无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 1-16.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240317 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240317
所属专题: 【结构材料】超高温结构陶瓷(202506); 【结构材料】热障与环境障涂层(202506)
• 综述 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2024-07-03
修回日期:2024-09-23
出版日期:2025-01-20
网络出版日期:2024-09-27
通讯作者:
田志林, 副教授. E-mail: tianzhlin@mail.sysu.edu.cn;作者简介:周帆(1991-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: zhouf88@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHOU Fan( ), TIAN Zhilin(
), TIAN Zhilin( ), LI Bin(
), LI Bin( )
)
Received:2024-07-03
Revised:2024-09-23
Published:2025-01-20
Online:2024-09-27
Contact:
TIAN Zhilin, associate professor. E-mail: tianzhlin@mail.sysu.edu.cn;About author:ZHOU Fan (1991-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhouf88@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
碳化物超高温陶瓷具有高熔点(>3000 ℃)、高硬度、低热导率、优异的耐高温性和良好的化学稳定性等优点, 是高超声速飞行器热防护系统的理想涂层材料。本文概述了碳化物超高温陶瓷(TiC、ZrC、HfC、NbC、TaC)的结构与性质, 总结了化学气相沉积法、等离子喷涂法和固相反应法制备碳化物超高温陶瓷涂层的研究进展, 分析了涂层微观结构、组分、结构设计以及热流密度对烧蚀行为的影响。研究表明, 添加第二相形成多元复合涂层和采用多层结构设计, 可以有效提升碳化物超高温陶瓷涂层的抗烧蚀性能。添加第二相形成复杂氧化物, 可使烧蚀后的氧化层适度烧结, 从而获得良好的结构完整性和阻氧性能。采用梯度分层和多层功能结构设计, 有效缓解了涂层热应力, 抑制了裂纹扩展, 并促进了不同层间的协同增强作用。最后, 结合研究现状, 对碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层发展面临的挑战与机遇进行了展望。
中图分类号:
周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16.
ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16.
| Carbide | TiC | ZrC | HfC | NbC | TaC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal structure | FCC | FCC | FCC | FCC | FCC |
| Space group | |||||
| Lattice parameter/Å | 4.334 | 4.692 | 4.638 | 4.470 | 4.455 |
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 4.899 | 6.634 | 12.686 | 7.803 | 14.498 |
| Melting point/K | 3413 | 3700 | 4223 | 3873 | 4256 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (20-1600 ℃)/(×10-6, K-1) | 8.09 | 7.32 | 6.88 | 7.61 | 6.90 |
| Thermal conductivity* at 25 ℃/(W·m-1·K-1) | 17.9 | 19.1 | 20.0 | 17.4 | 24.7 |
| Vickers hardness*/GPa | 25.20-30.31 | 16.40-25.00 | 18.46-25.12 | 15.10-23.00 | 13.90-19.90 |
| Young's modulus**/GPa | 481.4 | 406.6 | 498.0 | 483.9 | 491.8 |
| Flexural strength*/MPa | 424-545 | 362-407 | 343-372 | 440 | 338-580 |
| Fracture toughness*/(MPa·m1/2) | 3.04-5.01 | 1.90-2.90 | 2.50-3.39 | 2.50-3.41 | 2.70-4.00 |
| Resistivity*/(μΩ·cm) | 83 | 45 | 72 | 50 | 33 |
表1 碳化物超高温陶瓷的性质[23⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-29,36⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓ -65]
Table 1 Properties of carbide UHTCs[23⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-29,36⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓ -65]
| Carbide | TiC | ZrC | HfC | NbC | TaC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal structure | FCC | FCC | FCC | FCC | FCC |
| Space group | |||||
| Lattice parameter/Å | 4.334 | 4.692 | 4.638 | 4.470 | 4.455 |
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 4.899 | 6.634 | 12.686 | 7.803 | 14.498 |
| Melting point/K | 3413 | 3700 | 4223 | 3873 | 4256 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (20-1600 ℃)/(×10-6, K-1) | 8.09 | 7.32 | 6.88 | 7.61 | 6.90 |
| Thermal conductivity* at 25 ℃/(W·m-1·K-1) | 17.9 | 19.1 | 20.0 | 17.4 | 24.7 |
| Vickers hardness*/GPa | 25.20-30.31 | 16.40-25.00 | 18.46-25.12 | 15.10-23.00 | 13.90-19.90 |
| Young's modulus**/GPa | 481.4 | 406.6 | 498.0 | 483.9 | 491.8 |
| Flexural strength*/MPa | 424-545 | 362-407 | 343-372 | 440 | 338-580 |
| Fracture toughness*/(MPa·m1/2) | 3.04-5.01 | 1.90-2.90 | 2.50-3.39 | 2.50-3.41 | 2.70-4.00 |
| Resistivity*/(μΩ·cm) | 83 | 45 | 72 | 50 | 33 |
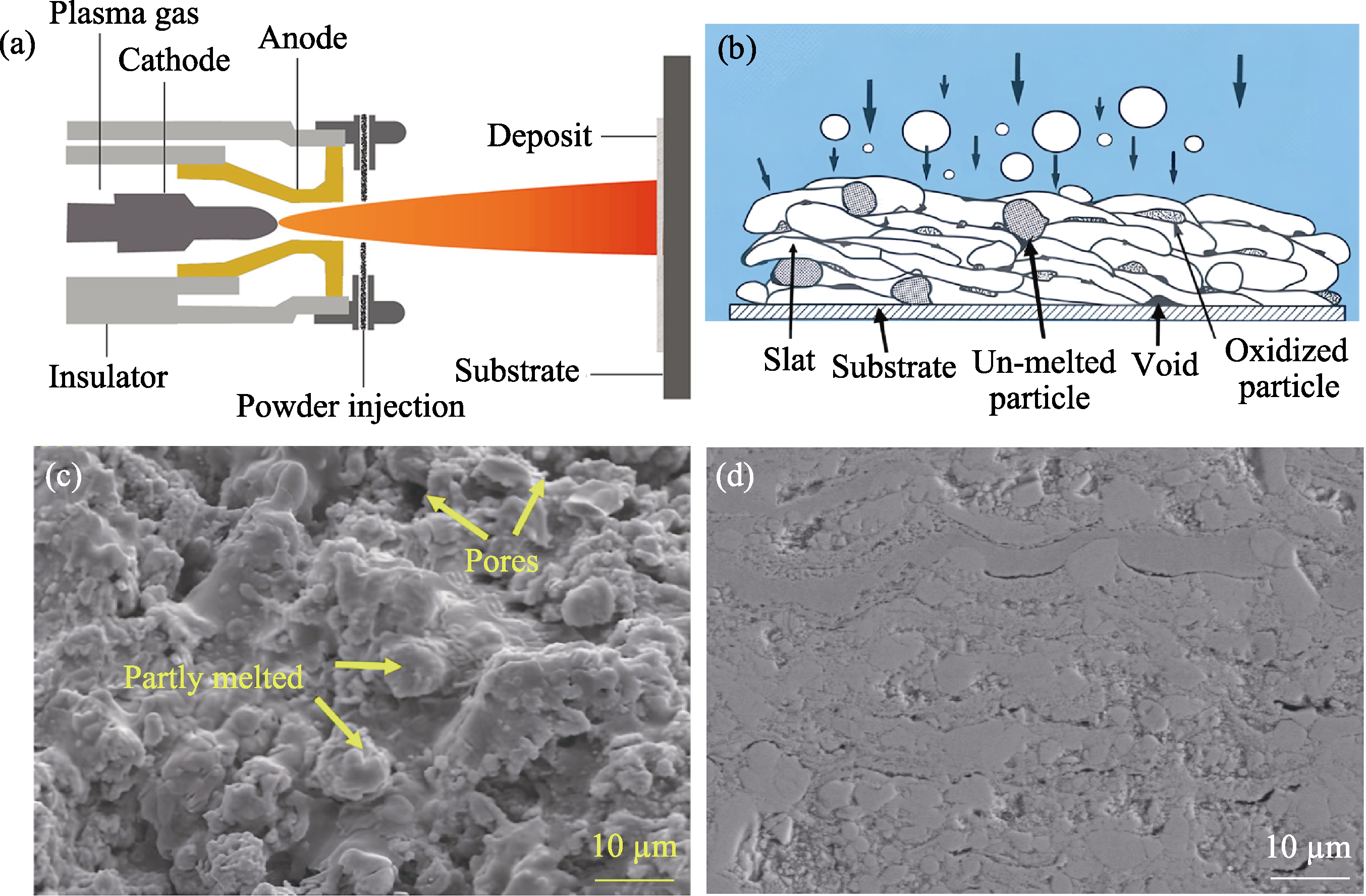
图4 (a)等离子喷涂系统示意图[121], (b)等离子喷涂涂层微观结构示意图[123], (c)等离子喷涂TiC涂层的表面形貌[125]和(d)等离子喷涂HfC涂层的截面微观结构[126]
Fig. 4 (a) Schematic diagram of plasma spraying system[121], (b) microstructure diagram of plasma sprayed coating[123], (c) surface morphology of plasma sprayed TiC coating[125], and (d) cross-sectional microstructure of plasma sprayed HfC coating[126]
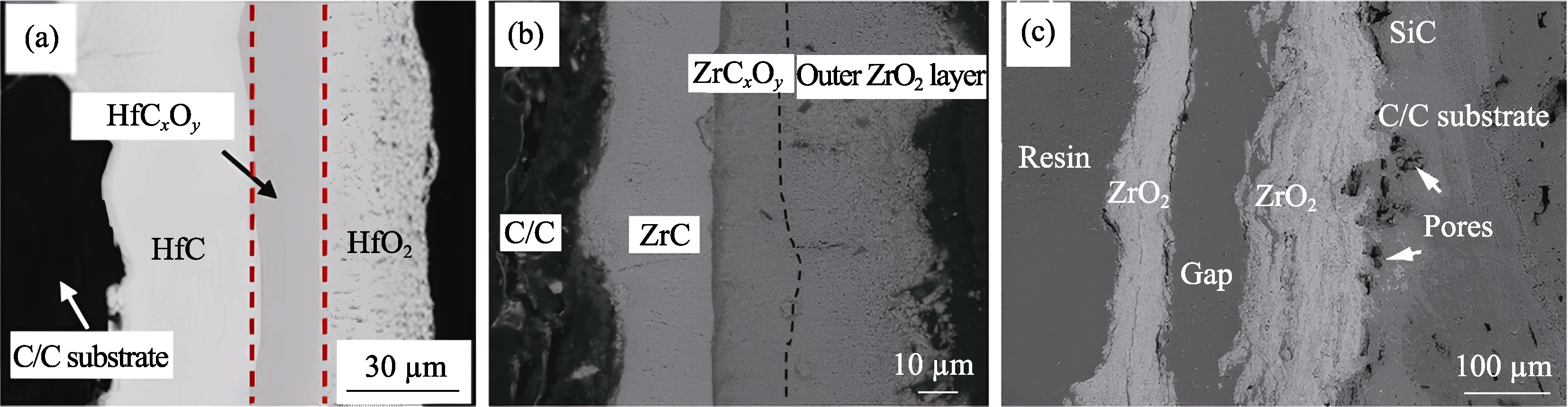
图6 涂层烧蚀后的截面微观结构[127,156 -157]
Fig. 6 Cross-sectional microstructures of the coatings after ablation (a) CVD HfC[156]; (b) CVD ZrC[157]; (c) APS ZrC[127]

图7 在4.2 MW/m2的热流密度条件下烧蚀30 s后ZrC-Zr6Ta2O17涂层中心区域的横截面BSE图像[147]
Fig. 7 Cross-sectional BSE images of the ZrC-Zr6Ta2O17 coatings in central region after 30 s ablation at a heat flux of 4.2 MW/m2[147] (a, b) ZrC coating; (c, d) ZrC-5%Zr6Ta2O17 coating; (e, f) ZrC-20%Zr6Ta2O17 coating
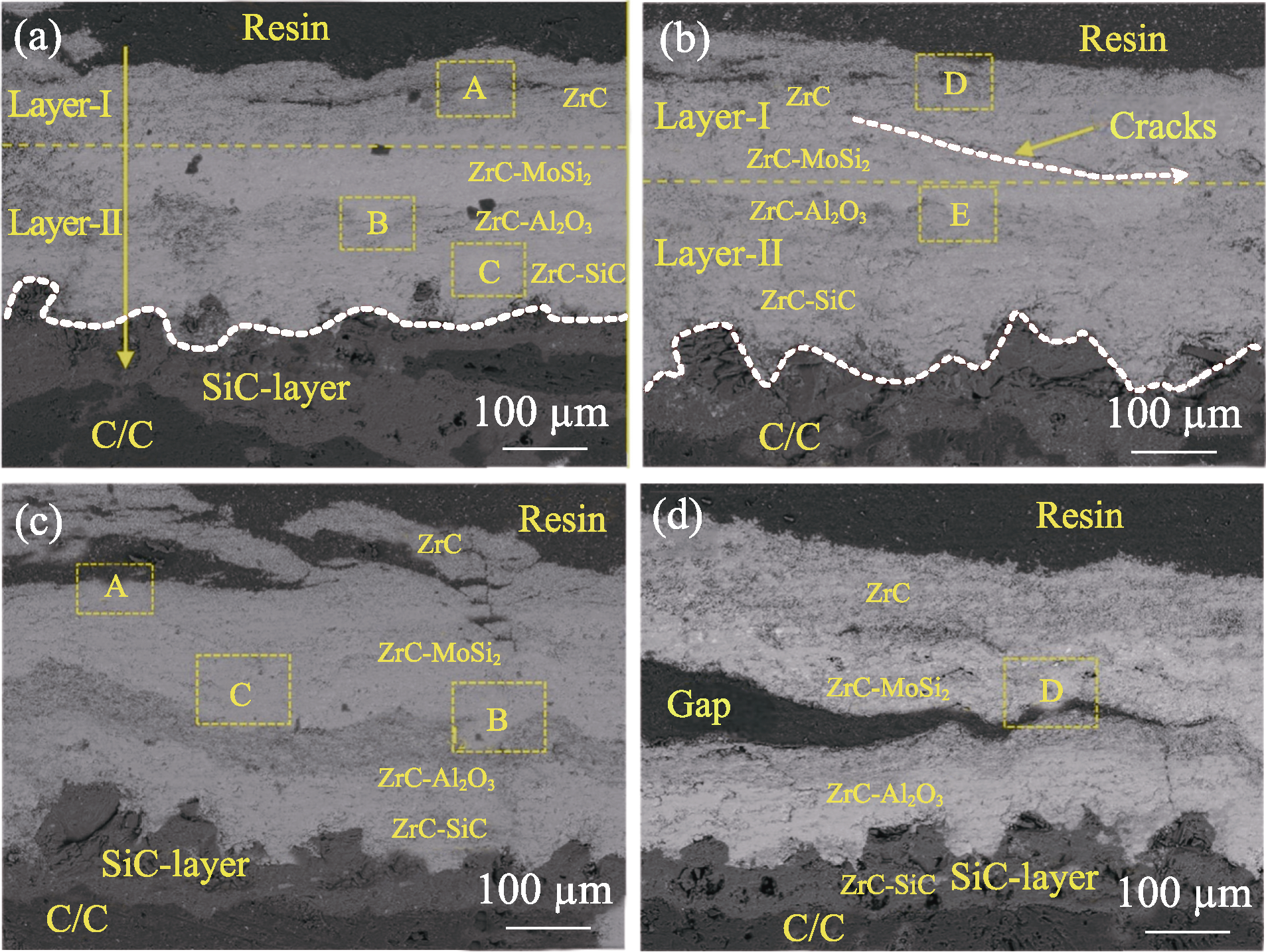
图8 烧蚀不同时间后多层涂层的截面SEM照片[148]
Fig. 8 Cross-sectional SEM images of the multilayer coatings after different ablation time[148] (a) 60 s; (b) 60 s×2; (c) 60 s×3; (d) 60 s×4
| No. | Coating | Mass ablation rate/(mg·s-1) | Linear ablation rate/(μm·s-1) | Ablation type | Heat flux/ (MW·m-2) | Ablation time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | APS ZrC | 1.378 | -1.928 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C2 | CVD HfC | 0.630 | 1.020 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C3 | CVD TaC | 1.500 | 3.240 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 30 s | [ |
| C4 | APS HfC | -0.260 | -2.100 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C5 | APS ZrC | 0.060 | 2.250 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C6 | CVD HfC | 2.020 | 1.250 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 90 s | [ |
| C7 | APS ZrC | 4.020 | -8.330 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C8 | APS ZrC | 2.020 | 5.750 | Oxy-acetylene* | 4.2 | 40 s | [ |
| C9 | APS ZrC | 0.270 | 0.530 | Plasma torch** | 10.0 | 90 s | [ |
| C10 | APS ZrC-SiC | 0.290 | 0.080 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C11 | APS HfC-TaC | 0.680 | -0.580 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C12 | APS HfC-Hf6Ta2O17 | -0.320 | -1.350 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C13 | CVD HfC-SiC | 0.153 | -0.998 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C14 | APS HfC-ZrC-TiC | 0.180 | 0.710 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C15 | APS (Hf1/4Zr1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)C | 0.810 | 0.190 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 180 s | [ |
| C16 | APS ZrC-SiHfOC | 0.099 | 0.200 | Plasma torch** | 10.0 | 90 s | [ |
| C17 | CVD (ZrC/SiC)3 | 0.750 | -0.028 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C18 | CVD SiC/TaC/SiC/TaC | 0.180 | -0.760 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 30 s | [ |
| C19 | CVD (SiC/HfC)3 | 0.241 | 0.120 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C20 | APS ZrC-SiC/ZrC-Al2O3/ZrC-MoSi2/ZrC | 0.231 | 0.156 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s × 3 | [ |
| C21 | APS ZrC/TaC/ZrC | 1.040 | -1.170 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C22 | APS ZrC/ZrC-LaB6/ZrC-SiC | -1.070 | -2.890 | Oxy-acetylene* | 4.2 | 40 s | [ |
| C23 | APS ZrC-SiC/ZrC-ZrO2/ZrO2-Y2O3 | -0.460 | -0.950 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 90 s × 2 | [ |
| C24 | CVD (SiC/HfC)4/SiC | 0.640 | 0.530 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s × 3 | [ |
表2 不同类型涂层的烧蚀率
Table 2 Ablation rates of different types of coatings
| No. | Coating | Mass ablation rate/(mg·s-1) | Linear ablation rate/(μm·s-1) | Ablation type | Heat flux/ (MW·m-2) | Ablation time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | APS ZrC | 1.378 | -1.928 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C2 | CVD HfC | 0.630 | 1.020 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C3 | CVD TaC | 1.500 | 3.240 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 30 s | [ |
| C4 | APS HfC | -0.260 | -2.100 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C5 | APS ZrC | 0.060 | 2.250 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C6 | CVD HfC | 2.020 | 1.250 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 90 s | [ |
| C7 | APS ZrC | 4.020 | -8.330 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C8 | APS ZrC | 2.020 | 5.750 | Oxy-acetylene* | 4.2 | 40 s | [ |
| C9 | APS ZrC | 0.270 | 0.530 | Plasma torch** | 10.0 | 90 s | [ |
| C10 | APS ZrC-SiC | 0.290 | 0.080 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C11 | APS HfC-TaC | 0.680 | -0.580 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C12 | APS HfC-Hf6Ta2O17 | -0.320 | -1.350 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C13 | CVD HfC-SiC | 0.153 | -0.998 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C14 | APS HfC-ZrC-TiC | 0.180 | 0.710 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C15 | APS (Hf1/4Zr1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)C | 0.810 | 0.190 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 180 s | [ |
| C16 | APS ZrC-SiHfOC | 0.099 | 0.200 | Plasma torch** | 10.0 | 90 s | [ |
| C17 | CVD (ZrC/SiC)3 | 0.750 | -0.028 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C18 | CVD SiC/TaC/SiC/TaC | 0.180 | -0.760 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 30 s | [ |
| C19 | CVD (SiC/HfC)3 | 0.241 | 0.120 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 120 s | [ |
| C20 | APS ZrC-SiC/ZrC-Al2O3/ZrC-MoSi2/ZrC | 0.231 | 0.156 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s × 3 | [ |
| C21 | APS ZrC/TaC/ZrC | 1.040 | -1.170 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s | [ |
| C22 | APS ZrC/ZrC-LaB6/ZrC-SiC | -1.070 | -2.890 | Oxy-acetylene* | 4.2 | 40 s | [ |
| C23 | APS ZrC-SiC/ZrC-ZrO2/ZrO2-Y2O3 | -0.460 | -0.950 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 90 s × 2 | [ |
| C24 | CVD (SiC/HfC)4/SiC | 0.640 | 0.530 | Oxy-acetylene* | 2.4 | 60 s × 3 | [ |

图9 不同类型涂层的烧蚀率[74,78,113⇓ -115,127,135,141,148,153,155,169⇓⇓⇓⇓ -174]
Fig. 9 Ablation rates of different types of coatings[74,78,113⇓ -115,127,135,141,148,153,155,169⇓⇓⇓⇓ -174]
| [1] | LE V T, HA N S, GOO N S. Advanced sandwich structures for thermal protection systems in hypersonic vehicles: a review. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 226: 109301. |
| [2] | DING Y B, YUE X K, CHEN G S, et al. Review of control and guidance technology on hypersonic vehicle. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(7): 1. |
| [3] | ZHANG S L, LI X, ZUO J Y, et al. Research progress on active thermal protection for hypersonic vehicles. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2020, 119: 100646. |
| [4] | YANG H S, LIANG H, GUO S G, et al. Research progress of hypersonic boundary layer transition control experiments. Advances in Aerodynamics, 2022, 4(1): 18. |
| [5] | SZIROCZAK D, SMITH H. A review of design issues specific to hypersonic flight vehicles. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2016, 84: 1. |
| [6] | UYANNA O, NAJAFI H. Thermal protection systems for space vehicles: a review on technology development, current challenges and future prospects. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 176: 341. |
| [7] | INFED F, HANDRICK K, LANGE H, et al. Development of thermal protective seal for hot structure control surface actuator rod. Acta Astronautica, 2012, 70: 122. |
| [8] | BOEHRK H, WEIHS H, ELSÄßER H. Hot structure flight data of a faceted atmospheric reentry thermal protection system. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 2019(1): 9754739. |
| [9] | WANG R N, LI N, ZHANG J P, et al. Ablation behavior of sharp leading-edge C/C-ZrC-SiC composites using 3000 ℃ oxyacetylene torch. Corrosion Science, 2022, 206: 110551. |
| [10] | ZHU S B, ZHANG G X, BAO Y L, et al. Progress in preparation and ablation resistance of ultra-high-temperature ceramics modified C/C composites for extreme environment. Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 2023, 62(1): 20220276. |
| [11] | JIN X C, FAN X L, LU C S, et al. Advances in oxidation and ablation resistance of high and ultra-high temperature ceramics modified or coated carbon/carbon composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(1): 1. |
| [12] | YANG Y Z, YANG J L, FANG D N. Research progress on thermal protection materials and structures of hypersonic vehicles. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2008, 29: 51. |
| [13] | XIE W, FU Q G, CHENG C Y, et al. Oxidation behavior of different La2O3-content modified SiC ceramic at 1700 ℃. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(8): 11560. |
| [14] | NI D W, CHENG Y, ZHANG J P, et al. Advances in ultra-high temperature ceramics, composites, and coatings. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(1): 1. |
| [15] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Ultra-high temperature ceramics: materials for extreme environments. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 129: 94. |
| [16] | WYATT B C, NEMANI S K, HILMAS G E, et al. Ultra-high temperature ceramics for extreme environments. Nature Reviews Materials, 2024, 9: 773. |
| [17] | GOLLA B R, MUKHOPADHYAY A, BASU B, et al. Review on ultra-high temperature boride ceramics. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 111: 100651. |
| [18] | JOHANSSON L I. Electronic and structural properties of transition-metal carbide and nitride surfaces. Surface Science Reports, 1995, 21(5/6): 177. |
| [19] | EDAMOTO K, OZAWA K, OTANI S. Interaction of oxygen with the polar HfC(111) surface: angle-resolved photoemission study. e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology, 2003, 1: 20. |
| [20] | VIÑES F, SOUSA C, LIU P, et al. A systematic density functional theory study of the electronic structure of bulk and (001) surface of transition-metals carbides. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2005, 122(17): 174709. |
| [21] | YANG G L, ZHOU Y L, TAO X M, et al. Properties and self-adsorptions for ZrC low-index surfaces: a first-principles study. Surface Science, 2023, 727: 122188. |
| [22] | BANDYOPADHYAY D, SHARMA R C, CHAKRABORTI N. The C-Hf-Ti system (carbon-hafnium-titanium). Journal of Phase Equilibria, 2000, 21(6): 535. |
| [23] | WEINBERGER C R, THOMPSON G B. Review of phase stability in the group IVB and VB transition-metal carbides. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(10): 4401. |
| [24] | DAVEY T, CHEN Y. Vacancy ordering in substoichiometric zirconium carbide: a review. International Journal of Ceramic Engineering & Science, 2022, 4(3): 134. |
| [25] | WANG Y, WEN B, JIAO X J, et al. The highest melting point material: searched by bayesian global optimization with deep potential molecular dynamics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(4): 803. |
| [26] | NISAR A, HASSAN R, AGARWAL A, et al. Ultra-high temperature ceramics: aspiration to overcome challenges in thermal protection systems. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(7): 8852. |
| [27] | DONG B X, YANG H Y, QIU F, et al. Design of TiCx nanoparticles and their morphology manipulating mechanisms by stoichiometric ratios: experiment and first-principle calculation. Materials & Design, 2019, 181: 107951. |
| [28] | BITTERMANN H, ROGL P. Critical assessment and thermodynamic calculation of the binary system hafnium-carbon (Hf-C). Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1997, 18(4): 344. |
| [29] | ZHOU Y, WATTS J, LI C, et al. Vacancy ordering in zirconium carbide with different carbon contents. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(14): 5814. |
| [30] | ZHOU Y, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, GRAHAM J, et al. From thermal conductive to thermal insulating: effect of carbon vacancy content on lattice thermal conductivity of ZrCx. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 82: 105. |
| [31] | OPEKA M M, TALMY I G, WUCHINA E J, et al. Mechanical, thermal, and oxidation properties of refractory hafnium and zirconium compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1999, 19(13/14): 2405. |
| [32] | YU X X, THOMPSON G B, WEINBERGER C R. Influence of carbon vacancy formation on the elastic constants and hardening mechanisms in transition metal carbides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(1): 95. |
| [33] | VINITSKII I M. Relation between the properties of monocarbides of groups IV-V transition metals and their carbon content. Soviet Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1972, 11(6): 488. |
| [34] | PAN Y. New insight into the effect of C concentration on the structural stability, elastic modulus, hardness and thermodynamic properties of NbC carbides. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2024, 121: 106676. |
| [35] | GUSEV A I. Effect of defectiveness of carbon sublattice on elastic properties and microstrains of disordered cubic tantalum carbide TaCy. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2022, 103: 105760. |
| [36] | NINO A, HIRABARA T, SUGIYAMA S, et al. Preparation and characterization of tantalum carbide (TaC) ceramics. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 52: 203. |
| [37] | SCITI D, GUICCIARDI S, NYGREN M. Densification and mechanical behavior of HfC and HfB2 fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(5): 1433. |
| [38] | BALKO J, CSANÁDI T, SEDLÁK R, et al. Nanoindentation and tribology of VC, NbC and ZrC refractory carbides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(14): 4371. |
| [39] | BABAPOOR A, ASL M S, AHMADI Z, et al. Effects of spark plasma sintering temperature on densification, hardness and thermal conductivity of titanium carbide. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14541. |
| [40] | ASL M S, AHMADI Z, NAMINI A S, et al. Spark plasma sintering of TiC-SiCw ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(16): 19808. |
| [41] | WANG X G, GUO W M, KAN Y M, et al. Densification behavior and properties of hot-pressed ZrC ceramics with Zr and graphite additives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2011, 31(6): 1103. |
| [42] | LONG Y, JAVED A, CHEN J, et al. Phase composition, microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrC coatings produced by chemical vapor deposition. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(1): 707. |
| [43] | SCITI D, GUICCIARDI S, NYGREN M. Spark plasma sintering and mechanical behaviour of ZrC-based composites. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(6): 638. |
| [44] | SMITH C J, YU X X, GUO Q, et al. Phase, hardness, and deformation slip behavior in mixed HfxTa1-xC. Acta Materialia, 2018, 145: 142. |
| [45] | LIU Y Z, JIANG Y H, ZHOU R, et al. First principles study the stability and mechanical properties of MC (M=Ti, V, Zr, Nb, Hf and Ta) compounds. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 582: 500. |
| [46] | CEDILLOS-BARRAZA O, GRASSO S, AL NASIRI N, et al. Sintering behaviour, solid solution formation and characterisation of TaC, HfC and TaC-HfC fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1539. |
| [47] | ZHANG C, GUPTA A, SEAL S, et al. Solid solution synthesis of tantalum carbide-hafnium carbide by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(5): 1853. |
| [48] | XU H Y, LI Y J, YANG J H, et al. Microstructure evolution of ultra-fine grained HfC ceramics with high hardness sintered under ultrahigh pressure by plastic deformation densification mechanism. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2024, 118: 106425. |
| [49] | LI H, MA S L, CHEN L X, et al. Carbon-deficient titanium carbide with highly enhanced hardness. Frontiers in Physics, 2020, 8: 364. |
| [50] | ENDO H, UEKI M, KUBO H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-pressed SiC-TiC composites. Journal of Materials Science, 1991, 26(14): 3769. |
| [51] | KORKLAN N, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Processing and room temperature mechanical properties of a zirconium carbide ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(1): 413. |
| [52] | CAI X L, ZHONG L S, WANG J F, et al. Microstructure and hardness of NbC coating produced in situ. Advanced Materials Research, 2015, 1120-1121: 745. |
| [53] | NINO A, TANAKA A, SUGIYAMA S, et al. Indentation size effect for the hardness of refractory carbides. Materials Transactions, 2010, 51(9): 1621. |
| [54] | WOYDT M, MOHRBACHER H. The tribological and mechanical properties of niobium carbides (NbC) bonded with cobalt or Fe3Al. Wear, 2014, 321: 1. |
| [55] |
ZHAO X Y, TOGARU M, GUO Q Y, et al. Carbon influence on fracture toughness of niobium carbides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(16): 5167.
DOI |
| [56] | DEMIRSKYI D, NISHIMURA T, SUZUKI T S, et al. Consolidation and high-temperature properties of ceramics in the TaC-NbC system. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(12): 7567. |
| [57] | CHENG L X, XIE Z P, LIU G W, et al. Densification and mechanical properties of TiC by SPS-effects of holding time, sintering temperature and pressure condition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(12): 3399. |
| [58] | TEBER A, SCHOENSTEIN F, TÊTARD F, et al. Effect of SPS process sintering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline TiC for tools application. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2012, 30(1): 64. |
| [59] | CHENG L X, XIE Z P, LIU G W. Spark plasma sintering of TiC-based composites toughened by submicron SiC particles. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(5): 5077. |
| [60] | HUO S J, WANG Y J, YAO M Y, et al. Novel TiC-based composites with enhanced mechanical properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(11): 5466. |
| [61] | WANG X F, WANG X G, YANG Q Q, et al. High-strength medium-entropy (Ti, Zr, Hf)C ceramics up to 1800 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(6): 2436. |
| [62] | DEMIRSKYI D, VASYLKIV O, YOSHIMI K. High-temperature deformation in bulk polycrystalline hafnium carbide consolidated using spark plasma sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7442. |
| [63] | LIU J X, KAN Y M, ZHANG G J. Pressureless sintering of tantalum carbide ceramics without additives. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(2): 370. |
| [64] | SCHWIND E C, REECE M J, CASTLE E, et al. Thermal and electrical properties of a high entropy carbide (Ta, Hf, Nb, Zr) at elevated temperatures. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(6): 4426. |
| [65] | BRUNE P M, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, et al. Thermal and electrical properties of single-phase high entropy carbide ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(9): 5893. |
| [66] | YAN N N, ZHANG J P, LIU T Y, et al. One-step preparation and ablation behavior of ZrC-SiC-Si coating for nose-shaped ZrC/C composites with gradient pore structure by vapor silicon infiltration. Corrosion Science, 2022, 206: 110505. |
| [67] | ZHUANG L, FU Q G. Bonding strength, thermal shock and oxidation resistance of interlocking (Zr, Hf)C-SiC/SiC double-layer coating for C/C composites. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 315: 436. |
| [68] | TIAN X F, SHI X H, YANG L, et al. Preparation and ablation properties of SiC nanowire-reinforced ZrC-SiC coating-matrix integrated C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(22): 31251. |
| [69] | CHEN H, ZHANG Y L, LI Z L, et al. Ultra-high temperature ablation behavior of CVD-Hf5TaC6 solid solution ceramic coating for C/C composites: experiment and first-principle calculation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 965: 171486. |
| [70] | CHU Y H, LI H J, WANG Y J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine bamboo-shaped SiC rod-reinforced HfC ceramic coating. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 235: 577. |
| [71] | REN J C, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. Influence of HfC nanowires on the growth behavior, microstructure and ablation resistance of CVD-HfC coating. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5): 5321. |
| [72] | TONG M D, FU Q G, HU D, et al. Improvement of ablation resistance of CVD-HfC/SiC coating on hemisphere shaped C/C composites by introducing diffusion interface. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 4067. |
| [73] | YANG Y, LI K Z, ZHAO Z G, et al. Deposition and ablation resistance of HfC-based coatings prepared on SiC-coated C/C composites by supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2016, 115(8): 473. |
| [74] | REN J C, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. Effects of the second phase on the microstructure and ablation resistance of HfC coating on C/C composites. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 344: 250. |
| [75] | FENG G H, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Mechanical properties and ablation resistance of La2O3-modified HfC-SiC coating for SiC-coated C/C composites. Corrosion Science, 2021, 182: 109259. |
| [76] | KIM H S, KANG B R, CHOI S M. Fabrication and characteristics of a HfC/TiC multilayer coating by a vacuum plasma spray process to protect C/C composites against oxidation. Corrosion Science, 2021, 178: 109068. |
| [77] | ZHANG Y Y, SUN J, GUO L X, et al. Ablation behavior under oxyacetylene torch of ZrC coating modified by SiC/TaC nanocomposites. Corrosion Science, 2022, 205: 110423. |
| [78] | TONG M D, FU Q G, ZHOU L, et al. Ablation behavior of a novel HfC-SiC gradient coating fabricated by a facile one-step chemical vapor co-deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(13): 4346. |
| [79] | LI B, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Preparation and ablation resistance of ZrC nanowires-reinforced CVD-ZrC coating on sharp leading edge C/C composites. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 584: 152617. |
| [80] | SUN L Z, YUAN G W, GAO L B, et al. Chemical vapour deposition. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1(1): 5. |
| [81] | MA X, CHEN S A, MEI M, et al. Influence of total pressure on the microstructures and growth mechanism of ZrC coatings prepared by chemical vapor deposition from the Zr-Br2-C3H6-H2-Ar system. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(4): 3501. |
| [82] | DOYLE P, LOPEZ-HONORATO E, VASUDEVAMURTHY G, et al. Characterization of fluidized bed chemical vapor deposition ZrC coatings on PyC/YSZ kernels deposited under differing conditions. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2024, 594: 155019. |
| [83] | YEO S, YOO S J, LEE H, et al. Ar-ion- and electron-irradiated ZrC layers in ZrC-SiC-coated surrogate TRISO fuel particles. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(5): 2730. |
| [84] | AIHARA J, UETA S, YASUDA A, et al. Effect of heat treatment on TEM microstructures of zirconium carbide coating layer in fuel particle for advanced high temperature gas cooled reactor. Materials Transactions, 2009, 50(11): 2631. |
| [85] | WAGNER P, WAHMAN L A, WHITE R W, et al. Factors influencing the chemical vapor deposition of ZrC. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1976, 62(2/3): 221. |
| [86] | HAUBNER R. The history of hard CVD coatings for tool applications at the University of Technology Vienna. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2013, 41: 22. |
| [87] | TONG M D, FU Q G, LIANG M Y, et al. Effect of PyC-SiC double-layer interface on ablation behaviour of impacted CVD-SiCnws/HfC coating. Corrosion Science, 2021, 191: 109741. |
| [88] | TONG M D, DING J H, LI N, et al. Effect of SiCnws@BN core shell upon impact-ablation performance of HfC coating on C/C composites. Corrosion Science, 2022, 209: 110707. |
| [89] | KONG J A, ZHANG Y L, WANG H H, et al. Sublayer design and ablation resistance of CVD-TaC alternate coatings with different crystallite morphologies for C/C composites. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 141: 1. |
| [90] | WANG Y, DOU Q, YANG J, et al. Residual stress and ablation behavior of CVD TaC coatings on graphite. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 277: 125627. |
| [91] | YANG X, CHENG X Y, LIU R Z, et al. Preparation and high temperature performance of NbC layer in TRISO particles. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(15): 6889. |
| [92] | LIU X L, DAI Y, WANG Z J, et al. Research progress on tantalum carbide coatings on carbon materials. New Carbon Materials, 2021, 36(6): 1049. |
| [93] | PRETORIUS J A, MALHERBE J B. Graphite phases in chemical vapour deposited grown ZrC/graphite layers. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2021, 477(2248): 20200784. |
| [94] | DENG J L, LU B F, HU K Y, et al. Thermodynamics equilibrium analysis on the chemical vapor deposition of HfC as coatings for ceramic matrix composites with HfClx(x=2-4)-CyHz(CH4, C2H4 and C3H6)-H2-Ar system. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2019, 2(1): 102. |
| [95] | SONG M, YANG Y F, XIANG M Q, et al. Synthesis of nano- sized TiC powders by designing chemical vapor deposition system in a fluidized bed reactor. Powder Technology, 2021, 380: 256. |
| [96] | CHEN Z K, XIONG X, HUANG B Y, et al. Phase composition and morphology of TaC coating on carbon fibers by chemical vapor infiltration. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516(23): 8248. |
| [97] | PARK J H, JUNG C H, KIM D J, et al. Effect of H2 dilution gas on the growth of ZrC during low pressure chemical vapor deposition in the ZrCl4-CH4-Ar system. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2008, 203(1/2): 87. |
| [98] | WANG Y L, LI Z H, XIONG X, et al. Action mechanism of hydrogen gas on deposition of HfC coating using HfCl4-CH4-H2-Ar system. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 903. |
| [99] | BIIRA S, CROUSE P L, BISSETT H, et al. The role of ZrCl4 partial pressure on the growth characteristics of chemical vapour deposited ZrC layers. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15133. |
| [100] | KIM D, KO M J, PARK J Y, et al. Influence of free carbon on the characteristics of ZrC and deposition of near-stoichiometric ZrC in TRISO coated particle fuel. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 451(1/2/3): 97. |
| [101] | YANG X, ZHANG F, YOU Y, et al. Growth process and mechanism of SiC layer deposited by CVD method at normal atmosphere. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15): 4495. |
| [102] | BLOCHER J M. Structure/property/process relationships in chemical vapor deposition CVD. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1974, 11(4): 680. |
| [103] | CHEN Z K, XIONG X, LONG Y. Influence of TaCl5 partial pressure on texture structure of TaC coating deposited by chemical vapor deposition. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(9): 4044. |
| [104] | KONG J A, ZHANG Y L, CHEN G H, et al. Ablation behavior of CVD-TaC coatings with different crystal structures for C/C composites under oxyacetylene flame. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(15): 6898. |
| [105] | MA X, LI Y, MEI M, et al. Effect of deposition time on microstructures and growth behavior of ZrC coatings prepared by low pressure chemical vapor deposition with the Br2-Zr-C3H6-H2-Ar System. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Materials Science Edition, 2017, 32(2): 284. |
| [106] | REN J C, ZHANG Y L, LI J H, et al. Effects of deposition temperature and time on HfC nanowires synthesized by CVD on SiC-coated C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(5): 5623. |
| [107] | CHEN H, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. (Hf0.5Ta0.5)C ultra-high temperature ceramic solid solution nanowires. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 147: 91. |
| [108] | CHEN H, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. Single-phase (Hf0.84Ta0.16)C solid solution nanowires growth via catalyst-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(1): 689. |
| [109] | LAMM B W, MCMURRAY J W, CAKMAK E, et al. Leveraging computational thermodynamics to guide SiC-ZrC chemical vapor deposition process development. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 444: 128672. |
| [110] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. Preparation and ablation behavior of HfC-SiC co-deposited coatings with different proportions. Corrosion Science, 2021, 192: 109853. |
| [111] | REN J C, FENG E R, ZHANG Y L, et al. Influences of deposition temperature, gas flow rate and ZrC content on the microstructure and anti-ablation performance of CVD-HfC-ZrC coating. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(1): 556. |
| [112] | REN J C, FENG E R, ZHANG Y L, et al. Microstructure and anti-ablation performance of HfC-TaC and HfC-ZrC coatings synthesized by CVD on C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8): 10147. |
| [113] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. Long-time ablation behavior of the multilayer alternating CVD-(SiC/HfC)3 coating for carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2021, 189: 109586. |
| [114] | LI B, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Ablation behavior of (ZrC/SiC)3 alternate coating prepared on sharp leading edge C/C composites by CVD. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 115: 129. |
| [115] | KONG J A, ZHANG Y L, GAI W H, et al. Influence of sublayer number on the ablative behaviors and synergistic effect of CVD-TaC/SiC alternate coatings. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(1): 68. |
| [116] | LYNAM A, ROMERO A R, XU F, et al. Thermal spraying of ultra-high temperature ceramics: a review on processing routes and performance. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2022, 31(4): 745. |
| [117] | SUN X L, ZHANG J K, PAN W G, et al. Research progress in surface strengthening technology of carbide-based coating. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 905: 164062. |
| [118] | CUI Y H, ZHANG Q, SHAO Y X, et al. Microstructure and properties of in-situ ZrB2-ZrC composite coatings by plasma spraying. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 409: 126846. |
| [119] | LIU S H, TRELLES J P, LI C J, et al. A review and progress of multiphase flows in atmospheric and low pressure plasma spray advanced coating. Materials Today Physics, 2022, 27: 100832. |
| [120] | LASHMI P G, ANANTHAPADMANABHAN P V, UNNIKRISHNAN G, et al. Present status and future prospects of plasma sprayed multilayered thermal barrier coating systems. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(8): 2731. |
| [121] | HEIMANN R B. The nature of plasma spraying. Coatings, 2023, 13(3): 622. |
| [122] | VARDELLE A, MOREAU C, THEMELIS N J, et al. A perspective on plasma spray technology. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2015, 35(3): 491. |
| [123] | FAUCHAIS P, VARDELLE A M. Thermal sprayed coatings used against corrosion and corrosive wear//JAZI H S. Advanced plasma spray applications. Rijeka: InTech, 2012: 34448. |
| [124] | LIU M J, ZHANG G, LU Y H, et al. Plasma spray-physical vapor deposition toward advanced thermal barrier coatings: a review. Rare Metals, 2020, 39(5): 479. |
| [125] | HONG D, NIUB Y R, LI H, et al. Comparison of microstructure and tribological properties of plasma-sprayed TiN, TiC and TiB2 coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 374: 181. |
| [126] | YOO H I, KIM H S, HONG B G, et al. Hafnium carbide protective layer coatings on carbon/carbon composites deposited with a vacuum plasma spray coating method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1581. |
| [127] | FENG G H, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Ablation behavior of ZrC and ZrO2 coatings on SiC coated C/C composites under oxyacetylene torch with different heat fluxes. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(15): 21721. |
| [128] | FENG G H, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Ablation resistance of TaC-modified HfC coating prepared by supersonic plasma spraying for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17936. |
| [129] | WANG Y J, LI H J, FU Q G, et al. Ablation behaviour of a TaC coating on SiC coated C/C composites at different temperatures. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(1): 359. |
| [130] | HE R X, LI K Z, GU S Y, et al. Comparing ablation properties of NbC and NbC-25 mol.% ZrC coating on SiC-coated C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(6): 7055. |
| [131] | HU C, GE X L, NIU Y R, et al. Influence of oxidation behavior of feedstock on microstructure and ablation resistance of plasma- sprayed zirconium carbide coating. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2015, 24(7): 1302. |
| [132] | LI W, WANG L, YANG Y, et al. Microstructure and properties of niobium carbide composite coatings prepared by plasma spraying. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(23): 33338. |
| [133] | PU H, NIU Y R, HU C, et al. Ablation of vacuum plasma sprayed TaC-based composite coatings. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(9): 11387. |
| [134] | HE R X, LI K Z, LIU L Q. Solubility, crystal growth, and film-formation mechanism of NbC-modified ZrC coating under oxyacetylene flame. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 625: 157123. |
| [135] | LI J C, ZHANG Y L, LV J S, et al. Sealing role of Ti-rich phase in HfC-ZrC-TiC coating for C/C composites during ablation above 2100 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2022, 205: 110474. |
| [136] | LUO X, YANG X, HUANG Q Z, et al. Ablative property and mechanism of ZrC-TaC/ZrC-SiC coatings on C/C composites under different heat fluxes. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2021, 30(6): 1582. |
| [137] | FENG G H, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Ablation resistance of HfC-TaC/HfC-SiC alternate coating for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites under cyclic ablation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3207. |
| [138] | YANG Y, LI K Z, ZHAO C. Ablation mechanism and morphology evolution of the HfC-SiC coating for C/C composites deposited by supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying. Advanced Composites Letters, 2019, 28: 1. |
| [139] | SHAO Y X, YANG Y, LI K R, et al. Reactive synthesis of ZrC-ZrSi2 composite coating by atmospheric plasma spraying. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 450: 128976. |
| [140] | SHUAI K, ZHANG Y L, FU Y Q, et al. MoSi2-HfC/TaC-HfC multi-phase coatings synthesized by supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying for C/C composites against ablation. Corrosion Science, 2021, 193: 109884. |
| [141] | FENG G H, YU Y L, YAO X Y, et al. Nanosized Hf6Ta2O17 particles reinforced HfC ceramic coating for high temperature applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(8): 3043. |
| [142] | PAN X H, NIU Y R, LIU T, et al. Ablation resistance and mechanism of ZrC-SiC-Yb2O3 ternary composite coatings fabricated by vacuum plasma spray. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3604. |
| [143] | JIA Y J, LI H J, YAO X Y, et al. Long-time ablation protection of carbon/carbon composites with different-La2O3-content modified ZrC coating. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4): 1046. |
| [144] | HUO C X, ZHOU L, GUO L J, et al. Effect of the Al2O3 additive on the high temperature ablation behavior of the ZrC-ZrO2 coating for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(17): 23180. |
| [145] | JIA Y J, LI H J, FU Q G, et al. Ablation resistance of supersonic- atmosphere-plasma-spraying ZrC coating doped with ZrO2 for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2017, 123: 40. |
| [146] | YANG Y, LI K Z, LIU G X, et al. Ablation mechanism of HfC-HfO2 protective coating for SiC-coated C/C composites in an oxyacetylene torch environment. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2017, 33(10): 1195. |
| [147] | HU D, FU Q G, DONG Z J, et al. Design of ablation resistant Zr-Ta-O-C composite coating for service above 2400 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2022, 200: 110221. |
| [148] | LI Y Y, LIU Y C, GUO C, et al. Ablation resistance of ZrC-based composite coating with multi-layer structure for carbon/carbon composites above 2200 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2022, 207: 110600. |
| [149] | LIU H Z, YANG X, FANG C Q, et al. Ablation resistance and mechanism of SiC/ZrC-ZrB2 double layer coating for C/C composites under plasma flame. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(9): 2538. |
| [150] | ZHANG P, FU Q G, LIU B, et al. Development of SiC-ZrC-based ultra-high temperature ceramic coatings via composite method of polymer precursor pyrolysis plus gaseous reactive infiltration. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 431: 127996. |
| [151] | SHI A H, YANG X, FANG C Q, et al. Mechanical and ablative properties improvement of HfC-SiC coatings upon introduction of TiC. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(12): 4735. |
| [152] | SCITI D, VINCI A, ZOLI L, et al. Propulsion tests on ultra-high- temperature ceramic matrix composites for reusable rocket nozzles. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(7): 1345. |
| [153] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y L, ZHANG T, et al. Cyclic ablation behavior and microstructure evolution of multi-layer coating on C/C composites under oxyacetylene torch. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(15): 21709. |
| [154] | LEE S, PARK G, KIM J G, et al. Evaluation system for ablative material in a high-temperature torch. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2019, 20(3): 620. |
| [155] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y L, CHEN R C, et al. Effect of microstructure on the ablation behavior and mechanical properties of CVD-HfC coating. Corrosion Science, 2021, 192: 109815. |
| [156] | WANG Y L, XIONG X, ZHAO X J, et al. Structural evolution and ablation mechanism of a hafnium carbide coating on a C/C composite in an oxyacetylene torch environment. Corrosion Science, 2012, 61: 156. |
| [157] | WANG S L, LI K Z, LI H J, et al. Structure evolution and ablation behavior of ZrC coating on C/C composites under single and cyclic oxyacetylene torch environment. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(10): 16003. |
| [158] | SUN W, XIONG X, HUANG B Y, et al. ZrC ablation protective coating for carbon/carbon composites. Carbon, 2009, 47(14): 3368. |
| [159] | PAN X H, NIU Y R, LIU T, et al. Ablation behaviors of ZrC-TiC coatings prepared by vacuum plasma spray: above 2000 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(11): 3292. |
| [160] | HE R X, LI K Z, ZHANG W H, et al. Film-forming investigation of NbC-modified HfC coating based on oxyacetylene ablation and argon-atmosphere heating above 2000 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2023, 220: 111303. |
| [161] | TAN Z Y, GUO J W, ZHU W. Ablation resistance of HfC-TaC- Hf6Ta2O17 composite coatings prepared by vacuum plasma spraying. Corrosion Science, 2023, 221: 111368. |
| [162] | FENG G H, YAO X Y, YU Y L, et al. Synthesis and performance characterization of hafnium-based multilayer coating applied over carbon/carbon composites with sharp leading edge. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 153: 254. |
| [163] | HU D, FU Q G, TONG M D, et al. Multiple cyclic ablation behaviors of multilayer ZrC-TaC coating with ZrC-SiC interface layer. Corrosion Science, 2022, 200: 110215. |
| [164] | QIAN W Q, HE K F, ZHOU Y. Estimation of surface heat flux for ablation and charring of thermal protection material. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 52(7): 1275. |
| [165] | CHEN Z Z, WANG H X, LI C R, et al. Oxyacetylene ablation of (Hf0.2Ti0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2)C at 1350-2050 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(6): 2700. |
| [166] | ZHANG H, HU B T, DAI B, et al. Excellent ablation resistance of Ti3AlC2 ceramics up to 1900 ℃ in nitrogen plasma flame. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(3): 1436. |
| [167] | MILLER-OANA M, NEFF P, VALDEZ M, et al. Oxidation behavior of aerospace materials in high enthalpy flows using an oxyacetylene torch facility. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(4): 1300. |
| [168] | WANG S L, LI K Z, LI H J, et al. Ablation behavior of CVD-ZrC coating under oxyacetylene torch environment with different heat fluxes. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 48: 108. |
| [169] | JIA Y J, LI H J, SUN J J, et al. Ablation resistance of SiC-modified ZrC coating prepared by SAPS for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2017, 14(3): 331. |
| [170] | HU D, FU Q G, LI X X, et al. Discussion on structural parameters of the multilayer ZrC/TaC coatings based on stress analysis and ablation behaviors ablation behaviors. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 435: 128243. |
| [171] | JIA Y J, LI H J, FU Q G, et al. A ZrC-SiC/ZrC-LaB6/ZrC multilayer ablation resistance coating for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 309: 545. |
| [172] | ZHANG X M, ZHANG Y Y, GUO L X, et al. Ablation resistance of ZrC coating modified by polymer-derived SiHfOC ceramic microspheres at ultrahigh temperature. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 182: 119 |
| [173] | LI J C, ZHAO J H, LI T, et al. Microstructure evolution and phase interface characterization in anti-ablation (Hf1/4Zr1/4Ta1/4Ti1/4)C-coated C/C composites. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2024, 281: 111569. |
| [174] | FENG G H, CHEN L, YAO X Y, et al. Design and characterization of zirconium-based multilayer coating for carbon/carbon composites against oxyacetylene ablation. Corrosion Science, 2021, 192: 109785. |
| [1] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||