无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1236-1244.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220240 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220240
池哲人1( ), 张辽2, 郭志前2(
), 张辽2, 郭志前2( ), 李永生1,3, 牛德超1(
), 李永生1,3, 牛德超1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-21
修回日期:2022-05-07
出版日期:2022-11-20
网络出版日期:2022-06-16
通讯作者:
郭志前, 教授. E-mail: guozq@ecust.edu.cn;作者简介:池哲人(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: chizheren@163.com
基金资助:
CHI Zheren1( ), ZHANG Liao2, GUO Zhiqian2(
), ZHANG Liao2, GUO Zhiqian2( ), LI Yongsheng1,3, NIU Dechao1(
), LI Yongsheng1,3, NIU Dechao1( )
)
Received:2022-04-21
Revised:2022-05-07
Published:2022-11-20
Online:2022-06-16
Contact:
GUO Zhiqian, professor. E-mail: guozq@ecust.edu.cn;About author:CHI Zheren (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: chizheren@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
近年来, 由于具有较好的近红外区吸收、结构可调等特点, 有机小分子光热剂在生物医药领域展示出广阔的应用前景。然而, 大部分有机小分子光热剂仍面临水溶性较差、生物稳定性不佳、光热转换效率较低等挑战。本研究发展了一种简便的合成方法, 制备了负载Flav7的氧化硅基杂化胶束(FPOMs)用于高效的光热治疗。首先利用嵌段共聚物PS132-b-PAA16自组装行为负载疏水近红外有机小分子Flav7得到胶束体系, 进一步引入3-巯基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPTMS)和聚乙二醇(PEG)对上述胶束体系进行结构固定和表面改性得到FPOMs。研究表明, 在808 nm波长激光的激发下, FPOMs展现出优异的光热稳定性和较高的光热转换效率(46.7%)。细胞实验证实FPOMs具有良好的生物相容性和光热毒性, 有望作为一类新型的纳米光热剂用于肿瘤高效安全光热治疗。
中图分类号:
池哲人, 张辽, 郭志前, 李永生, 牛德超. 氧化硅基杂化胶束负载Flav7光热剂的合成与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1236-1244.
CHI Zheren, ZHANG Liao, GUO Zhiqian, LI Yongsheng, NIU Dechao. Flav7-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Synthesis and Photothermal Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1236-1244.
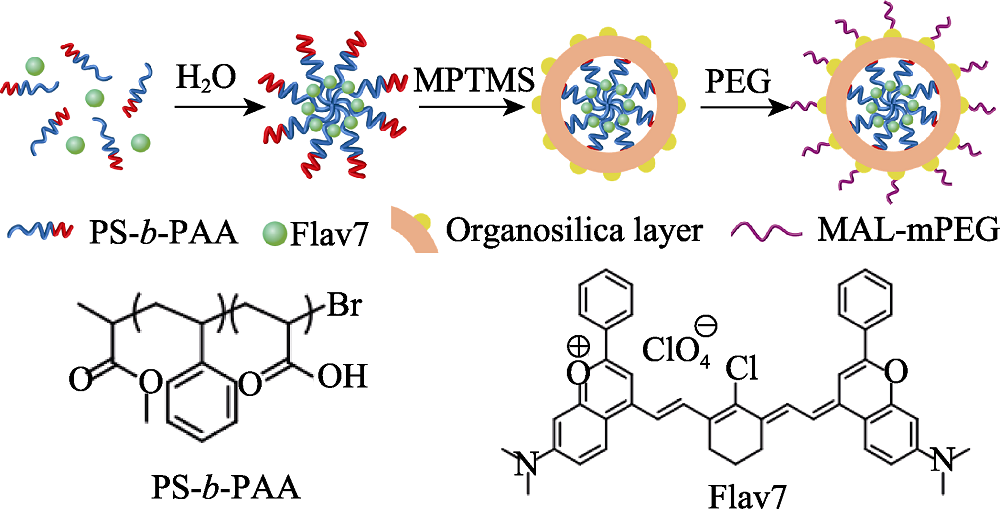
图2 FPOMs的合成示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration for the fabrication of FPOMs MPTMS: 3-Mercaptopropyl trimethoxsilicon; PEG: Polyethylene glycol; MAL-mPEG: Maleimide-methoxy (polyethylene glycol); PS-b-PAA: Polystyrene-block-polyacrylic acid; FPOMs: Flav7-PEGylated- organosilica-micelles The color figure can be obtained from online edition
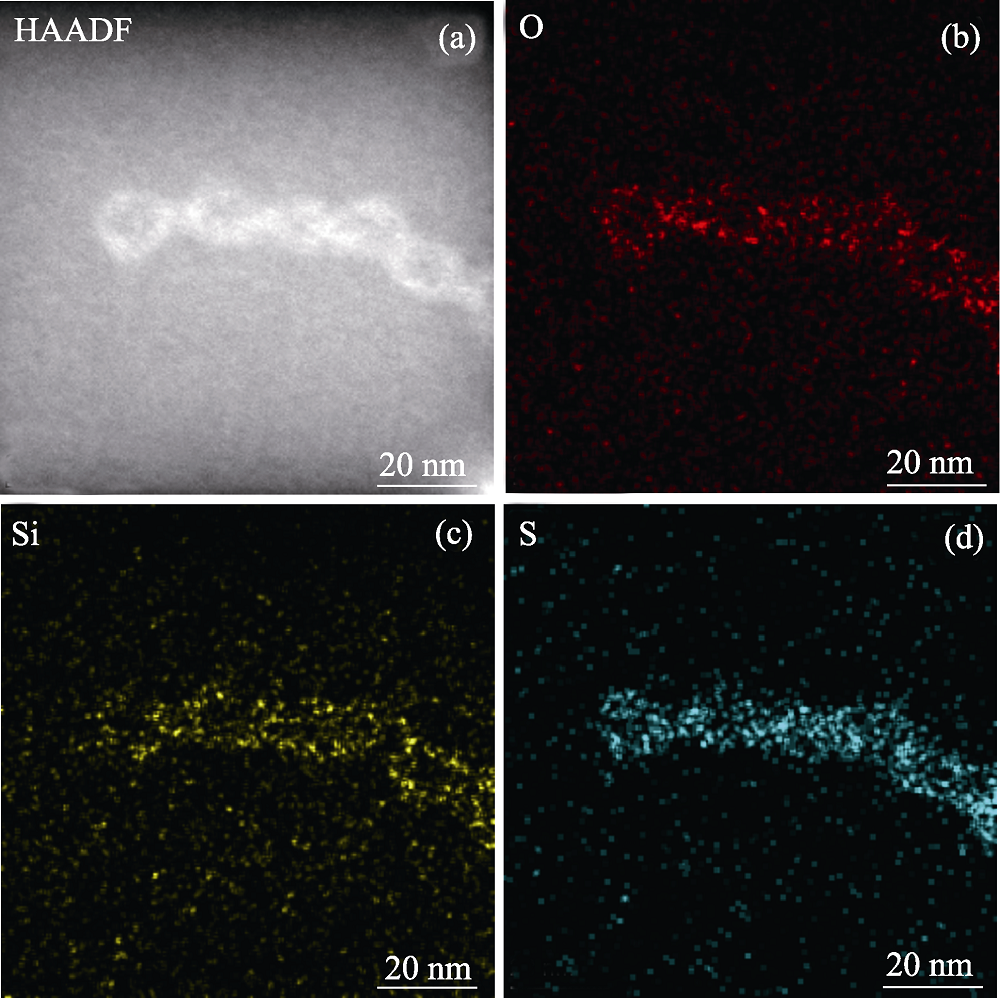
图4 FPOMs的面扫描元素分析
Fig. 4 Element mapping scanning images of Flav7-PEGylated- urganosilica-micelles (FPOMs) (a) Image of HAADF; (b-d) Images of O (b), Si (c) and S (d) The color figures can be obtained from online edition
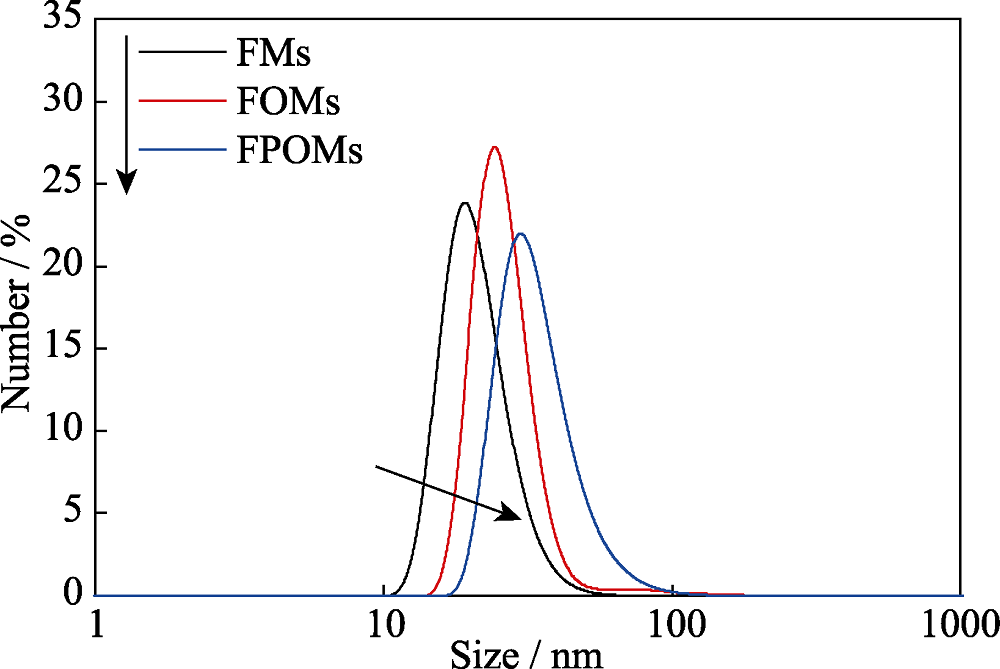
图5 FMs, FOMs和FPOMs的流体动力学粒径
Fig. 5 Hydrodynamic sizes of FMs, FOMs and FPOMs FMs: Flav7-micelles; FOMs: Flav7-organosilica-micelles; FPOMs: Flav7-PEGylated-organosilica-micelles The color figure can be obtained from online edition
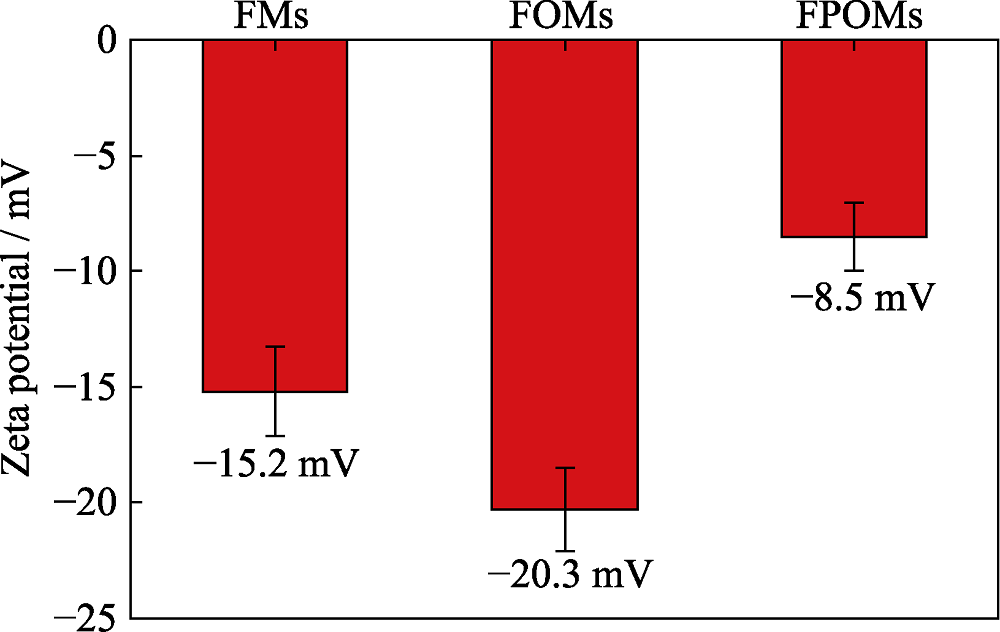
图6 FMs, FOMs和FPOMs的Zeta电位
Fig. 6 Zeta potentials of FMs, FOMs and FPOMs FMs: Flav7-Micelles; FOMs: Flav7-organosilica-micelles; FPOMs: Flav7-PEGylated-organosilica-micelles The color figure can be obtained from online edition
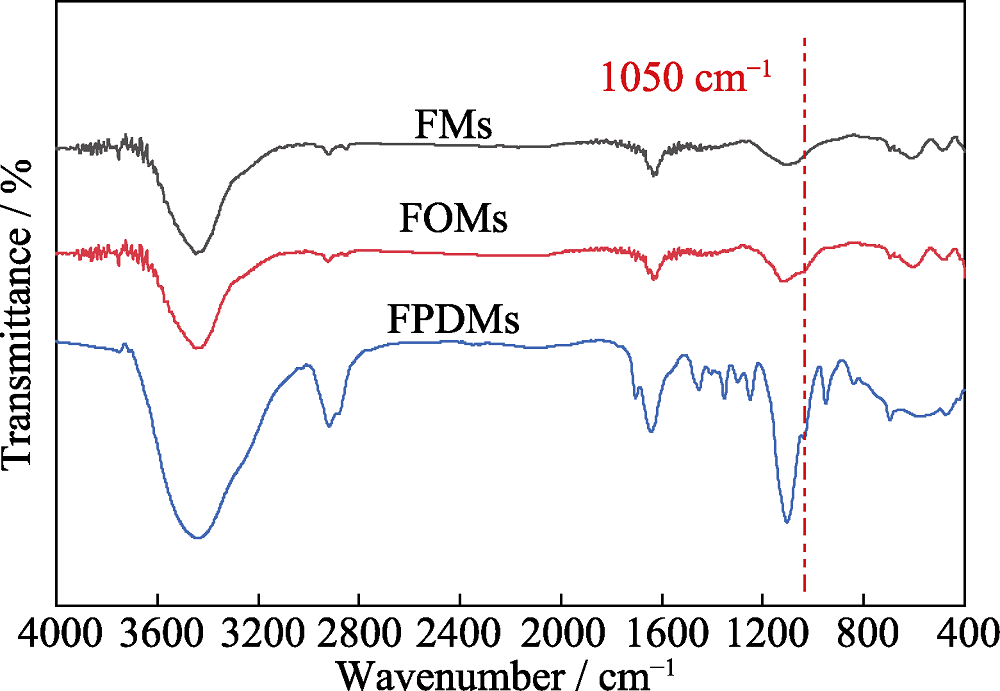
图7 FMs, FOMs和FPOMs的傅里叶红外光谱图
Fig. 7 FT-IR spectra of FMs, FOMs and FPOMs FMs: Flav7-Micelles; FOMs: Flav7-organosilica-micelles; FPOMs: Flav7-PEGylated-organosilica-micelles
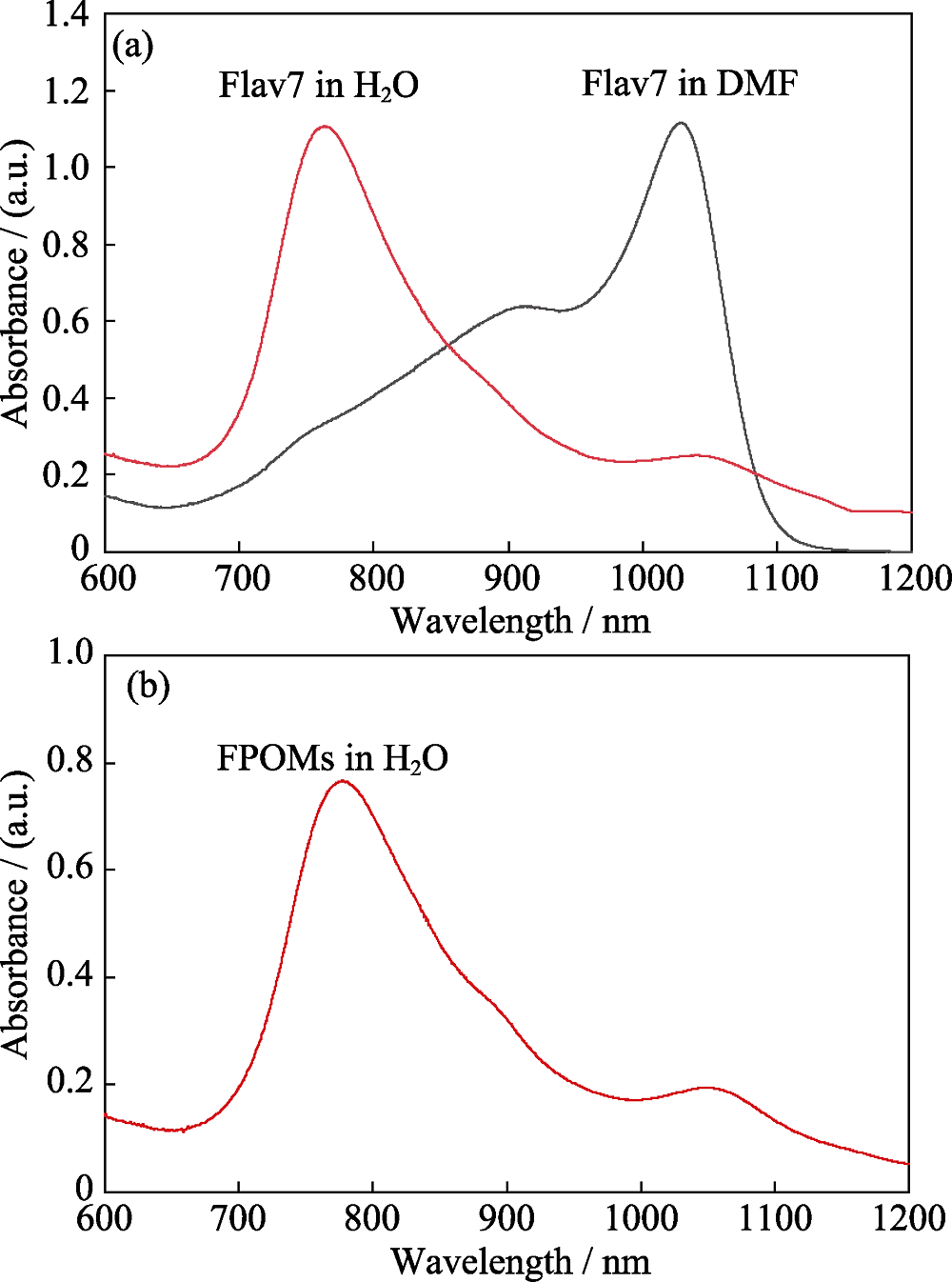
图8 Flav7(a)和FPOMs(b)在DMF或水中的吸收光谱
Fig. 8 Absorption spectra of Flav7 (a) and FPOMs (b) in DMF or in water FPOMs: Flav7-PEGylated-organosilica-micelles; DMF: N,N- dimethylformamide
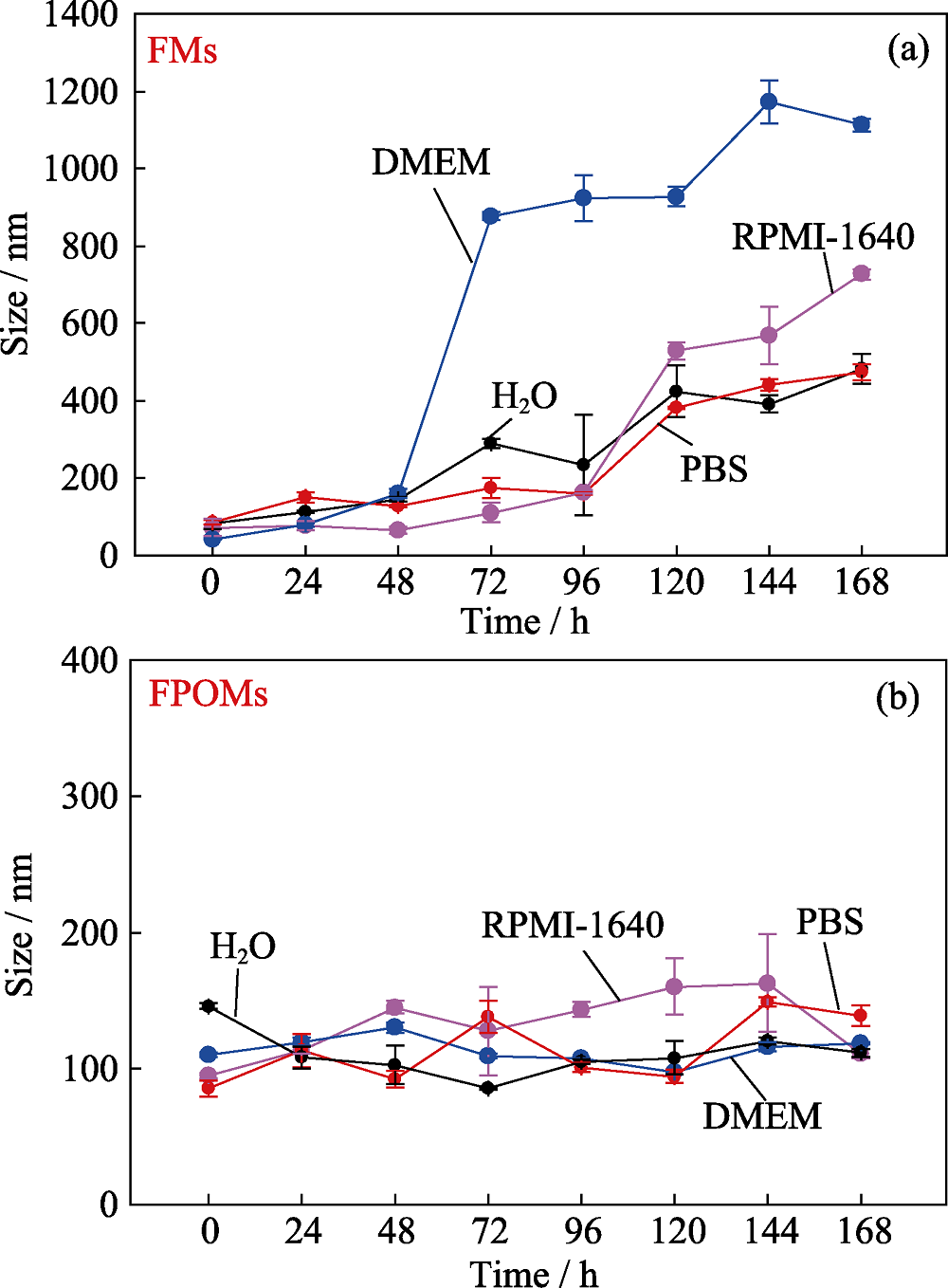
图9 FMs(a)和FPOMs(b)在不同生理介质中的流体动力学粒径随时间的变化图
Fig. 9 Hydrodynamic sizes of FMs (a) and FPOMs (b) in H2O, PBS (pH 7.4), RPMI-1640 medium (10% serum) and DMEM medium (10% serum) for a week The color figures can be obtained from online edition
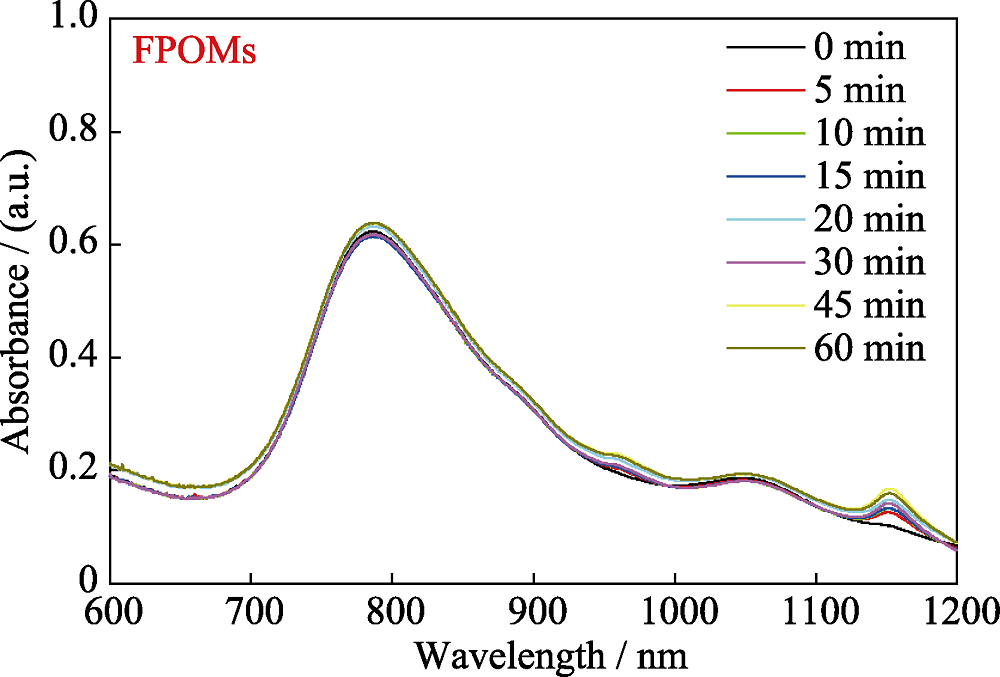
图10 FPOMs在808 nm激光持续照射0~60 min时的吸收光谱
Fig. 10. Absorption spectra of FPOMs under 808 nm laser irradiation for 0-60 min The color figure can be obtained from online edition
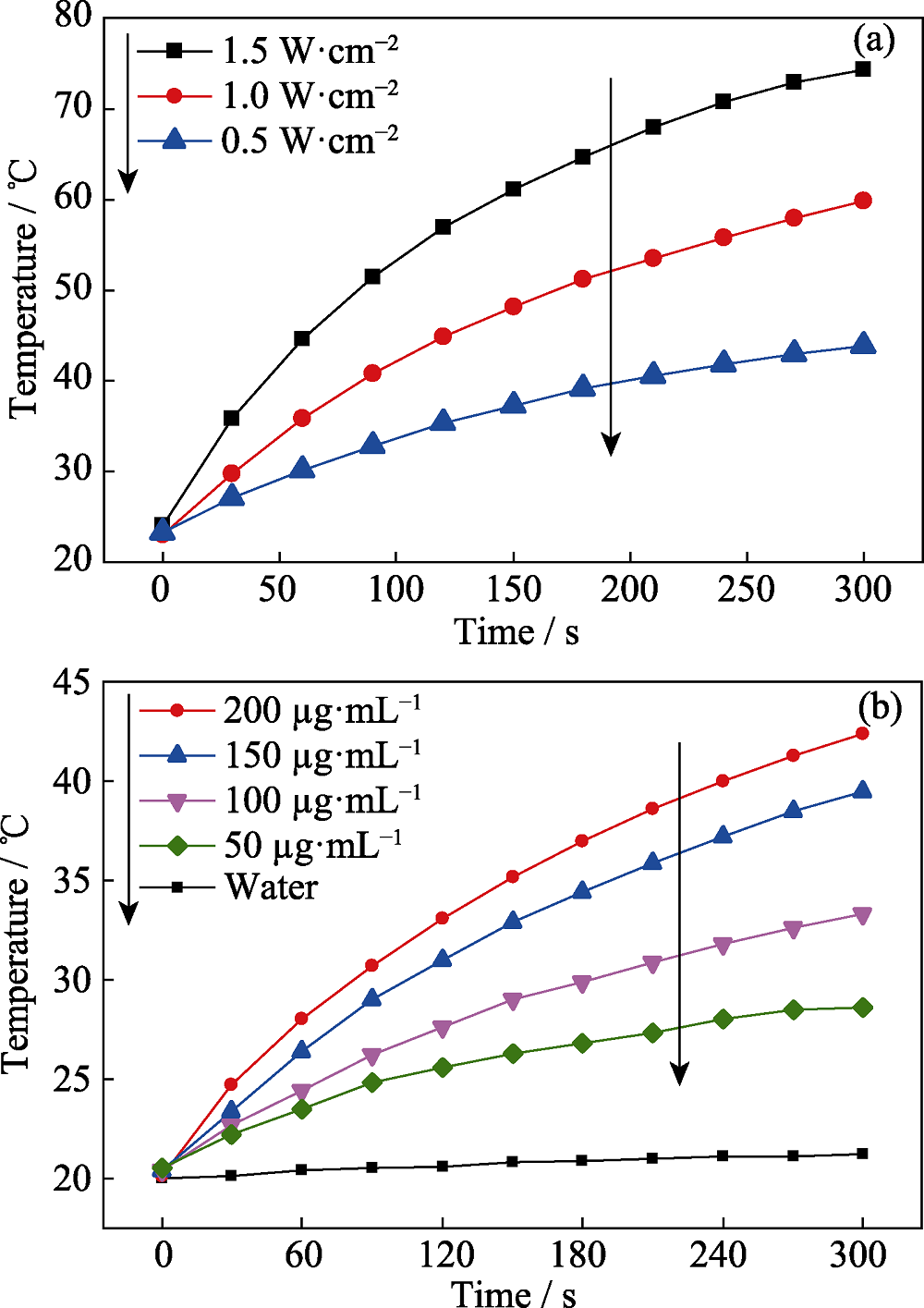
图12 FPOMs的光热性能
Fig. 12 Photothermal property of FPOMs (a) FPOMs (600 μg/mL) under different power densities of 808 nm laser irradiation; (b) FPOMs at different concentrations under 808 nm (1.0 W/cm2) laser irradiation The color figures can be obtained from online edition
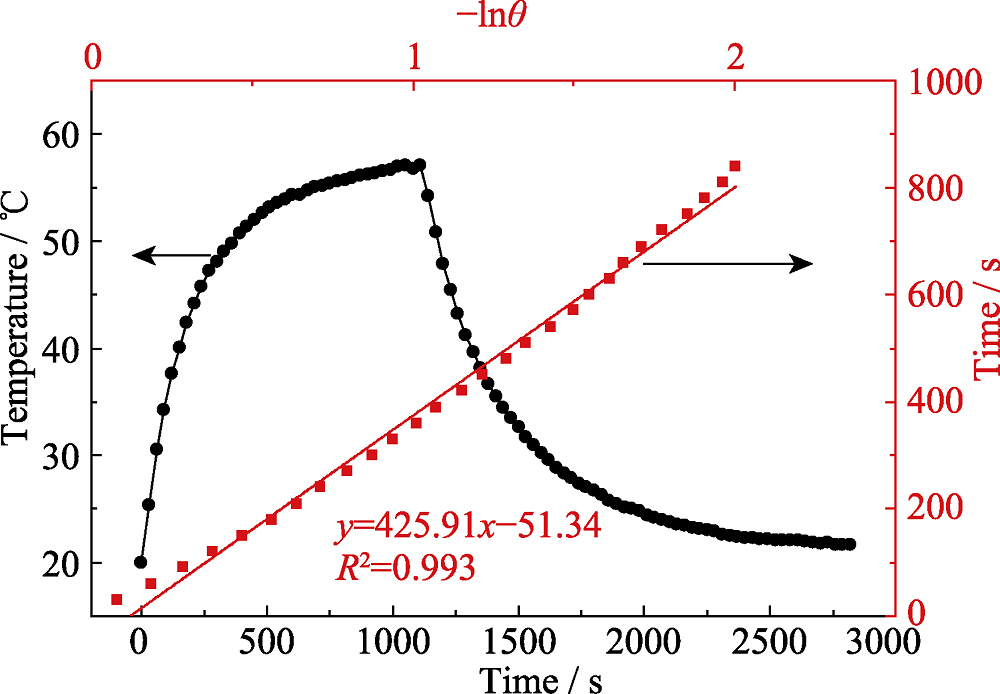
图14 FPOMs的光热转换效率(1.0 W/cm2, 808 nm)
Fig. 14 Photothermal conversion efficiency of FPOMs (1.0 W/cm2, 808 nm) The color figure can be obtained from online edition
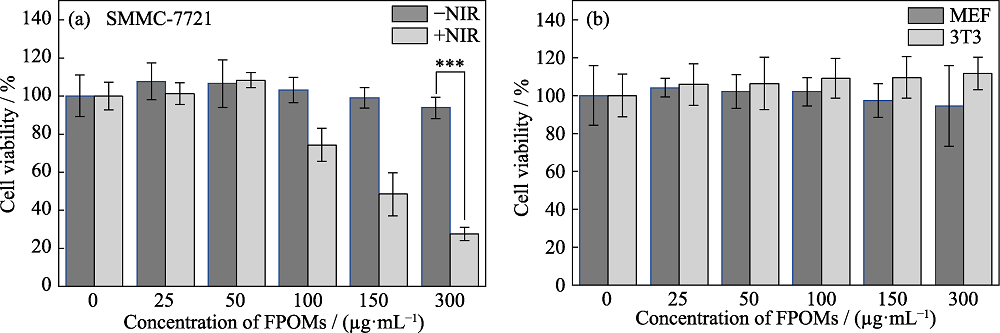
图15 FPOMs处理后的细胞经激光照射后的细胞存活率
Fig. 15 Relative cell viabilities of FPOMs treated cells after laser irradiation at 808 nm (1.0 W/cm2) for 5 min (a) SMMC-7721 cancer cells with or without laser irradiation (***p < 0.001); (b) MEF and 3T3 cells The color figures can be obtained from online edition
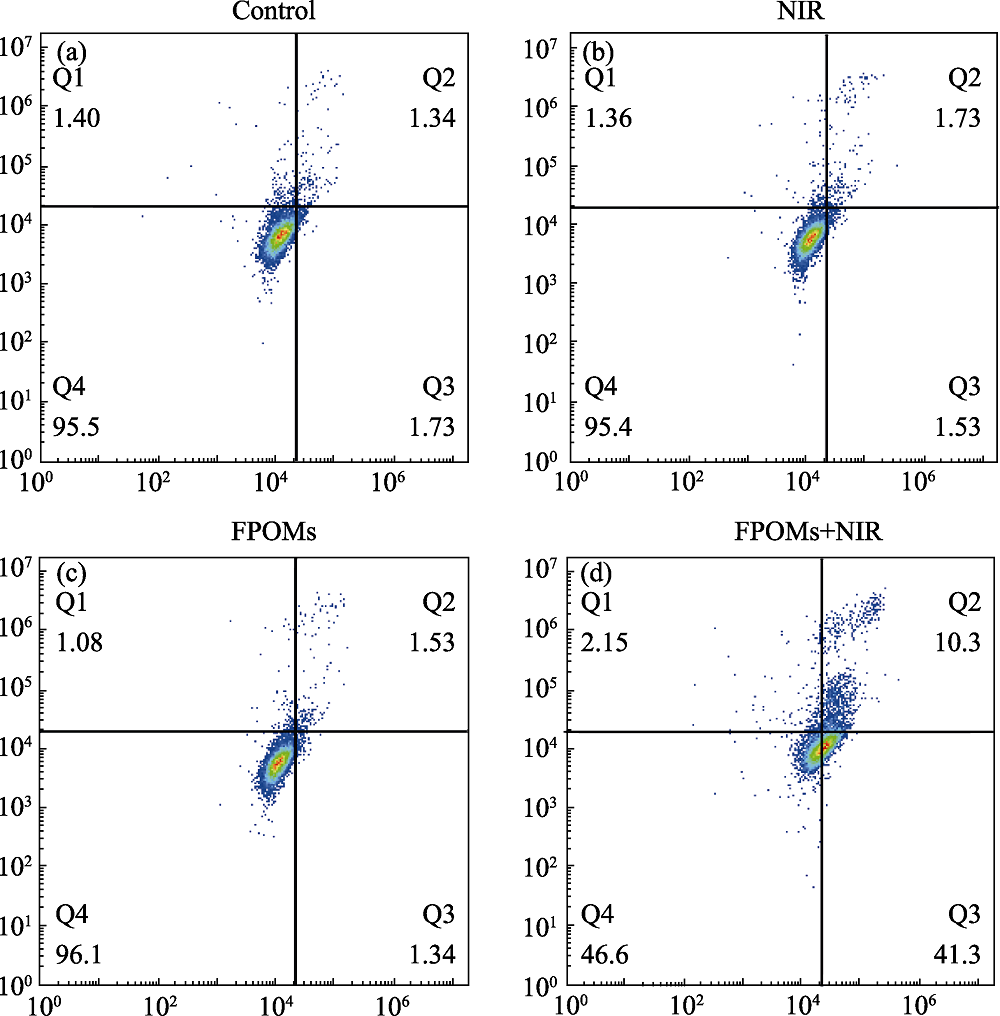
图16 流式细胞仪分析SMMC-7721细胞经不同处理并染色后的细胞凋亡
Fig. 16 Flow cytometry analysis of SMMC-7721 cells with different treatment and staining by Annexin-V/PI reagents (a) Control; (b) Laser irradiation only; (c) FPOMs only; (d) FPOMs and laser irradiation The color figure can be obtained from online edition
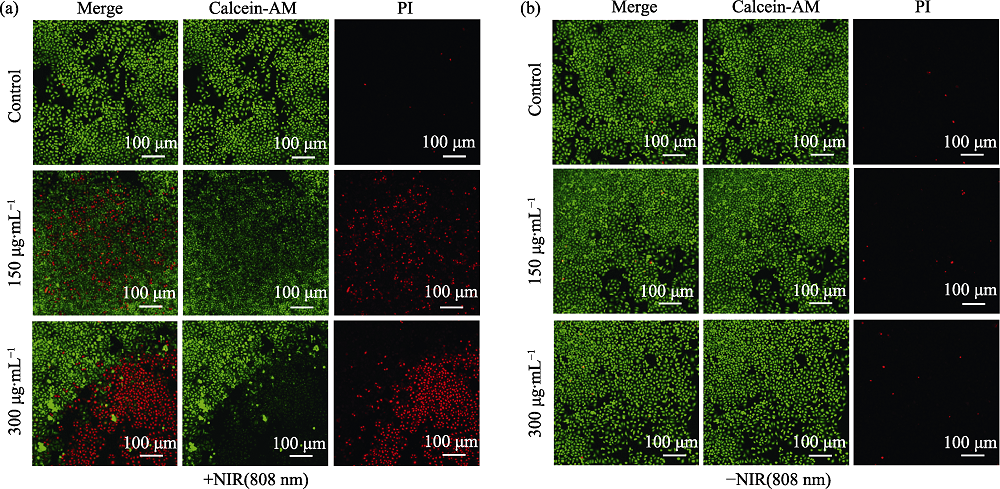
图17 SMMC-7721细胞与不同浓度FPOMs共孵育后的激光共聚焦显微镜照片
Fig. 17 Confocal laser scanning microscope images of SMMC-7721 cells with FPOMs (0, 150, and 300 μg/mL) treated by (a) or not by (b) laser irradiation (808 nm, 1.0 W/cm2, 5 min). The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| [1] |
XU C, PU K. Second near-infrared photothermal materials for combinational nanotheranostics. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(2): 1111-1137.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | ZHI D, YANG T, O'HAGAN J, et al. Photothermal therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 325: 52-71. |
| [3] |
JUNG H S, VERWILST P, SHARMA A, et al. Organic molecule- based photothermal agents: an expanding photothermal therapy universe. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(7): 2280-2297.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CHEN Y W, SU Y L, HU S H, et al. Functionalized graphene nanocomposites for enhancing photothermal therapy in tumor treatment. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 105: 190-204. |
| [5] |
LIU Y, BHATTARAI P, DAI Z, et al. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(7): 2053-2108.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HUANG X, JAIN P K, EL-SAYED I H, et al. Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Lasers in Medical Science, 2008, 23 (3): 217-228.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LI J, RAO J, PU K. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials, 2018, 155: 217-235. |
| [8] |
SONG X, CHEN Q, LIU Z. Recent advances in the development of organic photothermal nano-agents. Nano Research, 2015, 8(2): 340-354.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
RAJORA M, LOU J, ZHENG G. Advancing porphyrin's biomedical utility via supramolecular chemistry. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(21): 6433-6469.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DOANE T L, BURDA C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(7): 2885-2911.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
ZOU L, WANG H, HE B, et al. Current approaches of photothermal therapy in treating cancer metastasis with nanotherapeutics. Theranostics, 2016, 6(6): 762-772.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
DOUGHTY A C, HOOVER A R, LAYTON E, et al. Nanomaterial applications in photothermal therapy for cancer. Materials, 2019, 12(5): 779-14.
DOI URL |
| [13] | WANG H, CHANG J, SHI M, et al. A dual-targeted organic photothermal agent for enhanced photothermal therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 131(4): 1069-1073. |
| [14] | CHENG Q, TIAN Y, DANG H, et al. Antiquenching macromolecular NIR-II probes with high-contrast brightness for imaging- guided photothermal therapy under 1064 nm irradiation. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022, 11: 2101697-10. |
| [15] |
COSCO E D, CARAM J R, BRUNS O T, et al. Flavylium polymethine fluorophores for near- and shortwave infrared imaging. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(42): 13126-13129.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI T, LI C, RUAN Z, et al. Polypeptide-conjugated second near- infrared organic fluorophore for image-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano, 2019, 13 (3): 3691-3702.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
NIU D, LI Y, MA Z, et al. Preparation of uniform, water-soluble, and multifunctional nanocomposites with tunable sizes. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20 (5): 773-780.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
FADDA A, EL-MEKAWY R E. Utility of quaternary ammonium salts in synthesis of some novel cyanine dyes as potential antibacterial and antitumor agents. Dyes and Pigments, 2013, 99(2): 512-519.
DOI URL |
| [19] | ROPER D K, AHN W, HOEPFNER M. Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111: 3636-3641. |
| [20] |
OSS-RONEN L, SCHMIDT J, ABETZ V, et al. Characterization of block copolymer self-assembly: from solution to nanoporous membranes. Macromolecules, 2012, 45(24): 9631-9642.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
NIU D, LI Y, SHI J. Silica/organosilica cross-linked block copolymer micelles: a versatile theranostic platform. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(3): 569-585.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
MALDINEY T, RICHARD C, SEGUIN J, et al. Effect of core diameter, surface coating, and PEG chain length on the biodistribution of persistent luminescence nanoparticles in mice. ACS Nano, 2011, 5 (2): 854-862.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
FENG H, LU X, WANG W, et al. Block copolymers: synthesis, self- assembly, and applications. Polymers (Basel), 2017, 9(10): 494-524.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JIANG Z, ZHANG C, WANG X, et al. A borondifluoride- complex-based photothermal agent with an 80% photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal therapy in the NIR-II window. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(41): 22376-22384.
DOI URL |
| [25] | WANG Y, NIU C, FAN S, et al. Indocyanine green loaded modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an effective photothermal nanoplatform. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21: 4789-15. |
| [26] | DING Y, WANG C, LU B, et al. Enhancing the stability and photothermal conversion efficiency of ICG by pillar[5]arene-based host-guest interaction. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 775436-8. |
| [27] |
LI C, LIN W, LIU S, et al. Structural optimization of organic fluorophores for highly efficient photothermal therapy. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 5(1): 284-292.
DOI URL |
| [28] | YOON H J, LEE H S, LIM J Y, et al. Liposomal indocyanine green for enhanced photothermal therapy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(7): 5683-5691. |
| [29] |
QIAN H, CHENG Q, TIAN Y, et al. An anti-aggregation NIR-II heptamethine-cyanine dye with a stereo-specific cyanine for imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9(11): 2688-2696.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [2] | 吴雪文, 刘素琴, 黄可龙. CTAB作为钒电池电解液添加剂的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(6): 641-646. |
| [3] | 何 燕, 王 攀, 邓安平, 杨 静, 黄应平, 杨 勇. 反相胶束介质制备纳米CdS及可见光降解孔雀绿[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(11): 1221-1227. |
| [4] | 张袖丽,李 丽,丁亚平. 硫酸钙纳米棒的简易合成与光致发光特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(6): 1491-1495. |
| [5] | 吴平伟,高濂. 气-液反应反胶束法制备CdS纳米颗粒[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(4): 937-941. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||