无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 45-54.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250218 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250218
马新超1( ), 智清1, 李威1, 陈毛1,2(
), 智清1, 李威1, 陈毛1,2( ), 王海龙1,2, 张锐1,2, 张帆3, 范冰冰1,2(
), 王海龙1,2, 张锐1,2, 张帆3, 范冰冰1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-20
修回日期:2025-06-30
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-07-20
通讯作者:
陈 毛, 副研究员. E-mail: mchen@zzu.edu.cn;作者简介:马新超(2004-), 男, 本科. E-mail: 2848489094@qq.com
基金资助:
MA Xinchao1( ), ZHI Qing1, LI Wei1, CHEN Mao1,2(
), ZHI Qing1, LI Wei1, CHEN Mao1,2( ), WANG Hailong1,2, ZHANG Rui1,2, ZHANG Fan3, FAN Bingbing1,2(
), WANG Hailong1,2, ZHANG Rui1,2, ZHANG Fan3, FAN Bingbing1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-20
Revised:2025-06-30
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-07-20
Contact:
CHEN Mao, associate professor. E-mail: mchen@zzu.edu.cn;About author:MA Xinchao (2004-), male, undergraduate. E-mail: 2848489094@qq.com
Supported by:摘要: 传统吸波材料在高温条件下易失效, 难以满足极端高温环境的性能需求。Fe2AlB2因其纳米层状结构以及优良的高温稳定性, 在高温吸波领域备受关注。本研究通过湿法球磨-氩气烧结工艺制备了Fe2AlB2粉末, 并系统研究了Fe2AlB2在高温下的氧化机制和吸波性能变化规律。同时, 借助电磁仿真软件对其在7 GHz微波下的吸收过程进行了雷达散射截面模拟。结果表明: Fe2AlB2起始氧化温度为671 ℃, 随着氧化温度的升高, 其表面形成致密Al2O3保护膜, 抗氧化性能显著增强; 当氧化温度超过1000 ℃时, Al2O3膜破裂, 主相转变为Fe2O3、Al4B2O9以及非晶态B2O3; 在300~800 ℃氧化温度范围内, 样品吸波性能随氧化温度升高而逐步提升, 尤其在10 GHz附近, 其介电损耗能力最为突出。当氧化温度升高至900 ℃时, 在频率f = 11.28 GHz下, 样品的反射损耗达到-42.60 dB, 相应的厚度为2.8 mm。Al2O3膜通过诱导“氧化膜-基体”界面极化损耗, 显著提高了介电损耗效率。本研究阐明了Fe2AlB2在不同温度的氧化机制及其对吸波性能的影响规律, 为其在高温吸波环境中的应用提供了理论基础。
中图分类号:
马新超, 智清, 李威, 陈毛, 王海龙, 张锐, 张帆, 范冰冰. Fe2AlB2的高温氧化机制及吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 45-54.
MA Xinchao, ZHI Qing, LI Wei, CHEN Mao, WANG Hailong, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Fan, FAN Bingbing. High-temperature Oxidation Mechanism and Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Fe2AlB2[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 45-54.

图2 Fe2AlB2粉体在不同温度下氧化2 h后的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Fe2AlB2 powders oxidized at different temperatures for 2 h (a) 300−600 ℃; (b) 700−900 ℃; (c) 1000−1200 ℃
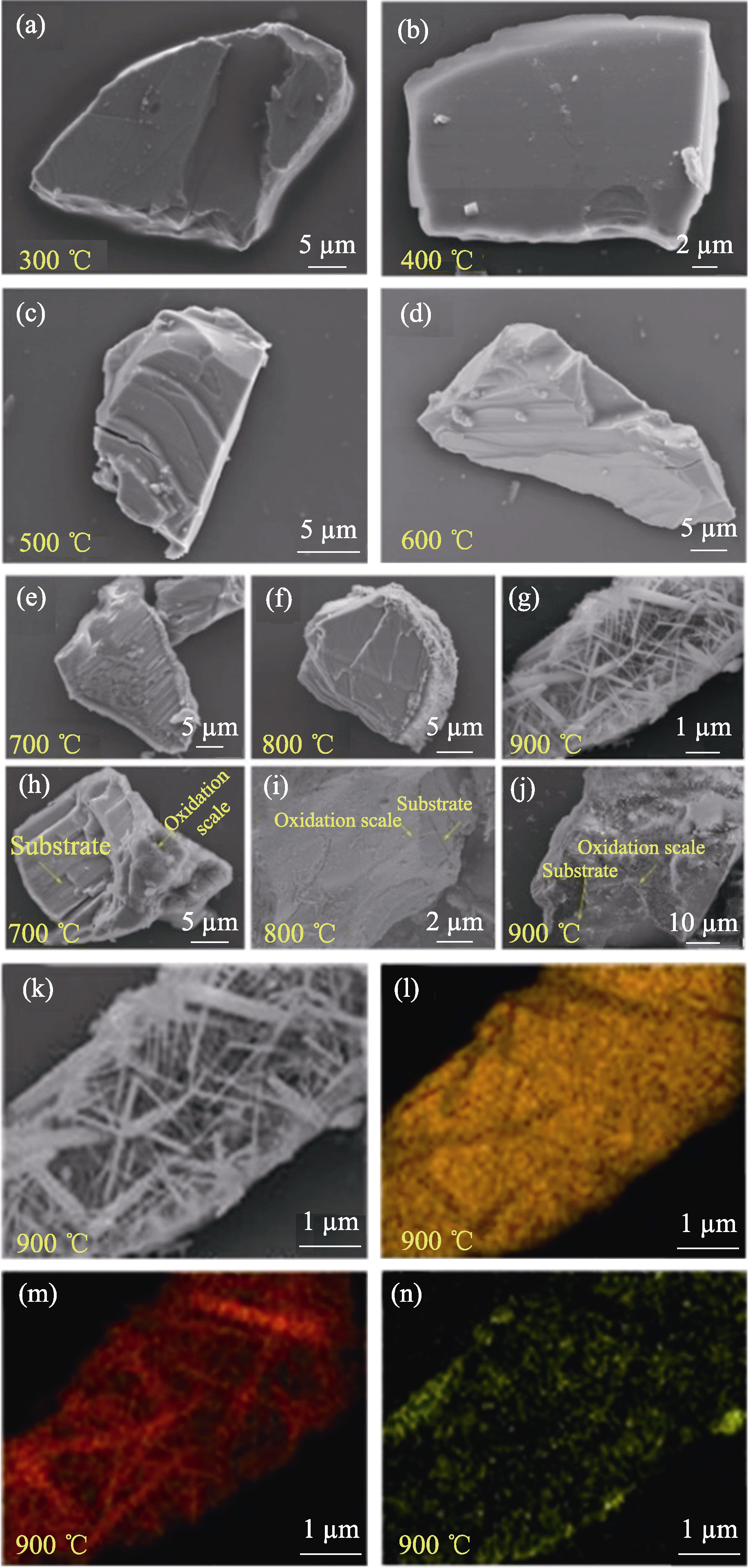
图4 Fe2AlB2粉体在不同温度下氧化2 h后的SEM照片和EDS分析
Fig. 4 SEM images and EDS mappings of Fe2AlB2 powders oxidized at different temperatures (a) 300 ℃; (b) 400 ℃; (c) 500 ℃; (d) 600 ℃; (e, h) 700 ℃; (f, i) 800 ℃; (g, j) 900 ℃; (k) SEM image of Fe2AlB2 powder oxidized at 900 ℃ for 2 h and (l-n) Corresponding elemental EDS mappings of (l) Al, (m) O and (n) Fe
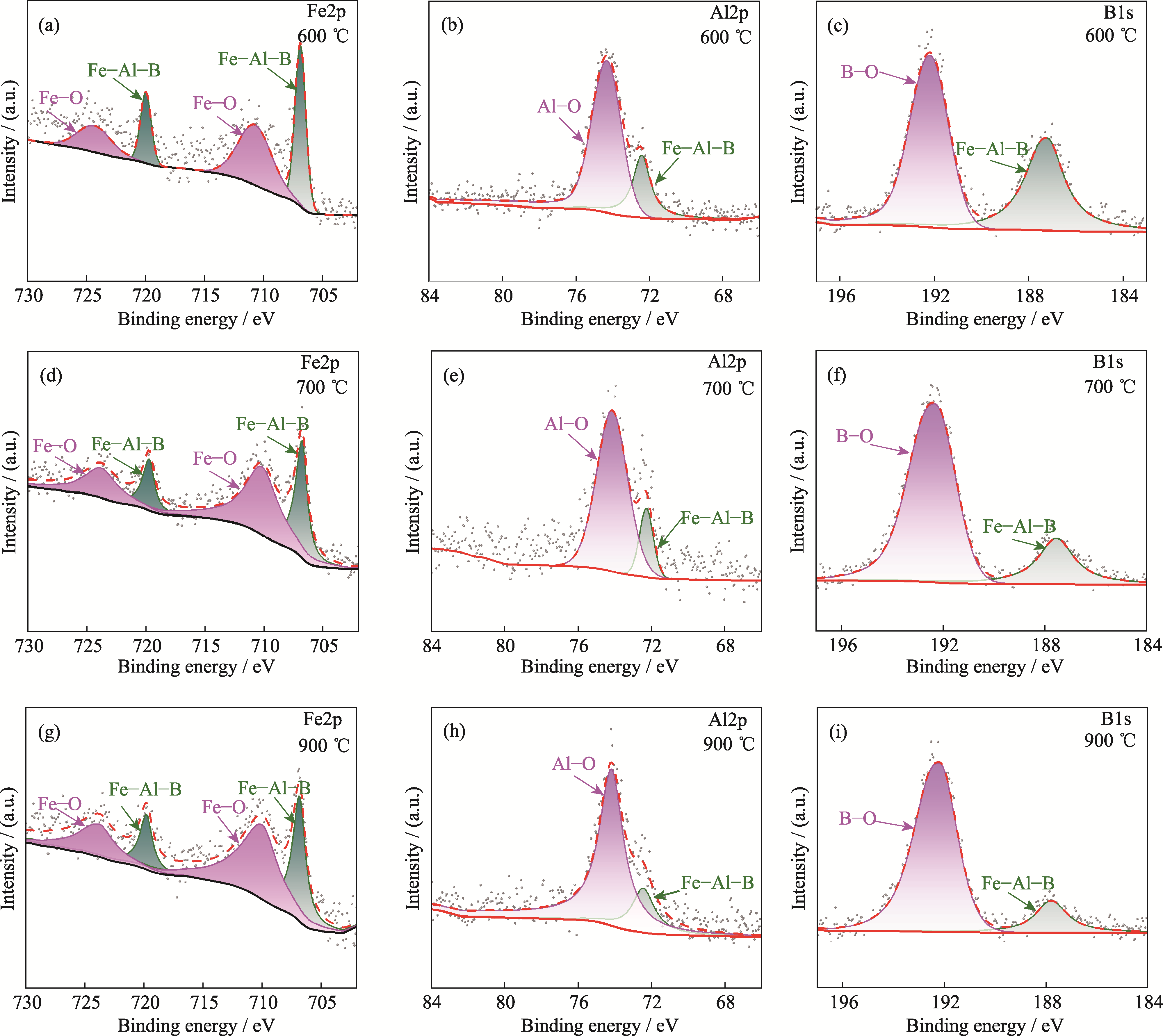
图5 Fe2AlB2粉体在不同温度下氧化2 h所得样品的Fe2p、Al2p和B1s XPS谱图
Fig. 5 Fe2p, Al2p and B1s XPS spectra of Fe2AlB2 powders oxidized at different temperatures for 2 h (a-c) 600 ℃; (d-f) 700 ℃; (g-i) 900 ℃
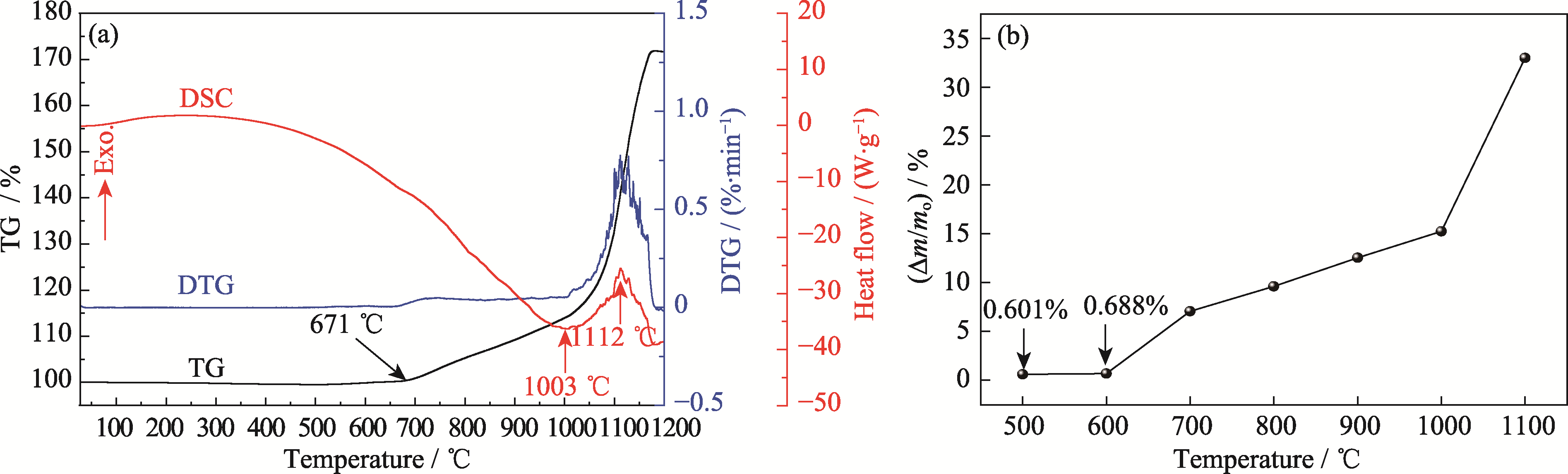
图6 Fe2AlB2粉体的TG-DTG-DSC曲线(a)及恒温氧化2 h后的增重曲线(b)
Fig. 6 TG-DTG-DSC curves (a) and weight gain curve after isothermal oxidation for 2 h (b) of Fe2AlB2 powders
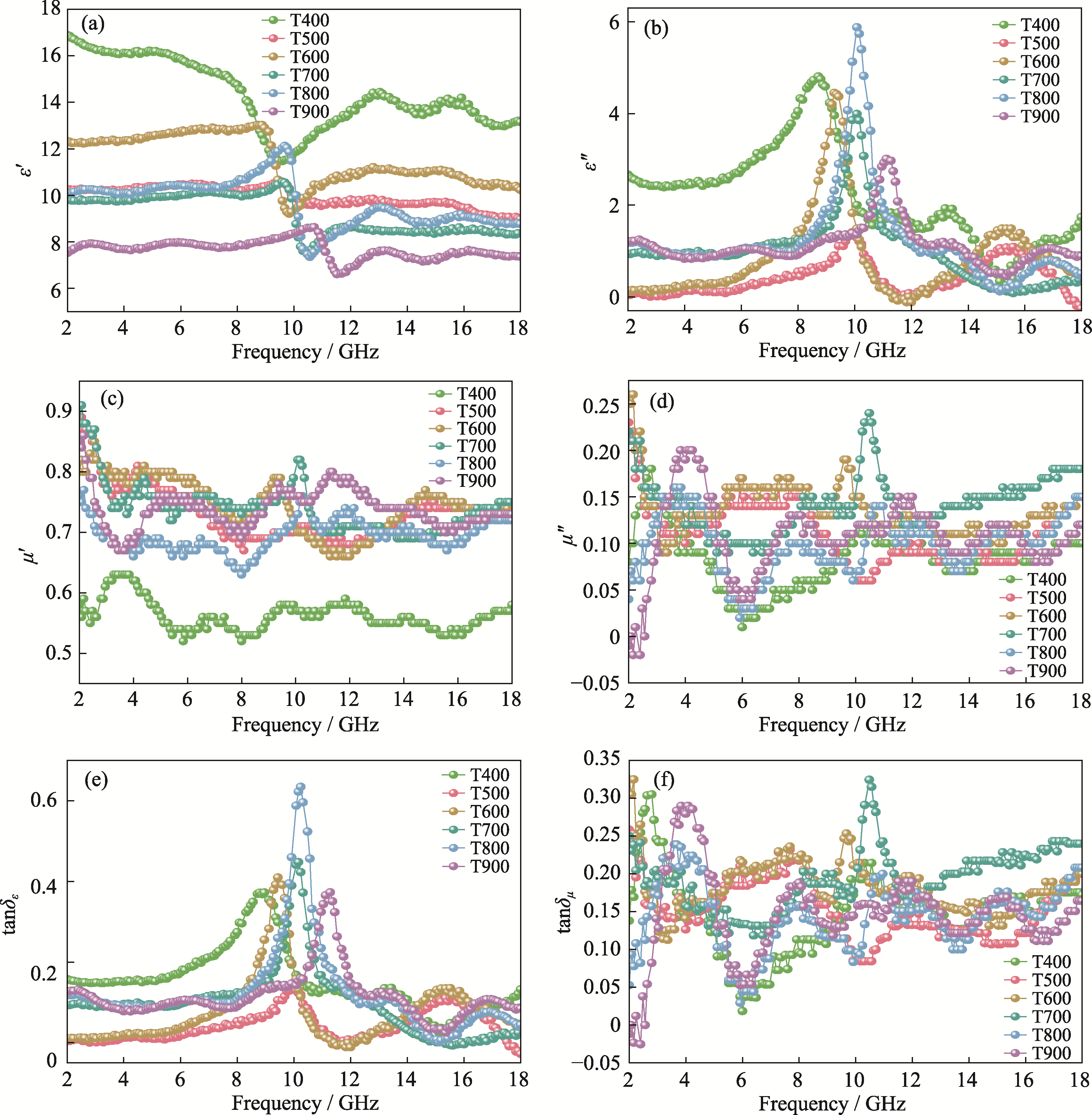
图7 T400~T900样品的电磁参数
Fig. 7 Electromagnetic parameters of T400−T900 samples (a) ${\varepsilon }'$; (b) ${\varepsilon }''$; (c) ${\mu }'$; (d) ${\mu }''$; (e) $\tan {{\delta }_{\varepsilon }}$; (f) $\tan {{\delta }_{\mu }}$. Colorful figures are available on website
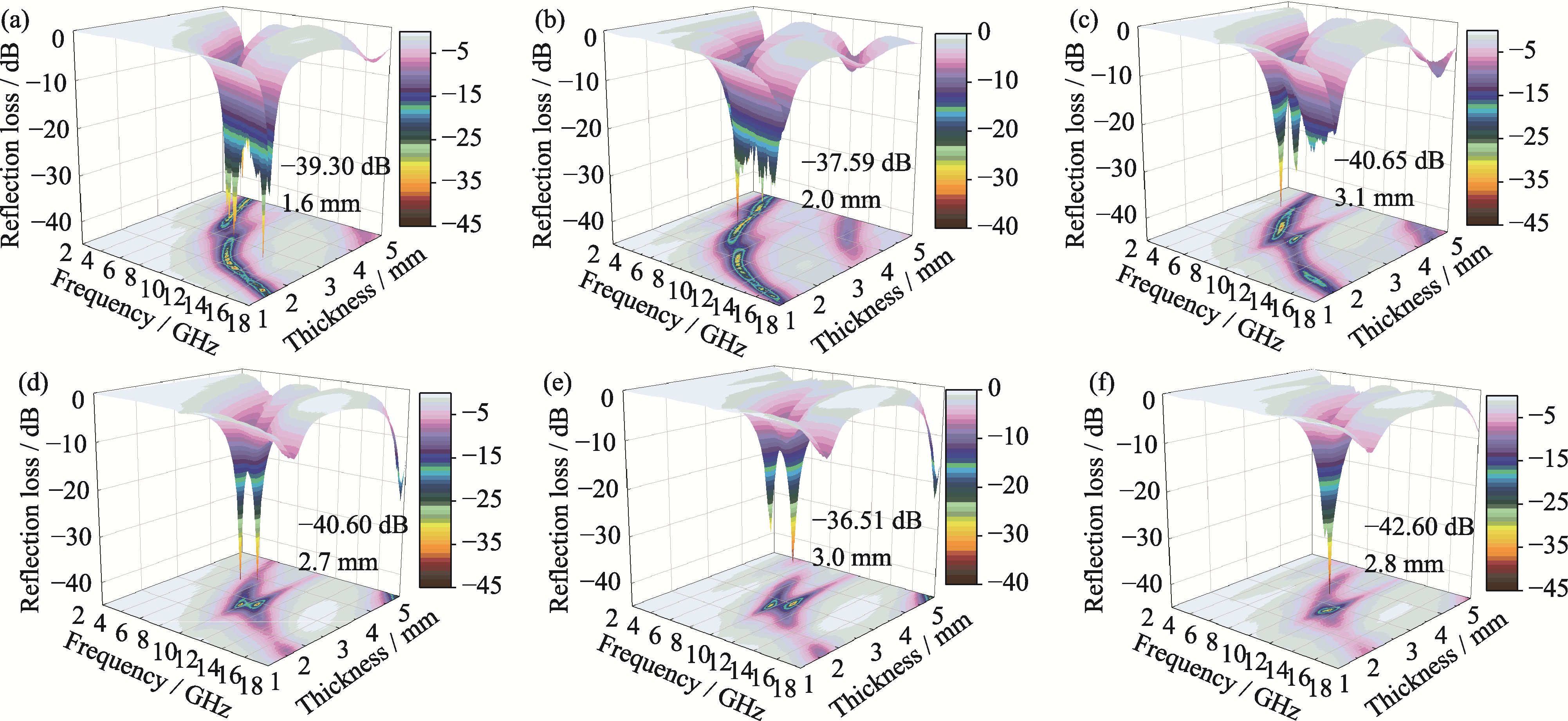
图8 不同氧化温度处理后样品的三维反射损耗曲线
Fig. 8 3D reflection loss curves of the samples oxidized at different temperatures (a) T400; (b) T500; (c) T600; (d) T700; (e) T800; (f) T900. Colorful figures are available on website

图9 不同温度氧化后样品的阻抗匹配曲线
Fig. 9 Impedance matching curves of the samples oxidized at different temperatures (a) T400; (b) T500; (c) T600; (d) T700; (e) T800; (f) T900. Colorful figures are available on website
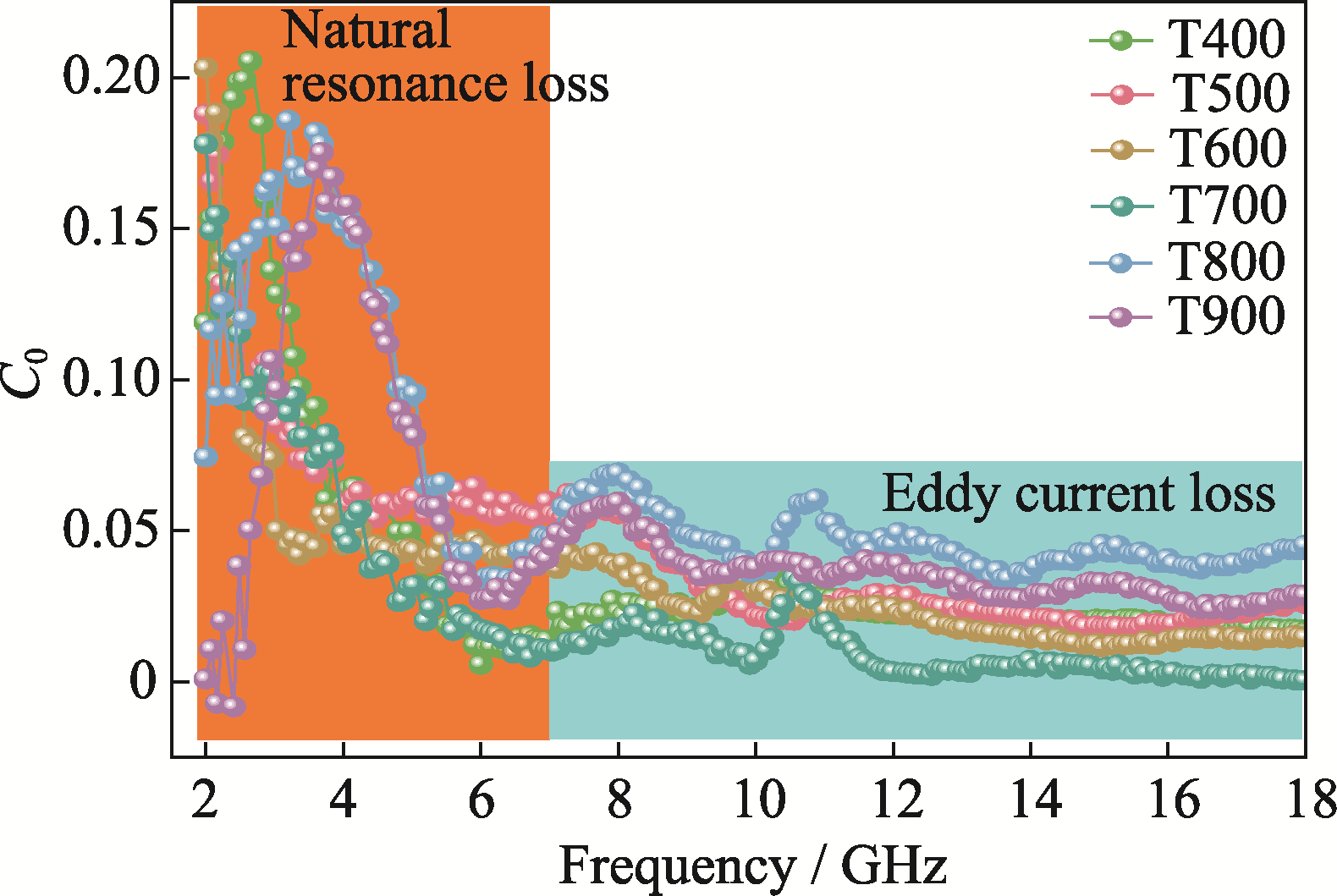
图10 不同温度氧化后样品的磁损耗系数与频率之间的关系曲线
Fig. 10 Curves of magnetic loss coefficient versus frequency for samples oxidized at different temperatures Colorful figure is available on website
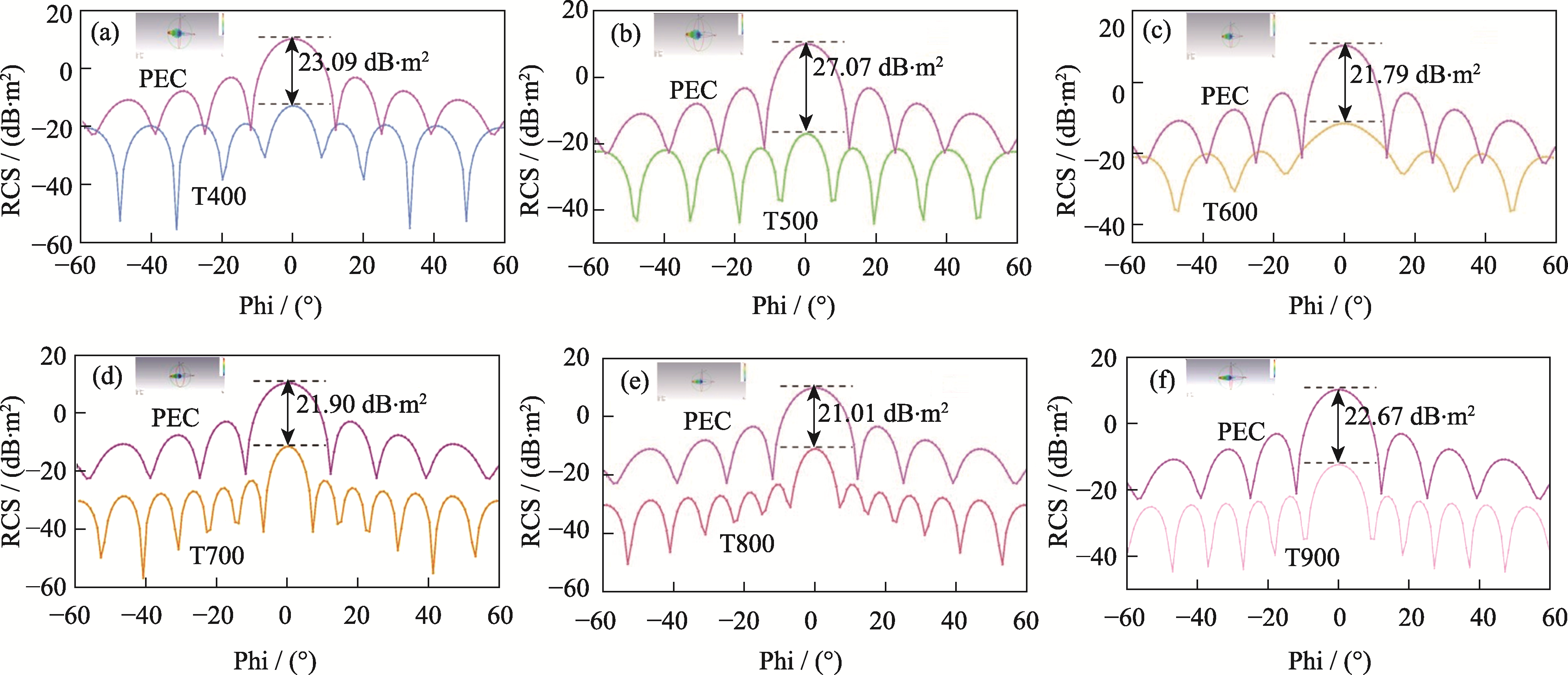
图11 三维雷达波散射信号和RCS模拟曲线
Fig. 11 Three-dimensional radar scattering signals and RCS simulation curves (a) T400; (b) T500; (c) T600; (d) T700; (e) T800; (f) T900
| [1] |
LI J L, XIANG J, YE Q, et al. Microwave absorption properties of double-layer absorbing coatings based on Ni0.4Co0.2Zn0.4Fe2O4 and BaTiO3nanofibers. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 479.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WU Z H, DENG Y, MENG Z Z, et al. Microwave absorbing properties of novel SiC/Cf composites containing SiC array modified coating. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 306.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 徐俊杰, 王岭, 王晓猛, 等. 耐高温吸波材料的研究进展. 现代技术陶瓷, 2024, 45(3): 189. |
| [4] | 刘艳明, 张依偲, 汪欣, 等. 三元层状MoAlB材料的研究进展. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2023, 52(7): 2639. |
| [5] |
KE L Q, HARMON B N, KRAMER M J. Electronic structure and magnetic properties in T2AlB2 (T=Fe, Mn, Cr, Co, and Ni) and their alloys. Physical Review B, 2017, 95(10): 104427.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 康新婷, 杨坤, 迟煜頔, 等. Fe-Al金属间化合物抗氧化性能研究现状. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(S2): 822. |
| [7] |
SHAH S H. Atomistic insight into ideal strength, fracture toughness, deformation, and failure mechanisms of magnetocaloric Fe2AlB2. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(9): 5868.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU J, LI S B, YAO B, et al. Thermal stability and thermal shock resistance of Fe2AlB2. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(13): 16035.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
POTANIN A Y, BASHKIROV E A, KARPENKOV A Y, et al. Fabrication of high-strength magnetocaloric Fe2AlB2 MAB phase ceramics via combustion synthesis and hot pressing. Materialia, 2024, 33: 101993.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SHARMA V, BARUA R. Synthesis, characterization, and magnetocaloric properties of the ternary boride Fe2AlB2 for caloric applications. Materials, 2024, 17(16): 3886.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ELMELIGY T A, MESSER O, SOKOL M, et al. Isothermal oxidation of bulk dense Fe2AlB2 and Mn2AlB2 phases in 700-1000 ℃ temperature range. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(1): 116801.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHI Q, WU C W, LI M R, et al. Fe2AlB2: a novel ferromagnetic material with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(21): 34182.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ELMASSALAMI M, OLIVEIRA D D, TAKEYA H. On the ferromagnetism of AlFe2B2. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2011, 323(16): 2133.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
NIU H H, JIANG X W, XIA Y D, et al. Construction of hydrangea-like core-shell SiO2@Ti3C2Tx@CoNi microspheres for tunable electromagnetic wave absorbers. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12 (4): 711.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JIAN G, LIU M R, ZHANG C, et al. Preparation of fully-coated Ag@TiO2 particle fillers for high-k composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 641.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
NATU V, KOTA S S, BARSOUM M W. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the MAB phases, MoAlB, M2AlB2 (M=Cr, Fe), Cr3AlB4 and their binary monoborides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(2): 305.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG W M, ZHAO B, XIANG H M, et al. One-step synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties of high entropy rare earth hexaborides (HE REB6) and high entropy rare earth hexaborides/borates (HE REB6/HE REBO3) composite powders. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(1): 62.
DOI |
| [18] |
PAN F, PEI K, CHEN G, et al. Integrated electromagnetic device with on-off heterointerface for intelligent switching between wave- absorption and wave-transmission. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(49): 2306599.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ONG C W, HUANG H, ZHENG B, et al. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy of nonmetallic materials: electronic structures of boron and BxOy. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 95(7): 3527.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
KONG F Y, FENG K, BAI Y L, et al. Oxidation behavior of high-purity nonstoichiometric Ti2AlC powders in flowing air. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 32(14): 2747.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG W T, XU J J, MA K, et al. Oxidation behavior at 1000- 1300 ℃ in air of Ti2AlC-20TiB2 synthesized by in-situ reaction/hot pressing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 31.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MA J R, SHU J C, CAO W Q, et al. A green fabrication and variable temperature electromagnetic properties for thermal stable microwave absorption towards flower-like Co3O4@rGO/SiO2 composites. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 166: 187.
DOI URL |
| [23] | SAMET M, LEVCHENKO V, BOITEUX G, et al. Electrode polarization vs. Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars interfacial polarization in dielectric spectra of materials: characteristic frequencies and scaling laws. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 142: 194703. |
| [24] |
SHI X L, CAO M S, YUAN J, et al. Dual nonlinear dielectric resonance and nesting microwave absorption peaks of hollow cobalt nanochains composites with negative permeability. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95(16): 163108.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ZHAO B, GUO X Q, ZHAO W Y, et al. Yolk-shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(42): 28917. |
| [1] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [2] | 张育育, 吴轶城, 孙佳, 付前刚. 聚合物转化SiHfCN陶瓷的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 681-690. |
| [3] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [4] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [5] | 郑斌, 康凯, 张青, 叶昉, 解静, 贾研, 孙国栋, 成来飞. 前驱体转化陶瓷法制备Ti3SiC2陶瓷及其热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 733-740. |
| [6] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [7] | 王皓轩, 刘巧沐, 王一光. 高熵过渡金属碳化物陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [8] | 武志红, 邓悦, 蒙真真, 张国丽, 张路平, 王宇斌. 含SiC阵列改性涂层的新型SiC/Cf复合材料吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 306-312. |
| [9] | 陈博文, 王敬晓, 姜佑霖, 周海军, 廖春景, 张翔宇, 阚艳梅, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 基于离心纺丝技术制备稳定的碳化锆纤维[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1385-1390. |
| [10] | 穆阳, 邓佳欣, 李皓, 周万城. 两种连续SiC纤维的高温介电及吸波性能对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 427-433. |
| [11] | 康越, 原博, 马天, 楚增勇, 张政军. 基于石墨烯的电磁波损耗材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1259-1273. |
| [12] | 刘 克, 王际童, 龙东辉, 凌立成. 低密度Fe3O4/中孔炭微球复合材料的可规模制备及吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1023-1028. |
| [13] | 张 旭, 董志军, 袁观明, 丛 野, 李轩科. 陶瓷前驱体配比对Si-Zr-B掺杂沥青基炭材料抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1311-1319. |
| [14] | 曹希文, 罗凌虹, 徐 序, 程 亮, 石纪军, 余 辉. MnCo2O4涂层对SUS430合金连接体的表面改性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(1): 63-68. |
| [15] | 毛金元, 刘 敏, 毛 杰, 邓春明, 曾德长, 徐 林. 等离子喷涂制备ZrB2-MoSi2复合涂层及其抗氧化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 282-286. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||