无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 469-476.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220591 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220591
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
王磊1( ), 李建军1,2(
), 李建军1,2( ), 宁军3, 胡天玉1,2, 王洪阳1, 张占群1, 武琳馨1
), 宁军3, 胡天玉1,2, 王洪阳1, 张占群1, 武琳馨1
收稿日期:2022-10-09
修回日期:2022-11-27
出版日期:2023-04-20
网络出版日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
李建军, 教授. E-mail: ljj.hero@126.com作者简介:王磊(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wangleidreamer@126.com
WANG Lei1( ), LI Jianjun1,2(
), LI Jianjun1,2( ), NING Jun3, HU Tianyu1,2, WANG Hongyang1, ZHANG Zhanqun1, WU Linxin1
), NING Jun3, HU Tianyu1,2, WANG Hongyang1, ZHANG Zhanqun1, WU Linxin1
Received:2022-10-09
Revised:2022-11-27
Published:2023-04-20
Online:2022-12-30
Contact:
LI Jianjun, professor. E-mail: ljj.hero@126.comAbout author:WANG Lei (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wangleidreamer@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用共沉淀水热法制备了CoFe2O4@Zeolite (CFZ), 并将其用于活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)降解合成染料。综合表征表明, 组成多孔壳层的CoFe2O4纳米颗粒均匀地覆盖在Na-A沸石上。CFZ的比表面积为107.06 m2/g, 是原始沸石比表面积的3倍。CFZ的饱和磁化强度为29.0 A·m2·kg-1, 可以进行有效磁分离。催化降解实验表明, CFZ/PMS体系对甲基橙(MO)的去除率远远高于单独使用CFZ或PMS。在最佳条件([MO]=50 mg/L、[PMS]=1.0 mmol/L、0.2 g/L CFZ、pH 8和T=25 ℃)下, MO去除率可达到97.1%。实验研究了pH、PMS用量、CFZ用量、MO浓度以及共存阴离子等因素对CFZ催化性能的影响。活性氧粒子淬灭实验表明, 1O2和O2•-在降解过程中起主导作用。CFZ具有良好的回收性能, 5次循环后MO去除效率仅下降2.4%。本文还详细讨论了CFZ/PMS体系的催化降解机理。
中图分类号:
王磊, 李建军, 宁军, 胡天玉, 王洪阳, 张占群, 武琳馨. CoFe2O4@Zeolite催化剂活化过一硫酸盐对甲基橙的强化降解: 性能与机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 469-476.
WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476.
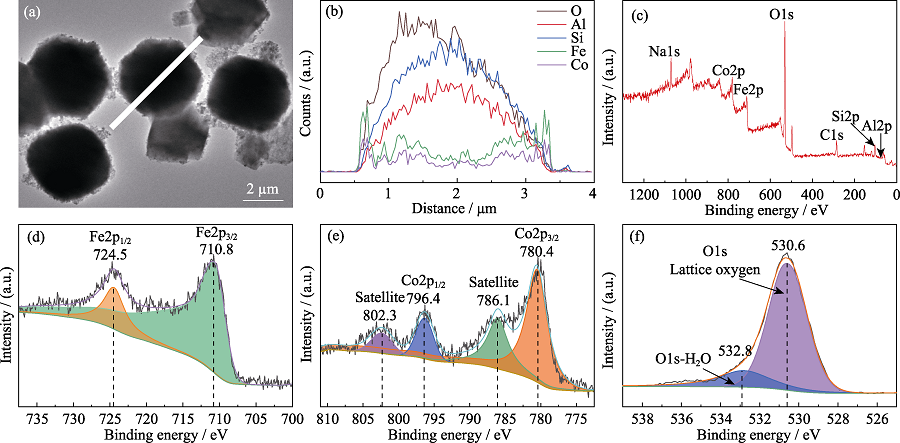
Fig. 3 (a) TEM image and (b) elemental line scanning spectra of CFZ, as well as XPS spectra of (c) survey, (d) Fe2p, (e) Co2p, and (f) O1s of CFZ Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 4 (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of the prepared zeolite and CFZ, (c) removal of MO in different systems (0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS] = 0.6 mmol/L, [MO] = 0.2 g/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃), and effects of (d) catalyst dosage, (e) initial solution pH and (f) PMS concentration on MO removal (0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS] = 1 mmol/L, [MO] = 50 mg/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃) Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | 30.13 | 0.08 | 15.00 |
| CFZ | 107.06 | 0.33 | 16.24 |
Table 1 SBET and pore size analysis data of the prepared zeolite and CFZ
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | 30.13 | 0.08 | 15.00 |
| CFZ | 107.06 | 0.33 | 16.24 |
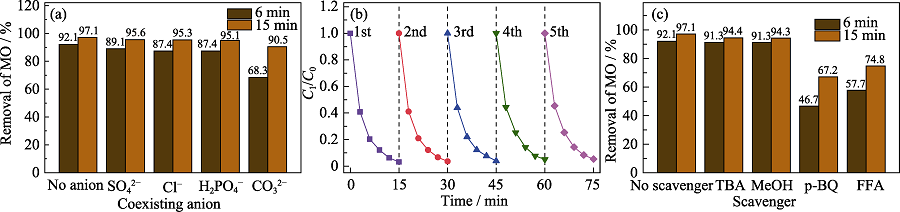
Fig. 5 Effects of (a) coexisting anions on MO removal, (b) cyclic experiments and (c) ROS quenching tests (0.2 g/L CFZ, under the conditions of [PMS] = 1 mmol/L, [MO] = [coexisting anions] = 50 mg/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃, [scavengers] = 100 mmol/L) Colorful figures are available on website
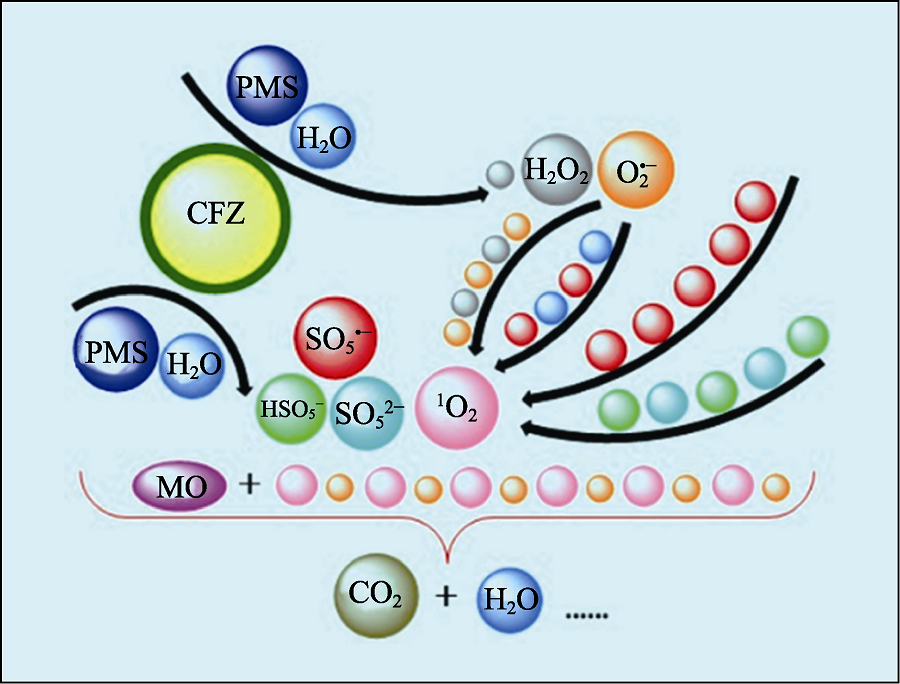
Fig. 6 Schematic of ROS generation and MO degradation The black arrows show the generation route of ROS and the balls with colors correspond to different reactants, intermediates or products Colorful figures are available on website
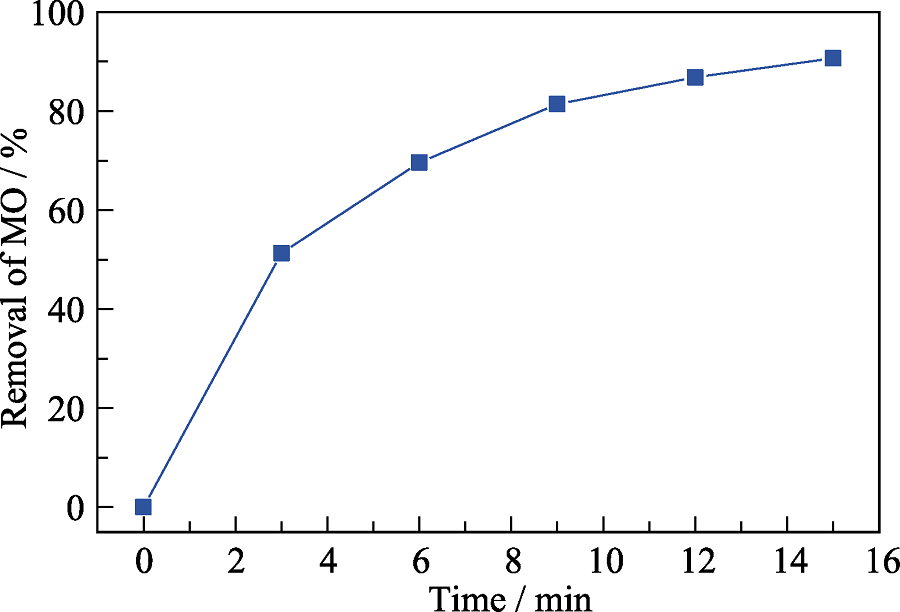
Fig. S2 Effect of high-concentration coexisting anions ([MO]=50 mg/L, [SO42-]=[CO32-]=[Cl-]=[H2PO42-]=1000 mg/L, 0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS]=1 mmol/L, pH 7, T=25 ℃)
| pH | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal efficiency/% | 73.96 | 91.83 | 94.22 | 93.99 | 94.96 |
Table S1 Removal efficiency of MB under different pH conditions
| pH | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal efficiency/% | 73.96 | 91.83 | 94.22 | 93.99 | 94.96 |
| [1] | LYU W, LI J, TRCHOVA M, et al. Fabrication of polyaniline/poly (vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite hybrid aerogels toward efficient adsorption of organic dye pollutants. J. Hazard Mater., 2022, 435: 129004. |
| [2] | SUN B, YUAN Y, LI H, et al. Waste-cellulose-derived porous carbon adsorbents for methyl orange removal. Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 371: 55. |
| [3] |
ZHANG S, LIU Y, MA R, et al. Molybdenum (VI)-oxo clusters incorporation activates g-C3N4 with simultaneously regulating charge transfer and reaction centers for boosting photocatalytic performance. Adv. Fun. Mater., 2022, 32(38):2204175.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ISSAKA E, AMU-DARKO J N, YAKUBU S, et al. Advanced catalytic ozonation for degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants-a review. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133208. |
| [5] | LIU B, JI J, ZHANG B, et al. Catalytic ozonation of VOCs at low temperature: a comprehensive review. J. Hazard Mater., 2022, 422: 126847. |
| [6] | OYEKUNLE D T, GENDY E A, IFTHIKAR J, et al. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 437: 135277. |
| [7] | PENG Y, TANG H, YAO B, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by spinel ferrite and their composites in degradation of organic pollutants: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 414: 128800. |
| [8] | ZHANG S, LIU Y, GU P, et al. Enhanced photodegradation of toxic organic pollutants using dual-oxygen-doped porous g-C3N4: mechanism exploration from both experimental and DFT studies. Appl.Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 248: 1. |
| [9] |
ZHANG S, SONG S, GU P, et al. Visible-light-driven activation of persulfate over cyano and hydroxyl group co-modified mesoporous g-C3N4 for boosting Bisphenol A degradation. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(10):5552.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
PARK J, CHOE J K, LEE W, et al. Highly fast and selective removal of nitrate in groundwater by bimetallic catalysts supported by fly ash-derived zeolite Na-X. Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2020, 7(11):3360.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LI J, GOU G, ZHAO H, et al. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by CoFe2O4-CeO2 composite: performance and catalytic mechanism. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 435: 134840. |
| [12] | BALAKRISHNAN R M, ILANGO I, GAMANA G, et al. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of ampicillin from aqueous solution. J. Water Proc. Eng., 2021, 40: 101823. |
| [13] | GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: review. Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 310: 41. |
| [14] | ZHENG X, NIU X, ZHANG D, et al. Metal-based catalysts for persulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation in heterogeneous ways: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 429: 132323. |
| [15] | WANG Q, SHAO Y, GAO N, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Al2O3-based CoFe2O4 for the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine sodium: kinetics and mechanism. Separ. and Purif. Tech., 2017, 189: 176. |
| [16] | KEFENI K K, MAMBA B B. Photocatalytic application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites in wastewater treatment: review. Sustain. Mater. Tech., 2020, 23: e00140. |
| [17] | SONG L, LI J, ZHANG Z, et al. La-containing magnetic zeolite synthesized from gangue by ball-milling method. Mater. Lett., 2021, 303: 130542. |
| [18] |
MARTINEZ-VARGAS S, MARTÍNEZ A I, HERNÁNDEZ- BETETA E E, et al. Arsenic adsorption on cobalt and manganese ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(11):6205.
DOI URL |
| [19] | CHAGAS C A, DE SOUZA E F, DE CARVALHO M C N A, et al. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the preferential oxidation of CO. Appl. Catal. A: Gener., 2016, 519: 139. |
| [20] | LIU Z, GAO Z, WU Q. Activation of persulfate by magnetic zirconium-doped manganese ferrite for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 423: 130283. |
| [21] | PENIDO E S, MELO L C A, GUILHERME L R G, et al. Cadmium binding mechanisms and adsorption capacity by novel phosphorus/magnesium-engineered biochars. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 671: 1134. |
| [22] | JI Y, LU J, WANG L, et al. Non-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation of sulfonamide antibiotics in water: kinetics, mechanisms, and implications for water treatment. Water Res., 2018, 147: 82. |
| [23] | LIU L, MI H, ZHANG M, et al. Efficient moxifloxacin degradation by CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles activated peroxymonosulfate: kinetics, pathways and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 407: 127201. |
| [24] | CHEN L, DING D, LIU C, et al. Degradation of norfloxacin by CoFe2O4-GO composite coupled with peroxymonosulfate: a comparative study and mechanistic consideration. Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 334: 273. |
| [25] | DU Y, MA W, LIU P, et al. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J. Hazard Mater., 2016, 308: 58. |
| [26] | HUNG C M, CHEN C W, HUANG C P, et al. Removal of 4-nonylphenol in activated sludge by peroxymonosulfate activated with sorghum distillery residue-derived biochar. Bioresour Technol., 2022, 360: 127564. |
| [27] | DUNG N T, TRANG T T, THAO V D, et al. Enhanced degradation of organic dyes by peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4-CoCO3/rGO hybrid activation: a comprehensive study. J. the Taiwan Instit. of Chem. Engin., 2022, 133: 104279. |
| [28] |
DUNG N T, THU T V, VAN NGUYEN T, et al. Catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate with manganese cobaltite nanoparticles for the degradation of organic dyes. RSC Adv., 2020, 10(7):3775.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | CHEN G, NENGZI L C, GAO Y, et al. Degradation of tartrazine by peroxymonosulfate through magnetic Fe2O3/Mn2O3 composites activation. Chine. Chemi. Lett., 2020, 31(10):2730. |
| [30] | XU P, XIE S, LIU X, et al. Electrochemical enhanced heterogenous activation of peroxymonosulfate using CuFe2O4 particle electrodes for the degradation of diclofenac. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446: 136941. |
| [31] |
ZHANG T, ZHU H, CROUE J P. Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(6):2784.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LI J, WAN Y, LI Y, et al. Surface Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle promoted the degradation of atrazine by peroxymonosulfate activation in the presence of hydroxylamine. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 256: 117782. |
| [33] | WANG Z, NENGZI L C, ZHANG X, et al. Novel NiCo2S4/CS membranes as efficient catalysts for activating persulfate and its high activity for degradation of nimesulide. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 381: 122517. |
| [34] | WANG S, CHEN Z, YAN P, et al. Enhanced degradation of iohexol in water by CuFe2O4activated peroxymonosulfate: efficiency, mechanism and degradation pathway. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133198. |
| [35] |
ZHANG L S, JIANG X H, ZHONG Z A, et al. Carbon nitride supported high-loading Fe single-atom catalyst for activation of peroxymonosulfate to generate 1O2 with 100% selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(40):21751.
DOI URL |
| [36] | WANG J, SHEN M, WANG H, et al. Red mud modified sludge biochar for the activation of peroxymonosulfate: singlet oxygen dominated mechanism and toxicity prediction. Sci. Total. Environ., 2020, 740: 140388. |
| [37] | ZHENG Y, ZHUANG W, ZHANG X, et al. Grape-like CNTs/ BaTiO3 nanocatalyst boosted hydraulic-driven piezo-activation of peroxymonosulfate for carbamazepine removal. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 449: 137826. |
| [38] | WANG X, ZHUANG Y, SHI B. Degradation of trichloroacetic acid by MOFs-templated CoFe/graphene aerogels in peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 450: 137799. |
| [39] | XU A, WU D, ZHANG R, et al. Bio-synthesis of Co-doped FeMnOx and its efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of moxifloxacin. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 435: 134695. |
| [40] | ZHAO Y, WANG H, JI J, et al. Degradation of ciprofloxacin by peroxymonosulfate activation using catalyst derived from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Cleaner Produc., 2022, 362: 132442. |
| [1] | 李建军, 陈芳明, 张梨梨, 王磊, 张丽亭, 陈慧雯, 薛长国, 徐良骥. CoFe2O4/MgAl-LDH催化剂活化过氧一硫酸盐促进抗生素降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 440-448. |
| [2] | 刘会来, 李志豪, 孔德峰, 陈星. 酞菁铁/MXene复合阴极的制备及电芬顿降解磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| [3] | 叶茂森, 王耀, 许冰, 王康康, 张胜楠, 冯建情. II/Z型Bi2MoO6/Ag2O/Bi2O3异质结可见光催化降解四环素[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 321-329. |
| [4] | 陈梦杰, 王倩倩, 吴成铁, 黄健. 基于DFT的描述符预测生物陶瓷的降解性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [5] | 蔡梦宇, 李杨虹淼, 杨彩云, 周雨婷, 吴昊. 基于活性污泥焚灰的类Fenton催化剂的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142. |
| [6] | 郑嘉乾, 卢霄, 鲁亚杰, 王迎军, 王臻, 卢建熙. 医用生物陶瓷的功能性生物适配机制及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 1-16. |
| [7] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [8] | 李铁, 李玥, 王颖异, 张珽. 石墨烯-铁酸铋纳米晶复合材料的制备及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 725-732. |
| [9] | 蔡苗, 陈子航, 曾实, 杜江慧, 熊娟. CuS纳米片修饰Bi5O7I复合材料用于光催化还原Cr(VI)水溶液[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [10] | 安伟佳, 李静, 王淑瑶, 胡金山, 蔺在元, 崔文权, 刘利, 解珺, 梁英华. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6复合光催化剂制备及光催化芬顿协同降解苯酚[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 615-622. |
| [11] | 熊金艳, 罗强, 赵凯, 张梦梦, 韩朝, 程刚. 界面电荷快速转移提升铜修饰氧化钨光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [12] | 兰青, 孙盛睿, 吴萍, 杨庆峰, 刘阳桥. 钴掺杂氧化铜/可见光协同活化PMS降解罗丹明B及其机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177. |
| [13] | 刘彩, 刘芳, 黄方, 王晓娟. 海藻基CDs-Cu-TiO2复合材料的制备及其光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [14] | 包峰, 常江. 硅酸钙纳米线复合电纺丝支架的制备及离子释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1199-1207. |
| [15] | 张信聪,郭珂,彭莲莲,吴结宇,张富民,朱伟东,傅仰河. NH2-UiO-66机械催化降解染料的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1023-1028. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||