 2210819.
DOI URL |
| [16] | YUN L X, WU H, SHEN Z G, et al. Ultrasmall CeO2 nanoparticles with rich oxygen defects as novel catalysts for efficient glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(16): 5278. |
| [17] | 梁云燕, 孙芳营, 尚利. 基于金纳米团簇类酶活性的比色传感研究. 分析化学, 2021, 49(6): 931. |
| [18] |
SUN S, LIU H, XIN Q, et al. Atomic engineering of clusterzyme for relieving acute neuroinflammation through lattice expansion. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(6): 2562.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
FU S, CHEN H, YANG W, et al. ROS-targeted depression therapy via BSA-incubated ceria nanoclusters. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(11): 4519.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG Y, WU Y, LIU Y, et al. BSA-mediated synthesis of bismuth sulfide nanotheranostic agents for tumor multimodal imaging and thermoradiotherapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(29): 5335.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
BLANCO E, SHEN H, FERRARI M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(9): 941.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
SUN Y, LU D, ZHANG H, et al. Titanium oxide electrocatalytic membrane filtration: “two faces” of oxygen vacancies in generation and transformation of reactive oxygen species. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 57(35): 13226.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KESAVARDHANA S, MALIREDDI R K S, KANNEGANTI T. Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Annual Review of Immunology, 2020, 38(1): 567.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
BHUSHAN B, APTE U. Liver regeneration after acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. The American Journal of Pathology, 2019, 189(4): 719.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO C, LI Z, CHEN J, et al. Site-specific biomimicry of antioxidative melanin formation and its application for acute liver injury therapy and imaging. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(34): 2102391.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ROTUNDO L, PYRSOPOULOS N. Liver injury induced by paracetamol and challenges associated with intentional and unintentional use. World Journal of Hepatology, 2020, 12(4): 125.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | 郑惠星.对乙酰氨基酚诱导小鼠急性肝损伤模型机理研究. 延吉: 延边大学硕士学位论文, 2015. |
| [28] |
ETEMADI Y, AKAKPO J Y, RAMACHANDRAN A, et al. Nrf2 as a therapeutic target in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: a case study with sulforaphane. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 2023, 37(12): e23505.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
KANG D, KIM C K, JEONG H, et al. Biocompatible custom ceria nanoparticles against reactive oxygen species resolve acute inflammatory reaction after intracerebral hemorrhage. Nano Research, 2017, 10(8): 2743.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 于慧杰, 盛国光. 三种品系小鼠对伴刀豆球蛋白A所致急性肝损伤的耐受性比较研究. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2014, 17(2): 168. |
| [31] |
SHAN X, LI J, LIU J, et al. Targeting ferroptosis by poly(acrylic) acid coated Mn3O4 nanoparticles alleviates acute liver injury. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 7598.
DOI |
| [32] |
XIA F, HU X, ZHANG B, et al. Ultrasmall ruthenium nanoparticles with boosted antioxidant activity upregulate regulatory T cells for highly efficient liver injury therapy. Small, 2022, 18(29): 2201558.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
MU J, LI C, SHI Y, et al. Protective effect of platinum nano-antioxidant and nitric oxide against hepatic ischemia- reperfusion injury. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2513.
DOI |
| [1] | 马新超, 智清, 李威, 陈毛, 王海龙, 张锐, 张帆, 范冰冰. Fe2AlB2的高温氧化机制及吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 45-54. |
| [2] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [3] | 李筱暄, 付前刚, 文子豪, 杨金山, 倪德伟, 张洁, 程源, 刘昱轩, 褚衍辉, 蔡飞燕, 王京阳, 张幸红. 极端环境用超高温陶瓷结构材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1045-1078. |
| [4] | 王文婷, 徐敬军, 马科, 李美栓, 李兴超, 李同起. 原位反应/热压合成Ti2AlC-20TiB2复合材料在1000~1300 ℃空气中的高温氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [5] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [6] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [7] | 郑斌, 康凯, 张青, 叶昉, 解静, 贾研, 孙国栋, 成来飞. 前驱体转化陶瓷法制备Ti3SiC2陶瓷及其热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 733-740. |
| [8] | 张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590. |
| [9] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [10] | 舒朝琴, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 熔盐法制备含钴氯磷灰石及其抗氧化性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [11] | 王皓轩, 刘巧沐, 王一光. 高熵过渡金属碳化物陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [12] | 张亚晨, 孟佳, 蔡坤, 盛晓晨, 乐军, 宋力昕. 基于声发射技术的Si-Cr-Ti高温抗氧化涂层弯曲失效机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [13] | 黄秀兵, 王鹏, 陶进长, 席作帅. CeO2修饰Mn-Fe-O复合材料及其NH3-SCR脱硝催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 573-580. |
| [14] | 余汉青, 董志军, 袁观明, 丛野, 李轩科, 罗永明. B-C掺杂SiC纤维的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 493-501. |
| [15] | 杨志宾, 岳彤联, 余向南, 吴苗苗. 钴掺杂氧化铈纳米粒子电催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 845-853. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||