无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 267-277.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210705 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20210705
所属专题: 增材制造专题(2022)
杨勇1,2( ), 郭啸天1,3, 唐杰1,2, 常浩天1,3, 黄政仁1,2, 胡秀兰3(
), 郭啸天1,3, 唐杰1,2, 常浩天1,3, 黄政仁1,2, 胡秀兰3( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-15
修回日期:2021-12-23
出版日期:2022-03-20
网络出版日期:2022-01-06
通讯作者:
胡秀兰, 教授. E-mail: whoxiulan@163.com
作者简介:杨 勇(1974-), 男, 研究员. E-mail: yangyong@mail.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
YANG Yong1,2( ), GUO Xiaotian1,3, TANG Jie1,2, CHANG Haotian1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,2, HU Xiulan3(
), GUO Xiaotian1,3, TANG Jie1,2, CHANG Haotian1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,2, HU Xiulan3( )
)
Received:2021-11-15
Revised:2021-12-23
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2022-01-06
Contact:
HU Xiulan, professor. E-mail: whoxiulan@163.com
About author:YANG Yong (1974-), male, professor. E-mail: yangyong@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目前光固化3D打印技术因打印成型精度高而被广泛应用于陶瓷增材制造, 其中非氧化物陶瓷如碳化硅、氮化硅等因打印材料粉体折射率和吸光度比较高, 光固化陶瓷浆料存在分散稳定性差、入射光难穿透并产生光固化反应的固化层厚度低等问题, 导致其固含量很难提高甚至于无法打印成型。高固含量的非氧化物陶瓷打印成型成为光固化3D打印的主要难点, 吸引了广大学者对其光固化机理、粉体调控等机制进行研究。本文系统地总结了几种非氧化物陶瓷光固化浆料的制备、光固化成型、有机物去除及烧结致密化的研究工作, 并就如何对光敏树脂组成进行调节、对陶瓷粉体进行改性的几种方法进行分析与讨论, 针对性地提出创新方案来改善非氧化物陶瓷的浆料性能、光固化打印优化和致密化缺陷修复及性能提升, 最终推动大尺寸、复杂结构的非氧化物陶瓷部件光固化增材制造高精度制备技术的进步。
中图分类号:
杨勇, 郭啸天, 唐杰, 常浩天, 黄政仁, 胡秀兰. 非氧化物陶瓷光固化增材制造研究进展及展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 267-277.
YANG Yong, GUO Xiaotian, TANG Jie, CHANG Haotian, HUANG Zhengren, HU Xiulan. Research Progress and Prospects of Non-oxide Ceramic in Stereolithography Additive Manufacturing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 267-277.
| Material | Absorbance (d/μm, λ/nm) | Refractive index (d/μm, λ/nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3[ | 0.044 (10, 405) | 1.787 (2.3, 365) |
| ZrO2[ | 0.003 (10, 405) | Low |
| ZTA[ | Low | Low |
| SiO2[ | Low | 1.564 (2.25, 365) |
| SiC[ | 0.479 (10, 405) | 2.553 (12.25, 467-691) |
| Si3N4[ | 0.180 (5, 405) | 2.023 (-, 632.8) |
| TiO2[ | Low | 2.493 (-, 632.8) |
| BN[ | High | High |
表1 陶瓷材料的折射率和吸光度
Table 1 Refractive index and absorbance of ceramic materials
| Material | Absorbance (d/μm, λ/nm) | Refractive index (d/μm, λ/nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3[ | 0.044 (10, 405) | 1.787 (2.3, 365) |
| ZrO2[ | 0.003 (10, 405) | Low |
| ZTA[ | Low | Low |
| SiO2[ | Low | 1.564 (2.25, 365) |
| SiC[ | 0.479 (10, 405) | 2.553 (12.25, 467-691) |
| Si3N4[ | 0.180 (5, 405) | 2.023 (-, 632.8) |
| TiO2[ | Low | 2.493 (-, 632.8) |
| BN[ | High | High |
| Material | Flexural strength/MPa | Elasticity modulus/GPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB-SiC[ | ≥330 | ≥340 | ≥4.1 |
| S-SiC[ | 349-431 | 308-342 | 3.77 |
| RB-SiC[ | (305±15) | - | - |
| RB-SiC*[ | 210.4 | - | - |
| (Cf)/SiC*[ | 262.6 | - | - |
表2 不同制造方式SiC陶瓷的结构与性能
Table 2 Structure and properties of SiC ceramics obtained by different manufacturing methods
| Material | Flexural strength/MPa | Elasticity modulus/GPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB-SiC[ | ≥330 | ≥340 | ≥4.1 |
| S-SiC[ | 349-431 | 308-342 | 3.77 |
| RB-SiC[ | (305±15) | - | - |
| RB-SiC*[ | 210.4 | - | - |
| (Cf)/SiC*[ | 262.6 | - | - |
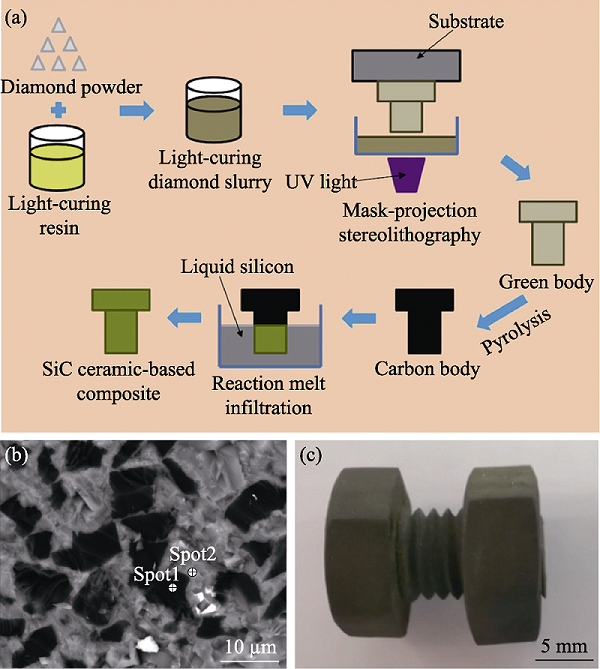
图4 光固化成型制备SiC陶瓷基复合材料[52]
Fig. 4 Preparation of SiC ceramic-based composite by stereolithography[52] (a) Prepared schematic of SiC ceramic-based composite by stereolithography; (b) SEM image of SiC ceramic-based composite with a diamond volume fraction of 15%; (c) SiC ceramic-based composite
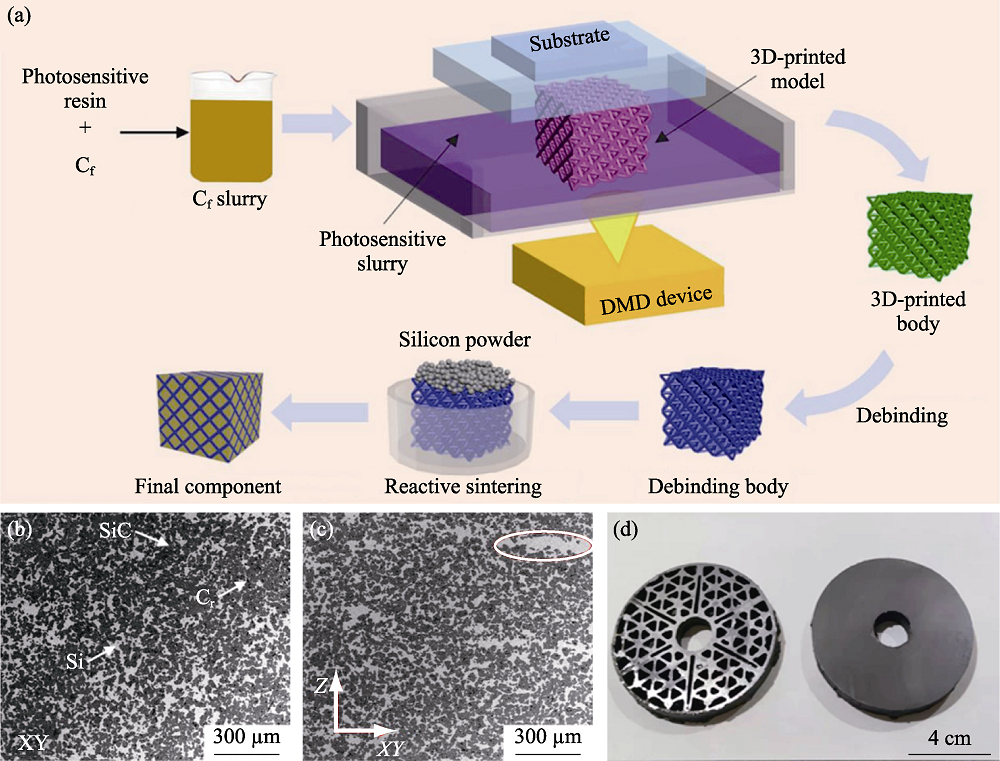
图5 数字光处理技术和液态硅渗透工艺制备Cf/SiC陶瓷复合材料[46]
Fig. 5 Preparation of Cf/SiC ceramic composites by digital light processing technology and liquid silicon infiltration process[46] (a) Prepared schematic of SiC composites; (b, c) SEM images of cross section and horizontal plane of Cf/SiC composite; (d) Sintered Cf/SiC composites
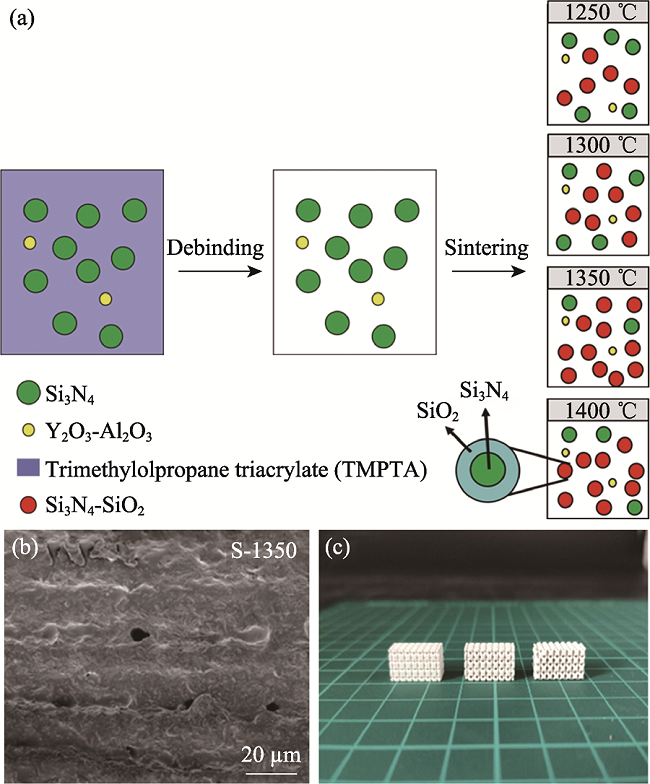
图6 数字光处理成型技术制备Si3N4-SiO2陶瓷[58]
Fig. 6 Preparation of Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics by digital light processing (DLP) technology[58] (a) Schematic synthetic reaction process of oxidation of silicon nitride at high temperature; (b) SEM image of fracture surface of Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics sintered at 1350 ℃; (c) Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics with lattice structure
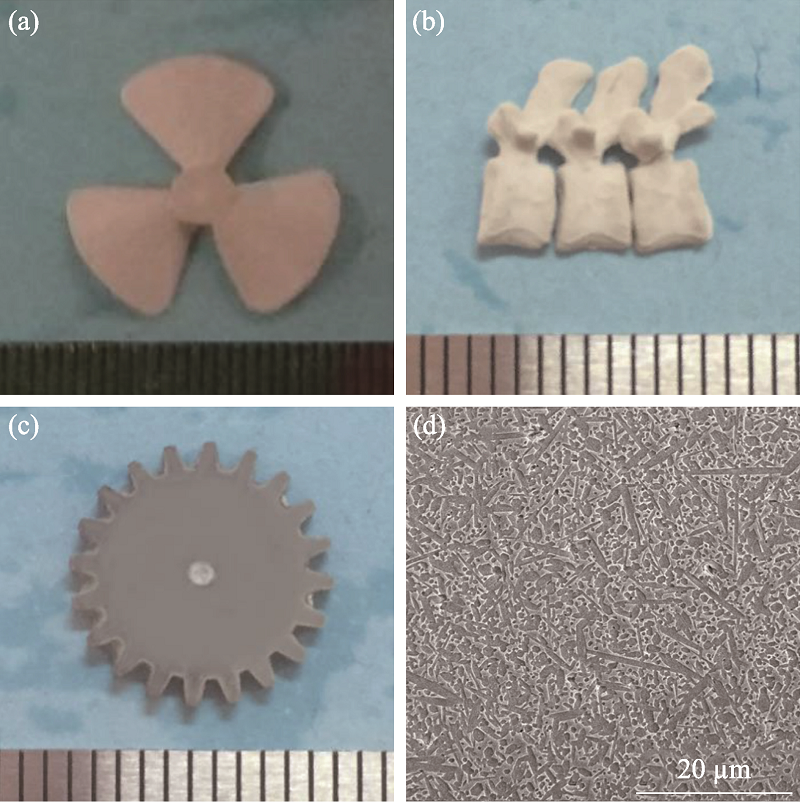
图7 基于数字光处理的立体光刻法制备表面氧化氮化硅粉末复杂形状陶瓷零件[60]
Fig. 7 Fabrication of complex shaped ceramic parts with surface- oxidized Si3N4 powder via digital light processing based stereolithography method[60] (a) Green Si3N4 body of a blade; (b) Green Si3N4 body of a vertebrae; (c) Sintered body of a Si3N4 gear; (d) SEM image of sintered body of a Si3N4 gear
| Material | Technology | Resin+photoinitiator | Dispersant | Powder | Cured thickness /μm | Solid content/% (in volume) | Bending strength /MPa | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+DVE-3+ TPO | KOS110 | 15 μm SiC | 78 | 30 | - | [ |
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+TPO | KOS110+ 17000 | 15 μm SiC+ ~40 nm SiC | - | 45 | 165.2 | [ |
| SiC | DLP | ACMO+HDDA+ TMPTA+BAPO | 4200 | 10 μm SiC | ≈60 | 40 | 50.18 | [ |
| Al2O3-Si3N4 | SLA | TMPTA+HDDA+ Irgacure 184 | PEG200+ glycerol | 1 μm Al2O3+ 200 nm Si3N4 | 40 | 47 | - | [ |
| SiO2-Si3N4 | DLP | TMPTA+Irgacure 184 | - | 3.45 μm Si3N4+ Y2O3+Al2O3 | 50-60 | 50 | (77±5) | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+819 | Copolymer | 200 nm oxidized Si3N4 | 51 | - | - | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | EA+819+HDDA+184 | Darvan | 800 nm (KH-560)Si3N4 | 50 | 45 | - | [ |
表3 高折射率、高吸光度陶瓷的光固化成型和烧结性能比较
Table 3 Comparison of molding and sintering performances in stereolithography of high refractive index and high absorbance ceramics
| Material | Technology | Resin+photoinitiator | Dispersant | Powder | Cured thickness /μm | Solid content/% (in volume) | Bending strength /MPa | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+DVE-3+ TPO | KOS110 | 15 μm SiC | 78 | 30 | - | [ |
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+TPO | KOS110+ 17000 | 15 μm SiC+ ~40 nm SiC | - | 45 | 165.2 | [ |
| SiC | DLP | ACMO+HDDA+ TMPTA+BAPO | 4200 | 10 μm SiC | ≈60 | 40 | 50.18 | [ |
| Al2O3-Si3N4 | SLA | TMPTA+HDDA+ Irgacure 184 | PEG200+ glycerol | 1 μm Al2O3+ 200 nm Si3N4 | 40 | 47 | - | [ |
| SiO2-Si3N4 | DLP | TMPTA+Irgacure 184 | - | 3.45 μm Si3N4+ Y2O3+Al2O3 | 50-60 | 50 | (77±5) | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+819 | Copolymer | 200 nm oxidized Si3N4 | 51 | - | - | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | EA+819+HDDA+184 | Darvan | 800 nm (KH-560)Si3N4 | 50 | 45 | - | [ |
| [1] |
HALLORAN J W. Ceramic stereolithography: additive manufacturing for ceramics by photopolymerization. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2016, 46(1): 19-40.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DUFAUD O, CORBEL S. Oxygen diffusion in ceramic suspensions for stereolithography. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2003, 92(1): 55-62.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WU H D, CHENG Y L, LIU W, et al. Effect of the particle size and the debinding process on the density of alumina ceramics fabricated by 3D printing based on stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(15): 17290-17294.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI W L, LIU W W, QI F, et al. Determination of micro-mechanical properties of additive manufactured alumina ceramics by nanoindentation and scratching. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 10612-10618.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SCHWENTENWEIN M, HOMA J. Additive manufacturing of dense alumina ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2015, 12(1): 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG K Q, XIE C, WANG G, et al. High solid loading, low viscosity photosensitive Al2O3 slurry for stereolithography based additive manufacturing. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(1): 203-208.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WU X Q, LIAN Q, LI D C, et al. Effects of soft-start exposure on the curing characteristics and flexural strength in ceramic projection stereolithography process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3788-3796.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
XU X H, ZHOU S X, WU J F, et al. Preparation of highly dispersive solid microspherical α-Al2O3 powder with a hydrophobic surface for stereolithography-based 3d printing technology. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 1895-1906.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X B, ZHONG H, ZHANG J X, et al. Fabrication of zirconia all-ceramic crown via DLP-based stereolithography. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(3): 844-853.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FU X S, ZOU B, XING H Y, et al. Effect of printing strategies on forming accuracy and mechanical properties of ZrO2 parts fabricated by SLA technology. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17630-17637.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HE R X, LIU W, WU Z W, et al. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP-stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(3): 3412-3416.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI X B, ZHONG H, ZHANG J X, et al. Dispersion and properties of zirconia suspensions for stereolithography. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(1): 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SUN J X, BINNER J, BAI J M. Effect of surface treatment on the dispersion of nano zirconia particles in non-aqueous suspensions for stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 1660-1667.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU H D, LIU W, HE R X, et al. Fabrication of dense zirconia- toughened alumina ceramics through a stereolithography-based additive manufacturing. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(1): 968-972.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIU X Y, ZOU B, XING H Y, et al. The preparation of ZrO2-Al2O3 composite ceramic by SLA-3D printing and sintering processing. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1): 937-944.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, LIU X Y, et al. Effect of particle size distribution on the preparation of ZTA ceramic paste applying for stereolithography 3D printing. Powder Technology, 2020, 359: 314-322.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Y Y, WANG Z Y, LIU S H, et al. Additive manufacturing of silica ceramics from aqueous acrylamide based suspension. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(17): 21328-21332.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHARTIER T, BADEV A, ABOULIATIM Y, et al. Stereolithography process: influence of the rheology of silica suspensions and of the medium on polymerization kinetics-cured depth and width. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(8): 1625-1634.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
BAE C J, KIM D, HALLORAN J W. Mechanical and kinetic studies on the refractory fused silica of integrally cored ceramic mold fabricated by additive manufacturing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2): 618-623.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LASGORCEIX M, CHAMPION E, CHARTIER T. Shaping by microstereolithography and sintering of macro-micro-porous silicon substituted hydroxyapatite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(4): 1091-1101.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG Z, HUANG C Z, WANG J, et al. Development of a novel aqueous hydroxyapatite suspension for stereolithography applied to bone tissue engineering. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3): 3902-3909.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PFAFFINGER M, HARTMANN M, SCHWENTENWEIN M, et al. Stabilization of tricalcium phosphate slurries against sedimentation for stereolithographic additive manufacturing and influence on the final mechanical properties. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2017, 14(4): 499-506.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CHEN Z W, LIU C B, LI J J, et al. Mechanical properties and microstructures of 3D printed bulk cordierite parts. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(15): 19257-19267.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
HE R J, ZHOU N P, ZHANG K Q, et al. Progress and challenges towards additive manufacturing of SiC ceramic. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 637-674.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SEFIU A R, DING Y X, SHU F X, et al. Photopolymerization- based additive manufacturing of ceramics: a systematic review. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(3): 442-471.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LIU Y, CHEN Z W. Research progress in photopolymerization- based 3D printing technology of ceramics. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020(9): 1-12. |
| [27] | TANG J, YANG Y, HUANG Z R. Research progress of silicon carbide ceramic slurry based 3D printing. Materials Reports, 35(S01): 8. |
| [28] |
GRIFFITH M L, HALLORAN J W. Scattering of ultraviolet radiation in turbid suspensions. Journal of Applied Physics, 1997, 81(6): 2538-2546.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography-based additive manufacturing of gray-colored SiC ceramic green body. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(12): 7198-7209.
DOI URL |
| [30] | WU K C, SEEFELDT K F, SOLOMON M J, et al. Prediction of ceramic stereolithography resin sensitivity from theory and measurement of diffusive photon transport. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98(2): 10. |
| [31] |
BURGER R, WENDLAND W L. Sedimentation and suspension flows: historical perspective and some recent developments. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2001, 41(2/3): 101-116.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
CHEN Z W, LI Z Y, LI J J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 661-687.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG M, XIE C, HE R J, et al. Polymer-derived silicon nitride ceramics by digital light processing based additive manufacturing. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(9): 5117-5126.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DE HAZAN Y, PENNER D. SiC and SiOC ceramic articles produced by stereolithography of acrylate modified polycarbosilane systems. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(16): 5205-5212.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
TANG J, GUO X T, CHANG H T, et al. The preparation of SiC ceramic photosensitive slurry for rapid stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7516-7524.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
VRANCKENAND K C, POSSEMIERS K, VAN DER VOORT P, et al. Surface modification of silica gels with aminoorganosilanes. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1995, 98(3): 235-241.
DOI URL |
| [37] | LIU D, MALGHAN S G. Role of polyacrylate in modifying interfacial properties and stability of silicon nitride particles in aqueous suspensions. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 1996, 110(1): 37-45. |
| [38] |
XIAO C X, NI Q, CHEN HAN, et al. Effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone on rheology of aqueous SiC suspensions dispersed with poly(aspartic acid). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 399: 108-111.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LIU G W, ZHANG X Z, YANG J, et al. Recent advances in joining of SiC-based materials (monolithic SiC and SiCf/SiC composites): joining processes, joint strength, and interfacial behavior. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019, 8(1): 19-38.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CHEN X W, CHENG G F, ZHANG J M, et al. Residual stress variation in SiCf/SiC composite during heat treatment and its effects on mechanical behavior. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(5): 567-575.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
EOM J H, KIM Y W, RAJU S. Processing and properties of macroporous silicon carbide ceramics: a review. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2013, 1(3): 220-242.
DOI URL |
| [42] | ZHAO R C, BAO J X. Lightweight structure and mirror blank formation of the SiC ceramic mirror with large caliber. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2014, 12(6): 65-69. |
| [43] |
WU H B, YAN Y J, LIU G L, et al. Effects of grain grading on microstructures and mechanical behaviors of pressureless solid-state-sintered SiC. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2015, 12(5): 976-984.
DOI URL |
| [44] | LI Y, GAO J Q, YANG J F. Preparation of complicated SiC green bodies via aqueous slip casting. Key Engineering Materials, 2010, 434-435: 88-91. |
| [45] |
BAI X J, DING G J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography additive manufacturing and sintering approaches of SiC ceramics. Open Ceramics, 2021, 5: 100046.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHANG H, YANG Y, HU K H, et al. Stereolithography-based additive manufacturing of lightweight and high-strength Cf/SiC ceramics. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 34: 101199.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Dispersion and stability of SiC ceramic slurry for stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(4): 4720-4729.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography 3D printing of SiC ceramic with potential for lightweight optical mirror. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11, Part B): 18785-18790.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
HU C Q, CHEN Y F, YANG T S, et al. Effect of SiC powder on the properties of SiC slurry for stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(9): 12442-12449.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
CAO J W, IDREES M, TIAN G Q, et al. Complex SiC-based structures with high specific strength fabricated by vat photopolymerization and one-step pyrolysis. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 48: 102430.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TIAN X Y, ZHANG W G, LI D C, et al. Reaction-bonded SiC derived from resin precursors by stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2012, 38(1): 589-597.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
CHEN R G, LIAN Q, HE X N, et al. A stereolithographic diamond-mixed resin slurry for complex SiC ceramic structures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 3991-3999.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, WANG X F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of SiC whiskers toughened Al2O3 paste for stereolithography 3D printing applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828(5): 154347.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZORAN K, VLADIMIR D K. Silicon nitride: the engineering material of the future. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(2): 535-552.
DOI URL |
| [55] | HAMPSHIRE S. Silicon nitride ceramics-review of structure, processing and properties. Journal of Achievements of Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, 2007, 24(1): 2685-2689. |
| [56] |
RILEY F L. Silicon nitride and related materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(2): 245-265.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, LIU X Y, et al. Fabrication strategy of complicated Al2O3-Si3N4 functionally graded materials by stereolithography 3D printing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 5797-5809.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
CHEN R F, DUAN W Y, WANG G, et al. Preparation of broadband transparent Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics by digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing technology. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(11): 5495-5504.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
LI X B, ZHANG J X, DUAN Y S, et al. Rheology and curability characterization of photosensitive slurries for 3D printing of Si3N4 ceramics. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10: 6438.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
HUANG R J, JIANG Q G, WU H D, et al. Fabrication of complex shaped ceramic parts with surface-oxidized Si3N4 powder via digital light processing based stereolithography method. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(4): 5158-5162.
DOI URL |
| [61] | SHEN X, GAO Y A, XU Z. Research and application of silane coupling agents. Shanghai Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 27(1): 14-17. |
| [62] |
LIU Y, ZHAN L N, HE Y, et al. Stereolithographical fabrication of dense Si3N4 ceramics by slurry optimization and pressure sintering. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 2063-2071.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
TIAN Z, YANG Y P, WANG Y, et al. Fabrication and properties of a high porosity H-BN-SiO2 ceramics fabricated by stereolithography- based 3D printing. Materials Letters, 2019, 236: 144-147.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
SHI B H, SHANG Y Y, ZHANG P, et al. Dynamic capillary-driven additive manufacturing of continuous carbon fiber composite. Matter, 2020, 2(6): 1594-1604.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 魏志帆, 陈国清, 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙. ZrB2-HfSi2复相陶瓷显微组织及其核-周结构形成机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [3] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [4] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [5] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [6] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [7] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [8] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [9] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [10] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [11] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [12] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [13] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [14] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [15] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||